Various types of reinforcement are a fairly popular building material for frame house construction. Piles, foundation blocks, beams, and floor slabs are made from reinforced concrete reinforced with metal rods. Reinforced concrete is also very often used for the construction of foundations, basements, building walls, lintels for window and door structures, balcony slabs, interfloor stairs in high-rise residential buildings. Steel rods are used to strengthen the floor screed. When using fittings in domestic conditions, they have to be connected to each other. The best way for this is the tubular technology of welding reinforcement.
Requirements and GOST
The rules for performing pool welding are set out in GOST 14098-91, which is devoted to the connection of reinforcement and embedded products in reinforced concrete structures.
Examples:
- It is prohibited to carry out work in conditions of unstable power supply, when the voltage deviates from the nominal voltage by more than 5%, or on faulty equipment (clause 1.15).
- Connecting double reinforcing bars using this method can only be carried out by welders with the appropriate certificate.
Mechanized welding of rods is carried out using the following grades of flux (clause 3.4.1):
- end-to-end - ANTs-I, AN-8, FN-7, AN-22;
- T-shape, incl. with columns - FK-3, ANC-1.
Welding with consumable electrode in shielding gases
This type of welding involves welding using automatic or semi-automatic welding machines; during the process, the welding wire is fed into the seam formation zone. The role of shielding gas is most often argon or carbon dioxide , which are supplied to the zone of action of the electric arc to ensure a good connection of metals and the absence of defects in the weld. High welding currents and the small diameter of the welding wire make it necessary to feed the wire into the weld pool at a high speed; the welding speed is 15-80 m/h.
This method is characterized by high productivity and high speed of the process, which contributes to its spread in the field of industrial production of metal structures and mechanical engineering.
Due to the absence of slag inclusions and the ability to accurately perform welding with very small thicknesses of material, this method has become widespread at various service stations and other car maintenance and repair enterprises.
Scope of application
Bath technology is used in the following industries:
- In construction. Most often, pool welding is used for splicing reinforcement with a diameter of more than 20 mm and manufacturing embedded parts for reinforced concrete structures.
- In transport networks and pipelines. This is how rails and large-sized flanges, assembled from several plates, are welded.
- In mechanical engineering. They manufacture composite shafts and other parts.
Mechanical engineering is one of the areas in which bath welding technology is used.
Equipment for manual arc welding
The equipment required for manual arc welding consists of:
- from a power source, which can be either portable or stationary, depending on the type of work performed by the welder;
- from a cable with an electrical holder in which an electrode coated with a special coating is fixed;
- from a reverse grounding cable to connect the workpiece being welded to the power source.
Also, do not forget about additional equipment, such as: a protective mask, welder’s gloves, various devices for removing slag and other things necessary for the convenience of the specialist.
Weld pool technology
The connection of reinforcing bars and other solid elements is carried out as follows:
- They are installed in the conductor with some clearance.
- Limit the space between the workpieces on 3 sides with special pads or a U-shaped bracket.
- The ends are heated with a consumable electrode until they liquefy. They must be constantly maintained in this condition, moving the tool from one product to another. Gradually, the gap between them will be filled with molten metal.
We recommend reading How explosion welding is carried out.
There are bath and bath-seam technologies. In the second case, the overlay is welded to the workpieces using flank seams. As a result, it strengthens the joint, absorbing part of the load.
Using one electrode
1 consumable is not enough to fill the weld pool. So, to connect reinforcement with a diameter of 28 mm, 3 electrodes with a thickness of 4 (mm) are required.
Since it is undesirable to interrupt work, consumables have to be changed quickly (the permissible pause is 3-5 seconds).
Beginner welders may not be able to cope with this task.
Single-electrode welding.
Multi-electrode welding
It is easier to form a seam simultaneously with several consumables - the so-called. comb of electrodes. Before starting work, they are attached to a steel plate with tacks so that part of it remains free. This shank is placed in an electrode holder.
After completing the weld, the cinders are beaten off and the plate is reused.
The execution technique does not differ from the 1-electrode method.
Three-electrode pool welding.
Great Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
Page 1
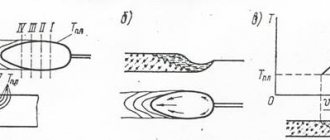
The weld pool moves along the workpiece being welded along with the heat source. After the molten metal of the weld pool solidifies, a seam is formed. The depth and shape of penetration depend on the concentration of the heat source, determined by the welding method and the strength of the welding current. Thus, deepening of weld pools occurs during electron beam and laser welding, as well as during arc welding of light metals using high-density current. In Fig. Figure 12.14 shows the cross-sectional shapes of welds for various welding methods. [2]
| Diagram of the weld pool ( / - crystallite axis. [3] |
The weld pool and the associated crystallization isotherm move along the weld axis at the welding speed. [4]
The weld pool has a small volume and quickly crystallizes due to increased heat transfer into the base metal. The temperature of the weld pool metal changes continuously, and the chemical reactions in the molten metal and slag do not reach equilibrium. Therefore, the release of the bath metal from gases cannot occur fully, and the deposited metal is enriched in oxygen and nitrogen and depleted in alloying elements. [5]
| Pipe welding machine (welding head PT-56. [6] |
The weld pool is a molten mass of metal and flux; after removing the welding arc during the cooling process, slag is released from the molten mass, which floats up and crystallizes, forming a glassy slag crust, and metal, which, crystallizing, forms a weld. Automatic submerged arc welding is carried out with continuous rotation of the pipe, while the welding head is located above the pipe. [7]
| Boiler drum blank prepared for electroslag welding. [8] |
The weld pool is reliably protected by a layer of liquid active slag. Thanks to this, the weld metal is homogeneous and does not have slag and gas inclusions. During the welding process, the same volume of molten slag is located above the weld pool; its consumption is determined by filling the gap between the weld surface and the sliders. [9]
The weld pool should be small in size, and its crystallization should occur at a speed that prevents the molten metal from flowing down. Taking into account all the requirements, submerged arc welding can be used for pipes with a diameter of at least 159 mm. [10]
The weld pool is characterized by width B, depth H and length L. The thermal power of the arc, the productivity of the melting process and the depth of penetration are largely determined by the value of the welding current. As the current increases, the length, width and depth of the weld pool increase. [12]
The weld pool and weld metal are protected from the influence of atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen in order to obtain the specified strength and plastic properties, chemical composition and structure of the deposited metal. [13]
The weld pool is located at a certain angle to the axis of the seam, which makes it easier to form a seam and keep the liquid metal from groaning. [15]
Pages: 1 2 3 4 5
www.ngpedia.ru
Pros and cons of the method
The advantages of bath welding include:
- High strength, reliability and durability of the connection.
- Ability to work in any spatial position.
- Ease of implementation. No complex and expensive equipment is required; traditional welding machines are used. Staples are produced in a wide range for any diameter of fittings.
- Possibility to produce rigid reinforcement frame of any size. An alternative method of fastening rods using tying wire in the case of large-sized structures is not able to provide such a result.
The disadvantages are:
- Increased consumption of electrodes.
- Energy consumption.
- Increased cost of work due to the loss of steel brackets - they are welded to the rods.
The last drawback can be mitigated by using reusable molds made of graphite or ceramics.
We recommend that you read
Welding reinforcement
Areas of use
The use of pool welding extends to all areas of construction and
mechanical engineering.
Therefore, enterprises whose activities are related to these industries often engage in welding work. This technology is used to weld structural elements not only in construction, but also in agriculture, the automotive industry, and the gas and oil industries. Bath welding is also widely used in the construction of country houses and personal buildings, apartment renovation during redevelopment and other household work.
Having studied the intricacies of welding, you can try to do it yourself. And if you have experience in such work, you can share it in the comments to this article.
How to perform pool welding
The workpieces to be joined are cleaned of dirt and rust. Otherwise, the seam will have many defects.
Necessary equipment
Use the following:
- AC or DC welding machine.
- A jig, clamps or other devices for stationary fixation of workpieces.
- Baths made of steel, copper, ceramics or graphite. The first type is disposable. There are 2 types of forms - for vertical and horizontal connections.
- Melting electrodes. The best quality is provided by consumables with a basic type of coating (calcium fluoride), for example UONI-13/45. There are no organic substances in this coating, so the melt is not saturated with hydrogen. It will be difficult for beginners to work with these consumables. It is better for them to use rutile MP-3, ANO or similar.
- Cylinder with inert gas. Protects the weld metal from oxidation when using a refractory electrode (semi-automatic and automatic welding).
We recommend reading What are MIG, MAG and MMA welding
When welding, a DC or AC welding machine is used.
The simplest welding transformer can be used as a machine. An inverter is more convenient to use. It has the following advantages:
- Small size and weight. The weight of the device is only 3 kg. The reduction in transformer dimensions is due to the use of a special circuit that increases the frequency of alternating current to 40-60 kHz.
- High open circuit voltage. This makes it easier to ignite the arc, which is especially necessary when using electrodes with basic coating. Due to the presence of fluorine, it makes combustion difficult.
- The presence of additional functions that facilitate ignition and maintenance of the arc (“hot start”, “discharge afterburner”, “anti-sticking”).
- High efficiency.
Baths are used:
- Disposable steel grades S14-Mn, S16-Mo, S15-Rs.
- Ceramic.
- From graphite grades EEG, EGO, GMZ, PPG, EG1.
- Made from copper M1 or M2.
The use of reusable pads has a double effect:
- steel consumption for each joint is reduced;
- a greater thickness of the protective layer of concrete is ensured, while in the presence of a steel form it is greatly reduced.
Mode selection
The main parameters of the welding mode are:
- consumable diameter;
- current strength.
The first value is selected according to the size of the workpieces. The data for this method is shown in the table:
| Diameter of welded rods, mm | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current, A at positive/negative air temperature |
| 20 | 5 | (225-235)/(250-260) |
| 22 | (235-250)/(260-280) | |
| 25 | (250-270)/(280-300) |
Parameters for vat seam welding - recommended and acceptable:
| Diameter of welded rods, mm | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current, A at positive/negative air temperature |
| 36-40 | 6(5) | 300(275)/330(300) |
| 50-55 | 6(5) | 330(300)/360(330) |
| 60 | 7(6) | 420(400)/450(430) |
| 70 | 8(6) | 500(450)/540(470) |
| 80 | 8(6) | 500(450)/550(480) |
Note: Acceptable values are shown in parentheses.
Advantages and disadvantages
The widespread use of pool welding is explained by its advantages:
- the technology does not require special equipment;
- it is convenient because it can be made in any arrangement of joints;
- with the help of welding, a single strong frame of the structure is achieved without reducing its rigidity;
- is an economical type of welding;
- can be used for household needs.
The disadvantages of vat seam welding include the requirement to maintain process continuity in order to maintain the liquid state of the metal during operation. Therefore, replacing electrodes during the process is not recommended. If such a replacement is necessary, it must be done very quickly.
Failure to comply with the temperature conditions greatly affects the quality of the seam. If the melt is cooled too quickly, a lot of slag can form.
Also, you should not allow the metal to melt too quickly, so the arc on the electrode must be extinguished periodically.
Describe manual consumable arc welding
Manual arc welding is performed with a consumable or non-consumable (carbon, graphite, tungsten, hafnium) electrode. When welding with a consumable electrode (Fig. 5.1), the arc burns between it and the product. The formation of the weld metal is carried out due to the electrode material and the melting of the base metal in the arc zone. When welding with a non-consumable electrode, filler material is supplied from the outside to form the weld metal into the arc zone.
Consumable electrode welding has found the greatest application, since it can be used in all spatial positions, welding ferrous, non-ferrous metals and various alloys. In this case, electrodes with a diameter of 1÷ 12 mm are used. However, the bulk of the work is performed with electrodes with a diameter of 3 ÷ 6 mm.
Electrodes are classified according to the material from which they are made, by purpose, by type of coating, by the properties of the weld metal, by the permissible spatial positions of welding or surfacing, by the type and polarity of the current.
According to their intended purpose, electrodes are divided into the following groups: for welding carbon and low-alloy structural steels - U; for welding heat-resistant alloy steels - T; for welding high-alloy steels with special properties - B; for surfacing layers with special properties - N.
48. Weldability. Basic technological methods for difficult and limited weldable steels .
Limited weldability steels have a carbon content of 0.36 to 0.45% and are prone to cracking. Welding requires mandatory heating. Poorly weldable steels contain carbon in amounts greater than 0.45%. When welding them, special technological processes are required.
Alloying steel with one or more alloying elements gives it certain physical and mechanical properties. As a rule, increasing the level of alloying and strength of steel leads to a deterioration in its weldability, and carbon plays a primary role in this.
Low alloy steels are well welded by all melting methods. Obtaining an equal-strength welded joint during welding, especially with heat-strengthened steels, causes certain difficulties. In zones far from the high-temperature region, cold plastic deformation occurs. When subsequent sutures are applied, these zones become areas of strain aging. This ultimately leads to a decrease in the plastic properties and an increase in the strength properties of the metal and, accordingly, to the appearance of cold cracks. In medium-alloy steels, the susceptibility to hardening increases, and therefore such steels are highly sensitive to the thermal cycle of welding. Their heat-affected zone turns out to be sharply hardened and, therefore, non-plastic under all welding conditions that ensure satisfactory formation of the weld. Therefore, in order to reduce the cooling rate of the heat-affected zone when welding these steels, preheating of the welded product is necessary.
When welding high-alloy chromium 08X13, 08X17T and some other steels, there are distinctive features: a high threshold of cold brittleness of steel, usually located in the positive temperature range; tendency to significant embrittlement in the heat-affected zone; low ductility and toughness of the weld metal made with welding materials of a chemical composition similar to steel; inability to eliminate embrittlement by heat treatment.
Welding of such steels must be performed with minimal heat input, since with an increase in heat input, the tendency of the welded joint zones to grain growth, the appearance of microcracks and a decrease in ductility increases. At the same time, the resistance of the welded joint to local damage and intercrystalline corrosion decreases. During the welding process, there is a risk of warping and an increased level of residual stress. After welding, in some cases heat treatment is required.
Electric arc welding of metal
Electric arc welding of metal is one of the methods of welding metals, the essence of which is to heat and melt the metal with an electric arc. This is one of the most common welding methods. This method was first discovered by the scientist N.G. Slavyanov. in 1888. To do this, he used a metal consumable electrode. Welding took place under a layer of flux. Electric arc welding of metal is carried out using direct current. In this case, the plus is on the part being welded, and the minus is on the electrode. The electric welding process is performed with both a consumable electrode and a non-consumable one. This welding method is widely used in repair work, installation, mechanical engineering, construction and other areas.