Beginning welders are often faced with a choice: what equipment to purchase for work. Knowing the difference between an inverter welding machine and a conventional one, it will be easier to choose a welder. Transformers and high-tech inverter converters have pros and cons. The devices differ in power indicators, functionality, and dimensions.
What is a regular welding machine?
The classic current source for generating an electric arc is a transformer. The welder lowers the mains voltage, and the current increases accordingly. Such equipment was used for manual welding everywhere until the beginning of the 21st century.
The operating principle of the transformer is based on the magnetic induction method. Electric current passing through the first winding magnetizes the core. An electromagnetic field arises, and under the influence of waves an electric current is formed in the wire of the secondary transformer winding. The output voltage depends on the number of secondary turns. The equipment generates high-ampere current with parameters necessary for welding.
Welding transformer layout
Advantages and disadvantages of welding transformers
First, about the advantages of transformer devices:
- simplicity of the device, the scheme of operation is clear to the student;
- maintainability, in case of breakdown the transformer can be repaired independently;
- the ability to work for a long time is ensured by low sensitivity to overheating during operation;
- impact resistance – the risk of mechanical damage during transportation is minimal;
- accessible service;
- low price;
- versatility, the device is used for welding various metals;
- there are no special storage requirements, the transformer is resistant to high humidity and dust.
The disadvantages of traditional welders are obvious:
- when the network sags, the transformer turns off; a stable voltage is needed for power supply;
- lack of precise adjustment of current parameters, large adjustment steps, difficult to set up equipment for welding thin-walled workpieces;
- heavy weight, it is difficult to move the equipment independently;
- significant dimensions;
- high power consumption.
It is worth considering that most transformers operate from a three-phase network. Beginners working with a transformer have problems with arc ignition and sticking. Seams are difficult to form without experience.
Features of transformers
The most accessible means for electric arc welding is a transformer. A good device is capable of connecting metal elements with a thickness of 1.5 to 30 mm. It can also be used for cutting steel when the temperature from the propane-oxygen flame is not enough.
The welding transformer has a simple structure, including two windings. The first receives alternating voltage from an outlet or panel. The devices can be designed for both single-phase and three-phase networks. For this reason they come in large and small sizes. Thanks to electromagnetic induction, the current (A) increases significantly and the voltage (V) decreases. A current of 80 to 500 A is generated on the secondary winding. There are also more powerful models. The maximum for the transformer is 48V at idle. This makes it safe to use when the welder comes into contact with the product being worked on.
This allows you to weld carbon steel, aluminum, and cast iron. Adjusting the current strength in large models is done by removing or bringing the windings closer. Small devices use step switching, cutting off part of the winding and reducing the voltage path.
Equipment advantages
Among the advantages of transformers, the following stand out:
- simple device and the ability to make repairs yourself;
- cheap cost of components;
- alternating current holds the arc well in a humid environment, so when welding pipes with leaking water, it is easier to weld;
- the ability to work as a transformer with electrodes with a diameter of 1.6 to 7 mm (large devices);
- high current strength (in portable models up to 300 A, and in stationary models more than 500 A), allowing you to weld thick metal;
- relatively cheap cost of store versions.
Disadvantages of equipment
The disadvantages of this welding equipment include:
- Step adjustment in small models. This does not allow you to accurately adjust the device to a specific metal thickness. For example, in mode “4” the current strength is not enough for full penetration, and in mode “5” burns already appear. To overcome the situation, welders use a spring located between the product and the ground cable, which creates additional resistance and reduces the current.
- Welding with a transformer is characterized by a stronger hum. This noise can become annoying to the welder throughout the day. To reduce its impact, the device should be placed away from the work site, but this requires longer cables.
- Spattering of molten metal occurs to a significant extent, which leads to excessive consumption of electrodes.
- Most machines can only lower the current to a certain value, usually around 80 A. This creates difficulties when welding thin sheet iron. In such situations, additional resistance must be used.
Which welding machine is better: inverter or transformer
Deciding what is best for welding metal in your own garage or home is not difficult. Comparative characteristics of power supplies will help. First, about the similarities: both are necessary for converting electric current, obtaining operating current parameters, only inverters are equipped with electronic converters.
A short example will help you compare the dimensions of inverter and transformer welding machines. To generate 160 A, you need a transformer weighing 20 kg or an inverter weighing 2.5 kg. The inverter has the highest power, however, transformers have high efficiency.
Advantages and disadvantages of transformers
The main advantages of transformer electric arc sources:
- High power;
- Relatively simple device;
- Easy repair and maintenance.
Among the shortcomings we note:
- Inability to work with an unstable power supply;
- High energy consumption;
- High connection power;
- Impressive dimensions, difficulty in transportation.
Due to the connection power and energy consumption, a transformer is not the best option for a household electrical network. At the same time, in production, under intensive use, it will delight you with its reliability.
Other types of welding equipment
A rectifier differs from a transformer apparatus by the presence of semiconductors that rectify the electric current, and welding capabilities are expanded. When changing poles, you can shift the area of maximum heating:
- with straight polarity, the electrode heats up more;
- in the reverse case, the workpieces to be welded are in the welding zone.
The difference between semi-automatic machines is the use of welding wire, which is fed into the heating zone automatically. Semi-automatic devices are created on a transformer and inverter basis. The transformer semiautomatic device with gas equipment is used in auto repair shops and in production; there are no special requirements for storage and transportation conditions. The inverter is more capricious and is necessary for working with thin metal, stainless alloys, and aluminum.
Separately, there are generators that convert the mechanical energy of the engine into electric current. Such devices produce direct and alternating current, operate on mains power and liquid fuel.
Welders prefer transformer devices for large volumes of work. For beginners, it is advisable to purchase small inverter models. Auto repair shops typically require a variety of equipment.
What is an inverter?
The need for welding work arises not only in industrial activities, but also at home, in the domestic sphere. Often such work appears for owners of private houses or summer cottages. Thanks to the purchase of welding equipment, you can solve any current problem in a short time.
Before choosing a suitable design for your home, you need to understand its purpose, functions and important details of use.
A welding inverter is a device thanks to which you can carry out any welding work at large production enterprises or for private use.
A worthy choice should depend not only on price, capabilities, and quality of work performed, but also taking into account the technical characteristics of the equipment, conditions and specific nuances during operation.
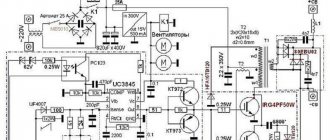
Electrical circuit of a welding inverter.
Important criteria to note when selecting and purchasing inverter welding equipment are as follows:
- The company needs to check the availability of printed circuit boards suitable for a specific design model. They are quite fragile, and repairs are very expensive. In other words, if a specialist has a lot of them, this indicates that the mechanism will most likely break down frequently in the future. In the absence of spare parts and the possibility of purchasing them only for individual order, we can talk about the performance and longevity of the equipment. Additionally, it is recommended to clarify the cost of repairs and production of parts.
- Availability of built-in ventilation. The welding process produces a lot of dust, so it is very important that the design has a cooling fan with a direct purpose. In addition, it must suck up dust. Most manufacturers integrate tunnel ventilation. Thanks to this internal mechanism, additional protection of all main parts from dirt and dust is provided, but the cost increases significantly.
- Protection against sudden voltage changes must be installed. Most welding inverters are sensitive to voltage surges due to built-in protective mechanisms that begin to work when there is a surge of 220 V.
By ensuring that the buyer gets enough information and is able to understand the differences between an inverter and a transformer, the process and task will be successfully completed without any difficulties.
The acquired knowledge will help not only specialists, but also beginners who do not understand the specifics of the instrument. The level of performance depends on the set temperature. It is this that affects the quality of functionality.
For example, due to high temperature - 40+, additional protection mechanisms may start working. However, such an indicator is quite rare in practice. With low temperatures the opposite is true.
Almost every modern equipment contains capacitors, microcontrollers, transistors, etc., which have an individual temperature range.
In cold weather, care must be taken to avoid condensation. At zero temperature, the device may simply not turn on, this will be indicated by a red light with an overload indicator.
When choosing this equipment, you need to familiarize yourself with the passport, operating conditions, permissible temperature, and also find out the possibility of repair services, warranty and the availability of the official website and detailed instructions for use from the manufacturer.
Comparison
There is, of course, more than one difference between an “inverter” and a “transformer” in the context of welding technology. The difference between the types of aggregate under consideration is especially obvious when comparing them in terms of:
- current supplied to the electrode;
- electricity sources used;
- sizes;
- weight;
- welding quality;
- prices;
- frost resistance.
A small table will help us to more clearly reflect the difference between an “inverter” and a “transformer”.
Source
HOW MUCH DO WE WEIGHT IN GRAMS?
An important advantage of inverters over transformers is their low weight and small dimensions. This becomes possible due to an increase in the voltage frequency: after all, when the frequency increases by 1000 times, the dimensions of the transformer decrease by 10 times. For some inverter models, the transformer itself is the size of a matchbox; The main mass is occupied by the radiator. It is not surprising that such an inverter can be easily hung on the shoulder: with a weight of less than 3 kilograms, some inverters allow you to easily work with electrodes with a diameter of even up to Ø4 mm. True, a reservation must be made here: in our Russian conditions, low weight often becomes a big disadvantage. The transformer is still the undisputed leader here: you can’t hide forty kilograms under a jacket.
BURN, BURN CLEARLY...
Perhaps the main disadvantages of transformers are poor arc stability along with low stability of the mode, which is highly dependent on network fluctuations. And here modern rivals - inverters - leave no chance for transformers. Thus, inverter sources provide a stabilized constant welding current that does not depend on fluctuations in the input voltage and thus ensures a stable arc and low spatter during welding. It is also important to have smooth adjustment of the welding current and the presence of special functions for controlling the welding current. For example, the Hot-Start function is widely used in inverters - in order to start welding without complications and unnecessary “strikes”, the inverter increases the initial current. If an inexperienced welder moves the electrode too quickly towards the workpiece, Arc-Force increases the current, speeding up the melting process and preventing sticking. If, nevertheless, the electrode is stuck, then, unlike conventional welding transformers, it will not become red-hot - the Anti-Sticking function will immediately reduce the current, protecting the network and the machine from overload, giving you time to tear off the electrode and continue welding. Among other things, the inverter consumes much less electricity, which gives greater possibilities for operation from a household electrical network and autonomous power sources (gasoline and diesel electric generators). For example, the power consumption of an inverter when operating with a Ø3mm electrode is equivalent to the consumption of two electric kettles, which is well within household standards. In general, welding with an inverter is much easier and more enjoyable than with a transformer.
Features of the inverter welding power source
An inverter for welding is more complex than a transformer. Intended to include:
- Control circuit;
- Rectifier;
- Electromagnetic interference suppression filter;
- High frequency transformer;
- Output rectifier.
The device first converts the mains current into direct current, then into high-frequency alternating current. Further, the voltage of the high-frequency current decreases, but the current increases. At the last stage, the high-frequency current of high strength and reduced voltage is converted into direct, welding current.
The process of generating the welding current is controlled by complex electronics - a microprocessor control unit.
conclusions
Home craftsmen sometimes stand at a crossroads, unable to decide what equipment to purchase for their needs - a bulky, but cheap transformer unit or a compact, expensive inverter. The first option is rare among modern models, so inverter devices are in great demand among Russian consumers because they are mobile, multifunctional and easy to use.
With constant use, such expensive equipment pays for itself within the first year of operation, but the choice remains with the user.