Situations arise when a defect in the pipeline has to be repaired when supplying water. More often, fistulas occur on welded pipes; they can be eliminated by electric welding the water pipe using surfacing electrodes. Although the welding will be weak, a serious accident, water leakage will be prevented.
Before welding, the main pressure is reduced to possible limits. Experience is required to perform the work. A beginner cannot cope with such welding. It is especially difficult to weld cast iron risers. Cast iron has high fluidity; when heated, structural changes occur in the metal, worsening performance characteristics.
Welding water pipes under pressure using electric welding
Why is it necessary to weld a pipe with water?
It is necessary to boil pipes with water in the following situations:
- when, after putting the system into operation, lack of penetration of joints is detected;
- sometimes when installing welded pipes, the main line turns out to be defective;
- when it is impossible to leave a large area without water;
- there is no way to drain the water or it is not economically feasible;
- you urgently need to install a shut-off valve or metering unit;
- Due to the slope, water remains in the pipe after the system is drained.
These are not all situations in which welding of pipelines with water is necessary.
Types of welding
The technological process for welding components of pipeline fittings can be:
- thermal;
- thermomechanical;
- mechanical;
- electromechanical.
In turn, thermal welding, which is actually fusion, is classified as:
- laser;
- electron beam arc;
- gas;
- plasma, etc.
Thanks to the magnetically controlled arc, thermomechanical welding can be performed. The latter can be butt contact.
Features of welding water pipes
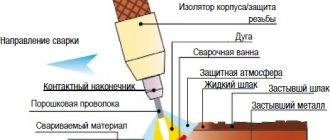
You can weld a pipe with water using electric arc, gas welding, or semi-automatic welding using surfacing wire. Electric welding of a water pipeline filled with water is associated with some features:
- The welding operating mode when sealing defects and water leaks is adjustable. If there is no risk of burns through a wall thinned by rust, the current strength when welding a cold water system filled with water is increased by 5–10%, depending on the type of alloy. By cooling the wall, the electrode will not stick to it during welding. Depending on the type of welding machine, welding is carried out using alternating or direct current. Variable is preferable; the arc during welding will be stable. The connection is formed even under a thick layer of water. If you need a high-quality seam, use direct current. Although the welding voltage will be unstable, the molten weld metal will penetrate deeper into the defect area when welding a pipeline with water.
- For operation, electrodes are selected according to the type of pipeline material. NZh-13 is suitable for welding stainless pipes, MNCh-2 or OZCH-2 is suitable for repairing cast iron risers, or you can weld gray high-carbon cast iron. When using an inverter as a current source for repair work on water pipelines, MR-3s, TsCh-4 electrodes are purchased; they melt at low currents and have a low melting point. The electrodes are pre-calcined, heated to 200°C and held for 40 minutes to an hour.
Edge processing
Before welding heating pipes, they will need to be checked for quality certificates and compliance with the specifications and installation design. It is necessary to carefully check whether the edges of the pipeline fittings differ in shape and size. If not, then it is necessary to achieve these characteristics through additional machining.
For this purpose, you can go through small-diameter pipes with chamferers, trimmers, pipe cutters or grinders. If the diameter of the tubular product is large, then it is better to use a waterjet cutting machine, a milling device or a grinding machine.
In case of obligatory overlaps or insertion of coils, you can resort to thermal welding methods, for example:
- air-arc cutting with subsequent grinding of the product to an amount of no more than half a millimeter;
- oxygen gas with further processing of the edges with abrasive;
- cutting and gouging with special electrodes without machining;
- air plasma cutting with processing not exceeding a millimeter.
Particular attention should be paid to the mandatory cleaning of pipes from debris before installation and further processing of the edges and adjacent surfaces up to ten millimeters.
What difficulties may arise
During repair welding of water pipes using electric welding, the quality of the seam from contact with water will be low. This repair of defects is a temporary measure. It is not provided for by GOST. When water pressure increases and the system is pressurized, the seam formed during welding can crack. Not all welders undertake this type of work. Surfacing of metal in the damaged zone often leads to multiple fistulas around the welding zone, because during welding the oxidation process is activated by contact with water. Instead of one fistula, many are formed.
Welding a pipeline containing water is a technologically complex job for a number of reasons:
- Due to the steam generated from the water during welding, you have to periodically wipe the mask; the work area is difficult to see.
- Water constantly cools the welding working area and prevents the metal from penetrating to great depths. Setting occurs immediately and crystallization begins.
- When pipelines located under the ceiling leak, work clothes get wet from the water. This is fraught with breakdown of current. The hand twitches and the electrode gets stuck.
Quality Control Methods
The science known as flaw detection is responsible for the quality of welded joints. It is worth noting that there are two types of it: destructive and non-destructive testing. The first method has been used less and less recently, since it involves opening the connection to detect defects there. Accordingly, in the future the joint will have to be restored, but it is possible that during the welding process there will be even more defects than there were before.
Non-destructive methods are considered much more effective. They include not only a visual inspection of the welded joint, but also an examination of both the seam itself and the heat-affected zone using X-rays or ultrasound. This quality testing technology is considered the best today, because it allows you to detect the presence of defects without opening the connection, which can be easily corrected in the future. Moreover, recently radiographic control has faded into the background, giving way to ultrasound.
How to weld a pipe with water
When welding pipes under pressure and sealing fistulas, conventional inverter welding is more often used.
Fistulas and water leaks occur due to incorrect choice of mode, impacts or corrosion damage. They are eliminated in good light - the damage should be visible from all sides. When making a vertical or horizontal seam, the electrode is held perpendicular to the pipe so that water does not flow down it. The defect is melted from top to bottom:
- a few drops of melt are applied at the top point; after the arc stops, the working area is hit a couple of times with a hammer so that the metal penetrates deeper into the defect;
- the same procedure is carried out, descending to the very bottom;
- when the water stops flowing and the steam disappears, strengthen the wall around the fistula, rising from bottom to top, and apply crescents. Create additional rollers and break them with a hammer.
It is necessary to work at low current to prevent burns on the wall damaged by corrosion.
Causes of fistulas
The reasons for the formation of fistulas on a water pipe most often come down to one denominator. This is the effect of corrosion.
The most suitable temperature indicator for corrosive formations is +15 degrees. Most often, pipe rolling materials are in this mode in the spring, summer and autumn periods.
Water located in the system also accelerates corrosive destruction. Over time, rust builds up inside metal pipelines.
The metal in such products becomes thinner every year. And then the moment comes when corrosion breaks through the wall completely. The result is a leak.
This problem must be eliminated immediately, without waiting until it turns into a big nuisance. If the leak is small, then it can be sealed under pressure without turning off the water supply.
The most common problems that result in a leaking heating pipe include:
- long operating time and severe corrosion;
- poor quality installation work, poor joints;
- loads of different types on the components of the heating system.
Since water is constantly under pressure in the pipe, and air temperature changes act on it from the outside, condensation can form, which leads to oxidation of the metal and accelerates corrosion processes.
Leaks can form not only in a metal pipeline, but also in a plastic one. Naturally, the problem most often arises as a result of mechanical damage or improper installation, since this material does not corrode.
Joint repair
There are situations when you need to re-weld the entire joint. First, the lower part of the joint is welded; it is welded through a window cut out in the upper part of the pipe. It can be made in any geometry: round, square, rectangular. This does not matter; it is important to provide access to the joint. The water is blocked by clogging the passage with rags; they are inserted on both sides to dry the work area as much as possible. The seam is made in small fragments, three centimeters each, in two passes. The second is done in the opposite direction. When the scale is knocked down, the rag is removed, water will flow into the pipe again. Proceed to the side parts. The final part of the work is welding the window, it is closed with the prepared patch, the seam is drawn in a circle. Walls thicker than 6 mm are boiled twice in different directions.
Sealing with adhesive bandage
Elimination of a fistula using this method is carried out in stages:
- Use a metal brush to clean the pipeline from dirt, treat its surface with acetone or gasoline and allow it to dry for 15 minutes.
- Tapes are cut from fiberglass, the length of which depends on the diameter of the pipe - it is necessary that the winding has at least 6 layers. The width of the material must exceed the cross-section of the pipeline by no less than one third.
- BF-2 glue is applied to the edges of the tape, then one side of it is covered with an epoxy adhesive with a spatula.
- The tool is pressed firmly against the fiberglass so that it is well saturated with glue.
- Then the tape is tightly wound onto a previously prepared surface so that its center covers the problem area.
- The bandage is secured with metal tape.
- After 24 hours, the repaired pipeline can be used.
If the system is laid in an unheated room where the temperature does not exceed 17 degrees, the pipeline can be used only after 4 days.
Pipeline tapping
When it is necessary to connect plumbing fixtures, install metering devices or shut-off valves, it is not necessary to remove water from the system; this can be too expensive.
The water outlet or tap is carried out according to the following scheme:
- the embedded element is adjusted to the pipeline;
- scalded along the entire contour;
- after this, a cut-in is drilled through the pipe or a disassembled ball valve;
- then a supply line is installed to the pipe or shut-off valves are assembled. After this, the water supply is turned on.
The insertion of fittings into the pipeline using the presented technology is carried out without reducing the pressure in the pipeline. The connected element is attached to them.
Rules for choosing a material to solve a problem
When the cause of the pipe damage has been established, it is necessary to look for acceptable repair methods. There are several of them. Only most are suitable for low water pressure in the water supply circuit or heating system.
The most common way out of a difficult situation is to use an industrial clamp (screed). This is a metal ring with thick walls, a rubberized inner surface and a fastening nut for a tie.
If you don’t have such a device at hand, then any piece of rubber (for example, from a bicycle inner tube) and wire or something similar will do .
But other methods of eliminating leaks when it comes to heating or hot water supply systems are unlikely to work. Thus, often used cold welding and special sealants are not relevant for wet surfaces.
Other instantly hardening composites (epoxy resin, dichloroethane) are also excluded, since they can be used on dry and disconnected water supply routes.
A minor leak in the pipeline can be repaired on your own . But this will only be a temporary measure. At the end of the heating season, it is recommended to carry out major repairs so that the system no longer fails.
Useful tips from experts
Main water supply system filled with water, a source of high humidity. There are professional secrets that allow you to carry out quality work. You need to reduce your exposure to water. This is achieved in several ways:
- A bolt of the appropriate diameter with a large head is driven into the fistula. The stream of water decreases and only drops form. If the fistula is round, it will clog completely. It will be enough to scald the cap and melt the metal around it. This method is suitable for any spatial location of the damage.
- A large nut is placed on the fistula, the leak is partially eliminated, the water does not fall on the electrode, but flows out through the internal hole of the hook. After this, the nut is scalded along the outer edge. After this, a bolt is screwed into it using fum or screwed in, a tight connection is formed, and the defect is eliminated. The appearance of the pipe becomes worse - this is a minus, but such repairs are quite effective and do not take much time.
- The volume of metal supplied to the weld pool increases. A few drops are not enough. The size of the drop depends on the thickness of the electrode. Sometimes they additionally take an electrode with a cleaned coating. The first electrode creates an arc, and when a melt pool is formed, a second one, which has no coating, is inserted into the holder. The volume of surfacing material increases, the hole is fused faster.
Taking into account the peculiarities of working with a filled pipe, you can repair the network yourself without flushing water from the system. It is necessary to select the correct electrodes according to the type of rod, type of coating, and regulate the operating current mode.
Initial heating of pipes
Thanks to the starting heating, it is possible to achieve correct thermoregulation during welding work. At the same time, the cooling rate of metal products is interconnected with the characteristics of the weld at a temperature of 500-800°C.
If, at the end of the welding process, the pipe material cools quickly, the result will be a fairly strong, but not plastic structure.
If desired, you can change the cooling speed of the edges, but this will require:
- adjusting their initial temperature;
- heating;
- taking into account the wall thickness of the water supply components.
With the help of initial heating, comfortable conditions are created for the active evacuation of diffusion hydrogen from the welding zone and the joint, and the product is also more protected from cracks.
When correctly determining the required initial heating temperature, special attention should be paid to such parameters as:
- material structure;
- wall thickness;
- outside air temperature;
- type of electrode coating.
Gas or electric heaters provide heating and maintaining a stable temperature at the welding joint. The heating area is the area of the product, which is about 75 mm from the joint in each direction.
Preventing the problem from recurring
It is easier to prevent problems in the heating circuit than to suddenly look for ways to eliminate them. So before the start of the heating season, communications are checked by testing, especially focusing on dangerous areas.
These include:
- level spans;
- threaded connections and welds;
- zone of joining sections at radiators;
- places of implantation of heating equipment;
- near fittings;
- hard-to-reach areas.
First, everything is checked by eye, then with the circuit running.