Pure copper ranks next in electrical conductivity after silver, which has the highest conductivity of all known conductors. High conductivity and resistance to atmospheric corrosion, combined with high ductility, make copper the main material for conductors - wires and busbars.
Copper is a metal that has a unique combination of various properties: excellent corrosion resistance, high degree of ductility, attractive color and texture, high thermal conductivity and good electrical conductivity. After purification from impurities, copper acquires a pinkish color when broken, becomes soft and malleable. Removing impurities significantly increases thermal and electrical conductivity, so most of all copper produced is used for the manufacture of electrical products.
Pure copper is a malleable and soft metal, quite heavy, an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, and can be easily processed by pressure. It is these qualities that make it possible to use copper products in electrical engineering. More than 70% of all copper produced goes into electrical products. Cables, electrical busbars, transformer windings and other electrical products are made from different types of copper.
In most cases, so-called technically pure copper, containing about 0.02-0.04% oxygen, is used for electrical needs, but for products that require maximum electrical conductivity, special, “oxygen-free” copper is used.
Want to know everything
When answering the question of what electrical copper is, it is not at all necessary to study lectures on a science such as chemistry and memorize certain common terms. It is enough to pay attention to the most important technical and operational characteristics of copper. It is worth considering the main methods of its production, scope of application, and also mention those who are engaged in the production of copper intended for the needs of the global electrical industry.
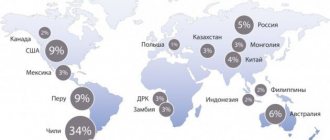
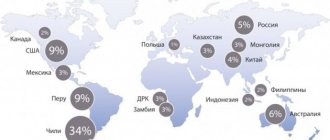
If we take into account the fact that approximately 80% of all currently mined copper is obtained as a result of processing various sulfide ores, it can be noted that the material is characterized by increased production costs. It is usually justified by its fairly wide range of uses.
Main characteristics of copper – electrical and standard
Copper, as a material, has in all respects a unique combination of a variety of properties. Among them are the following advantageous characteristics:
- Ideal parameters of resistance to destructive corrosion;
- High level of elasticity;
- The presence of an attractive color and texture;
- High thermal conductivity parameters;
- Ideal electrical conductivity.
After copper is completely cleared of various impurities, it takes on a pinkish tint at the break and also becomes very soft in structure. Removing a large number of various impurities significantly increases its electrical and thermal conductivity. For this reason, most of all copper produced is used to make various electrical products.
In a large number of cases, special technically pure copper is used to achieve basic electrical needs. It contains approximately 0.02-0.04% oxygen. For products that require maximum electrical conductivity, special copper that does not contain oxygen is used.
Among the most important quality characteristics are factors such as:
- Specific gravity is approximately 8.93 g/cm3;
- Resistance parameters at 20 degrees are approximately 0.0167 Ohm x mm2/m;
- Temperature indicators for effective melting, which is 1083 degrees.
Currently, enterprises from high-quality copper produce a wide variety of products, which include wires, cables, windings for transformers, as well as electrical busbars.
Basic methods for obtaining copper
High-quality electrical copper is a pure metal, because any, even insignificant, impurity significantly reduces electrical conductivity. For example, just 0.002% of a substance such as aluminum, despite the fact that it is also a conductor, can cause the degree of conductivity to decrease by about 10%. What can we say about those impurities that are not conductors at all. It is for this reason that any technical defect cannot be acceptable.
To obtain the highest quality and purest copper, a method called electrorefining is used, it is based on a process such as electrolysis. Ideal conditions are created to promote the separation of impurities from the copper particles itself. Usually they are deposited on one electrode, so as a result you can get special electromechanical copper, the purity of which is 99.999% of the required level, intended for various electrical needs.
Another quite important area of application can be noted - the production of alloys based on copper or with the addition of it. It is interesting that copper, which is soft in structure, in combination with other metals forms not at all soft, but, on the contrary, very hard alloys, that is, solutions. In them, atoms from various metals are distributed very evenly.
If you add a special product of the fire refining process to red copper, adding a small amount of arsenic will seriously increase its strength parameters, but at the same time the capabilities of such a process as welding will be degraded.
Application area of copper
In terms of demand, the entire volume of copper consumed on the world market “diverges” in the following proportions:
- Modern electrical engineering and similar high-quality products – approximately 70%;
- Structural elements of construction projects – 15%;
- Parts from machines and other elements – about 5%;
- Diverse transport areas account for 4%;
- Everything else, including military needs, accounts for approximately 6%.
Regarding the branches of modern industry, the first place here is given to construction. This includes about 40% of the total volume of copper that is currently produced.
An area of modern industry such as electronics takes up approximately 25%, mechanical engineering accounts for 14%, and the transport area accounts for about 11%. The remainder of 9% goes to widespread consumption.
Since low-oxygen and oxygen-free copper has ideal casting qualities, it can be used in the manufacturing process of ground-made pipes, for the production of high-quality modern chemical-technological equipment, productive automobile radiators and standard household water pipes.
Manufacturers of quality copper
All copper must fully comply with the requirements of GOST 434-78. They produce special copper buses at such industrial enterprises as:
- MMC Norilsk Nickel, which is one of the largest and main producers in Russia;
- UMMC Holding;
- CJSC Russian Copper Company. The company has 11 enterprises in Kazakhstan and four large regions of Russia.
These are large enterprises, but there are also smaller ones.
Various useful parts
The general technology for manufacturing copper busbars is the same at all enterprises without exception, but the modern buyer is interested in the cost, which, with high quality, will be more affordable. It is worth noting that modern Russian enterprises do not compete in terms of quality, since it is all quite high, but exclusively in cost policy.
In order to achieve certain conditions during the operation of the main current-carrying parts, various innovative solutions and modern technical approaches are used in production:
- Collector strip, that is, a certain alloy of silver and high-quality copper, which is superior to ordinary pure copper in basic technical and operational qualities;
- Electrical profiles used in industry, having a rectangular shape for special purposes;
- Completely hard, clean surface and semi-hard tires;
- There are tires with a special rounding of all the small-sized sides of the cross-section being produced, and so on.
Due to this rounding, the durability of the existing insulation coating can be achieved, since there are no sharp bends in shape at all corners. The total amount of copper is also seriously saved without a simultaneous loss of quality conductivity. Another advantage is the efficient distribution of the entire current load, and as equally as possible over the entire cross-section.
Busbars that have a higher purity of the entire surface present are designed for a specific electrolytic coating of the next contact area with silver. Thus, it is possible to achieve a significant reduction in the overall contact resistance value.
Regarding the purchase of cables made of high-quality electrical copper:
How is copper obtained?
Copper used in wires and cables is of fairly high purity. To obtain it, copper ores (sulfide, oxide and mixed) are used. Let me remind you what sulfide ores are - they are fossil raw materials that are mined in nature and consist of heavy metal (ore), sulfur (sulfide) and various impurities.
Sulfide ores account for almost all copper production and reserves (among ore production). The most common minerals in terms of deposits and feasibility of extraction among sulfide ores are chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), chalcocite (Cu2S), bornite (Cu5FeS4).
| mineral name | chemical formula | % copper | color |
| chalcopyrite | CuFeS2 | 34,5 | gold, yellow |
| chalcocite | Cu2S | 79,8 | black, gray, blue |
| bornite | Cu5FeS4 | 63,3 | red, copper |
In general, in the first stage, copper-containing ores are mined.
The mined ores must then be purified of all impurities and foreign metals to produce copper. For these purposes, the following methods are used: pyrometallurgical, hydrometallurgical and electrolysis. For example, after the pyrometallurgical method we will receive copper ingots in which the copper itself will be 90 percent. Not bad, but it could be better.
Then this blister copper is brought to 99.99% purity using electrolytic purification and we get what is used in the energy industry.
The influence of impurities on the properties of copper
The issue of copper purity is quite important:
- in the presence of 0.02% aluminum impurity, electrical conductivity decreases by approximately 10%. But aluminum is a fairly good conductor.
- in the presence of 0.1% phosphorus, the resistance increases by 55%, therefore the conductivity decreases as the reciprocal of the resistance
- if there is bismuth or lead in copper in an amount of more than 0.001%, then this causes red brittleness (cracking during hot pressure treatment)
- Oxygen in copper makes soldering difficult and increases resistivity. To avoid this, a phosphorus additive is introduced
- hydrogen - forms microcracks and increases brittleness
If several impurities are present, then there are situations where they interact and their influence increases significantly.
For the use of copper to transmit electricity, the presence of impurities has only a negative effect.
Advantages of copper conductors
It is not without reason that copper is chosen as a raw material for the manufacture of cable products. Compared to aluminum, it has a number of advantages:
- The resistance of copper wires is lower than that of aluminum. This allows the use of a smaller cross-sectional diameter and reduces heating losses.
- Good corrosion resistance. Complete replacement of supply networks is carried out after 30-35 years of operation.
- Plastic. Copper wire is very flexible, which makes the installation process easier and eliminates kinks.
Brands of copper wires and cables: markings, characteristics, manufacturers and application features
There are tens of thousands of different wires and cables on sale. Some of them are made according to GOST standards, and the rest are foreign analogues. Among all the variety, copper products are widely used. We will talk about them today. In order not to get confused in terminology, let’s first clarify what a copper cable and wire are.
Brief contents of the article:
Brands of copper wires and where they are used
The wire is a single, multi-core structure without insulation or in a rubber or plastic braid. Today, wire cores are made of copper or aluminum. Copper is used to make reliable, power conductors. It differs from aluminum in a large number of positive features. The conductor has lower resistance. This reduces the cross-sectional diameter and reduces heat losses during heating. The cable has good corrosion resistance. Complete replacement of supply networks is carried out after thirty years of operation. Copper is more flexible compared to aluminum. This makes the installation process easier and eliminates kinks.
Section calculation
The cross-section of a copper wire is the area that the core has in cross section. The value is influenced by the long-term permissible load and current strength.
The easiest way to calculate the cross-section is to use data from tables that take into account operating conditions and maximum current. To do this, you will need two more indicators - the total power of electrical consumers (kW or W) and voltage (V). The first is indicated in technical data sheets or on the housings of devices, and the second for city apartments is 220 V.
Next, the obtained power values are found in special tables and compared with the diameter of the conductor. Remember that in calculations it is necessary to leave a small margin in diameter. After all, when connecting new equipment, the load will increase.
Brands of copper wires
Each copper wire consists of a conductor of electrical copper. Inside it there are several more isolated cores in the inner shell. On top, depending on the type, the product is covered with a protective screen. Often has metal armor.
Depending on their purpose, cables can be power, control, or radio frequency. The best-selling brands of copper wires are:
VVG is a power device with a maximum number of cores of 5 pieces, 98% resistance to humidity and temperature. Works in a network with 1000 volt parameters. It has a black or gray outer shell, white, yellow or blue insulation. It has a non-flammable appearance - VVGng.
NYM
- copper wire with a polyvinyl chloride non-flammable insulating layer. The space is filled with coated rubber, which is why the cable has high strength and heat resistance. The number of veins in it reaches 5 pieces. It differs from VVG in that it costs more. It is produced in a round shape. This is inconvenient if you need to carry out internal laying. The conductor can be installed outdoors. Its bending radius allows for work of any complexity.
KG
- flexible copper wire, which is used at constant or alternating voltage to power portable equipment, welding machines.
Alloy characteristics
The electrical conductivity of metals can depend not only on the amount of impurities present in them, but also on other indicators. For example, as the heating temperature increases, the ability of copper to pass current through itself decreases. Even the method of its manufacture affects the electrical conductivity of such wire. In everyday life and in production, both soft annealed copper conductors and hard-drawn ones can be used. The first variety has a higher ability to pass current through itself.
However, the additives used and their quantity have the greatest influence on the electrical conductivity of copper. The table below provides the reader with comprehensive information regarding the current carrying capacity of the most common alloys of this metal.
Electrical conductivity of copper alloys
Condition (O - annealed, T - hard-drawn)
Tin bronze (0.75%)
Cadmium bronze (0.9%)
Aluminum bronze (2.5% A1, 2% Sn)
Phosphor bronze (7% Sn, 0.1% P)
The electrical conductivity of brass and copper is comparable. However, for the first metal this figure is, of course, slightly lower. But at the same time it is higher than that of bronzes. Brass is used quite widely as a conductor. It passes current worse than copper, but at the same time it costs less. Most often, contacts, clamps and various parts for radio equipment are made from brass.