Welding wire SV-08A – Forging, welding, blacksmithing
Welding wire SV-08A is used for automatic submerged arc welding of carbon steels with a yield strength of 235-285 MPa and for the production of electrodes with increased toughness and weld plasticity, intended for welding low-alloy and low-carbon steel.
The letter “A” in the name of this wire indicates the increased purity of the chemical composition of the metal in terms of phosphorus and sulfur content, “CB” means welding, and “08” means carbon content (C).
The influence of the content of carbon, phosphorus, manganese and sulfur in the welding wire on the mechanical characteristics of the weld
- Carbon content – as the carbon content (C) in the welding wire decreases, the deposited weld becomes more ductile.
- Sulfur and phosphorus content - with a decrease in the content of phosphorus (P) and sulfur (S), the reliability of the weld joint increases.
- Manganese content – manganese (Mn) strengthens the weld joint.
Chemical composition of welding wire SV-08A
- Carbon (C) - less than 0.10%.
- Manganese (Mn) - 0.35 - 0.60%.
- Silicon (Si) - less than 0.30%.
- Sulfur (S) - less than 0.03%.
- Phosphorus (P) - less than 0.03%.
- Copper (Cu) - less than 0.25%.
- Chromium (Cr) - less than 0.12%.
- Nickel (Ni) - less than 0.25%.
The wire is supplied in skeins, which are packed in polyethylene and paper. Delivery can also be carried out without packaging or in heavy-duty bays weighing 1-1.3 tons. Welding wire SV-08A is manufactured with a diameter from 0.8 to 7.0 mm. To ensure good contact in the welding machine in order to ensure minimal voltage losses, wire with diameters of 0.8; 1.0; 1.2; 1.4 and 1.6 mm are produced with a copper coating with a thickness of at least 0.15 mm.
Requirements for welding wire
The main requirement for welding wire is that the composition of the wire matches the composition of the metal from which the parts and structures being welded are made. The melting temperature of the welding wire should be almost equal to the temperature of the metal being welded, the melting process itself should occur evenly, and the wire should be clean and not oxidized.
kovka-svarka.net
Activated wire
For welding in a gas environment, a special wire is used, which is called activated. It contains salts of alkaline earth and alkali metals, which are easily ionized.
The wire sheath is made of Sv08G2S steel, which is thicker than flux-cored wire, and inside there is the specified filler powder in an amount not exceeding 7% of the weight of the sheath. This allows you to stabilize the arc and form a high-quality seam during welding.
Welding wire SV08A 3.0; 4.0; 5.0; 6.0
SV08A (1000 kg) TU 14-4-828-77 diameter from 2.0 mm to 6.0 mm Welding wire SV-08A is used for welding carbon structures with an oxy-acylene flame
Welding wire is one of the integral elements of the welding process, necessary to ensure high-quality welding.
Welding wire is divided according to purpose, processing method, composition and production algorithm.
Examples of welding wire applications:
1) welding wire is used as a consumable electrode when using semi-automatic electric arc welding. In this case, the welding wire can be either flux-cored or solid, self-shielded or gas-shielded. If the welding wire is used in a shielding gas environment, then during welding it is possible to change the metal composition of the seam by adjusting the composition of the welding wire and shielding gas used.
2) when using argon arc welding with a non-consumable electrode, welding wire is used as an additive. The use of an additive is necessary to strengthen the seam or fill the groove of the edges of the base metal, with a thickness of more than 3 mm. The wire can be fed either manually or using a feed mechanism.
Welding wire can also be gas welding, stainless aluminum, copper-plated and non-copper-plated.
Application of various brands of welding wires:
Welding wire SV-08G2S is used for welding low-alloy and low-carbon steels in carbon dioxide, in various gas mixtures and submerged arcs.
Stainless steel welding wire is used for welding stainless steels such as 08x18n10t, 12x18n9t, 08x18n10 and others. Industries in which this wire is used: pipeline manufacturing, petrochemical engineering, energy and food industry, etc.
Aluminum welding wire is used for welding aluminum structures and Al-Mg, Al-Mn alloys.
Copper-plated welding wire is used for gas arc welding of carbon and low-carbon steels, shipbuilding and structural steels, as well as steel for high-pressure vessels.
Welding wire is used for the manufacture of electrodes and electric arc welding.
krafft.tiu.ru
Cored wire
It is a tubular wire filled with powdery filler - charge. The shell is made of steel (usually low-carbon) tape with a thickness of 0.2-0.5 mm. The charge is a mixture of powders from gas-forming, slag-forming components, as well as alloying additives that protect the welding zone, weld pool and heat-affected zone.
1. Steel charge 2. Charge
Flux-cored wires can reduce electrode metal spatter and increase welding productivity.
Before welding, it is recommended to calcinate flux-cored wires at a temperature of 230-250°C for two hours. Welding with unheated wire is allowed, but only with an increased electrode extension of up to 40-60 mm. It is recommended that the distance from the current-carrying tip to the nozzle exit be 15-25 mm.
Wire GOST 2246 for welding. Wire SV08A
GOST 2246-70 defines the characteristics of welding wire of various grades. In addition, it can be used for surfacing and for the production of electrodes.
GOST 2246-70 wire for welding is divided depending on the steel grade into:
- low-carbon welding wire - grades SV08, SV08A, SV08GA
- alloyed welding wire - grades SV08GS, SV12GS, SV08G2S, SV10GN, SV08GSMT, SV15GSTYUTSA (EP-439), SV20GSTYUA, SV18KhGS and others
- high-alloy welding wire - grades SV12Х13, SV12Х11НМФ, SV10Х11НВМФ, SV13Х25Т, SV01Х19Н9, SV20Х13, SV06Х14, SV08Х14ГНТ, SV10Х17Т and others.
Depending on the type of coating, we produce: black and copper-plated welding wire.
Some brands of welding wire, for example, SV08A and SV08 wire, are also used for the manufacture of welding electrodes of different brands - UONI 13/55, MR-3, UONI 13/45, ANO-21, etc.
The chemical composition is given in the table:
Element, % Low-carbon alloy steel grade Sv08 Sv08A Sv08GA Sv08GS Sv08G2S Sv08ХМ S no more than Mn Si no more than PS Cr no more than Ni no more than Al no more than Cu no more
| 0,10 | 0,10 | 0,10 | 0,10 | 0,10 | 0,06-0,10 |
| 0,35-0,60 | 0,35-0,60 | 0,80-1,1 | 1,40-1,70 | 1,80-2,10 | 0,35-0,60 |
| 0,03 | 0,03 | 0,06 | 0,60-0,85 | 0,70-0,95 | 0,12-0,30 |
| 0,040 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 | 0,030 |
| 0,040 | 0,030 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,025 | 0,025 |
| 0,15 | 0,12 | 0,10 | 0,20 | 0,20 | 0,9-1,2 |
| 0,30 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,30 |
| 0,01 | 0,01 | — | — | — | — |
| 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 | 0,25 |
Wire GOST 2246-70, depending on the diameter and steel grade used, can be supplied in coils of 80-100 kg, in large coils of 800-1000 kg, as well as on special plastic spools or metal frames.
Welding wire is usually packaged in cloth or moisture-proof paper. Wire for the production of SV08A and SV08 electrodes in coils is supplied without packaging.
profmetiz.ru
Types of welding wire by composition and diameter
- Flux cored is a hollow welding wire with a special flux filler. In this case, flux evaporation forms a protective gas bubble in the weld pool, which allows the use of consumables without a gas flow. Welding with flux-cored wires can be carried out under intense wind currents. The technique of using self-shielding wire is similar to the technology of welding using conventional wire material. Flux-cored wire has differences in marking with the designation “PP” and “PS”; with digital indication of brand and diameter.
- Copper-plated welding wire - with a copper alloy coating up to 6 microns thick. The key role of this layer is to ensure the tightest possible contact between the structures being welded. Welds created using such wire are distinguished by high mechanical endurance and weak response to strong temperature changes. Another indisputable advantage is the saving of consumables by up to 40% compared to welding with conventional wire. Note - this variety is absolutely not suitable for welding stainless steels.
- Aluminum welding wire used for welding in a protective gas environment with automatic and semi-automatic units. The consumable material is used for welding products made of aluminum alloys. The aluminum additive requires hermetically sealed storage due to the fairly rapid oxidation of the aluminum layer with oxygen in the open air.
- Welding wire for stainless steel. Material in this category is alloyed with chromium or nickel. Accordingly, the marking will contain the symbols “H” or “X”, as well as numbers for the percentage of alloying elements.
For use in semi-automatic welding units, wire with diameters of 0.6 mm, 0.8 mm, 1 mm, 1.2 mm, 1.6 mm is produced. Flux cored (flux) wires are manufactured in a thickness range from 0.6 to 6 mm. Filler rods, like the wire materials used for the manufacture of electrodes, are produced in a range of diameters from 1.6 to 5 mm.
Welding wire for surfacing. Chemical composition of welding wire.
Welding wire for surfacing. Chemical composition of welding wire. 5.00/5 (100.00%) 11 voted
Surfacing wire is manufactured in accordance with GOST 2246-70, intended for all types of surfacing and electrode production. According to GOST, wire is produced in diameters: 0.3; 0.5; 0.8; 1.0; 1.2; 1.4; 1.6; 2.0; 2.5; 3.0; 4.0; 5.0; 6.0; 6.5; 8.0; 10.0; 12 mm. In the manufacture of electrodes, wire with a diameter of 1.6 to 8.0 mm is used.
Wire is supplied to the customer in coils weighing no more than 40 kg and with internal diameters from 150 to 750 mm. For ease of installation on the welding machine, the surfacing wire can be wound onto spools. The spools of surfacing wire should be wrapped in waterproof paper. Each skein must have a tag with the company name, wire brand and batch number.
Store the wire in dry rooms, protected from precipitation, corrosion and dirt. It is possible to coat the wire with copper for better protection against corrosion.
GOST 2246-70 welding wire.
According to GOST 2246-70, 77 different grades of surfacing wire are produced, which in turn, depending on the chemical composition, can be divided into groups:
— low-carbon surfacing wire;
— alloyed surfacing wire;
— high-alloy surfacing wire.
Table 1 below shows some of these brands.
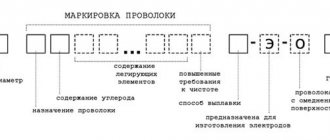
Marking of welding wire.
Using wire Sv-08A as an example, let’s look at what each letter and number means.
Sv-08A
— index St means that it is welding;
— numbers 08 indicate the percentage of carbon content in the wire;
— the letter A indicates the content of the main elements in the wire. In high-alloy wires, the letter A denotes nitrogen; in low-carbon and alloyed wires, the letter A indicates increased purity of the metal in terms of sulfur and phosphorus content.
If there are still numbers at the end of the designation after the letter, then they indicate the percentage content of this element, for example:
Sv-10G2
This means that this wire composition contains up to 2% manganese. The letter G means manganese, and the number next to it is its percentage in hundredths.
If there is no number next to an element, this means that its content in the surfacing wire is insignificant and amounts to less than one percent.
If at the end of the designation there is a double letter AA (Sv-08AA), this means a lower content of sulfur and phosphorus compared to Sv-08A wire.
Chemical composition of welding wire.
Table 1. Chemical composition of welding wire according to GOST 2246-70.
| Wire grade | Chemical composition, % | |||||||||
| Carbon | Silicon | Manganese | Chromium | Nickel | Molybdenum | Titanium | Sulfur | Phosphorus | Other items | |
| No more | ||||||||||
| Low carbon wire | ||||||||||
| Sv-08 | 0,10 | 0,03 | 0,35-0,60 | 0,15 | 0,30 | — | — | 0,040 | 0,040 | Aluminum No more than 0.01 |
| Sv-08A | 0,10 | 0,03 | 0,35-0,60 | 0,12 | 0,25 | — | — | 0,030 | 0,030 | |
| Sv-08AA | 0,10 | 0,03 | 0,35-0,60 | 0,10 | 0,25 | — | — | 0,020 | 0,020 | — |
| Sv-08GA | 0,10 | 0,03 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,10 | 0,25 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-10GA | 0,12 | 0,03 | 1,10-1,40 | 0,20 | 0,30 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-10G2 | 0,12 | 0,03 | 1,50-1,90 | 0,20 | 0,30 | — | — | 0,030 | 0,030 | — |
| Alloy wire | ||||||||||
| Sv-08GS | 0,10 | 0,60-0,85 | 1,40-1,70 | 0,20 | 0,25 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-12GS | 0,14 | 0,60-0,90 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,20 | 0,30 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-08G2S | 0,05-0,11 | 0,70-0,95 | 1,80-2,10 | 0,20 | 0,25 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-15GSTYUTSA (EP-439) | 0,12-0,18 | 0,45-0,85 | 0,60-1,00 | 0,30 | 0,40 | — | 0,05-0,20 | 0,025 | 0,025 | Aluminum 0.20-0.50 Zirconium 0,05-0,15 Cerium not less than 0.4 |
| Sv-18HGS | 0,15-0,22 | 0,90-1,20 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,80-1,10 | 0,30 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| High alloy wire | ||||||||||
| Sv-12X13 | 0,09-0,14 | 0,30-0,70 | 0,30-0,70 | 12,00-14,00 | No more than 0.60 | — | — | 0,025 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-06Х19Н9Т | No more than 0.08 | 0,40-1,00 | 1,00-2,00 | 18,00-20,00 | 8,00-10,00 | — | 0,50-1,00 | 0,015 | 0,030 | — |
| Sv-07Х19Н10Б | 0,05-0,09 | No more than 0.70 | 1,50-2,00 | 18,50-20,50 | 9,00-10,50 | — | — | 0,018 | 0,025 | Niobium 1.20-1.50 |
| Sv-10X16N25AM6 | 0,08-0,12 | No more than 0.60 | 1,00-2,00 | 15,00-17,00 | 24,00-27,00 | 5,50-7,00 | — | 0,018 | 0,025 | Nitrogen 0.10-0.20 |
Was the article useful?! Share with your friends!!!
mechanicinfo.ru
Surfacing wire
Surfacing is the technological process of applying a layer of metal to the surface of a product by fusion welding. It is used to restore the original dimensions of parts and to give the surface layers of the part special properties required for its successful operation.
When surfacing by fusion welding, a pool of liquid metal is formed, which includes part of the molten metal of the product and the deposited electrode metal. Thus, the metal of the electrode turns out to be diluted with the metal of the product. When restoring worn parts, unless it is necessary to increase their wear resistance or other properties, electrodes and filler wire of a composition are used that ensures the production of deposited metal that is similar or close to the composition of the metal of the product. If, according to operational requirements, it is necessary to increase wear resistance, heat resistance and other properties, a variety of alloyed electrodes and wires are used, which, taking into account the partial dilution of the deposited metal, ensure the formation of a surface layer of the required quality. In addition to increased alloying, technological methods are used to reduce the proportion of the base metal in the surfacing, in particular, they reduce the welding energy (surfacing at low currents), increase the transverse vibrations of the electrode, etc.
The main raw material for arc surfacing of metal on worn parts is steel surfacing wire. They produce 19 grades of surfacing wire, including: 8 grades - from carbon steel Np-25, Np-30, Np-35, Np-40, Np-45, Yp-50, Np-65, Np- 80); 8 grades—alloy steel (Np-40G, Np-50G, Np-65G, Np-ZOGSA, Np-30Kh5, Np-40Kh2G2M, Np-5KhNM, Np-50KhFA); 3 grades - made of high-alloy steel (Np-30X13, Np-40X13, Np-PZA).
Steel surfacing wire is produced in the following diameters, mm: 0.3; 0.5, 0.8; 1; 1.2; 1.4; 1.6; 1.8; 2; 2.5; 3; 4; 5, 6; 6.5; 8. The hardness and purpose of the surfacing wire are shown in the table below.
Hardness and purpose of surfacing wire
| Wire grade | Approximate hardness of deposited metal | Welded products |
| Np-25 | NV 160…220 | Axes, spindles, shafts |
| Np-30 | ||
| Np-35 | ||
| Np-40 | NV 170…230 | |
| Np-45 | ||
| Np-50 | NV 180…240 | Tension wheels, trolley ramps, support |
| Np-65 | NV 220…300 | Support rollers, axles |
| Np-80 | NV 260…340 | Crankshafts, cardan shaft crosspieces |
| Np-40G | NV 180…240 | Axes, spindles, rollers, shafts |
| Np-50G | NV 200…270 | Tension wheels, support rollers for tracked vehicles |
| Np-65G | NV 230…310 | Crane wheels, support roller axles |
| NP-ZOHGSA | NV 220…300 | Crimping rolls, crane wheels |
| N l-30X5 | HRC3 37.. 42 | Rolling rolls of section rolling mills |
| NP-40ХЗГ2МФ | HRC3 38…44 | Parts exposed to impact and abrasive HOCV |
| Np-40Х2Г2М | HRC3 54…56 (after hardening) | Machine parts working with dynamic loads (crankshafts, steering knuckles: axles of road wheels) |
| Np-55ХНМ 60 | HRC3 40…50 | Forging and punching dies, forging machine rolls |
| NP-50HFA | HRC3 43…50 | Splined shafts, crankshafts of internal combustion engines |
| NP-30Х13 | HRC3 38…45 | Hydraulic press plungers, crankshaft journals, dies |
| NP-40X13 | HRC, 45…52 | Support rollers for tractors and excavators, conveyor parts |
| Np-GIZA | NV 220…280 | Railway crosspieces, crusher jaws, bucket teeth |
How to choose the right welding wire
- For welding low-carbon and low-alloy steel parts, it is recommended to use copper-plated wire (type 09G2S) in a carbon dioxide atmosphere. Copper coating will provide the welds with the necessary strength and tensile strength.
- Stainless alloys (austenitic and austenitic-ferritic alloyed with chromium or nickel) are welded with stainless wire alloyed with the same elements. The protective gas environment is inert argon or helium with the addition of a carbon dioxide mixture.
- Aluminum welding wire is used for welding aluminum alloys. An important nuance is the need to carefully remove the oxide film from the surfaces being welded.
- Powder “self-protective” film is used for welding a wide class of ferrous metals, where the use of gas cylinders is impossible or impractical. The only negative is the high cost of consumables.
- The diameter of the welding wire is selected in accordance with the thickness of the parts being welded. For example, it is better to weld products with thin walls using wire with a diameter of 0.8-1 mm. If the surfaces to be welded have a thickness of more than 5 mm, then the diameter of the wire material must be at least 1.6-2 mm.
will offer you a wide range of welding wire of various brands, allowing you to make the right choice for high-quality welding of various types of metals.