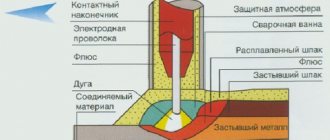
Galvanized steel is in constant demand and has gained popularity in many consumer areas. The material has gained such popularity due to its resistance to aggressive external influences. Galvanized steel is highly resistant to corrosion and can last for quite a long time. This is achieved by applying a zinc layer with a thickness of 2 to 150 microns to steel sheets. However, zinc coating not only protects steel products from adverse influences, but also a factor that significantly complicates the metal processing process, in particular its welding.
In order to answer the question: how to cook galvanizing , it is necessary to consider in more detail all aspects associated with this process.
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN WELDING GALVANIZED
The main nuances that should be taken into account during the galvanizing welding are the melting point of zinc and the toxicity of the vapors it produces.
The difficulty of welding galvanized products is due to the fact that the melting point of steel is 1100C, and the zinc coating melts at 906C. This discrepancy does not allow the use of conventional welding methods due to the risk of damage to the protective layer and loss of oxidation resistance of the product.
Adverse manifestations during the welding process of galvanized metal are that:
- At a temperature of 906 degrees, zinc melts and goes into a gaseous state;
- Penetrating into the base, the released vapors destroy the structure of the metal;
- There is a violation of the galvanized seam;
- Toxic vapors enter the surrounding area.
That is why the processing of galvanized products requires additional preparatory measures and careful selection of the equipment used.
The layer of zinc that covers
Steels are coated with zinc-containing compounds to protect them from corrosion. Under difficult operating conditions, the appearance of light oxides and severe rust can be prevented using a relatively simple coating. As a result, the service life of the material is extended significantly.
The melting point of galvanized steel is the same as that of regular steel, but the zinc itself melts earlier. It evaporates and, as a chemical element, interacts with oxygen and other elements.
The resulting substances are toxic to humans - they lead to damage to the respiratory system (up to edema), the appearance of cancer and various pathologies. Severe poisoning can lead to death. The presence of zinc is a health hazard, so work planning and safety precautions are fundamental factors.
STEPS OF WORK WITH GALVANIZATION
Removing zinc coating
This procedure is necessary to ensure that molten zinc, once in the weld area, does not deteriorate its quality. There are three main methods of stripping:
Mechanical
This method of stripping galvanized steel is carried out using harsh abrasives, metal brushes and sandpaper.
Chemical
It involves exposing the coating to acid or alkali. After the required exposure, the product is thoroughly washed and dried.
Thermal
It involves firing the edges of the product using a gas burner. It should be taken into account that exposure to high temperatures provokes the release of toxic fumes.
Selection of electrodes
In order to choose which electrodes to use for galvanizing , it is necessary to take into account a number of nuances. The choice of electrodes is carried out taking into account the type of steel being welded.
There are 2 main types of electrodes:
- With rutile coating (ANO-4, MR-3, OZS-4). Suitable for welding steel with low carbon content. The presence of titanium oxide greatly simplifies arc ignition, guarantees the strength of the weld and its tightness, and also minimizes spattering;
- With strongly basic fluxes (UONI13/45, UONI13/55, DSK-50). Suitable for low alloy steels.
Selection of filler material
The main requirement for wire used as a filler material is a low melting point, varying from 900 to 1100 degrees. Compliance with this condition will allow you to achieve a high-quality seam, since in this case the wire will melt without damaging or melting the material itself.
How to weld pipes
The approaches to installation and repair of pipelines made of metal alloys with zinc coating are the same as when working with other products.
Fluxes can be used. First, the pipes to be welded must be thoroughly cleaned outside and inside, then heated. If the diameter does not exceed 3 mm, the edges do not need to be specially processed.
For pipes with a large diameter, the edges are opened by 90 degrees and blunted by 1.5 mm. The gap width during welding in both cases is 2-3 mm. Softened flux is applied to the galvanized surface in double the amount used for uncoated steel pipes.
If the pipe diameter does not exceed 250 mm and the metal thickness is 6 mm, choose nozzles with a size of up to 2 mm. To weld wider pipes made of thick metal, nozzles with sizes from 2 mm to 4 mm are needed.
Good quality at high speed of execution is ensured by electric arc welding of any zinc-coated pipes. A highly qualified welder, the correct choice of electrodes, and optimal process speed will ensure the quality of the galvanized connection. To prevent oxidation processes after work is completed, the welding site and adjacent areas must be treated with special compounds.
WHAT ARE THERE TYPES OF WIRE FOR GALVANIZED WELDING
- CuSi3. Wire with 97% copper content. The intended purpose is welding copper products. Using galvanized steel for welding is advisable and allows you to achieve an easily machined connection. The downside in this case is that such a connection will not have a very high strength index. It is worth considering that the silicon contained in the alloy has high fluidity, which requires increased caution when working;
- Autrod 19.30. The intended purpose is welding galvanized products. The combination of silicon, manganese and sulfur allows you to achieve a fairly strong connection;
- CuSi2Mn. Creates a connection with very high strength values. Due to an increase in the indicator, the process of further processing becomes more complicated;
- CuAl8. The target direction is welding of metal processed with a combined zinc-aluminum alloy.
Removing the coating
There are several methods for welding galvanized steel. The choice depends on the quality of the metal, the thickness of the coating on it, and the prospects for using the structure.
The easiest way is to remove the surface layer of galvanization mechanically. Any hard abrasives are suitable for this. Galvanizing requires a lot of effort when cleaning.
You can remove the layer thermally, but when heated, harmful fumes are again possible. There are chemical ways to remove the coating in the area of future seams.
The concern is the remains of unprotected metal areas near the seam. Galvanization with such exposed areas may be subject to corrosion in the future, which will cause damage to the entire structure .
GENERAL RULES AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR WELDING GALVANIZED
Regardless of the type of galvanizing welding, it is necessary:
- Perform the seam using the flow method by means of frequent tearing off of the electrode;
- Extension of the cooking bath is carried out gradually to avoid the risk of damage;
- If the zinc coating has not been removed, it is necessary to wait until it completely burns out until the steel itself begins to melt. Otherwise, after cooling, cracking and swelling of the seam is possible;
- Galvanized steel, the thickness of which exceeds 4 mm, must be processed along the edges using the chamfer method, the depth of which is 1/3 of the sheet thickness;
- All work is carried out in strict compliance with protection and safety measures. For these purposes, masks with forced air injection and powerful ventilation systems are used.
Point method
Galvanization with Al, Mn, Si additives (so-called TRIP steels) is widely used in the automotive industry. Materials can be successfully welded when resistance spot welding is performed correctly.
When carrying out serial operations, in accordance with reference indicators, the shape and dimensions of the electrodes are selected, taking into account the thickness of the galvanized material.
The resulting connection point is characterized by strength, which is higher than that of the original sheets. When checking a seam for rupture, the rupture line does not pass through the welding point, but nearby.
Inverter-type welding machines operate on direct or alternating current. A method that provides good results requires a lot of energy.
Contact equipment that supplies three types of pulses is popular: for preheating the working area, directly welding galvanized steel, and subsequent heat treatment.
When spot welding any materials, including galvanized steel, the electrodes noticeably wear out. Therefore, at stationary welding stations there is an automatic possibility of adjusting modes and adjusting the process as a whole.
It is almost impossible to do this using manual technology. During one cycle, changing the size and shape of the seam is unacceptable. Spot welding in industrial flows is carried out using modern, fully automated equipment.
TYPES OF WELDING GALVANIZED STEEL
Semi-automatic galvanizing welding
This welding method has a number of features:
- Connection. The “+” terminal is connected to the burner, and the “-” terminal is connected to the surface;
- Current strength. Increasing the current leads to an increase in the additive feed rate;
- Selecting a current stripper. When selecting, the diameter of the wire section is taken into account. It is necessary to replace it in time, without waiting for significant wear;
- Selecting an additive supply hose. It is necessary to choose rigid hoses that do not allow kinks and disruption of the supply of filler material;
- Accounting for sheet thickness. Thin sheets 1mm thick. and less, are subjected to spot welding;
- Voltage. If voltage drops are possible, it is recommended to use wire of the smallest diameter, which has a high melting rate necessary to compensate for the lack of network voltage;
- Technique without the use of protective gas. In this case, the “+” terminal is connected to a galvanized surface.
Advantages of the method:
- Ability to work without creating a protective atmosphere;
- Good seam evenness;
- Ease of compliance with current parameters.
Negative qualities:
- It is not recommended to carry out welding in gusts of wind and in the presence of powerful ventilation systems;
- Large gas cylinders are required;
- Rigid additive supply hoses are required.
Welding with inverter
Features of galvanized welding when working using the inverter method:
- Selecting the electrode diameter. The optimal cross-section will be a diameter of no more than 2 mm;
- Taking into account the fusibility of electrodes. The higher the melting coefficients, the lower the current values;
- Movement technique. It is necessary to maintain smooth movement of the arc;
- Maintaining the angle of inclination. Maintaining an angle within 45 degrees avoids the risk of burnout.
- Compliance with polarity distribution. Due to the fact that this welding method is applied mainly to thin sheet metal, it must be taken into account that in this case the work is carried out by a current of reverse polarity. This means that “+” is connected to the electrode, and “-” is connected to the galvanized surface.
Stages of the process of welding galvanized steel when working with a pipeline.
- Preparation. The thickness of the workpiece is taken into account. If it exceeds 3mm, the surface is beveled at an angle of 80 degrees to a distance of 1-1.5mm along the surface of the seam. The ends of the product are cleaned of nicks and dirt and degreased. The elements to be welded are laid out evenly, maintaining a gap of 3 mm. A 2mm layer of flux is applied along the weld seam.
- Welding. It is carried out in the following stages: - parts to be welded are heated at a distance of at least 300 mm from the edges to be welded; — the flux is heated to a transparent state; — the additive is applied to the surface and melted using a gas burner until the void is completely filled; - the solder is placed in front of the burner flame. Allowable tilt angles are 95 degrees for the torch and 15-30 for the wire.
- Ending the process. The flux is removed and the seam is cleaned. Upon completion of cleaning, the surface is treated with an anti-corrosion compound.
Spot welding
galvanized spot welding method is most widely used in the automotive industry. The resulting point is highly durable. The break line does not affect the welding area, but runs along the surface of the sheet. It should be taken into account that the use of the point method leads to accelerated wear of the electrodes and requires high energy costs. In this regard, it is most advisable to carry out automatic adjustment of modes and settings in professional welding workplaces.
Use of a semi-automatic device
A good result is obtained when welding galvanized steel using a semi-automatic machine with correctly selected additives. Practice has confirmed the effectiveness of additives containing copper in combination with silicon, aluminum or manganese. These can be the following substances: CuSi3, CuAl8, CuSi2Mn. The strength of the connection and the ease of subsequent machining depend on the ratio of the components.
The combination of copper and silicon, which galvanization contains, contributes to the formation of a not very strong, but easily processed seam.
Inorganic copper-aluminum composite is primarily recommended for products containing aluminum in weldable structures.
A three-component substance of copper, silicon and manganese provides a weld with increased strength. Subsequently, considerable effort must be made to process it.
Copper melts at a temperature lower than the melting point of steel alloys. Therefore, such welding of galvanized steel is very similar to soldering.
The wire, like an additive, must be fed into the working area smoothly and accurately into the tip that ensures contact. For feeding, it is better to use a drive with 4 rollers, and carefully select the tip according to size.
If everything is done professionally and correctly, then both the base metal and the seam are protected from corrosion with minimal initial energy consumption for welding.
The work area is cleaned strictly within the designated dimensions. There is no spattering of materials when heated to welding temperature. In this case, galvanization is welded firmly.
To ensure process stability, the power source and adjustment modes are carefully selected. The maximum quality of a galvanized weld is achieved with a pulsed current in an inert argon environment. Helium, carbon dioxide or other inert gaseous substances can also be used as protective gases.
Technological subtleties
The technology for welding galvanized pipes involves the use of special devices that can weld several parts without damaging the surface.
In order for the work to be of high quality, a special flux layer must be applied to the intended welding site. With its help, the base material will not burn out during melting.
Pipe size chart for welding.
Welding of galvanized sheet occurs as follows:
- It is necessary to apply flux in a viscous-liquid state to the surface of the area to be welded.
- Directly during operation, the surface of the material with a flux layer will melt, but will not evaporate or burn out.
- After welding is completed, the flux layer will not allow corrosion to penetrate the surface of the material and damage it.
It should be noted that this technology is used when welding galvanized pipes for water supply communications. If flux suddenly gets inside the pipeline, it does not have a negative effect on people, since it tends to completely dissolve in water.
Also, each specialist must adhere to all safety measures, which include performing work only in a room with good ventilation or outside.
If this condition is not met, the master is at risk of blocking the respiratory tract due to excessive amounts of zinc entering the body, which leads to serious consequences.
Anyone who welds galvanized pipes must wear rubber gloves with insulating fabric and a respirator. To avoid swelling of the zinc surface, it is recommended to apply hydrochloric acid after all treatments of the product.
Useful tips
Experts are advised to pay special attention to some points:
- After cleaning the joint with a steel brush, restoration of the zinc coating with special protective compounds is required. They come in aerosol packages and small containers. They are used to process the seam and the connection point of the terminal (crocodile clip).
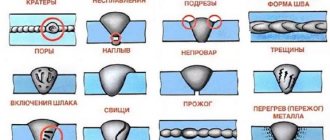
- At the joints, the current is increased to 15 amperes, and the speed of the electrode is reduced; a dense bead should be formed that can withstand the dynamic bending load.
- A short arc allows you to control the quality of the seam, and there is less spattering of the bathtub metal. The likelihood of sparks burning through the zinc coating is reduced.
- The equipment is configured for low-current modes. On semi-automatic devices the “Synergic” mode is set, on inverters – 5-10 amperes below the table values.
- Beginners should not forget to check the quality of the seam. After removing the slag, it is visually inspected and gently tapped, this makes it easier to identify the defect.