| Name | engine's type | welding current, A | additional options | chassis | dimensions, mm | Weight, kg |
| ADD-4004M | D-144 (air cooled) | 400 | constant welding current | No | 2050 x 1000 x 1300 | 900 |
| ADD-4004MP | 400 | mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 2300 | 1520 | |
| ADD-4004MV | 400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V | No | 2050 x 1000 x 1300 | 980 | |
| ADD-4004MVP | 400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 2300 | 1600 | |
| ADD-4004M | D-242 (water cooling) | 400 | constant welding current | No | 2250 x 1000 x 1580 | 1120 |
| ADD-4004MP | 400 | mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 2580 | 1740 | |
| ADD-4004MV | 400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V | No | 2250 x 1000 x 1580 | 1200 | |
| ADD-4004MVP | 400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 2580 | 1820 | |
| ADD-2x2501 | D-144 (air cooled) | 2x250/1x400 | constant welding current | No | 2420 x 1000 x 1300 | 1120 |
| ADD-2x2501P | 2x250/1x400 | mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 1300 | 1740 | |
| ADD-2x2501V | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V | No | 2420 x 1000 x 1300 | 1250 | |
| ADD-2x2501 (B) | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, with idle voltage reduction unit | No | 2420 x 1000 x 1300 | 1250 | |
| ADD-2x2501VP | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 1300 | 1870 | |
| ADD-2x2501 | D-242 (water cooling) | 2x250/1x400 | constant welding current | No | 2250 x 1000 x 1580 | 1260 |
| ADD-2x2501P | 2x250/1x400 | mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 1580 | 1880 | |
| ADD-2x2501V | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V | No | 2250 x 1000 x 1580 | 1340 | |
| ADD-2x2501 (B) | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, with idle voltage reduction unit | No | 2250 x 1000 x 1580 | 1340 | |
| ADD-2x2501VP | 2x250/1x400 | with additional generator 4 KW, 220V, mobile | Yes | 3265 x 2135 x 1580 | 1960 | |
| ADD-2x2501VP | 2x250/1x400 | on a special biaxial chassis with a container for gas-cutting equipment, a container for tools, a pre-heater, additional. generator, spark arrester | Yes | 6250 x 2470 x 2650 | 3320 |
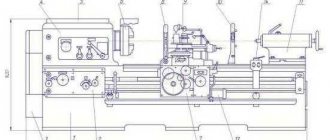
Universal diesel welding unit ADDU-4001P on chassis
Universal diesel welding unit (MMA, MIG/MAG) on a chassis. The unit can carry out welding in MMA mode at direct current up to 400A, welding in semi-automatic mode (MIG/MAG) using a feed mechanism and a torch.
Technical characteristics of the universal diesel welding unit ADDU-4001P on a chassis
Mobile welding units, generators
Electric arc welding technology involves the use of an electric arc to melt metals. Today, a wide variety of welding units are produced for this type of welding. These can be compact household units weighing no more than 40 kg or more powerful mobile welding units equipped with a generator. Such installations are used for work in hard-to-reach field areas using their own power source.
An example of a motorized welding machine is the ADD-4004 diesel unit. This device is manufactured in . The tool ensures the efficient operation of the 1st welding station, is powered by its own power supply, which can also be used to operate other electrical equipment.
Such models of devices are installed on two-wheeled and four-wheeled chassis; they can be used in field, stationary conditions.
Universal diesel welding unit ADDU-4001PR
Universal diesel welding unit ADDU-4001PR (MMA, MIG/MAG, plasma cutting). The unit can carry out welding in MMA mode at direct current up to 400A, welding in semi-automatic mode (MIG/MAG)…
Technical characteristics of the universal diesel welding unit ADDU-4001PR
Intel® Core™ i3-4005U Processor (3MB Cache, 1.70GHz) Product Specifications
Date of issue
Date of first introduction of the product.
Lithography
Lithography refers to the semiconductor technology used to make an integrated circuit and is specified in nanometers (nm), which indicates the size of the features built on the semiconductor.
Number of Cores
Cores are a hardware term that describes the number of independent central processing units in a single computing component (chip or chip).
Number of threads
A thread, or stream of execution, is a programming term that refers to a basic, ordered sequence of instructions that can be transmitted or processed by a single CPU core.
Base CPU frequency
The processor's base frequency describes the speed at which the processor's transistors turn on and off. The base frequency of the processor is the operating point at which the TDP is determined. Frequency is usually measured in gigahertz (GHz) or billions of cycles per second.
Cache
CPU Cache is an area of fast memory located on the processor. Intel® Smart Cache is an architecture that allows all cores to dynamically share access to the last level cache.
Bus speed
A bus is a subsystem that transfers data between computer components or between computers.
Types include front-end bus (FSB), which transfers data between the CPU and the memory controller hub; Direct Media Interface (DMI), which is a point-to-point connection between the Intel Integrated Memory Controller and the Intel I/O Controller Hub on the computer motherboard; and Quick Path Interconnect (QPI), which is a point-to-point connection between the CPU and the on-chip memory controller.
TDP
Thermal design power (TDP) is the average power in watts that the processor dissipates when running at base frequency with all cores active in an Intel-defined high-complexity workload. For thermal solution requirements, see technical data sheet.
Built-in options available
Affordable Embedded Options denotes products that offer increased availability for purchasing smart systems and embedded solutions. Product certification applications and conditions of use can be found in the Product Release Qualification Report (PRQ). Contact your Intel representative for details.
Find products with available built-in options
Maximum memory capacity (depends on memory type)
Maximum memory refers to the maximum amount of memory supported by the processor.
Memory types
Intel® processors
come in four different types: single-channel, dual-channel, triple-channel, and flexible.
Maximum number of memory channels
The number of memory channels refers to the bandwidth performance of the actual application.
Max Memory Bandwidth
Max. Memory bandwidth is the maximum speed at which data can be read or stored in semiconductor memory by the processor (in GB/s).
Supported ECC memory
‡
ECC memory support indicates the processor's support for memory with error correction code. ECC memory is a type of system memory that can detect and correct common types of internal data corruption. Note that ECC memory support requires both processor and chipset support.
Find products with supported ECC memory‡
CPU graphics
‡
"Processor graphics" refers to the graphics processing circuitry integrated into the processor, providing graphics, computing, multimedia, and display capabilities. Intel® HD Graphics, Iris™ Graphics, Iris Plus Graphics and Iris Pro Graphics deliver enhanced media conversion, high frame rates and 4K Ultra HD (UHD) video. See the Intel® Graphics Technology page for more information.
Graphics Base Clock
Graphics Base frequency refers to the nominal/guaranteed graphics rendering clock speed in MHz.
Max dynamic graphics frequency
Max. Dynamic graphics frequency refers to the maximum graphics rendering clock speed (in MHz) that can be supported by Intel® HD Graphics with dynamic frequency feature.
Max.
graphics video memory
The maximum amount of memory available for processor graphics. Processor graphics run in the same physical memory as the CPU (subject to OS, driver, and other system limitations).
Graphics output
Graphics Output defines the interfaces available for communication with display devices.
Maximum Resolution (HDMI)
‡
Maximum Resolution (HDMI) is the maximum resolution supported by the processor via HDMI (24 bits per pixel and 60 Hz). The display resolution of a system or device depends on many system design factors; The actual resolution on your system may be lower.
Maximum resolution (DP)‡
Maximum resolution (DP) is the maximum resolution supported by the processor through the DP interface (24 bits per pixel and 60 Hz). The display resolution of a system or device depends on many system design factors; The actual resolution on your system may be lower.
Maximum Resolution (VGA)‡
Maximum resolution (VGA) is the maximum resolution supported by the processor through the VGA interface (24 bits per pixel and 60 Hz). The display resolution of a system or device depends on many system design factors; The actual resolution on your system may be lower.
DirectX* Support
DirectX* Support indicates support for a specific version of Microsoft's set of APIs (application programming interfaces) for processing multimedia computing tasks.
OpenGL* Support
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a cross-language, multi-platform API (application programming interface) for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics.
Intel® InTru™ 3D Technology
Intel® InTru™ 3D Technology delivers stereoscopic 3-D Blu-ray* playback at full 1080p resolution via HDMI* 1.4 and premium audio.
Intel® Flexible Display Interface (Intel® FDI)
The Intel® Flexible Display Interface is an innovative way to display two independently controllable channels of integrated graphics.
Intel® Clear Video HD Technology
Intel® Clear Video HD Technology, like its predecessor Intel® Clear Video Technology, is a set of image decoding and processing technologies built into integrated processor graphics that enhance video playback, delivering cleaner, clearer images that are more natural, accurate and Vibrant colors, clear, and stable video. Intel® Clear Video HD Technology adds video enhancements for richer colors and more realistic skin tones.
PCI support
PCI support indicates the type of support for the peripheral component connection standard
PCI Express version
PCI Express Revision is a supported version of the PCI Express standard. Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (or PCIe) is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard for connecting hardware devices to a computer. Different versions of PCI Express support different data transfer rates.
PCI Express Configurations
‡
PCI Express (PCIe) configurations describe the available PCIe lane configurations that can be used to communicate with PCIe devices.
Maximum number of PCI Express lanes
The PCI Express (PCIe) lane consists of two differential signaling pairs, one for receiving data and one for transmitting data, and is the basic building block of the PCIe bus. The maximum number of PCI Express lanes is the total number of lanes supported.
USB version
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard technology for connecting peripheral devices to a computer.
Total number of SATA ports
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a high-speed standard for connecting storage devices such as hard drives and optical drives to the motherboard.
Built-in LAN
Integrated LAN indicates the presence of an integrated Intel Ethernet MAC address or the presence of LAN ports built into the system board.
Integrated IDE
IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) is a storage interface standard that indicates that the drive controller is integrated into the drive rather than as a separate component on the motherboard.
Supported sockets
The socket is a component that provides mechanical and electrical connections between the processor and the motherboard.
T
JOINT
Junction temperature is the maximum temperature allowed on the processor die.
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
‡
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology dynamically increases processor frequency as needed, taking advantage of thermal and power reserves to give you a burst of speed when you need it and improved energy efficiency when you don't.
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
‡
Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel® HT) provides two processing threads per physical core. Multithreaded applications can do more work in parallel by completing tasks earlier.
Find products with Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology‡
Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x)
‡
Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x) allows a single hardware platform to function as multiple "virtual" platforms. It offers improved manageability by limiting downtime and maintaining performance by separating compute operations into separate partitions.
Find products with Intel® Virtualization Technology (VT-x)‡
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d)
‡
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d) continues existing support for IA-32 (VT-x) and Itanium® Processor (VT-i) virtualization while adding new support for I/O device virtualization. Intel VT-d can Help end users improve system security, reliability, and I/O device performance in virtualized environments.
Find products with Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d)‡
Intel® VT-x with Extended Page Tables (EPT)
‡
Intel® VT-x with Extended Page Tables (EPT), also known as Second Level Address Translation (SLAT), provides acceleration for memory-intensive virtualized applications.
Advanced page tables on platforms with Intel® Virtualization Technology reduce memory and power overhead and improve battery life by optimizing page table management in hardware.
Intel® Transactional Synchronization Extensions
Intel® Transactional Synchronization Extensions (Intel® TSX) is a set of instructions that add hardware support for transactional memory to improve the performance of multi-threaded software.
Intel® 64
‡ Intel® 64 architecture
delivers 64-bit computing on servers, workstations, desktops, and mobile platforms when combined with supporting software.
Intel 64 architecture improves performance by allowing systems to use more than 4 GB of both virtual and physical memory.
Find products with Intel® 64‡
Command set
Instruction set refers to the basic set of commands and instructions that the microprocessor understands and can execute. The value shown indicates which Intel instruction set the processor is compatible with.
Command Set Extensions
Instruction set extensions are additional instructions that can improve performance when the same operations are performed on multiple data objects. These may include SSE (SIMD Streaming Extensions) and AVX (Advanced Vector Extensions).
Idle states
Idle states (C-states) are used to save power when the processor is idle. C0 is the operating state, meaning the CPU is doing useful work. C1 is the first wait state, C2 is the second, and so on, where more energy-saving actions are taken for numerically higher C-states.
Advanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology is an advanced means of delivering high performance while meeting the power-saving needs of mobile systems.
Traditional Intel SpeedStep® technology switches voltage and frequency in tandem between high and low levels in response to processor load. Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® technology builds on this architecture using design strategies such as separation between voltage and frequency changes, and clock separation and recovery.
Thermal monitoring technologies
Thermal Monitoring Technologies protects the processor chassis and system from thermal failure with multiple thermal management features. The built-in Digital Temperature Sensor (DTS) detects core temperature, and thermal management features reduce chassis power consumption and therefore temperatures when needed to stay cool. within normal operating limits.
Intel® ME Firmware Version
Intel® Management Engine Firmware
(Intel® ME FW) leverages native platform capabilities, management and security applications to remotely manage networked computing resources over an out-of-band channel.
Intel® HD Audio Technology
Intel® High Definition Audio (Intel® HD Audio) can reproduce more channels at higher quality than previous integrated audio formats. Plus, Intel® HD Audio has the technology needed to support the latest, high-quality audio content.
Intel® Matrix Storage Technology
Intel® Matrix Storage Technology brings security, performance, and expandability to desktop and mobile platforms. Whether they use one or more hard drives, users can take advantage of increased performance and reduced power consumption. By using more than one drive, the user can gain additional protection against data loss in the event of a hard drive failure.
Predecessor to Intel® Rapid Storage Technology
Intel® Identity Protection Technology
‡
Intel® Identity Protection Technology is built-in security token technology that helps provide a simple, tamper-resistant method for protecting access to your online customers and business data from threats and fraud. Intel® IPT provides hardware-based authentication of a user's unique PC to websites , financial institutions and network services; confirmation that it is not malware trying to log into the system. Intel® IPT can be a key component in two-factor authentication solutions to protect your information on websites and when logging into businesses.
Intel® Rapid Storage Technology
Intel® Rapid Storage Technology brings security, performance, and expandability to desktop and mobile platforms.
Whether they use one or more hard drives, users can benefit from increased performance and reduced power consumption. By using more than one drive, the user can gain additional protection against data loss in the event of a hard drive failure. Successor to Intel® Matrix storage technology.
Intel® Smart Connect Technology
Intel® Smart Connect Technology automatically updates apps like email and social networks while your PC sleeps. With Intel Smart Connect Technology, you don't have to wait for apps to update after your PC wakes from sleep mode.
Intel® Smart Response Technology
Technology
combines the performance of a small SSD with the large capacity of a hard drive.
New Intel® AES Commands
New Intel® AES Instructions (Intel® AES-NI) is a set of instructions that enable fast and secure encryption and decryption of data. AES-NI is valuable for a wide range of cryptographic applications, such as: applications that perform bulk encryption/decryption, authentication, random number generation and authenticated encryption.
Find products using new Intel® AES instructions
Security Key
Intel® Secure Key consists of a digital random number generator that creates truly random numbers to strengthen encryption algorithms.
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
‡
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology for Secure Computing is a universal set of hardware extensions for Intel® processors and chipsets that extend the digital office platform with security features such as measured startup and secure execution. This creates an environment where applications can run in their own space, protected from all other software on the system.
Find products with Intel® Trusted Execution Technology‡
Execute disable bit
‡
Execute Disable Bit is a hardware-based security feature that can reduce exposure to viruses and malicious code attacks, and prevent malicious software from executing and spreading on a server or network.
Anti-theft technology
Intel® Anti-Theft Technology (Intel® AT) helps protect your laptop if it's lost or stolen. Intel® AT requires a service subscription from an Intel® AT-enabled service provider.
% PDF-1.4 % 60 0 obj > endobj xref 60 130 0000000016 00000 n. 0000003419 00000 n. 0000003530 00000 n. 0000004881 00000 n. 0000005022 00000 n. 0000005651 00000 p. 0000006223 00000 p. 0000006680 00000 n. 0000007121 00000 n. 0000007545 00000 n. 0000007859 00000 n. 0000008325 00000 n. 0000008732 00000 n. 0000008823 00000 n. 0000009281 00000 n. 0000009790 00000 n. 0000009840 00000 n. 0000009888 00000 n. 0000009937 00000 n. 0000010050 00000 p. 0000010161 00000 p. 0000010471 00000 p. 0000010887 00000 p. 0000011384 00000 p. 0000011479 00000 p.
0000011853 00000 p. 0000012370 00000 p. 0000012929 00000 p. 0000013024 00000 p. 0000013440 00000 p. 0000013943 00000 p. 000001430 3 00000 p. 0000015783 00000 p. 0000016173 00000 p. 0000016571 00000 p. 0000016887 00000 p. 0000018512 00000 p. 0000019382 00000 p. 0000020734 00000 p. 0000022251 00000 p. 0000023800 00000 p. 0000023968 00000 p. 0000025631 00000 p. 0000046043 00000 p. 0000047 529 00000 p. 0000049424 00000 p. 0000054545 00000 p. 0000058196 00000 p. 0000060345 00000 p. 0000064577 00000 p. 0000066101 00000 p. 0000066358 00000 p. 0000066441 00000 p. 0000066496 00000 p. 0000066572 00000 p. 0000066865 00000 p. 000006695 7 00000 p. 0000067054 00000 p. 0000067200 00000 n. 0000070196 00000 p. 0000071020 00000 p. 0000071463 00000 p. 0000071546 00000 p. 0000071702 00000 p. 0000071772 00000 p. 000007185 7 00000 p. 0000075201 00000 p. 0000075474 00000 p. 0000075647 00000 p. 0000075674 00000 p. 0000075980 00000 p. 0000076074 00000 p. 0000076684 00000 p.
0000076978 00000 p. 0000077063 00000 p. 0000079794 00000 p. 0000080144 00000 p. 0000080578 00000 p. 0000082335 00000 p. 000008264 8 00000 p. 0000083032 00000 p. 0000085257 00000 p. 0000085602 00000 p. 0000086001 00000 p. 0000086977 00000 p. 0000087281 00000 p. 0000087640 00000 p. 0000123931 00000 n. 0000123970 00000 n. 0000167938 00000 n. 0000167977 00000 n. 0000168080 00000 n. 0000168187 00000 n. 0000168308 00000 n. 0000168457 00000 n. 0000168788 00000 n. 0000169084 00000 n. 0000169490 00000 n. 0000169883 00000 n. 0000170254 00000 n. 0000170610 00000 n. 0000170983 00000 n. 0000171362 00000 n. 0000178154 00000 n. 0000178193 00000 n. 0000184899 00000 n. 0000184938 00000 n. 0000191644 00000 n. 0000191683 00000 n. 0000200954 00000 n. 0000205452 00000 n. 0000209950 00000 n. 0000302269 00000 n. 0001021066 00000 p. 0001022037 00000 p. 0001022296 00000 p. 0001022595 00000 p. 0001031102 00000 p. 0001091085 00000 p. 000109959 2 00000 p. 0001114116 00000 p.
Characteristics
Add a comment Cancel reply
Transformer type electric welding machine
Professional welding machine of simple type. It is bulky due to the volume and weight of the step-down transformer, which changes the voltage to the operating optimum, and the need for forced cooling of the installation. The current strength is regulated by changing the distance between the moving and stationary windings or by a ballast rheostat .
Benefits of use:
- The efficiency of transformers is within 90%.
- Simplicity of design, rare failures.
- Easy to maintain, long-term operation.
- Relatively cheap compared to others.
Minuses:
- Demand for highly qualified welders.
- Arc stability is lower compared to an inverter.
- Dimensions and weight.
Homemade crafts are alive and well
Creating a personal energy-independent unit based on a purchased 4 kW generator and a home-made or ready-made welding machine is justified and advisable. The idea of mobility and autonomy should be complemented by:
- Install additionally to expand the generator function 1–2 sockets;
- Enclose the equipment in all-weather removable cases made of plastic or metal;
- Organize additional cooling with a fan;
- Place the block on the wheels.
Work specifics
Apparatus for welding work ADD-4004 = one workplace. Installation is possible on a two to four wheeled chassis. Used in all kinds of circumstances and even in the absence of electricity. High power.
The ADD-4004 device operates on continuous current for arc welding. During operation, electrodes with a diameter of up to 6 millimeters are used. Electrode type - any. The device has an inductor generator. Excellent performance in diverse environments.