In the modern world, there is not a single industrial enterprise that does not use electric arc welding in its production activities. Thanks to this factor, the domestic market for semi-automatic devices is constantly growing and actively developing.
Today it is represented by a wide range of technical means, specific devices and consumables, the most popular of which is welding wire for semi-automatic machines. This important component must match its characteristics as closely as possible to the properties of the metal from which the parts being connected are made. Therefore, a large number of filler products have been developed that are most suitable for a certain type of work.
Types of wire
Welding wire is an indispensable element for successful work operations in various industries and utilities. With its help, several metal segments are connected into a solid structure.
The features of this filler material include ease of use and excellent quality of work performed. Proper selection of wire not only improves the reliability of the weld, but also significantly increases productivity.
Wire for semi-automatic machines is usually supplied in coils, coils and coils. The weight of the first type of packaging sometimes reaches 1.3 tons. The weight of the second type of container can vary from 15 to 120 kilograms. The mass indicators of the third form of packaging range from 5 to 18 kilograms.
Often the wire is placed in boxes or plastic bags. If the product does not have packaging, then before use the wire is dried at a temperature of 200°C.
Powder
This wire is a hollow object made of metal, the free space of which is filled with powder and flux.
These materials help protect the seam from exposure to oxygen and harmful substances formed during the welding process. An important factor here is also ensuring the safety of the respiratory system of the specialist performing technological work.
The use of special additives in welding wire facilitates ignition of the arc and helps reduce metal spattering, which has the most favorable effect on the formation of a high-quality seam. The arc burns in a flux medium, which allows you to protect the area of the welded area from the negative influence of the environment.
For work using flux-cored wire, heavy gas cylinders are not required, which are associated with many hassles: storage, refilling and possible leakage.
Copper-plated
Copper-plated wire is a product designed to work with carbon and low-carbon steels. It is coated with a special copper compound and is used for welding objects in a protective gas environment.
Features of the method
The connection of metal parts using semi-automatic welding occurs as a result of the continuous supply of a fusible electrode. A hollow tube of a certain diameter acts as an electrode. Melting occurs from an electric arc.
In industry, there are two ways of operating a semi-automatic machine:
- the use of a gas environment is necessary subject to the requirement of protecting the seam from oxygen;
- welding without gas frees the welder from the difficulties associated with moving equipment, as well as constantly replenishing the container.
In order to avoid labor costs, it is recommended to use semi-automatic welding without a gas environment. A flexible tube is used; the material has a cavity inside; during the manufacturing process, the void is filled with flux, it is heated, and gas is released. The seam is protected from the action of foreign substances. The benefits include:
- powering the device from the central network using wires;
- mobility of the device;
- continuous supply without stopping to replace the electrode.
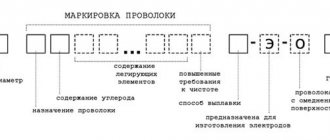
Marking
The basic requirements regulating all issues of production of wire for welding work are presented by GOST 2246-70 . Today, about 80 varieties of this type of product are manufactured. And in order to understand what a particular type of product is, it is assigned a certain label, which helps to understand the composition of the product and its characteristics. A good example is the popular welding wire sv08g2s .
Its decoding is represented by the following values:
- The combination of the letters “st” indicates that this product refers to welding wire;
- The combination of numbers “08” indicates the amount of carbon (in hundredths) contained in the product;
- The letter “g” emphasizes the presence of manganese in the wire;
- The number “2” is the volume of manganese in the element;
- The letter “c” indicates the presence of silicon in the wire, but if there is no number after the letter designation, this means that the product contains less than 1%, but more than 0.5%.
Based on the markings stated above, we can say that the presented product is an alloyed low-carbon wire, which contains additives such as silicon and manganese.
Preparing for work
One of the features of welding without gas supply is the reverse polarity of the current source. When setting the wire feed, you must make sure that the diameter of the feed socket in the feed roller matches the diameter of the wire. The pressure roller does not need to be tightly tightened, since the soft shell may become wrinkled; to prevent this from happening, when feeding, the torch tip must be screwed to the body only after the end of the wire rod appears from the channel hole. Only after this should the tip be installed. There is no need to adjust the nozzle as there will be no gas supply through it during operation.
The diameter of the wire
Wire for semi-automatic devices comes in the following diameters:
- 0.6 mm;
- 0.8 mm;
- 1.0 mm;
- 1.2 mm;
- 1.6 mm.
Such dimensional indicators allow us to fully satisfy the needs of professional welders. For highly specialized purposes, products with a diameter from 3.0 to 6.0 millimeters are perfect.
The required wire size is selected in accordance with the characteristics of the welding current and the thickness of the elements being connected.
Recommendations
You need to understand that for each type of welding wire there are a large number of classifications. This depends on the application conditions, shielding gas and many other factors. All this must be taken into account when choosing consumables and further work.
If you decide to use a solid cord, its composition must be similar to the composition of the metal with which you will be working. This is because the mixture contains different amounts of deoxidizers, so you need to carefully select the variety.
When using powder electrodes, you need to take into account that they are carbon and low-alloy steels and cast iron. Their classification is based on the mechanical properties of the metal used for welding.
Popular brands
The most popular brands of welding wire presented on the domestic market are:
- Sv-08GSMT. This type of product belongs to copper materials and is used in welding operations using automatic and semi-automatic machines. The wire works well with carbon metals and alloys that contain a low percentage of alloying components. It is characterized by a high level of resistance to tensile loads. This parameter is in the range of 1000-1300 MPa. This grade of wire is widely used for joining thin-walled parts operating under high pressure. Welding is carried out in an environment of protective gases (argon and carbon dioxide);
- Sv-06Х19Н9Т. This grade of wire is intended for working with stainless steel in a protective gas environment. Thanks to the content of elements such as chromium, manganese and nickel, it has good corrosion resistance. Used in the production of food industry products;
- PP2DS. This is a representative of cored wire. This brand allows operations to be carried out in strong winds, which gas shielded welding cannot do. The wire is intended for connecting parts made of steel (carbon and low-alloy), cast iron and non-ferrous metals. Used in shipbuilding and oil industry;
- OK Autrod 19.40 . This wire is from a foreign manufacturer ESAB. It is used for working with rolled aluminum bronzes and for surfacing anti-corrosion layers on metal parts. Its yield strength is 175 MPa, and its strength reaches 400 MPa. Welding operations are carried out in pure argon. This product is used in the chemical industry and automotive industry.
Semi-automatic welding process without gas
To obtain a high-quality welding seam, work experience and strict adherence to the algorithm of actions are required. Before starting work, protective measures must be taken. A 10-meter working area is provided around the workplace, in which there are no flammable or explosive objects. Access to the area by unauthorized persons must be prohibited.
To configure the equipment you need:
Semi-automatic welding scheme without gas
- set the current value for welding depending on the thickness of the workpiece being welded (according to the manufacturer’s instructions);
- set the optimal feeding mode for the wire electrode - the gears should rotate the wire evenly without damaging it;
- switch the polarity of the current to direct;
- turn on the “Forward” wire scrolling, open the flux shutter, press the “Start” button while simultaneously striking the electrode;
- carry out welding on a test workpiece and, if necessary, make changes;
- With a stable arc and uniform wire movement, the welding process can begin.
The process begins from the top of the seam, moving the “gun” from top to bottom. Since the heat from the combustion of the flux spreads upward, this trajectory allows you to maintain the temperature in the weld pool. Move the burner smoothly, but quickly enough to prevent the formation of melt drops. It is necessary to control the tilt of the “gun” - slightly upward.
Useful tips
To weld metal with a high-quality semi-automatic machine, you should listen to the professionals:
- To clean aluminum, it is not advisable to use metal brushes that have been used to clean other metals; it is better to knit a new one, without foreign inclusions. It is better to use chemical treatment of the metal with acid followed by washing.
- When welding aluminum semi-automatically in argon using a four-cycle pulsed current, the metal warms up faster, creating a high temperature in the melt zone. The likelihood of a residual oxide layer getting into the seam is reduced.
- Internal linear voltages can be reduced by reducing the current towards the final stage of welding. They begin work, on the contrary, at maximum mode in order to break through the oxidized layer.
- When working semi-automatically in a carbon dioxide environment, do not make sudden movements; the nozzle should melt evenly.
- When a protective atmosphere is used, the work area is protected from drafts so that gusts of wind do not blow the gas cloud away.
- When working, it is necessary to observe safety precautions, use special clothing, personal protective equipment, including for the respiratory system; some alloying additives have a toxic effect on the body.
Semi-automatic welding of aluminum at home requires certain skills. Beginners can weld metal poorly, then it will warp and the seam will crack. Before you take on important connections, you need to “get your teeth into it,” learn how to maintain the optimal distance, and develop a speed limit.
Special properties of aluminum
The widespread use of aluminum is explained by its low specific gravity, fairly stable strength and corrosion resistance. But its behavior during heat treatment creates difficulties when connecting aluminum structures and parts by welding. This is explained by the specific physical and chemical properties of aluminum:
- it does not change its color when heated strongly, so it is difficult to understand from the color the degree of heating of the metal;
- has a wide melting temperature range, unlike steel alloys, and begins to melt at a low temperature threshold, losing its strength;
- does not show a tendency to magnetization;
- has high thermal conductivity (on average 5 times more than steel alloys), therefore, when the joint zone is heated, heat intensively spreads throughout the entire part being welded. In order not to lose it, before carrying out welding work, especially large aluminum products, they are pre-heated;
Due to the active interaction of aluminum with oxygen in the air, an oxide film is formed on its surface. Once a certain thickness is reached, it then begins to protect the aluminum from further oxidation. At the same time, the oxide film creates difficulties during welding, because it melts at a temperature of 2050-2200°C, in contrast to the metal itself, which has a melting point in the region of 660°C.
How to weld thick metal using a semi-automatic machine
Having previously found out how thick the metal is to be welded, you can prepare it for this process according to all the rules. To weld thick metal - parts with a wall thickness of more than 4 mm - you need to chamfer the intended joints. Please note that this can be done using gas cutting, but hand and pneumatic chisels are also used. Metal sheets with a thickness of 5 - 15 mm are equipped with V-shaped bevels; for parts with a thickness of more than 15 mm, an X-shaped bevel is assumed.
semi-automatically welded thick metal
The seam when connecting thick surfaces, especially with T-joints, must be strengthened with the help of two more, located on its upper and lower edges. The arc must not be drawn along a straight line, but must be made in zigzag or reciprocating movements. The weld metal should extend onto the surface of the product to a width equal to the thickness of this part. To obtain a reliable connection, cascade or slide welding is most often used.
When welding thick metal, there is a high probability that the anti-corrosion coating of the part will be damaged. Therefore, after welding, the part must be treated with special compounds. If it is made of low-alloy steel, then preheating will not hurt. Heat treatment will soften the product, preparing it for further work.
How to weld thick metal while maintaining the original qualities of the part? To reduce deformation or completely prevent it, thick metal products are securely fixed using clamps before welding. This can be done on a workbench, assembly table or steel plate.