The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
People who weld as part of their job or simply use this technology in home repair work know the expression “catching bunnies.” In welding parlance, this means getting eye disease from working with welding equipment without safety glasses. Among doctors, such damage to the organ of vision is called “photokeratitis” or “electro-ophthalmia”. It occurs when the cornea of the eye is exposed to a powerful stream of ultraviolet radiation.
In order to understand the mechanism of its development and possible methods of prevention, it is necessary to dwell in more detail on the physical and physiological basis of ultraviolet rays.
A bit of physics and technology
In most types of welding that are used in construction, the connection of products occurs under the action of a welding arc. A welding arc is an electric charge that arises between two electrodes in a mixture of gases, has high power and persists for a long time. It has ultra-high temperature and high current density. The physical properties of the welding arc are such that when it is formed, an additional release of a large flux of ultraviolet radiation occurs.
Ultraviolet radiation is radiation with a wavelength from 10 to 400 nm. Occupies an intermediate position between visible light, whose wavelength exceeds 380 nm, and X-ray radiation with a wavelength shorter than 10 nm.
Ultraviolet radiation is not uniform and can be divided into four parts depending on its wavelength. There are:
- UVA rays, or near ultraviolet, with wavelengths of 315-400 nm;
- UV-B rays, or 280-315 nm;
- UV-C rays, or far ultraviolet, with wavelengths of 100-280 nm;
- extreme ultraviolet 10-100 nm.
The biological effect that ultraviolet radiation has on the human body directly depends on its wavelength. The longer they are, the weaker the influence.
UVA rays are practically not felt by humans.
Ultraviolet rays with a length of 280-315 nm have a strong effect on the skin and mucous membranes and, with prolonged exposure, can cause burns.
The most aggressive are UV rays shorter than 280 nm, which can easily penetrate deep into the tissues of the body. For example, they can pass through all media of the eye and reach the retina, causing its damage.
The composition of ultraviolet radiation arising in the welding arc is dominated by UV rays with a wavelength from 100 to 300 nm.
Pathogenesis
Ultraviolet waves are mostly absorbed by the cornea. However, the short-wave spectrum of ultraviolet radiation negatively affects the corneal tissue, causing burns. Long-term exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eye can lead to the appearance of superficial punctate keratopathy , pinguecula and pterygium (benign growth of the conjunctiva caused by prolonged photochemical irritation), squamous metaplasia .
Ultraviolet radiation has an irritating effect on the surface epithelial cells of the cornea, which leads to thinning of the corneal layer. In most cases, swelling of the mucous membrane, inflammation and superficial punctate keratitis . With severe damage, complete desquamation of corneal epithelial cells may occur. Complete restoration (epithelialization) of damaged areas of the cornea takes from 36 to 72 hours.
A little medicine
The outside of the eye is covered with a special transparent structure called the cornea. It is a lens consisting of transparent connective tissue covered on the outside with epithelium. Its cells are capable of absorbing ultraviolet radiation. The reaction of the cornea to UV rays depends on their wavelength, time and intensity of exposure. With prolonged exposure to a powerful stream of short-wave UV radiation, the DNA of epithelial cells is destroyed. As a result, their death develops, which manifests itself in the form of a burn.
In response to UV rays, an inflammatory reaction occurs in the cornea, which is characterized by four classic symptoms:
- swelling;
- redness;
- increased body temperature;
- pain.
These clinical signs develop due to the reaction of blood vessels and nerves entwining the anterior surface of the eyeball.
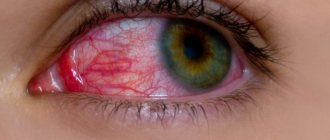
Under the influence of UV rays, small capillaries located at the junction of the cornea and the sclera expand, causing it to swell. Dilated, blood-filled vessels of the conjunctiva give it a red color.
The cornea is rich in nerve endings, so any damage to it causes severe pain.
Full restoration of its functions occurs within 3-4 days.
A distinctive feature of a burn with UV rays from thermal and chemical burns is that its effect is cumulative, that is, accumulative. Symptoms do not appear immediately after exposure, but appear gradually, reaching a maximum 6-12 hours after injury.
General information
Intensive economic development of society creates many potential opportunities for eye diseases caused by exposure to occupational factors, among which chemical, thermal burns and radiation damage to the eyes (chemical burn of the cornea, thermal burn of the cornea of the eye, radiation burns of the eye from infrared, ultraviolet or ionizing radiation) are widespread.
Almost 80-90 percent are thermal and chemical burns of the cornea and about 10-12% are radiation burns, among which ultraviolet burns of the eye mucosa are especially common. At the same time, damage to the cornea of the eye by ultraviolet radiation is widespread both in industrial and domestic conditions during quartzing of a room (burn with a quartz lamp) or when observing lightning or flashes in the sun with an unprotected eye. Also, a burn injury to the cornea can be caused by visible/reflected light - with strong reflection of ultraviolet rays from highly reflective surfaces - ice/snow cover in the mountains (snow ophthalmia/mountain snow blindness), water surfaces and others. The intensity of ultraviolet radiation increases by 4-6% for every 350 m above sea level. Snow (ice) cover reflects almost 85% of UV rays.
Such lesions of the organ of vision are associated with the focusing of the optical system of the eye on the retina of direct/mirror-reflected light energy and, as a consequence, coagulation of the corresponding area of the fundus of the eye. When the burn area is affected by the area of the macula/optic disc, visual acuity sharply and persistently decreases. However, the presence of a burn on the periphery of the fundus of the eye, as a rule, does not cause discomfort or serious consequences. Ultraviolet radiation is widespread in nature, and despite the filtering of the most harmful short-wave (from 200 to 300 nm) UVR wavelength range by the ozone layer (Fig. below), the risk of getting a burn to the retina if safety measures are not followed still exists.
In production
photoophthalmia associated with radiation from various electrical sources (most often electric welding, electric arc furnaces, quartz lamps, etc.), which are designated by the term electroophthalmia (photoelectric keratoconjunctivitis ).
In various industries (mechanical engineering, construction work, aviation/automotive industry, etc.), where electric welding is used, electroophthalmia accounts for about 3.5% of all industrial eye injuries with disability. However, in practice, real indicators of ultraviolet damage to the cornea of the eye far exceed this figure, since mild cases of electroophthalmia are mild and, in most cases, without loss of ability to work and, accordingly, are not recorded. The code for electroophthalmia according to ICD-10 is H16.1. By profession: 28% of all cases of electroophthalmia occur in welders, the rest - in workers of various professions who, due to working conditions, are in close proximity to welders (auxiliary workers, assemblers, crane operators, mechanics, etc.). Electroophthalmia often occurs among staff of treatment rooms/physiotherapeutic/dental rooms, operating rooms when irradiating premises with a quartz lamp, as well as among visitors to solariums, patients suffering from skin diseases ( atopic dermatitis , psoriasis , vitiligo ), for which quartz irradiation is widely practiced. As a rule, ultraviolet rays cause acute damage to the conjunctiva and cornea. Sympathetic ophthalmia with damage to one eye (inflammation of the choroid in one eye after a burn to the other eye) practically does not occur.
Signs of eye burns from UV rays
The main complaints in case of eye burns from welding are:
- Pain in the eyes;
- feeling of sand, specks in the eye;
- lacrimation;
- spasm of the eyelids (blepharospasm);
- photophobia;
- decreased visual acuity;
- headache;
- increase in body temperature (not higher than 38 C°)
When examining the eye, swelling of the cornea is noted, it becomes looser, thickens, loses its natural shine, and may become cloudy. In severe cases, erosions and bubbles form on its surface. The vessels of the conjunctiva are clearly visible, filled with blood - “red eyes”.
Degrees
Based on the severity of manifestations and consequences, there are 4 degrees of eye burns:
- Easy. 1st degree. Redness of the skin and mucous membrane of the eye, swelling, eroded surfaces appear on the cornea. All these signs lead to pain and decreased vision.
- Average. 2nd degree. At this degree, blisters appear on the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye, and superficial clouding of the cornea occurs.
- Heavy. 3rd degree. Deep clouding of the cornea and necrosis of the eyelids occur.
- Particularly heavy. 4th degree. Deep necrosis of all eye tissues
First aid
Any phototrauma of the eye requires a mandatory visit to an ophthalmologist to assess the degree of damage to the cornea.
To relieve symptoms at home, before consulting a doctor, you can use:
- sunglasses, darkening windows with curtains, using night lights;
- painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs by mouth;
- natural tear preparations.
The protective regime is of great importance precisely in the first day after the onset of symptoms, when photophobia and blepharospasm are most pronounced. Using sunglasses, avoiding bright lamps, and darkening windows with curtains will help your eyes get through this difficult period easier.
There is no need to apply protective bandages to the eyes, as they slow down the healing process of the cornea and create additional discomfort for the victim.
To relieve pain, painkillers such as Nurofen, Indomethacin, Nimesil, Diclofenac in tablets and capsules can be used. Use 1 tablet (capsules) 2-3 times a day after meals for 3 days.
To speed up the healing of epithelial damage and prevent corneal dryness, natural tear preparations can be used, for example, Visin Pure Tear, Natural Tear. They are instilled 1-2 drops into each eye every 2 hours.
Prohibited:
- instill any drops into the eyes, except those written above, without first consulting a doctor;
- use traditional medicine methods (tea lotions, honey solution, aloe) in the first day after injury;
- rub your eyes.
Treatment prescribed by an eye doctor. After consultation, the ophthalmologist may prescribe:
- antibiotics in the form of eye drops, this is necessary to prevent the development of microbial inflammation of the injured cornea;
- anesthetic solutions (lidocaine, dicaine) to relieve pain in the eyes;
- perivasal novocaine blockades (carried out in a clinic);
- medications that dilate the pupil.
Complications of corneal burns during welding. Late seeking medical help can cause the development of the following pathological changes in the cornea:
- cloudiness with the development of a cataract;
- scarring;
- ulcers;
- chronic inflammation.
When to see a doctor
It is important to understand that a burn to the retina can lead to blindness. This means that the victim’s quality of life will deteriorate: he will lose the ability to self-care, become incapacitated, etc., so you need to see a doctor for any degree of damage.
Special indications for sending a victim to a medical facility or calling an ambulance are:
- increasing pain that does not respond to pain relief with medications;
- noticeable deep tissue damage;
- the presence of metal particles that cannot be removed;
- state of shock.
Prevention
Since any illness or injury is easier to prevent than to treat, compliance with safety rules when welding works plays a major role in the prevention of electroophthalmia.
A properly fitted welder's mask will protect your eyes from the harmful ultraviolet radiation of the welding arc.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors
Consequences of corneal damage and complications
In the vast majority of cases, there are no negative consequences for electroophthalmia, and with proper treatment, symptoms subside within 48-72 hours, and vision is completely restored. Less commonly, the patient remains hypersensitive to bright light for a long time. Complications of the healing process are rare and, as a rule, are caused by the addition of an infection. It is extremely rare for a severe ultraviolet burn with pronounced changes in the cornea to develop sympathetic ophthalmia ( uveitis - inflammation of the choroid in one eye after injury/burn in the other eye).
Diagnostics
Additional diagnostics are aimed at identifying the degree of damage to the organ of vision and the nature of the complications that have developed. It includes the following methods:
- Assessment of visual acuity, which at the NEARMEDIC center is carried out on absolutely all patients who apply;
- Biomicroscopic scanning of the eyeball;
- Fluorescent test to determine the size of the epithelial defect;
- Ultrasound scanning of the eye and orbits;
- Optical tomography, which allows you to evaluate in detail the structure of the eye if there is clouding of the cornea;
- Electrophysiological methods that give an accurate idea of the degree of retinal damage. They help determine how much of its functional ability to perceive light impulses is preserved and whether there is damage to the optic nerve.
All patients undergo an immunological profile assessment after corneal transplantation. This is necessary for the timely identification of possible reactions of biomaterial rejection and their correction.
Symptoms of the lesion
You can understand that the eyes are affected by UV rays after welding by the following symptoms:
- slight burning sensation;
- pain;
- feeling of sand;
- inflamed vessels in the white body of the eye;
- threads of conjunctivitis.
Based on these signs, it can be established that a slight burn to the eyes occurred after welding. There are moderate to severe degrees of damage, characterized by sensitivity to light, corneal erosion, swelling of the eyelid, and blurred vision.
The extreme, severe degree is characterized by the inability to open the eyelids, tissue necrosis, and the onset of blindness. Visually, the cornea takes on a faded and colorless appearance. When your eyes hurt after welding, what to do depends on the degree of damage. For burns of any complexity, at home or at work, it is important to provide first aid.
How to protect yourself during treatment?
To recover faster from a burn or eye injury, you should behave carefully:
- Lower your head or turn away if there is a strong wind.
- In bad weather, when it snows or rains, it is better to stay at home to avoid a relapse.
- Use glass sunglasses, preferably chameleons.
- Protect your eyes from dust, sand, and midges. Do not renovate the apartment: whitewashing, painting. Do not use hairspray or air fresheners.
How to relieve pain: first honey. help for burns from electric welding
What do welders usually do after they “catch bunnies”? Rinse eyes with water and apply tea bags or raw potato slices. This relieves the symptoms, but not rarely, the problem itself is not solved.
If you have electrophthalmia, you should immediately visit a doctor to get qualified help. However, this is not always possible to do immediately, which means it is necessary to take certain measures:
- Rinse eyes with running, clean water.
- If there is a possibility of foreign particles getting into the eye, you should try to remove them.
- Close your eyes and apply a cold compress. Treat the outside of the eyelids with any antiseptic ointment.
- If the pain is severe, take a painkiller tablet.