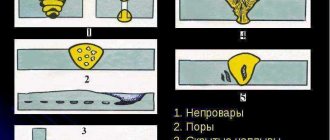
Rubber injection molding
The production of rubber technical products by injecting a heated rubber mixture into a prepared mold is called rubber injection molding.
After injection, the vulcanization process occurs, that is, the rubber mixture turns into rubber with predetermined properties. The first experience in producing rubber products by casting was obtained many years ago. The rubber mixture was placed in a specially made mold and, using a punch, it was pressed into the free cavity of the mold. The finished product is formed in a closed shape. This approach reduces the likelihood of burrs, and the products themselves accurately replicate the required configuration of the future part.
In this case, the payback of the forms occurs quite quickly.
Silicone rubber injection molding equipment
The form consists of several parts - several rings and a core. Between the lower and middle rings there is a volume in which the product is formed. A heated rubber mixture is injected into the space between the upper and middle rings. During casting, the mixture, under the influence of external pressure, leaves the upper chamber and enters the lower chamber through the casting passages. After cooling, a finished part is formed in it.
It should be understood that a large amount of time is required for assembling, disassembling the injection mold, removing the finished part and filling the rubber mixture; we must not forget about the timely maintenance of injection molding equipment.
Dosing
Rubber molding is a continuous technological process. The pre-prepared mixture is placed in a container, from where it enters a hopper with a rotating auger. The mixture is fed into the mold under pressure created by the screw.
Dosing process in injection molding
As the mold is filled, the screw stops rotating. Conditions must be created in the container with the auger so that the rubber mixture does not scorch.
Mixing
For casting rubber into molds, pre-prepared and mixed mixtures are used. But, when it is processed in an injection molding machine, while moving along the screw channel, additional mixing occurs.
List of feature articles
Molding of industrial rubber products
Increasingly, in mass production of rubber goods, you can find high-performance injection molding machines (TPAs), which have replaced the slow presses familiar in this area of processing.
The accumulated experience of casting rubber goods on injection molding machines shows that, in contrast to products produced by pressing, injection molded products are obtained more precisely in size, have a better appearance and distribution of physical and mechanical properties during operation, the quality of rubber-metal products is much higher due to the increase in the adhesion strength of the metal rubber, which in turn is ensured by uniform pressure during pre-pressing in the mold. The high economic efficiency of the injection molding process is explained by:
— high equipment performance; — the possibility of automation and mechanization of the process;
— with properly selected equipment and high-quality equipment, you can improve the quality of products, which in turn will eliminate additional processing processes.
The above advantages of casting rubber products on injection molding machines allow the author to dwell in more detail on the features of this method.
Rubber rubber injection molding
is the process of injecting a heated rubber mixture into a heated closed mold, followed by vulcanization of the mixture and obtaining a product with predetermined properties.
The process of casting rubber products on modern injection molding machines consists of the following stages: 1- loading of a pre-prepared rubber mixture into the material cylinder of the injection molding machine;
2- thorough mixing of the composition and heating it in order to transfer it to a plastic state; 3- injection into a heated and pre-closed mold; 4- pre-pressing and vulcanization in the mold; 5- opening the mold and removing the product; 6- separation of the gating system and flash. Let us note some features of the stages of the process of obtaining a rubber product.
1. Preparation of the rubber mixture
Most often it is carried out in a separate room in mixers and on rollers.
In the mixer, ingredients (vulcanizers, fillers, plasticizers, antioxidants, dyes, etc.) are introduced into the crushed and plasticized rubber and thoroughly homogenized - it is at this stage, due to the introduction of certain components into the recipe, that the future technical properties of the finished product are formed
. Next, the rollers produce a belt of raw rubber mixture, having a width and thickness suitable in size (and rarely limited in length) to the size of the loading hole of the material cylinder of the injection molding machine. If the rubber mixture is prepared “for future use”, then it must be wound onto reels and lined with oiled paper to prevent the layers from sticking together. The rubber compound can be made from a wide range of rubbers (starting with natural rubber or such popular ones as butyl rubber, styrene butadiene rubber, nitrile butadiene rubber and isoprene and siloxane rubbers) depending on what properties you want to impart to the final rubber product.
It is important to remember that the mixture must be resistant to scorching at high vulcanization rates. Today, this problem is easily solved by adding a wide range of “smart” catalysts and/or crosslinking inhibitors.
The process of loading the mixture into the injection molding machine is carried out by a belt feeder.
2. Mixing
occurs in the material cylinder of the injection molding machine, where the screw rotates and, due to the occurrence of shear stresses, heats the rubber mixture.
It is important to remember that the heating temperature of the mixture, on the one hand, must be less than the temperature of scorching (premature cross-linking), and on the other, be equal to the temperature that ensures the optimal speed of passage of the mixture through the sprue and mold channels.
3. Injection
. After the mixture, captured by the turns of the auger, has collected in the front part of the material cylinder at the shut-off valve, the auger makes a translational movement and squeezes out, or in technical terms injects, the composition into the mold cavity through the gating channels.
Injection speed
and the flow of the melt (filling the mold) will depend on: - the viscosity of the rubber mixture and its “responsiveness” to increased temperature; — dimensions and configuration of the product and the gating system of the mold; — injection pressure.
Injection volume
(the volume of the mixture injected in one cycle) is equal to the sum of the volumes of the cast products, the gating system and the extrusions, and must be less than the maximum injection volume of the injection molding machine.
You can read more about calculating the parameters of an injection molding machine here
4. Pre-pressing and vulcanization
The mold closing force must be greater than the product of the pressure of the mixture in the mold and the cross-sectional area of the manufactured product in the parting plane. Correctly calculated clamping force and precision of mold manufacturing, if not eliminate the presence of flash, then significantly minimize it.
The differences between the PF for rubber molding and plastic molding are few in number, but significant: - The PF for rubber molding has channels for air removal - pressure release channels.
— The central sprue in molds for rubber goods is thermostatically controlled so that its temperature is lower than the vulcanization temperature, which will ensure the unhindered passage of the subsequent injection volume.
— The sprue channels are designed in such a way that they provide a minimum path for baking the melt in order to avoid overheating with premature vulcanization and “goat” of the mold.
— If the mold has a hot runner system, then the hot runner in the mold for rubber goods is made lockable.
In the photo you can see four shut-off screwed-in injectors. By the way, four injectors do not mean a four-cavity mold. There are complex systems in which each injector injects into a distribution channel, in this case there are 8 products for 4 injectors. Or you may come across a product with a complex configuration, and in order to spill it in a single copy, you need to use more than one injector.
The vulcanization time in the PF is greater than the sum of the times of injection, opening and closing the mold and the time of product removal, so PFs for rubber products are often made multi-position, which allows increasing productivity by saving time at the vulcanization stage.
The operation of the two-position mold can be seen in the video filmed at the K2019 exhibition
5. Process of extracting finished rubber goods
from the mold cavity is associated with difficulties associated with the adhesion of the product to the mold. In this regard, the product is removed:
— increasingly through robots.
Robots provide greater productivity and cost-effectiveness of the process.
- manually;
- with the help of estimates;
- by blowing.
6. Separation of the gating system and flash
can be done in two ways:
— with the help of a robot, while removing the product from the mold;
— in a cryomill, where the products are placed together with the gating system, cooled to a state of brittleness and mixed. Under friction and shock loads, the flash and sprue are separated from the finished rubber goods. After separation, the uncured sprue can return to the first stage of the process and try to become a product again. The stitched gating system, for obvious reasons, is deprived of such a chance, and therefore will be re-crushed and added to the asphalt or covering of playgrounds.
We also thank the Russian representative office of BORCHE for the provided photographic materials.
DIY liquid rubber
You can make liquid rubber mass at home and this is a more affordable way than looking for raw rubber. You will only need to buy 1 pack of borax and 2 bottles of PVA glue. The preparation itself is as follows:
- Mix borax with 0.5 tbsp. water until the liquid becomes clear.
- Add glue and mix well again.
If necessary, you can paint the rubber in the desired color. To do this, first add dye to the glue and only then mix it with diluted borax.
You can use homemade liquid rubber immediately or put it in the refrigerator. There it can be stored in liquid form for some time without solidifying.
Where is silicone used?
This material is used in almost all spheres of human life - in construction, everyday life, medicine and production. Silicone has earned popularity due to its unique and valuable qualities that are absent from analogues of this substance.
Silicone is capable of reducing and increasing the adhesion process, as well as imparting hydrophobic properties to the target object. This universal material is able to maintain its basic parameters at extremely high, low temperatures and in conditions of high humidity. In addition, silicones have dielectric characteristics, bioinertness, a high degree of elasticity, are durable and environmentally friendly.
On an industrial scale, silicone liquids and emulsions based on them are used as anti-adhesive lubricants for large heavy molds, the production of water-repellent liquids, greases, special oils, shock-absorbing, coolants, coolants, sealants and dielectric compounds. Particularly popular are defoamers made on the basis of silicone mixtures.
This material is used to produce silicone alkides and silicone polyesters for various coatings, which must be particularly durable and resistant. It follows that different types of gaskets, bushings, rings, cuffs, plugs and other parts can be used at temperatures from minus 60°C to plus 200°C.
Another property of silicone is resistance to substances such as ozone, radiation, sea water, ultraviolet radiation, boiling water, alcohol, acid solutions, alkalis, mineral oils, various fuels and electrical discharges.
Types of molds
Products can be direct or injection molded, stationary or removable.
Also, molds differ in the technology of production of rubber products. They are:
- Compression. They are usually two plates, between which a pre-formed blank is laid. Such devices are suitable for small-scale production of large-sized products or the manufacture of products from expensive raw materials.
- Injection. They are casting systems used on vertical or horizontal presses. They are used for large-scale automated production.
- Injection-compression (open). Suitable for the production of parts that do not allow residues of flash, membranes, and medical products.
Recovery methods
Restored rubber part using kerosene method Rubber elements, under the influence of external factors, lose their original properties, become less elastic, and harden. Their continued use will not bring the desired effect; seals, for example, will not be able to make the system completely sealed. Purchasing new rubber elements is sometimes difficult due to the lack of products of the required sizes or their inflated cost.
The following substances can soften rubber:
- Kerosene. Allows you to make rubber parts soft, affecting the structure of the material. After processing, the rubber element becomes completely elastic. The recovery technology is as follows:
- fill a small container with kerosene (select the container size depending on the size of the product to be restored);
- place the part in a container with kerosene for 3 hours;
- after the specified time, check the product for softness, if the result is satisfactory: remove the material and rinse with warm running water;
- Dry the material naturally, without using a hair dryer or battery.
- Ammonia alcohol. The process for restoring old material is as follows:
- dilute the specified alcohol with water in a ratio of 1:7;
- place the rubber material in the resulting solution for half an hour;
- after the specified time, remove the part and rinse with warm running water;
- Allow the part to dry completely before using it.
Please note: you cannot keep rubber in a solution of ammonia and water for more than an hour. If the material is not elastic after 30 minutes, use another recovery method.
- Rubbing alcohol followed by glycerin. Technology for “reanimation” of rubber parts:
- fill the container with medical alcohol;
- place the part that requires restoration in alcohol for several hours;
- after the specified time, check the condition of the product, if it is soft enough, remove the element from the solution and wash with warm soapy water;
- rub glycerin into the surface of the part using a sponge (cloth);
- remove any remaining glycerin from the surface of the product.
Instead of glycerin, it is allowed to use automobile oil; it is rubbed into the surface of the product, then the part is left for half an hour before use. During this period, the rubber becomes quite elastic.
- Castor oil and silicone. Let’s make a reservation right away - this method allows you to quickly “reanimate” old rubber, but the restoration effect will not last long; after a few days the product will become hard. For this method, follow the sequence:
- coat the part with silicone;
- wait 10 minutes;
- After the specified time has passed, the part can be used.
Please note: a similar effect is achieved by using castor oil. It is rubbed into the surface of the part, after which it becomes soft and elastic.
We recommend watching a video about softening rubber using ammonia:
Rubber injection molding. Classification. Which method should you choose?
What types of rubber molding are there? What type of casting process is suitable for your products?
There are a number of factors that need to be considered when determining the type of casting process required. Some of them include: • Product size and geometry; • Weight; • Required material; • Amount of parts required. When you require high tolerances and product quality, Rezinoplast offers its customers cost-effective rubber molding solutions. Let's look at all the types. Compression Molding
Compression molding is a process consisting of several elements: obtaining the required rubber mixture and making a preform in the shape of the final product. The blank provides excess material while completely filling the space. After laying, the mold is closed and heated. Due to the increased temperature and pressure, the workpiece fills the mold. When the cavity is filled, the excess in the mold fills the lining grooves. At the end of the process, the excess rubber is removed, usually by hand, leaving the finished molded product in the mold cavity.
Compression molding is often chosen for medium-hard products in low-volume production. Or for manufacturing from particularly expensive materials. This process helps minimize the amount of overfill or scrap created during the rubber molding process.
When creating complex rubber products obtained by pressing, some mold designs are more labor-intensive to put rubber into them. In addition, the compression molding process for rigid rubber compounds is not well suited to material consumption requirements.
Advantages of the compression method:
• Cost-effective tooling • Maximum number of cavities • Cost-effective process for medium precision Compression molding can be a cost-effective solution in situations where: - When a mold is available; — Low required volume; — The need for gluing rubber to metal; — The cross-section of the part is very large and requires a long curing time. Compression molding applications range from simple O-rings to complex brake diaphragms. Rezinoplast also offers various rubber products molded using the compression method or services for the production of rubber goods using our equipment.
Transfer casting
As with compression molding, transfer molding requires secondary processing of raw materials. However, it differs in that the polymer material is placed in a chamber in front of the mold, located between the top plate and the piston. After feeding the material into the container and closing the mold, it is melted in the chamber and injected through a narrow nozzle. This method of transfer transfer through the sprue helps to increase the uniformity of the temperature field in the mass of material, as well as improve its homogenization.
Some advantages of transfer molding over compression molding:
• Large number of nests; • Blanks can be cut by hand from raw materials, thereby reducing the likelihood of contamination that may occur in the injection screw during injection molding. • Manufacturing of more critical parts. The form is static and does not open due to excess. This keeps the part geometry accurate and the parting lines smaller and less noticeable; • Economical process for medium and high precision components; The main disadvantage of transfer molding is the increased amount of waste. This can be seen by the remaining rubber in the heating chamber, which can either be recycled or discarded.
Rubber injection molding
Rubber injection molding successfully modifies the plastic process by heating the rubber and applying significantly more pressure per square centimeter of surface area as it is molded. This is different from the plastic injection molding process, where the materials are cooled under less pressure. Thanks to various innovations, injection molding has become one of the most efficient ways to create molded rubber products in many cases.
The injection and injection molding process begins with efficient material preparation. After thorough kneading and shaping, the sample is crushed into strips 5-7 centimeters wide. These strips are then fed into a screw, which in turn fills the cylinder with the appropriate predetermined amount of rubber material. A device capable of cutting rubber workpieces efficiently and easily is described in the previous article: “Cutting tools for the production of rubber and silicone products.”
Advantages of injection molding:
1. Lack of blanks. • Production of blanks is a labor-intensive step that can potentially affect the finished product due to differences in weight and shape; 2. There is no operator intervention in the production process; • Because blanks are eliminated, the need for operators to place blanks in a mold (compression molding) or chamber (transfer molding) is eliminated; 3. The injection nozzle preheats the material before feeding; • Heat reduces viscosity, allowing it to flow and spread throughout the mold more easily; • The process provides the ability to reduce curing time; • Is in the process of vulcanization due to the heat generated during injection; 4. Reduced cycle time; 5. Cost-effective process for large volumes of medium and high precision components; 6. Minimum waste. s
Injection molding is one of the most common methods of molding products. The reason for this is high-quality equipment that can work not only with rubber, but also with silicone.
The manufacturer of rubber products, Rezinoplast, uses all of the listed methods for molding products in production. If you have a need for details, we will help you choose.
We carry out rubber molding to order!
Removing flash
Removing excess edges or burrs from a molded rubber product can be accomplished in several ways. Depending on the material, part size and quantity.
Common methods: • Manual trimming; • Cryogenic treatment; • Scoring machines; • Precision grinding.
Casting the mold
The compound is a two-component material consisting of silicone paste and a hardener (catalyst). It's not exactly DIY silicone. But still.
By mixing these components in the correct proportions, you will get a miracle mixture for casting any shape you like.
The catalyst does not allow the silicone to harden as quickly as in the first case.
So. You have a very beautiful mold and you need to copy it in silicone format.
- Take the container and make sure it has no cracks or leaks.
- Place a model of a plastic or plaster toy in the shape of a bear in it.
- Fill the box with the model with dry mixture or sand to understand how much silicone will be needed for pouring in milliliters.
- We treat our bear with soapy water or sunflower oil and fill it with silicone.
- Think in advance about how you will seal this box hermetically.
- We wait approximately 15 minutes.
- We disassemble the container and check that the silicone does not stick to the fingers.
- Use a utility knife to cut the silicone lengthwise.
- Now replicate this form using the resulting silicone mold as much as you want.
Using liquid or cast silicone, you can make molds on platinum.
- We treat foam or gypsum platinum with the same soap solution.
- Apply liquid silicone with a brush.
- First we work on the details, the top layers generously.
- Let it dry. This will take time.
- Remove the silicone. Sleight of hand, as they say, and no fraud.
Making a rubber mold.
Unfortunately, there is no time yet to make a simple form, photograph and describe the process. I decided to show the process of how I made the mold for my Mustang. This is, of course, a very complicated form, but for general acquaintance I think it will be interesting. I’ll try to show everything later with simple products, for example, how to make a mold for soap or a candle.
Of course, we need to start with a master model of the work that we want to reproduce. In my case, these were different horses. Sizes from 2 cm to 14 cm in height.
I will pour by dividing the mustang into 3 parts: stand-tail-the figurine itself.
To make a mold, you need to purchase the most important thing - rubber. Rubber is sold in cans, usually 1 kg. Supplied complete with a hardener (catalyst). After mixing, it hardens in an average of 18 -24 hours. Depends on the amount of catalyst and the temperature of the environment. It’s better to take your time and keep it for 24 hours at the specified temperature specified by the manufacturer.
First you need to study the model well and identify its problem areas. that is, those places where air can accumulate during casting and the casting material (plastic, wax, soap, chocolate) will not pass and, accordingly, a defect will result. There you need to install vents through which the air will escape during filling.
I decided to pour the horse through the belly: I turn it over and determine the negative angles... All the places where air could theoretically accumulate.
To determine, I turn the figure over.
I marked the problem areas in red - in these places I put holes and a sprue in the stomach (thick for pouring the main mass).
Here is an approximate simplified diagram, let’s say this is some kind of bobby.
And this is how it looked during the manufacturing process.
I secured the sprue with glue, and inserted the stops into the pre-drilled holes with a very thin jewelry drill. Now we need to build a sealed formwork around it, into which we will later pour the rubber. I made it from PVC panels, coated it (sealed it with sculptural plasticine).
Everything must be very reliable, without cracks, otherwise the expensive rubber will go out of shape and the effort and money spent will be lost. The main thing is not to rush and think through everything carefully, coat it very thoroughly.
You will get something like this design.
The lines on the model are auxiliary lines along which I am subsequently going to cut the shape.
Now all I have to do is stir the required amount of rubber mass, fill the mold and put the whole thing in the pressure chamber.
24 hours have passed. I removed the formwork and got a cutter inside which there is a master model.
Now you need to cut out the model from there. And you will get a mold for subsequent casting.
I usually use liquid polyurethane compounds. They are expensive, but produce very high quality castings. From one mold you can get from 10 to 20 castings, after which the mold corrodes and you have to make a new one. From the mustang mold I managed to get 12 pieces, for example. The cost of rubber material for this form was approximately 1200 rubles.
After I cut out the model, I pour the material into the mold and after 10-15 minutes I take out the cast model.
The most difficult thing is to think through the cutting line correctly, otherwise you won’t be able to get the castings - they will all break off in problem areas. And you will have to redo the form. As you understand, this is again an expense. I could allow myself to experiment with shapes on my model. It is difficult to explain and show all the nuances; everything will come with practice. One thing we can advise is to start with the simplest and smallest forms possible, then this will save money and give you the opportunity to practice and work out all the techniques for working with molding rubbers and injection materials.
Actually, this is what I got after casting - this is a bone simulator cast from Protocast plastic.
The process of removing from a cut mold. The thick one is the sprue through which I poured the figure. Thin tubes come from the hooves; the more of them, the better the casting. But the more complex the form.
This is what happened in the end.
And several other painted figures made using the same technology.
Next time I'll show you how to make a simple mold without a pressure chamber.
Which product to buy to restore shine?
When choosing a solution for treating tires, first of all, you need to pay attention to its composition. The result will depend on it
For summer it is possible to use a water-based one, but for winter it is better if the product is silicone. Automotive stores offer a wide range of inks and they are all divided into two types:
- Shiny ones are lubricants that contain a large amount of silicone. After applying them, the tires will become shiny and their appearance more attractive. Disadvantage: they act for a short period of time; after exposure to dust or dirt, they may lose their original appearance.
- Matte. They are used not only when processing tires, but also for the entire car. Once the rubber is coated with this type of liquid, it will take on a deep black color. The disadvantage of this type of blackening is the short lifespan after contact with water, as a result of which their appearance becomes even worse than before staining.
You can use various means for blackening tires every day, if it’s not too expensive for your wallet. But it will be much more effective to use it to achieve a specific result after understanding the properties, purpose and consequences of processing. On various forums you can often find discussions on the topic of blackening, its necessity and meaning. After studying several such discussions, reading reviews and personal experience of use, we came to the conclusion that the best means for blackening rubber include the 5 liquids presented below.
Blackening of wheels. Life hack against special means.
Rubber is considered one of the most common materials today. Over time, the basic characteristics may decrease significantly. A fairly common question is how to soften rubber.
This procedure can be performed independently at home, it is important to follow all recommendations
Silicone parts
Silicone is a biologically inert material. Due to its special chemical structure, it is superior to other elastomers in terms of resistance to chemical/temperature influences. It is used to make parts for industrial equipment, medical devices, equipment for difficult operating conditions, and non-standard elements that come into contact with food products.
We have equipment and specialists for developing drawings, polymer mixtures, and equipment for producing silicone parts from scratch. We produce molded/extruded parts – standard and according to customer drawings.
- Development of technical documentation.
- Determination of optimal release technology.
- Development and production of equipment.
- Preparing the mixture.
- Release of technical batch.
- Quality tests.
- Serial release.
- Shipment of finished products to any region of Russia.
The project is supported by full-time process engineers who control the process from document development to quality testing. Finished elements undergo quality control at the injection molding stage, as well as shipment. We organize serial production of large batches, as well as test ones before launching into mass production.
The range and technical characteristics of manufactured rubber goods are presented in the catalogue. We will help you determine how to calculate the cost of producing a silicone product and its profitability. We will evaluate the prospects and advise on the terms and conditions of the order.
To place an order, send us a technical specification describing the scope of application or call +7-496-217-13-68.
What is needed to restore the elasticity of rubber
Rubber is considered one of the most elastic materials. It is for this reason that it is used in the manufacture of various seals. After the load stops acting on the seal, it is able to return to its dimensions. This moment determines the spread of the question of how to restore the elasticity of rubber. Over time, this property is also lost. If the surface wears too much, cracks appear, due to which the insulating qualities are significantly reduced.
You can soften rubber at home using common substances. The most commonly used substances are:
- Kerosene can easily restore the elasticity index. This substance is ideal for processing small products; it can be softened by soaking them.
- Ammonia can be used to soften the structure. To do this, it is enough to create a small bath in which the product is lowered for several hours.
When soaking rubber in a restoration liquid, it is worth considering that the material can significantly increase in size. To remove the substance from the surface, the product is thoroughly washed with soap and water.
In some cases, you can use hot water to soften the rubber. This method is used to restore the insulation of the refrigerator doorway. The achieved effect can be enhanced by wetting the surface with silicone.
Seals made from the material in question are also used in the production of windows. To improve the insulating qualities of the rubber bands, they are wiped with silicone and glycerin from time to time. Such substances can be purchased without any problems.
Using silicone sealant
Nothing complicated either. Even easier than everything that came before.
- Squeeze any silicone sealant onto a plate.
- Add potato starch.
- Knead the rubber dough.
- This mass is ideal for making molds.
- Lubricate the workpiece, which can be anything, with oil or hand cream.
- Cover with silicone.
- Let's forget about this matter until tomorrow.
- The silicone has frozen, cut it lengthwise with a stationery knife, take out the workpiece - you're done! Everything ingenious is simple.
Second option. We roll a ball from the same dough and press the blank of the future mold into it. Well, let's say a coin. Smooth out the edges. After the same few hours, we check the degree of hardening of the silicone. We take out the money, the mold is ready!
Blackening rubber with laundry soap
It’s hard to imagine that such a seemingly ordinary product as laundry soap can help with tire renewal. For this method, you will only need water, soap and a car wash brush with medium-hard bristles (approximately 70%). To carry out this procedure, you must immediately clean the tire from dust and dirt, then lather the brush thickly and rub the rubber. There is also another way, for this you will need to grind the soap with a knife or grater and dissolve it in warm water. After preparing the solution, you need to rub the tires well. Both methods are quite effective, after which your wheels will shine like new. The most important advantage of this method is its accessibility, ease of execution and low cost. There is also another side to the coin; this method is not recommended for frequent use, because soap dries out the rubber and significantly reduces their service life. Therefore, think again before applying any liquids to rubber, so that you don’t have to replace it later.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rubber Molding
Rubber molding has a number of advantages over other methods of producing finished rubber products. Injection molding allows not only to reduce losses of raw materials, but also significantly speeds up the production process, according to various sources, by 20 - 30%. In addition, this technological process can be automated and can be performed without human intervention.
Screw injection molding machines
At the same time, screw-type injection molding machines have a rather complex design, and this limits their use.
Necessary materials
We purchase liquid glass and ethyl alcohol. Mix the ingredients in equal proportions 1:1. The container can be any plastic container.
Silicone hardens quickly when exposed to air, so you need to cook quickly or in small quantities.
When mixing liquid glass and alcohol, add a dye, such as gouache, according to your mood, so that the final result is the desired color.
Frequently asked questions and answers:
What is silicone?
What does silicone look like?
The appearance depends on its components, the degree of density (liquid, gel-like, solid) and the presence of coloring substances. Color varies from clear to any color.
What is coating silicone?
How to make liquid silicone?
It is important to know the type of silicone in order to select the right solvent. Sometimes gasoline and alcohol are used. How to melt silicone at home?
How to melt silicone at home?
Finely chop the silicone into a container (resistant to high temperatures), sort if it is colored. You can put it in the microwave, but you shouldn’t do this in an apartment because of the subsequent unpleasant odor
It’s better to try to melt it over a fire, it’s important not to overheat, otherwise it will spoil
Production stages
The equipment is created in several stages:
- Preparation of technical specifications. It provides detailed information about the characteristics of the product and what production technology it is intended for (for example, casting or direct compression).
- Creating a sketch. At this stage, the appearance of the product is determined - the presence of logos, icons and other design elements. After this, design documentation (drawings) is created. When developing it, the characteristics of materials, manufacturability of products, operating conditions and much more are taken into account. After the drawings are ready, a 3D model is designed, which clearly shows what the future mold will look like.
- Manufacturing. Molds for rubber products are made from various grades of steel. Most often, tool alloy steels are used, which, after hardening, are distinguished by high surface hardness and increased wear resistance. Some parts of the equipment undergo additional processing (grinding, polishing) to achieve the required quality and accuracy. Forming surfaces are chrome plated to reduce wear.
- Examination. The finished mold undergoes careful control by the quality control department for compliance with technical specifications and design documentation. For testing, special high-precision measuring instruments are used. Multi-level control allows you to avoid defects and various equipment defects.
We are ready to offer:
- Design services and development of design documentation. You receive a complete set of drawings and 3D models. All documentation is prepared in accordance with the ESKD.
- Parts and products for military-industrial complex enterprises. We have a license from IiIS VVT for the design, production and supply of military equipment, including dual-use military equipment.
- Delivery to any point in Moscow and other cities of the Russian Federation, as well as CIS countries.
How to make rubber elastic
Experts recommend considering each specific case, which can significantly increase the efficiency of the work being carried out. You can soften the rubber as follows:
- Hardness increases if the rubber is kept dry for a long time. Elasticity is restored by wetting the surface with oil. Softening is recommended to be carried out periodically to achieve the desired result.
- Car wipers can be lubricated with silicone grease, which softens the surface. Of course, it is possible to restore an old structure only if there are no mechanical defects.
In addition, you can find special compounds on sale that can soften the structure after application.
Why blacken rubber and what will it give?
First of all, you need to understand what blackening of tires is, and so - this is the process of treating rubber with a specially designed liquid, which does not paint it black, but enhances the blackness and covers it with a protective layer. This product not only gives more shine, but also protects the wheels well from dirt, dust, and prevents cracking. In addition, inks soften the rubber, thereby making it elastic, which helps maintain its integrity for a fairly long period.
Effect before and after treatment
Advantages of tire blackening:
- Tire wear will be significantly reduced.
- Protection against pollution.
- Masking of minor defects using a layer of silicone glue.
- Tire service life.
Inks can be purchased at any auto store, their price starts from 200 rubles, but if you decide to save your budget, you can carry out this procedure at home, so next we will deal with the most popular methods of blackening tires.
Types of silicone rubber
Silicone has a structure in the form of silicon - an oxygen chain. Organic molecules connected to silicon molecules are attached to the side.
Silicone
Sometimes lateral bonds link together the molecular chains that form the basis of silicone. By changing the length of such a chain, the number of attached organic groups and the bonds they form, it is possible to obtain silicone rubbers with different technical characteristics.
Silicones can be divided into groups:
- liquids;
- elastomers;
- resin.
Silicones are separated based on their molecular weight, level of cross-linking, and the number of organic groups connected to the silicon molecules.
Not a single type of rubber, either natural or synthetic, is capable of ensuring the operation of products at temperatures of about 300 degrees.
Silicone rubber Elastosil
As an example, we can consider Elastosil silicone rubber, which perhaps has all the characteristics inherent in silicone. This rubber is resistant to oil and wear. It is used for casting parts operating in an oil environment under the influence of elevated temperatures. In addition, the following types of silicone rubber are produced under the Elastosil brand: Rubber containing barium sulfate in the formulation. It is used in X-ray machines. Frost-resistant rubber that remains operational at temperatures of – 100 degrees. This type of rubber is resistant to radiation.
Cable rubber
Cable rubber with good insulating properties, resistance to elevated temperatures and resistance to radiation. This type of rubber does not burn or ignite.
Manufacturing technology of rubber products
Lecture 23
23.1.
Manufacturing technology of rubber products
Rubbers are plastics with a sparsely networked structure, in which the binder is a polymer in a highly plastic state. In rubber, the binder is natural rubber (NK) or synthetic rubber (SC). Rubbers are characterized by high plasticity, due to the structural features of their molecules. Linear and weakly branched rubber molecules have a zigzag or spiral configuration and differ
Pure rubber creeps at room temperature, especially at elevated temperatures, and dissolves well in organic solvents. Such rubber cannot be used in finished products. To increase elastic and other physical and mechanical properties, a rare network molecular structure is formed in rubber. This is carried out by vulcanization - by introducing chemical substances into rubbers - vulcanizers that form transverse chemical bonds between the units of rubber macromolecules. The mechanical properties of rubber are determined by the results of tensile and hardness tests. When pressing a blunt needle or a steel ball with a diameter of 5 mm, the hardness is assessed by the magnitude of the measured deformation.
During operation, under the influence of external factors (light, temperature, ozone, oxygen, radiation, etc.), rubbers change their properties - they age. The aging of rubber is assessed by the aging coefficient. Determined by keeping standardized samples in a thermostat at a temperature of -70 °C for 144 hours, which corresponds to the natural aging of rubber for 3 years:
23.2. Technology for preparing rubber mixtures and shaping rubber parts
In addition to the base - rubbers - the following are added to the rubber composition: vulcanizing agents, vulcanization accelerators, fillers, plasticizers and dyes.
Vulcanizing substances (sulfur, zinc or magnesium oxides and nitro compounds) are directly involved in the formation of bonds between macromolecules. Their content in rubbers is 5-7%, and in hard rubbers, such as ebonite, up to 30%.
Fillers
Based on their effect on rubbers, they are divided into active and inert. Active fillers (carbon black, silicon oxide) increase the hardness and strength of rubber and increase its abrasion resistance. Inert fillers (talc, chalk, etc.) are introduced into rubber compositions in order to reduce their cost.
Plasticizers
(technical petroleum jelly, paraffin, stearic acid, mineral and vegetable oils, etc.), present in the rubber composition (8-30%), facilitate their processing, increase elasticity and frost resistance.
Antioxidants
slow down the aging process, prevent the addition of oxygen. As a result, rubber macromolecules are torn into pieces and shortened. This leads to loss of elasticity, embrittlement and the appearance of a network of cracks on the surface. Antioxidants distinguish between chemical and physical action. Chemical antioxidants (aldol, neozone), interacting with oxygen, delay its oxidation. Physical antioxidants (paraffin, wax, forming surface films, impede the diffusion of oxygen).
Dyes
(ocher, ultramarine) perform not only decorative functions, but also delay light aging by absorbing short-wavelength light.
The decisive role in the formation of the basic properties of rubbers belongs to rubbers. Natural rubber is obtained from the sap (latex) extracted from the trunks of rubber trees. Latex contains 30 - 37% rubber, the particles of which have a round shape with a diameter of 0.14 - 0.6 microns. Latex rubber is isolated by coagulation using organic acids (formic or acetic). Then the loose curd is washed with water, rolled into sheets and dried. The most widespread varieties of natural rubber: smoked sheet, amber in color and light in color.
Natural rubber is a soft elastic material with a density of 0.91-0.94 g/cm. It dissolves well in organic solvents (gasoline, benzene, chloroform). During long-term storage, crystallization is possible.
At a temperature of -70 °C, natural rubber loses its elasticity and becomes brittle. Heating natural rubber above 70 °C makes it plastic, and at temperatures above 200 °C it decomposes. Rubbers based on natural rubber have high strength and elasticity, and high electrical insulating properties.
Synthetic rubbers, characterized by a variety of properties, have become more widely used in the production of rubber. Synthetic rubber is obtained from alcohol, petroleum, associated gases from oil production, natural gas, etc.
Butadiene rubber
. It is a non-crystallizing rubber, characterized by reduced tensile strength, soluble in inorganic solvents. The frost resistance of butadiene rubber is low and ranges from -40 to -50 °C. SKB rubber is often used to make special rubber.
Nitrile butadiene rubber. They have low electrical insulating properties. They are resistant to gasoline and petroleum oils and are superior to nairite in these indicators. The heat resistance is superior to natural rubber. They also produce oil hoses.
23.3.
Preparation of rubber mixtures and shaping of rubber parts
The technology of preparing rubber mixtures consists of a number of operations performed in a certain sequence. The main operations are preparing the ingredients, mixing them and obtaining a semi-finished product of the required shape.
Before mixing the ingredients, the rubber is cut into pieces and plasticized by repeated passing through rollers heated to 40-50 ° C. This improves the ability of rubber to mix with other components. When mixing, not only the exact proportions are strictly observed, but also the sequence of mixing the ingredients. Antioxidants are usually introduced into the mixture first, and vulcanizers (sulfur or oxides of zinc, magnesium) and vulcanization accelerators are added last. The mixing process is carried out in closed rubber mixers or on rolling machines. The resulting mass is calendered.
Calendering of rubber mixtures is carried out on special calender machines - and as a result, raw rubber is obtained in the form of sheets or strips of a certain thickness. By design, the calenders represent a three-roll stand of a sheet rolling mill. Two rolls, the top and middle, have a temperature of 60-90 °C, and the bottom - 15 °C. The rubber mass, passing between the upper rollers, heats up, envelops the middle roller and exits through the gap between the middle and lower rollers.
Sheets of calendered raw rubber (not vulcanized) are wound onto wooden bobbins, having previously been separated by release paper and thereby preventing them from sticking together. In this form, raw rubber can be stored at 5-20 °C for up to three months, and certain types of rubber for six months.
23.4. Forming rubber parts
Parts of the required shape and size are made from raw rubber using pressing and injection molding methods. Each method has its own inherent technological capabilities and is used to manufacture a certain type of part.
Pressing
. Parts made from raw rubber are molded in special molds on hydraulic presses under a pressure of 5-10 MPa. The workpiece is placed in a mold, if necessary, with reinforcing material, and under pressure it takes the required shape. If the pressing took place in a cold state, the molded product is then subjected to vulcanization. At. During hot pressing and molding, vulcanization occurs. They produce sealing rings, couplings, and V-belts.
Injection molding is a more progressive method. In this case, the mold is filled with a preheated plastic raw rubber mixture under a pressure of 30-150 MPa.
The rubber mixture takes on a shape corresponding to the working cavity of the mold. The strength of rubber products increases when their walls are reinforced with steel wire, mesh, nylon or glass thread.
Complex products - tires, flexible armored hoses and sleeves - are produced by sequentially winding layers of rubber and insulating and reinforcing materials (fabric, metal wires) onto a hollow metal rod.
Curing. Hot vulcanization is carried out in boilers, in automatic presses, continuously under pressure under strict temperature conditions in the range of 130-150 °C. The vulcanization medium can be hot air, steam, hot water, or molten salt.
During vulcanization, a chemical interaction of rubber with a vulcanizing substance (sulfur, peroxide or mi compounds) takes place at the site of the double bond:
Vulcanization can be carried out at room temperature. In this case, there is no sulfur in the raw rubber, and the product is treated in a solution or solutions of sulfur dichloride or in an atmosphere of sulfur dioxide. Vulcanization can be carried out using ultra-high frequency or y-radiation,
As a result of vulcanization, the strength and elasticity of rubber, resistance to aging and the action of various organic solvents increase, and electrical insulating properties change.
Rubbers are characterized by large reversible deformation, reaching 1000%, at relatively low stresses.
Heating, as a rule, reduces the strength properties of rubber.
At low negative temperatures, rubber almost completely loses its highly elastic properties and turns into a glassy state.
Blackening tires with glycerin and water
The most common method is to use glycerin, which can be easily purchased at the pharmacy. Glycerin is a colorless, viscous and very hygroscopic liquid, miscible with water in any proportions. In order to blacken tires at home, you will need only five jars of 25 ml or three of 40 ml, the preparation method is quite simple, you just need to mix glycerin with water in a ratio of 50 to 50 (1:1).
If you need a greasy solution, then you can use 5 parts of glycerin to 3 parts of water, then you will need not to spray the liquid, as in the first case, but simply apply carefully with a pre-moistened sponge. Also, some experimental drivers use proportions such as 1:3 (high fat effect), 1:5 (light shine) or 1:7 (light matte effect), it all depends on the degree of tire burnout.
The most important advantages of this method are:
- Availability of materials.
- Profitability and minimal financial costs, its cost is about 9 rubles.
- Possibility of fast cooking.
- Possibility of frequent use, and can also be used on black plastic elements of the car body, for example on the bumper.
Flaws:
- the fragility of using the tire, namely drying and cracking of the rubber at low air humidity;
- after application, the rubber will have a shine, but since it is a fatty, sweetish liquid, although the tire will shine, it will literally immediately begin to attract dust;
- After the first contact with water, it is washed off.
The shiny effect can last only 2-3 days and only if there are no heavy rains, so washing the car after application is not recommended, otherwise the tires will return to their previous appearance.
Frequently asked questions - answers
What can replace silicone molds?
An excellent alternative is glass and ceramics.
What is the electrical conductivity of silicone?
Has very low electrical conductivity.
Which silicone is best for making molds?
The best series are E-Series, Mold Star Series, Equinox Series, Rebound Series.
How to glue silicone products at home?
You can use special glue for elastic products, silicone sealant, or melt the torn edges with fire and connect them.
How to make liquid rubber at home?
The necessary ingredients are borax (1 pack), PVA glue (2 bottles), water (0.5 cups), dye, containers and something for stirring. Combine borax and water in one container, stir until clear. The other contains glue and dye. Mix the contents of both containers and wait until the liquid hardens.
How long does it take for silicone to cure?
The drying period is influenced by many factors - humidity and air temperature, layer thickness. On average, a film is formed in 15 minutes, and the substance hardens in 24 hours. Acid sealant dries in 4-6 hours, neutral sealant dries in 24 hours. Also, the approximate “ready” time is always indicated on the packaging.
A car surrounded by care stands out from the crowd. The car enthusiast washes and polishes the body, polishes the plastic moldings. Tires are often the object of intense cleaning. As you know, these parts lose their original appearance during the first year of operation. This is due to weather conditions and dust scourge. The result is that the car shines, and the tires give off a characteristic gray tint, which only repels the eye.
Technology for the production of rubber products
The basis of any rubber part is a rubber-based compound. The technological process is determined by the characteristics of the final product. The main raw materials are synthetic rubbers.
The production of rubber and silicone products in Russia includes three stages. The first stage is preparing the rubber mixture. Rubber is brought into a plastic state and mixed with other components that impart the necessary properties.
The second stage is molding. This is done in three ways:
- Calendering is the production of rubber sheets of a given thickness on a sheet rolling mill.
- Pressing – production of shaped parts: sealing rings, cuffs, V-belts. Raw materials are pressed in metal matrices using hot or cold methods.
- Injection molding is the production of parts with complex shapes. The mold is filled with the raw mixture, and high pressure ensures uniform distribution of the raw material along the walls.
The third stage is vulcanization. It secures the physical and mechanical properties of the material. Vulcanization is carried out with hot air, steam, hot water, molten salt. Under the influence of temperature, a chemical reaction between salt and rubber develops, which reduces ductility and simultaneously increases the resistance of the part to organic solvents.
Equipment for the production of rubber and silicone products is technologically complex, so for many manufacturers it is more profitable to order individual elements from third-party enterprises. This reduces the costs of organizing workshops, purchasing equipment, hiring, and training staff.
How to soften rubber at home?
At home, you can soften rubber by using various materials. The most widespread are:
- Ammonia.
- Kerosene.
- Castor oil and silicone.
Restoring rubber at home
High temperatures also cause the rubber to become softer, but wear resistance decreases.
Kerosene
When considering how to soften rubber, many people pay attention to the possibility of using kerosene. Such a substance can restore elasticity.
Features of the application are that the product is soaked in a special bath, after which the surface is thoroughly washed and dried. If the length of the product is large, then it can be rolled up. It is kept in kerosene to soften for several hours, since kerosene does not act immediately.
Ammonia
This substance is widely used and can also make the product softer. The procedure looks like this:
- Select a container of suitable volume.
- Ammonia is diluted in water to obtain the required solution.
- The product is placed in the solution for an hour to soften.
- After this, the softened element is removed and washed with clean water.
Drying is carried out at room temperature. It is worth considering that high and low temperatures always have a negative impact on the condition of the rubber.
Silicone and castor oil
A short-term effect can be achieved by using silicone and castor oil. Among the application features, we note the following points:
- Silicone has only a temporary effect. It can be purchased in specialized stores.
- After lubrication, you need to wait a while. The silicone can be absorbed into the structure, making it more flexible.
After half an hour the rubber will be ready for use. It is worth considering that the achieved effect will be temporary
When considering what can be used to soften such material, you can pay attention to castor oil
Injection molding of rubber compounds
Casting in plunger presses. N.V. Kopaltsev proposed, developed and put into production a method for making blanks by pressing the rubber mixture into a vulcanization mold on plunger injection presses with one working hydraulic cylinder. The heated rubber mixture (Fig. 9) is loaded into the injection cylinder 7. From here, the mixture is forced out by the pressure of the pressure rod 2 into the mold 3 placed under the cylinder. In the bottom of the cylinder and in the lid of the mold there are injection channels 4 and 5. To facilitate their alignment between the mold and The cylinder places the centering washer 6. The pressure rod is attached to the upper cross-beam of the press 7; the mold is installed on the bottom plate of the press 8. The translational movement of the bottom plate brings the mold and washer into contact with the bottom of the cylinder, and then introduces the pressure rod into the injection cylinder. The rubber mixture is compressed, its fluidity increases, and through the injection hole the mixture in the form of a thin cord enters the mold cavity. Lifting of the bottom plate is continued until the entire mold cavity is filled with the rubber mixture. This moment is determined by the release of the mixture through the control hole in the mold. The number of castings that can be made from one fill into a casting cylinder depends on the capacity of the molds; It is possible to accurately dose the filling into a replaceable container to fill one form. The composition of the rubber mixture and the type of rubber in it affect the casting conditions; but the use of the casting method also affects the properties of rubber. The modulus of nitrile butadiene rubbers increases with this processing method; the modulus of butyl rubber decreases. Since hot castings are sent for vulcanization during casting, the vulcanization cycle is reduced in some cases to 20 s.
Injection presses of 1000 and 3000 kN (Fig. 10) are basically close to hydraulic vulcanizing presses, but instead of heating plates, they have a movable cross-beam with an injection cylinder, moving in guides. The frame is balanced by a counterweight; To return it to its original position, there are return cylinders on the sides of the press.
A two-cylinder injection press [12] differs from a single-cylinder one in the following ways. The frame of the casting cylinder is fixed, but the pressure rod attached to the upper cross-beam is movable and represents the plunger of the upper hydraulic cylinder. The lift of the plunger in the lower cylinder and associated platen is used to lift and close the mold against the stationary frame. By lowering the plunger of the upper hydraulic cylinder, the rubber mixture is pressed out of the injection cylinder into the mold. The plunger of the upper cylinder has a reverse stroke for changing bookmarks in the casting cylinder.
The rubber mixture, compressed in the injection cylinder by the pressure rod, is displaced towards the injection hole. The speed and nature of the flow of the mixture from the cylinder into the casting hole and its further flow in the mold depend on a number of production factors. When the rubber mixture, extruded into the mold in the form of one or more cords, fills the mold cavity, the flow of the mixture stops; the pressure inside the cast workpiece increases and acts on the walls of the mold. If the horizontal projection of the mold cavity is less than the area of the pressure rod, then the pressure of the rubber mixture on the mold will be lower than the working force, and the movement of the hydraulic plunger will automatically stop. If the horizontal cross-section of the mold cavity is larger than the area of the rod, then the pressure developing inside the mold can lead to the opening of the mold. Hence, to make large castings, it is necessary either to increase the diameter of the pressure rod, or to equip the molds with mechanical shutters, or to use not one but two-cylinder presses. Once the mold is removed from the injection press, the release of pressure built up in the cast piece sometimes causes the mold to open with an expanding rubber compound. Subsequent pressing of the mold during vulcanization will cause the formation of burrs. This can be avoided if you practice casting in molds that are firmly closed in advance and immediately plug the casting channel after casting. This “compact casting” technique, providing high pressure in the mold during vulcanization, improves the quality of products. To fill the mold, one sprue channel in the mold lid is sufficient. For large or complex castings, multiple sprues are made. The presence of several sprue channels leads to a corresponding number of rubber joints in the cast workpiece. Surface grip depends not only on the properties of the rubber and the cleanliness of the surface of the channels, but also on their shape. If there is contamination (grease, talcum powder, etc.), the junction may not be strong enough. Therefore, slot-shaped gating channels are more convenient for casting ring blanks. Processing one mold on a 1000 kN press takes 25-30 s, including casting a 10 N mixture, which lasts about 10 s.
Injection molding significantly reduces the number of operations for preparing the workpiece (there is no need for calendering, cutting workpieces, manual gluing, etc.), ensures good filling of the mold and accurately doses the workpiece according to the volume of the mold cavity. This method is more convenient than molding when producing large-sized products or products with complex shapes. It has also successfully replaced rolling or roll forming in the production of hollow cylindrical blanks. Filling the mold with a hot (80-100°C) rubber mixture leads to a reduction in vulcanization time compared to molding without preheating the blanks.
In the production of large-sized or particularly complex castings in small-scale production, injection molding has a different technical design. To do this, use the forms discussed below with injection molding extensions. In the production of ebonite accumulator tanks, special vulcanization-cement-molding presses are used.
Casting in worm press units. The difficulty in using conventional worm presses as injection molding machines for direct filling of molds is the insufficient pressure of the rubber mixture inside the head. To create a monolithic, dense workpiece in this way, a pressure of at least (5.0-6.0)-107 Pa is required for mixtures of synthetic rubbers and above 8.0-107 Pa for mixtures of natural rubber. However, a conventional worm press gives a pressure in the head of the order of (1.2 - 1.4) -107 Pa.
To eliminate this drawback, the K-2 automated injection press was created.
Its casting head (Fig. 11) has a double-thrust worm, a mechanism to prevent the rubber mixture from returning back, a cooled body, at the end of which a nozzle is attached. The rubber mixture is fed into the press through a window in the housing, grabbed onto the mold and held closed while filling with the rubber mixture and during vulcanization.
The hydraulic press is used to create external pressure on the mold and to keep it closed when filling with rubber mixture and during vulcanization.
Casting in screw-plunger machines was studied by A. R. Galle and others.
In foreign practice in rubber and plastics production, worm casting machines with a locking device have been used. Such a unit, which performs casting and vulcanization operations, consists of two parts: a) a worm press that supplies the mixture and imparts the necessary pressure to it; b) a press with which the halves of the mold are pressed against each other during casting and vulcanization operations.
In Fig. 12 this unit is shown in an open (non-working) state and in a closed (working) state. An essential feature of the worm press unit is a blocking device at the outlet of the mixture into the head and a control valve in the nozzle part of the chamber. Gears are used as a pressure blocking device (Fig. 13), through which a pressure of about 15.0-107 Pa is maintained in the worm chamber below this device. The presence of this device also prevents the rubber from rotating together with the worm or being squeezed back into the loading hole. The main worm ends in an auxiliary worm of small diameter, which works in conjunction with the annular gap. The exiting mixture has the form of a tube with an outer diameter of 11.1 mm and a wall thickness of 1.6 mm. There is an automatic control valve in the nozzle part of the worm chamber. When the worm is stopped, a spring at the top presses the valve in the conical part of the nozzle. This valve gate is open only while the worm is rotating. The plunger for pressing the mold provides a pressure of about 4.0 • 107 Pa, based on the cross-sectional area along the parting line of the molds. The axial force required for this is 2000–5000 kN. The press plates to which the mold is attached are heated by resistance elements. Since the rubber mixture filling the mold is already heated, vulcanization of products, for example, made from chloroprene rubber at 176 °C lasts 3 minutes, at 182 °C - 2 minutes. The entire work process is automated and begins when the operator presses the start button to begin work.
A description of the unit for the automatic production of rubber O-rings, soles and other products is available in the literature. Such a unit performs the following technological operations: heating the mixture on rollers; calendering; cutting of blanks; pressing; vulcanization; deburring. Previously, all these operations were performed separately.
The rubber mixture from the Banbury rubber mixer is supplied to the heating rollers of the unit, where it is heated to 65°C. The cut strip is fed along a conveyor to vulcanization molds, which cut out blanks of the required size. Vulcanization is carried out at 143-176 ° C during the movement of molds between heating elements. Upon completion of curing, the finished products are pushed out of the molds at the other end of the unit using plungers. The molds are cleaned there with brushes, and then they are used in the next cycle.
Products are obtained with minimal burrs, since blanks of the required size are cut from the tape using a mold. Burrs are removed by freezing. The molds are moved by a chain.
Currently, a model of the unit has been created, adapted for the production of non-metallic parts.
Discuss on the forum
Heating
In a situation where it is not possible to put a hose on a round part or pipe, immersing the desired part of the product in boiling water will help. After waiting a little, you need to remove the hose from the water and, without wasting time, install it in its proper place. This will be quite easy to do, since the high temperature will steam the material.
Sometimes a problem arises with removing rubber elements from some structural parts. In this case, air heating will be effective. A hairdryer is used. Under the influence of a hot jet, the material will expand, as a result of which it will be possible to twist and tighten the element that has become pliable.
Using these simple methods, you can soften hardened rubber, thereby increasing the service life of popular products.
Production of rubber medical products
Silicone rubber is one of the few materials suitable for medical equipment. Its advantages are chemical resistance, elasticity, and hygienic qualities. Silicone has been used in medicine for more than 50 years, and no analogues have yet been found.
Medical products made of rubber / silicone
• Gloves. • Condoms. • Implants. • Hot water bottles. • Tubes, probes, catheters. • Mouth guards.
Honey. products made from artificial rubber are not susceptible to biological fluids, resistant to chemicals, and high humidity. Their operating temperature range is from -70 to +200 degrees. They are not afraid of repeated heat treatment or disinfection with harsh means.
Our production of medical and other rubber products in Moscow allows us to produce a wide range of rubber goods for medical institutions, including non-standard rubber goods. The quality is confirmed by sanitary certificates and certificates of conformity.
Total
You can buy tire ink, or you can make it yourself. In the store you will have to pay at least 200 rubles. The cost of a homemade product is estimated at much lower numbers.
So, a simple composition based on glycerin and water, diluted 1:7, will cost about 15-20 rubles - the cost of one bottle of alcohol composition, which is more than enough for one treatment. The recipe with shoe polish, glycerin and cola is much more expensive, but the result is more durable. An alternative is to treat the tires with shoe polish or black shoe polish. The view is good and resistant to water.
Since the beginning of the 2000s, automotive cosmetology has been experiencing a real “renaissance”, if the processes taking place in it can be attributed to this trend. This movement gained particular popularity during the arrival of manufacturers and the expansion of the range of goods at affordable prices. Almost every system had several dozen types of improvements that could previously have been dreamed of. The widespread interest affected both foreign cars and the domestic auto industry. The technique of blackening tires has become very popular in both cases. But there are few people willing to pay, especially if a similar effect can be achieved using homemade rubber ink.
Self-made rubber dye with your own hands shows good results