A standard heating system includes many elements. Each of them performs its own task, as a result of which the design works smoothly and accurately. One of these elements is a heating check valve that controls the flow of coolant.
We will introduce all types of check valves used today in the organization of heating circuits. The article we presented describes their design features in detail and provides technical characteristics. Do-it-yourselfers will find installation manuals and valuable advice here.
How does this system work?
The movement of the coolant (water) through the pipes is due to the fact that as the temperature increases and decreases, the mass and density of the liquid changes.
A decrease in the mass and density of water occurs when it is heated in the boiler. At this time, the pipes contain colder water that has already given up its heat and has greater mass and density. In this case, under the influence of gravitational forces, cold water in the radiator is replaced by hot water. In order to understand exactly how a gravitational heating system functions, you just need to remember your physics course. The water heated in the boiler, being lighter, freely rises through the pipes of the central riser. At this moment, heavy cold water descends into the heating boiler. Hot water, having reached the top point, is evenly distributed over the radiators. In them, cold water sinks to the bottom of the battery, and then leaves it completely, because it is simply “replaced” by hot water.
When hot coolant enters the radiator, the process of heat transfer occurs. That is, the radiator materials gradually heat up, transferring heat directly into the room. Next, the cooled coolant is again replaced by hot water. This process is continuous. The liquid circulates as long as it is heated - that is, while the boiler is operating.
Options for piping heating radiators
Installation of heating radiators involves connecting them to pipelines. There are three main connection methods:
- saddle;
- one-sided;
- diagonal.
Connection options
If you install radiators with a bottom connection, you have no choice. Each manufacturer strictly binds the supply and return, and its recommendations must be strictly followed, since otherwise you simply will not get heat. There are more options with a side connection (more about them is written here).
Strapping with one-sided connection
One-way connection is most often used in apartments. It can be double-pipe or single-pipe (the most common option). Metal pipes are still used in apartments, so we’ll consider the option of tying the radiator with steel pipes on pipes. In addition to pipes of a suitable diameter, you need two ball valves, two tees and two bends - parts with external threads at both ends.
Lateral connection with bypass (one-pipe system)
All this is connected as shown in the photo. With a one-pipe system, a bypass is required - it allows you to turn off the radiator without stopping or draining the system. You cannot put the tap on the bypass - you will block the flow of coolant through the riser, which is unlikely to make your neighbors happy and, most likely, you will be fined.
All threaded connections are sealed with fum tape or linen winding, over which packaging paste is applied. When screwing the valve into the radiator manifold, much winding is not required. Too much of it can lead to the appearance of microcracks and subsequent destruction. This is true for almost all types of heating devices, except cast iron. When installing all the others, please do not be fanatical.
Welding option
If you have the skills/opportunity to use welding, you can weld the bypass. This is what the piping of radiators in apartments usually looks like.
With a two-pipe system, a bypass is not needed. The supply is connected to the upper entrance, the return is connected to the lower entrance, taps, of course, are needed.
One-way piping with a two-pipe system
With bottom wiring (pipes laid on the floor), this type of connection is made very rarely - it turns out inconvenient and ugly; in this case, it is much better to use a diagonal connection.
Strapping with diagonal connection
Installing heating radiators with diagonal connections is the best option in terms of heat transfer. In this case it is the highest. With bottom wiring, this type of connection is easy to implement (example in the photo) - the supply on this side is at the top, the return on the other is at the bottom.
A single-pipe system with vertical risers (in apartments) does not look as good, but people put up with it because of the higher efficiency.
Coolant supply from above
Please note that with a one-pipe system, a bypass is again required
Coolant supply from below
Strapping with saddle connection
With bottom wiring or hidden pipes, installing heating radiators in this way is the most convenient and least noticeable.
With a saddle connection and lower single-pipe wiring, there are two options - with and without bypass. Without a bypass, the taps are still installed; if necessary, you can remove the radiator and install a temporary jumper between the taps - a squeegee (a piece of pipe of the required length with threads at the ends).
Saddle connection for one-pipe system
With vertical wiring (risers in high-rise buildings), this type of connection can be seen rarely - the heat losses are too large (12-15%).
Relief valve
If the pressure in the system exceeds the norm, then the risk of accidents, damage to the circuit and even a boiler explosion is inevitable. In view of this, installers use a pressure relief valve in the heating system, which will prevent pressure surges in the event of an accident or overheating of the coolant. When choosing a place to install fittings of this type, it should be taken into account that the greatest likelihood of an increase in coolant pressure occurs in the boiler as a result of overheating of the coolant.
Even modern boiler models that have a gas valve installed for the boiler are not one hundred percent insured against emergency situations.
It is recommended to install a heating relief valve as close as possible to the boiler, on the supply pipe.
When choosing a model, you should pay attention to valves equipped with additional options in the form of pressure gauges and air vents. Such valves are more reliable and practical
Petal
Another type of shut-off valve is a reed check valve, or gravity check valve. It contains a spring with low resistance and low elasticity. In some cases there is no such spring at all.
The operation of a reed check valve for heating is based on the laws of physics related to gravity and pressure. The valve design includes a flap with a sealing gasket, which is mounted on an axis in the upper part of the pipe section. The peculiarity of such valves is that they only work when installed horizontally.
Warm floor
You should not trust sources that claim that a heated floor can be laid together with a radiator system and nothing will happen to it. For heated floors, the maximum temperature should be no more than 55C. Therefore, for such a heating circuit, it is best to install a Maybes and Buderus pump group with temperature control (for floor-standing boilers), or a Termex group from Maybes for wall-mounted boilers. These groups are installed on the circuit of heated floors. Installation location - near the boiler, where the decoupling of the heating circuits begins.
Boiler connection
Connecting a boiler (storage water heater) does not require superpowers. The main thing in this matter is to make connections according to the diagram and to properly seal all connections. Modern automatic boilers have a special connector for connecting and monitoring the operation of the boiler.
Wall-mounted boiler and boiler.
Boiler connection diagram.
Connecting the boiler to a floor-standing boiler.
Types of valves
Heating systems can use elements of different types. Their classification is based on several criteria.
First of all, pay attention to the metal, since the operating features of the device depend on this. The most popular are brass, steel, cast iron
Next, we will consider the main types of shut-off valves.
Poppet valve
This type of device assumes the presence of a disk responsible for closing the cross-section in the pipeline in the event of changes in conditions in the circuit.
Features of operation
:
- The disc fits into a seat, which is equipped with a seal.
- From the inside, the structural element is attached to a rod that can move freely along the sleeve.
- The spring located between the disc part and the body ensures reliable pressing of the disc to the seat.
Steel disc check valve
To prevent water flow in the opposite direction, install a lifting or flow-type disc element.
Ball valve
Ball (ball) valves are distinguished by the presence of a ball as an actuator. Rubber or aluminum is used to make the element. If the spring is triggered when the water current changes, the ball blocks the flow area, falling into the seat. Being under the top cover, it moves along an inclined channel.
Check ball valve
Disc and ball shut-off valves are designed for installation in a standard type heating system. But in the case of large diameter pipes, it does not guarantee adequate protection.
Butterfly valve
To ensure uninterrupted operation of the system, which uses larger pipes, a butterfly valve is designed. It is mounted on both the supply and return.
The name of this type of device is due to the presence of two spring flaps, which are easily opened by the coolant in the case of normal pressure in the system. In the event of an emergency, closed doors prevent water from flowing in the opposite direction.
Double-leaf cast iron wafer check valve
A special axis intersecting the flow area on which the flaps are fixed is responsible for preventing improper circulation. It is believed that this modification of the check valve is the most reliable. The device is suitable for high pressure systems.
Reed valve
A reed check valve for a heating system also has another name - gravity. The main feature is a low-elastic spring with low resistance. In some models there is no spring at all. Gravity valves are equipped with an additional element such as a spring-loaded flap. It has a seal and is mounted on an axis in the upper part of the section. Backflow protection is provided by gravity and flow pressure.
Heating reed check valve
Installation recommendations
A check valve is installed to prevent changes in the direction of fluid flow in pipes. It is a mandatory element in heating systems with forced circulation and gravity heating. Installation on the pipe is required before connecting to the boiler pipe. It is mounted after the circulation pump.
In addition, a protective device is installed in the pump piping - on the reserve pipe. This is necessary in case of a power outage or pump failure. In this case, the forced circulation circuit is closed using taps, and the liquid flow is directed into a pipe with a check valve.
Another application option is the arrangement of a heating make-up unit. It is necessary to automatically add water to the main line when its volume or pressure critically decreases. The check valve for this circuit performs protective functions - it prevents the movement of coolant into the water supply system when the pressure in it critically decreases.
The protective device can be used to install underfloor heating systems and mixing units. In some cases, it is recommended to install it in the radiator piping on the bypass. The main thing is that it should not destabilize the operation of the heat supply. To do this, it is necessary to periodically check it, and if its performance deteriorates, repair or replace it.
Source
Check valve installation rules
When deciding where to install a check valve for heating, you need to be guided, first of all, by the requirements of the project. If the wiring diagram requires a check valve, it must be installed in the right place and taking into account all requirements and standards. As a rule, such fittings are installed at the time of piping the heating boiler.
Please note that for proper installation of a check valve, you need to correctly select its type in accordance with the operating pressure and temperature of the coolant
In addition, it is important to install the product in the manner specified by the manufacturer in the technical data sheet for the fittings. As a rule, the location of check valves is determined at the design stage of the heating system.
As a rule, the location of check valves is determined at the design stage of the heating system.
Installing check valves on a heating system allows you to cope with several tasks at once. First of all, such devices allow you to prevent negative consequences for the heating system in the event of emergency situations. In addition, this is a kind of insurance against unnecessary repair costs in the future. Another important point is the consistency of the operation of various devices looped into one system. This is achieved precisely through the installation of shut-off valves. They also install a make-up valve for the heating system, which in certain cases is simply necessary.
Thus, if you are concerned about the durability and reliability of your heating and do not want to incur additional costs in the future, then you should definitely consider having a check valve in your heating circuit.
Operating principle
The design of a check valve - both ball and any other type - consists of a body, which can be made of steel or cast iron, and a shut-off element. A metal ball is used as the latter in a ball valve; in other types of valves it can be a spring metal plate - a leaf or a cylindrical spool.
In the initial state, when the ball check valve does not allow the medium transported through the pipeline to pass through it, its passage hole is closed by a ball, which is acted upon by a spring mechanism. Under the influence of pressure created by the working medium, the spring begins to compress and the hole in the valve opens, allowing gas or liquid to move through the pipeline in the required direction. When the pressure of the working medium drops, which can happen due to a stoppage of the pumping equipment, a leak, or for a number of other reasons, the spring mechanism again presses the ball to the outlet of the passage hole, locking the valve and preventing the gas or liquid from moving in the opposite direction.
Operating principle of ball check valve
Thermal valve
The thermal control valve for a heating radiator is one of the most effective types of fittings. The valve allows you to increase the functionality of the circuit and make the heating process simple, comfortable and rational.
It can be automatic or mechanical. A mechanical thermal valve for heating consists of two main parts. This is a thermal head and valve. The automatic analogue has a more complex design.
An automatic thermal valve is characterized by the presence of the following elements:
- temperature sensor of built-in or remote format; programmer; automatic control system.
An automatic thermal valve regulates the temperature in the circuit according to the settings previously specified by the user. This device has a fairly high cost and allows you to optimize the operation of the system as much as possible.
Rules for drawing up a heating scheme with natural circulation
Knowing the basic principles of operation of a heat supply system with natural circulation and choosing the optimal scheme, you can begin to assemble it. This stage is no less important than the previous ones, since further heating operation will depend on the technical parameters of the components.
Heating pipes
It is necessary to take into account all the features of this system. In schemes with forced circulation, compensation of hydraulic losses occurs due to the operation of the circulation pump. For systems with natural circulation in closed heating, such a mechanism does not exist
Therefore, to minimize losses, you should pay attention to the following points in the design and selection of components:
- Heating pipes. Their diameter should be from DN32 to DN40. This compensates for the friction of water on the inner surface. It is also recommended to choose polymer products with a smooth wall. Their actual outer diameter is from 40 to 50 mm;
- Highway routing diagram. It is necessary to avoid rotating units that increase hydraulic resistance in the system;
- Height of the accelerating riser. In a heating scheme for a two-story house with natural circulation, it should be higher than the ceiling of the second floor. The expansion tank is located in the attic;
- Characteristics of shut-off valves. Its presence should not affect the system parameters.
To better understand the operating principles of the heating circuit of a two-story house with natural circulation, an analogy can be drawn with well-known communicating vessels. In this case, the boiler will be located below the level of the radiators, therefore the liquid flow will circulate in its direction. That is why when developing a diagram and installing a heating system with natural circulation, it must be located as low as possible.
To prevent changes in water flow, a special valve is installed on the return pipe. This phenomenon may occur when the system is first started, when the difference in coolant temperatures is small.
Boiler for gravity systems
Since such circuits are mainly needed for heating independent of electricity, the boilers must operate without the use of electricity. These can be any non-automated units, except pellet and electric ones.
Most often, solid fuel boilers operate in natural circulation systems. They are all good, but in many models the fuel burns out quickly. And if there is severe frost outside, and the house is not sufficiently insulated, then in order to maintain an acceptable temperature at night you have to get up and add fuel. This situation is especially common where people heat with wood. The solution is to buy a long-burning boiler (non-volatile, of course). For example, in Lithuanian solid fuel boilers Stropuva, under certain conditions, wood burns for up to 30 hours, and coal (anthracite) for up to several days. Candle boilers have slightly worse characteristics: the minimum burning time for wood is 7 hours, for coal - 34 hours. There are boilers without automation and pumps from the German company Buderus, the Czech Viadrus and the Polish-Ukrainian Wikchlach, as well as the Russian company Ogonyok.
Non-volatile long-burning boiler Stropuva
There are gas-independent boilers made in Russia, for example Conord. which are produced in Rostov-on-Don. They can be used in systems with natural circulation. The same plant produces energy-independent universal boilers “Don”, which are also suitable for operation without electricity. Floor-standing gas boilers from the Italian company Bertta, the Novella Autonom model, and some other units from European and Asian manufacturers operate in systems with natural circulation.
The second way to increase the time between fires is to increase the inertia of the system. For this purpose, heat accumulators (TA) are installed. They work well with solid fuel boilers, which do not have the ability to regulate the combustion intensity: excess heat is transferred to a heat accumulator, in which energy is accumulated and consumed as the coolant in the main system cools. Connecting such a device has its own characteristics: it must be located on the supply pipeline below. Moreover, for efficient heat extraction and normal operation - as close as possible to the boiler. However, for gravitational systems this solution is far from the best. They return to normal circulation quite slowly, but are self-regulating: the colder the room, the more the coolant cools as it passes through the radiators. The greater the temperature difference, the greater the density difference and the faster the coolant moves. And the installed TA makes the heating more inertial, and it takes much more time and fuel to accelerate. True, the heat is released longer. In general, it's up to you.
To stabilize the temperature, a heat accumulator is installed in the system
Stove heating with natural circulation has approximately the same problems. Here the role of a heat accumulator is played by the furnace array itself and a lot of energy (fuel) is also required to accelerate the system. But in the case of using TA, it is usually possible to exclude it, but in the case of a stove this is unrealistic.
What problems does a check valve solve?
The valve is needed to regulate the flow of water, which should move strictly in one direction. When heating premises using boiler equipment, there is a risk of pressure changes in the system, air entering the circuit and other malfunctions. As a result, hot water will begin to move in the opposite direction. The absence of a check valve in the system will inevitably lead to a serious accident.
Main tasks of a check valve
:
- Ensuring unhindered passage of hot water.
- Preventing the flow of coolant in the opposite direction.
In this case, the device should not affect the technical and operational characteristics of water.
Advantages and disadvantages
A check valve with a filter helps prevent the plate from jamming in any position.
The check valve has advantages and disadvantages that are common to all types of devices. There will be no hot flow into the riser if cold liquid flows there. This extends the performance of system elements that are designed for a certain temperature. The devices are easy to install and do not create noise during the passage of liquid. Check valves solve the problem only in a specific area; additional control devices are installed for other circuits.
Some mechanisms allow the occurrence of water hammer when the flow passes through the working unit, but this feature of the valve only harms a system with a large diameter. The valves become dirty from the water flow if the system operates with an energy carrier without propylene glycol or other additives. In this case, the disc or plate may become stuck in the open or closed position.
Pump speed in the heating system
Most household appliances are equipped with adjustable rotation speeds, which can be 3-7 units. By increasing the speed, the pressure increases, the coolant moves faster, and heating the room takes less time. To correctly calculate the speed, a surface laser thermometer (plumbers have it) is useful.
What to do:
- bring the heating system into operating mode;
- measure the temperature of the inlet and outlet pipes;
- if the temperature difference is more than 20 degrees, you need to increase the pump speed;
- after 30 minutes, measure the thermometer again;
- when the temperature difference is less than 10 degrees, the speed must be reduced.
The optimal difference between the temperature at the inlet and outlet pipes is approximately 15 degrees
It is important to know that you cannot switch the speed of the device in operating mode; you must first turn off the pump, reconfigure the regulator, then turn it on again
You can do without a thermometer by installing temperature sensors on the lines. When the temperature difference is more than 20 C and less than 10 C, the system does not operate efficiently. Cooled water in the return increases the load on the heating boiler and increases fuel consumption. And if the water enters the return too hot, then it does not have time to cool, transferring heat to the radiators - this is also bad.
Heating system diagrams.
Two-pipe wiring.
One-pipe wiring.
Collector system.
Pipe calculation:
- For a collector system - when calculating, it is necessary to take into account that each radiator will have its own pair of pipes. With such a system, when the pipes are hidden underground or embedded in a screed, the pipes can be laid along the shortest route to save on length.
- For a two-pipe system, the calculation takes the perimeter of the rooms, multiplies it by two, plus adds bends for connecting to radiators, piping the boiler and distribution networks (risers).
- With a one-pipe system, all radiators are connected with one pipe, so this is the most economical system. It works no worse than a two-pipe system. The main disadvantage, unlike collector and two-pipe systems, is the inability to turn off a separate radiator or reduce its power with a thermostatic valve.
Equipment:
- Distribution combs - it is better to immediately purchase them with shut-off valves (taps)
- Connecting fittings for radiators, thermostatic valves, Mayevsky taps.
- Fittings, tees, adapters, couplings, crosses, clips for fastening pipes - selected according to the type of pipes selected.
- To install pipes made of polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene and metal-plastic on press fittings, special equipment is required
The simplest system that you can install yourself is -
- Polypropylene pipes
- Aluminum radiators
- Wall-mounted or floor-mounted automatic boiler.
In this case, there will be no need to install separate units for heated floors and hot water supply.
Double-circuit boiler - connection.
Wiring of a wall-mounted boiler.
Piping of a floor-standing boiler.
The calculation of radiators for a system with forced circulation is carried out in the same way as for a system with forced circulation.
Manifold connection of radiators. Two-pipe system with bottom connection.
Two-pipe connection of radiators: Piping of convectors.
- Tee
- Thermostatic valve – regulates heating
- Stopcock
- Adapters - connections
- Mayevsky crane - mechanical air vent
- Radiator adapter (different for left and right).
Two-pipe conventional connection.
Rules for choosing a locking device
Choosing a check valve intended for a heating system is a responsible undertaking. If knowledge in this area is minimal, it is best to seek help from specialists. This will ensure that your new heating system is functional and safe.
You need to know that, regardless of their type, all check valves differ in the way they are connected to the pipeline.
Sleeve check valves are very easy to install. However, the threaded connection cannot withstand high pressure, so they have limitations in use
Coupling devices are equipped with a connecting threaded unit, which greatly facilitates their connection to the main line. Most often, such a unit is equipped with disc valves intended for installation in autonomous heating systems of an apartment or private house. Their distinguishing feature is their small diameter. Most often it is no larger than DU-50.
Flange products are a structure assembled on the basis of a part that has holes for fastenings. Using the latter, it is connected to the main pipeline. A flange connection is much stronger than a threaded connection.
For this reason, flanged valves are widely used in the construction of large-diameter pipelines. Ball type devices are most in demand.
Wafer devices are designed for installation between two pipe flanges. They are lightweight and compact. Very often, both types of reed-type valves are produced in wafer design.
On sale you can find check valves that are installed by welding. This option can be used, for example, when installing heating from polypropylene pipes.
Flanged type check valves are securely attached to the pipe. This connection can withstand high pressure, which allows the devices to be used in centralized pipelines
Another important selection criterion is the material from which the device is made. It could be stainless steel. This option is considered optimal for highways with a diameter of less than 0.04 m.
The metal is practically not subject to corrosion processes and can withstand loads of up to 10 atm. This allows the valve to operate in the system trouble-free and for a very long time, but its cost is quite high. Brass valves have a lower price. They are subject to corrosion, but this process occurs very slowly, which significantly increases their service life.
However, their mechanical strength is much lower than that of stainless steel. Nevertheless, they can withstand the loads that arise in a household network quite easily. The most durable valves are made of cast iron - they successfully cope with critical pressure values, have significant dimensions and impressive weight.
Due to the nature of production, only body parts with a diameter greater than 40 mm can be made of cast iron. For this reason, they are used extremely rarely for the installation of autonomous heating systems.
It is desirable that not only the body, but also all internal elements of the check valve are made of metal. Plastic usually has less strength, which can lead to premature failure of the part.
When choosing a check valve, you need to remember one more rule - its diameter must exactly match the parameters of the through hole
It is very important that the operating pressure of the system does not exceed the maximum permissible values for operation established by the manufacturer of the selected model
Types of valves
Depending on the design of the locking device, there are the following types of check valves:
- disc-shaped;
- gravitational (petal);
- ball;
- bivalve.
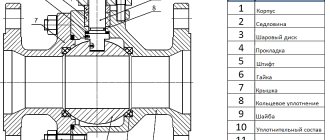
Disc devices block the flow area using a disk that fits into a seat with a seal. From the inside, the disk is attached to a rod that moves freely in the sleeve. On it, between the disc element and the body, there is a cylindrical or conical spring that reliably presses the disk to the seat.
Valves with a disk as a locking element are produced in two types: flow-through and lifting. In a valve with direct liquid flow, the disk closes one of the inlet holes, and during opening the coolant moves without changing direction. The product is often used in heating and hot water systems; its purpose is to prevent stray flows in circuits with several boilers. The design of the product is shown in the figure:
In lifting devices, the valve is located inside the reinforcement and is in a horizontal position. The fluid flow props up the “plate” with the spring from below, lifts it and rushes upward. After overcoming the obstacle, the water turns again and continues in the same direction. Such valves are usually used in piping boilers of medium or high power and are rarely installed in private homes.
The low resistance of the gravity check valve is due to a spring with very low elasticity. In some models it is not there at all; the device works due to two forces: gravity and the pressure of the reverse flow, should such appear. The lid with a seal that closes the passage of liquid is suspended from the upper part to the axis and is slightly spring-loaded. The hydraulic resistance to flow is minimal; in addition, the working cross-section of the channel practically does not decrease. But there is another side to the coin: the fittings can only function in a horizontal position.
In fact, a back pressure ball valve is not much different from a poppet valve. The role of the locking element here is played not by the disk, but by the ball. For example, in a flanged valve with a diameter of 50 mm or more, a ball made of rubber or aluminum alloy moves freely along an inclined channel. During the “correct” movement of water, it is located under the top cover of the product, the spring is compressed. At the moment when the flow changes direction, the check valve with the ball closes due to the fact that the spring straightens, the latter lowers and sits in the seat.
For all their advantages and simplicity of design, these products are very rarely installed in heating systems of private houses. There are several areas in which they are used: plumbing, sewerage and heating. Typically, ball valves are installed in heat supply systems or other networks of industrial enterprises.
Butterfly valves are intended for installation in large pipelines and for operation in systems with high pressure. In them, the flow area intersects the axis on which 2 spring-loaded flaps are installed. The principle of operation is still the same: the doors open under the influence of coolant pressure. If due to some circumstances the liquid flows in the other direction, the flaps will quickly slam shut and the flow will be blocked.
Power calculation
The effective thermal output of the boiler is calculated using the same methods as in all other cases.
By area
The simplest method is the calculation based on the area of the room recommended by SNiP. 1 kW of thermal power should be per 10 m2 of room area. For the southern regions, a coefficient of 0.7 - 0.9 is taken, for the central zone of the country - 1.2 - 1.3, for the Far North - 1.5-2.0.
Like any rough calculation, this method neglects many factors:
- Ceiling height. It is not always the standard 2.5 meters.
- Heat leaks through openings.
- The location of the room is inside the house or near external walls.
All calculation methods give large errors, so thermal power is usually included in the project with some margin.
By volume, taking into account additional factors
Another method of calculation will give a more accurate picture.
- The basis is a thermal power of 40 watts per cubic meter of air volume in the room.
- Regional coefficients apply in this case as well.
- Each standard size window adds 100 watts to our calculations. Each door is 200.
- The location of the room near the external wall will give, depending on its thickness and material, a coefficient of 1.1 - 1.3.
- A private house, which has not warm neighboring apartments below and above, but a street, is calculated with a coefficient of 1.5.
However: this calculation will also be VERY approximate. Suffice it to say that in private houses built using energy-saving technologies, the design includes a heating power of 50-60 watts per SQUARE meter. Too much is determined by heat leakage through walls and ceilings.
Heating system installation
Installation of a closed heating system begins with choosing a suitable boiler according to two criteria - the type of boiler and its power. Recently, solid fuel boilers have become popular. Although they are more cumbersome, they are cheaper to operate. The power of the boiler depends on many factors.
Important! How should power be calculated? The calculation instructions assume the following: with a ceiling height of up to three meters, average insulation of a two- or three-story private house, 1 kW of heating boiler power is required to heat every 10 m2. As practice shows, the price of such a boiler is about 1,000 US dollars
The type of heating devices (heating radiators or radiators) is selected based on the available funds. All types of radiators give off heat approximately equally, and their service life is also not very different. If we choose steel radiators, their cost for such a house will also be about 1,000 US dollars.
- pipes – 500;
- pump – 100;
- tank – 50;
- fittings, taps, filters – 500;
- design and installation – another 1,000.
In total, the very approximate cost of installing a closed heating system in a private house will cost 1,000+1,000+500+100+50+500+1000 = 4,150 US dollars.
Location of heating devices in the building
So, the equipment has been installed, the pipes have been laid. It is possible to fill a closed heating system with water.
Taking into account the pros and cons that a closed heating system with natural circulation has, and roughly estimating the cost of installing a system with forced circulation, we can conclude that there is no fundamental difference between such systems. The only thing that can be said is that a system with forced circulation is more profitable from an installation point of view and the equipment in it lasts longer.
Increasing temperatures
Another factor is the difference between the density of cold and hot water. Let us note the following fact - heating with natural circulation is of a self-regulating type. Thus, if you increase the heating temperature of water, its flow rate changes and the circulation pressure becomes higher.
Strong heating of the liquid greatly contributes to faster circulation. But this only happens in a cold room: when the air temperature in them reaches a certain point, the batteries will cool much more slowly.
The density of both the water heated in the boiler and the water that has already entered the radiators will be almost equal. The pressure will decrease, the rapid circulation of water will be replaced by measured circulation within the system.
As soon as the temperature in the premises of a private house drops again to a certain level, this will serve as a signal to increase the pressure. The system will try to equalize temperature conditions. To do this, you will have to restart the rapid circulation process. This is where the ability to self-regulate comes from.
Briefly, the rule is as follows: a one-time change in the temperature and volume of water allows you to obtain the desired thermal output from the radiators for heating the premises.
As a result, comfortable temperature conditions are maintained.
Closed heating system in a private house
Designing a private house involves calculating the layout of the heating system, which can be open or closed (involving the installation of an expansion tank). The second option is considered the most preferred by cottage owners, as it makes it possible to significantly save on resource consumption. The main advantage of such a system is that the coolant does not come into contact with air, which means it does not expose the equipment to corrosion.
Features and varieties
The main element of a closed-type heating system is the boiler, to which a pipeline is connected. A tank and circulation pump are also installed. Typically, this heating method implies that the carrier moves through the pipes forcibly. This is a power dependent method as the devices run on electricity. When the power goes out, care must be taken to continue activities as normal. To do this, install a special adapter - a bypass, which blocks the pump and converts it into a closed heating system with natural circulation.
If we are talking about a single-pipe heating option, it is important to ensure uniform distribution of the media across the radiators in a private house. A pipe is run from the boiler throughout all rooms, to which the batteries are mounted.
Without the pump running, only the elements in the immediate vicinity of the heater will be hot. The remaining rooms will retain cold air. This problem is solved by a closed heating system with forced circulation. Thanks to the circuit, a pressure is created at which the carrier receives a certain speed sufficient to supply all radiators.
A clever meter that saves electricity Pays for itself in 2 months!
In the two-pipe version, the approach is also rational, especially for servicing large areas. This type of heating involves connecting two parallel lines. One by one, the hot liquid disperses through the batteries under pressure if it is forced. Through another pipe, the cooled medium returns to the boiler, bypassing the expansion tank.
There is a horizontal and vertical routing of the highway. The first type involves combining all batteries into a single line connected to a common riser. Most often this method is used in multi-apartment buildings. The second option is considered more effective and is usually installed in a private home. The supply pipes are located at the top, which ensures good heat transfer in closed systems.
The size of the tank depends on the volume of the media. The parameter should be 10% of all heating equipment. Boilers with automation allow you to control processes, regulate pressure and temperature. The overheating sensor activates the safety valve at the moment the liquid boils, protecting the equipment from breakdowns. Anti-freeze equipment works in the same way.
Peripheral secondary part
A check valve is an element of the heating system, consisting of a plastic or metal base, which performs the function of completely shutting off the coolant supply. This happens when the flow begins to move in the opposite direction. The metal disk is attached to a spring, which is under pressure when the flow moves in one direction, and when it moves in the opposite direction, the spring is activated to block the passage in the pipe. The valve device has not only a disk and a spring, but also a sealing gasket. This component helps keep the disc in place tightly. Because of this, there is practically no possibility of pipe leakage. Butterfly valves are widely used in domestic heating systems.
Three way heating valve
To regulate the water temperature in a two-pipe and manifold system, a three-way mixing valve is installed in the heating system. It connects to the supply and return pipes.
Operation of a three-way valve in heating
The operating principle of a three-way mixing valve in a heating system is to mix hot and cold water in the pipelines. This allows you to set the required level of heating of the coolant without changing the operating mode of the boiler.
The determining factor in choosing a three-way valve model is the control element, which can be of the following types:
- Hydraulic;
- Pneumatic;
- Electric.
In autonomous heating, models with an electric drive are most often installed. They can be connected to system control elements
It is important to set the mixing mode correctly so as not to worsen the heat supply parameters
The selection and installation of heating valves should only be carried out after an accurate calculation of the system. As a result of this work, the parameters of all components are determined, and based on this data, a choice is made from existing models.
To better understand the functional features of a three-way valve, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the video:
Installation and configuration rules
The valve must be installed in the direction of the main current; for this there is an arrow on the body. The joints are sealed using paronite, but the gasket is placed so that the internal diameter of the passage device does not decrease. The condition is important to prevent water hammer in the pipeline network.
The device is installed so that other elements of the highway do not affect its operation. The section of pipe containing the valve may be supported by a metal frame to prevent vibration or other disturbances. A mesh is placed in front of the passage mechanism for rough cleaning of solid impurities.