The demand for semi-automatic welding machines in the welding equipment market continues to grow every year. This is due to their obvious advantages: affordable cost, wide range of operating modes, ease of setup and operation. However, it is not always possible for a novice master to figure out how to use a semi-automatic machine correctly. The first thing you need to know is the structure and operating principle of the unit, as well as basic recommendations for choosing wire for welding.
Semi-automatic welding is
A type of arc welding, during which the welding process occurs due to the simultaneous automatic supply of the electrode wire with the influence of a shielding gas on it.
The shielding gas used during welding completely protects the heated and molten base and electrode materials from exposure to air, which both slows down the welding process and can completely stop it.
Next, we will look at the basic principles of working with a semi-automatic machine, the selection and preparation of this type of tool.
The importance of understanding the process
Just understanding the operating principle of a semi-automatic welding machine is usually not enough to fully master all the techniques of working with it. For proper operation of the equipment, among other things, you should know the design of a semi-automatic welding machine.
Having the necessary information and work experience, some welders refuse to purchase a ready-made branded product and give preference to home-made devices, usually used for domestic purposes.
The simplest solution to the problem is considered to be an approach in which a ready-made, but outdated (used) welding unit is taken as a basis.
To assemble a working semi-automatic machine based on an inverter device, you will additionally need knowledge of the basics of electronics, which will significantly facilitate the understanding of how the semi-automatic welding circuit works.
The task is to organize the supply of shielding gas and filler wire to the welding zone.
Operating principle of semi-automatic machine
Semi-automatic welding machines are mostly simple equipment. Its main parts are an adjustable direct current source, which supplies the welding voltage, as well as a special mechanism designed to feed the welding wire into the welding arc zone, and the feed is performed at an adjustable speed.
The arc has reliable protection thanks to the gas flow created by the burner, where it enters from a cylinder with the same gas. The electrode feed speed and welding voltage are adjusted simultaneously.
As already mentioned, the welding wire must be fed into the arc zone at a strictly defined speed. Only in this case will the welding process proceed stably. Otherwise, at the slightest break in the wire feed, the arc breaks, and this leads not only to a decrease in the quality of the weld, but also to other more serious consequences, which include, first of all, burn-through of the seam, melting of the electrode tip and other failures and defects.
For high-quality feeding, it is necessary to check the drive rollers before work. It is necessary that the feed roller has a V-shaped groove, the size of which must match the size of the wire, and that this groove is in good condition, that is, not worn out.
Often when people experience poor feed, they will increase the clamping force on the drive rolls, which can only make the feed worse as the wire can become deformed. In addition, the burner guide channel can be damaged for the same reason.
During operation, the welding wire passes through the torch through a guide channel, which over time tends to become dirty and wear out. As a result, the resistance of the electrode feed increases, until the wire stops completely.
This should not be allowed; it is better to notice these changes in time and replace the guide channel with a new one, installing which you need to be very careful, since if its length, external and internal diameters do not match, serious feeding problems may arise. In other words, the whole point of replacement is lost and normal welding is still not possible.
In order to reduce wire contamination, as well as premature wear of the guide channel, it is better to choose a semi-automatic machine with a closed feed mechanism. This approach to wire feeding significantly better protects it from dust, moisture, oxidation, etc.
Now a few words about the contact tip of the torch, through which the actual welding current is supplied to the electrode (welding wire). It is clear that for high-quality welding, the wire must have high-quality and reliable contact with this tip. It is necessary to monitor the degree of wear of this part of the semi-automatic welding machine in order to replace it in a timely manner.
All these seemingly little things are of great importance for high-quality welding performed using a semi-automatic machine. Good condition of equipment is the key to success, and poor care of it is the first and surest step to the occurrence of all kinds of malfunctions.
Components and operating principle
As part of the automation of the metal processing process at home, a homemade inverter semi-automatic welding machine significantly facilitates the work and significantly increases the strength of the seam.
The solution to this problem can be further simplified if we take the diagram of a standard inverter unit as the basis for a future home-made semi-automatic machine.
To independently manufacture a semi-automatic welding machine, you will need to slightly modify the load current converter, supplementing it with a number of modern electronic elements.
The schematic diagram of the inverter device that provides the generation of operating current for the semi-automatic machine can be found in the picture.
The electronic method of converting the supply voltage significantly simplifies the adjustment of the operating parameters of the welding current. The electronic converter affects the discrete components of the circuit, as a result the device operates more stably.
The semi-automatic welding operations themselves are organized on the principle of fusing workpieces in argon or carbon dioxide vapor with the simultaneous supply of filler wire to the working area. Taking into account the peculiarities of organizing the welding process, the equipment includes the following mandatory components:
a gas cylinder with carbon dioxide or argon complete with a hose for delivering them to the weld pool;- a container (drum or cassette) with a mechanism that ensures continuous supply of filler wire;
- holder with a built-in channel for moving it;
- power supply, control module and electrical circuits connecting them.
Each of these units performs its own function, allowing the semi-automatic welding machine to fully operate. Thanks to the clear functional delineation of individual blocks, assembling a semi-automatic machine with your own hands is not difficult.
Rules for working with a semi-automatic machine
We list a number of requirements, or rather rules, that should not be neglected when using an automatic welding machine:
- Before starting to operate the semi-automatic welding machine, you should carefully study the operating instructions;
- when welding, you need to ensure strict polarity - “plus” should be on the torch, and “minus” should be on the part being welded;
- To avoid unpleasant situations associated with human injury, when threading wire into the torch, you should not point the nozzle at yourself or other people. Here you need to be very careful, because the end of the wire can pierce your palm or other part of the body;
- It is strictly forbidden to move the semiautomatic device during operation by pulling it by the burner or cable; there are handles for this;
- in order not to damage the eyes and other parts of the face, you should work with a semi-automatic welding machine only in a special protective mask that has a light filter, the marking of which must correspond to the current range used in welding, and for additional protection you should use glasses with glass lenses, since glass does not transmit ultraviolet radiation;
- for long and trouble-free operation of the device, it is necessary to clean all its insides from dirt and dust twice a year;
- if, during an external inspection of the device, damage was discovered in the cable or burner sleeve, they must be immediately eliminated using insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, and it is better to replace worn parts with new ones;
- the shape of the groove must clearly correspond to the electrode material: V-shaped smooth is used for solid steel wire, V-shaped with notches for flux-cored wire, U-shaped for alloys and soft metals;
- during operation, it is prohibited to touch the live parts of the semi-automatic welding machine, as well as to work with its covers removed;
- the room in which welding is performed must be well ventilated, since aerosols released during work are extremely harmful;
- Fire safety rules should be strictly observed;
- We must not forget that during welding the welding seam heats up to very high temperatures, so it is strictly forbidden to touch these places;
- It’s no secret that a semi-automatic machine, like any welding machine, is a source of electromagnetic radiation, which has an extremely harmful effect on human health. Not all people can work in such conditions, so you must first undergo a medical examination;
- It is strictly forbidden to weld vessels and pipelines together with liquids, as well as vessels in which flammable and flammable liquids were previously stored;
- do not overload the semi-automatic machine, work only under the conditions specified in the operating instructions, since this, firstly, is dangerous to the health of the operator, and, secondly, reduces the service life of the semi-automatic machine itself;
- since a person is a carrier of static electricity, touching the elements of the electronic board is strictly prohibited, in this case they may breakdown;
- The lid of the feed mechanism niche must be tightly and securely closed during operation so as not to become a source of injury to the operator;
- welding should not be performed in a continuous mode, it should be alternated with regulated breaks, the duration of which and the intervals between them should be selected in accordance with the manufacturers' recommendations;
- while operating the semi-automatic welding machine, it is strictly forbidden to switch the stages of the transformer installed on the welding power source;
- all welding work should be performed only in clothing specially designed for this purpose, in addition, clothing must be completely dry in order to protect yourself from possible electric shock;
- The flow rate of the shielding gas, which can be argon, helium, carbon dioxide or mixtures thereof, must be calculated optimally, since it forms a protective environment in the arc zone; in addition, the gas must be selected in accordance with the type of material being welded, as well as its thickness. The cylinder must be secured horizontally and securely enough.
Electrode wire selection
Electrode wire is an accessory without which the welding machine cannot operate. It is supplied using a special mechanism and performs the function of an electrode.
For semi-automatic machines there are two groups of materials for welding:
- solid wire;
- flux cored electrode wire.
There are more than 76 varieties of the first option. But most often, only a small part of them is used. The remaining types of equipment are highly specialized and are used in production. The main thing to consider when choosing wire is the type of metal from which the structure will be welded. Most often, you have to automatically weld low-carbon and low-alloy steels using non-copper-plated and copper-plated wire.
Copper-clad wire is the most popular among welders due to its anti-corrosion coating. But not everyone knows that when copper is smelted, harmful fumes are released into the air. Non-copper-plated wire is more harmless and has a corrosion-protective coating.
Semi-automatic machines also use flux-cored wire, which does not require protective gas during cooking. The electrode wire has a special marking, for example, this: SV-08G2S . It is deciphered as follows:
- SV – welded wire;
- 08 – means that the mass fraction of carbon in the composition of the equipment is 0.08%;
- G – this letter denotes manganese, which is contained in the wire;
- 2 – the number indicates that the manganese content is 2%;
- C – this letter indicates the presence of silicon in the equipment; if there is no number after the letter, then it contains no more than 1%.
The following is a table in which the letter designations of all additives included in the composition of the welding wire are deciphered.
For example, using the table, you can decipher the marking SV-06Х21Н7БТ, which means: welding wire has 0.06% carbon, 21% chromium, and nickel - 7%; the wire is alloyed with two metals, niobium and titanium.
For welding low-alloy steels (this is 90% of all rolled metal), 08G2S wire with a diameter of 0.6 mm is used. It can be used both at home and for body repairs. In addition, it can be used on units with current up to 500A. For welding stainless steels, wire of the S01X19N9 grade is used. Aluminum and copper are boiled in an argon atmosphere corresponding to the composition of the wire. Aluminum is welded by grades SV-97, SV-A85 and SV-AMts. For copper welding, equipment of the SV-97, SV-A85 and SV-AMts brands is used.
Advice! If you are going to work semi-automatically in field conditions or in the open air, then you can use cored wire, which does not require blowing with protective gas.
The diameter of the electrode wire is selected in accordance with the thickness of the metal being welded.
Semi-automatic welding without gas
Among the vast number of types of welding, welding without the use of gas is becoming the most promising and in demand.
Semi-automatic welding of this type is carried out using flux-cored wire or, as experts call it, flux-cored welding wire.
Flux-cored wire is a steel tube, but inside this tube there is a special powder - welding flux, similar to the coating of conventional electrodes.
By exposing the flux-cored wire to high temperature, the flux is burned, which provides a protective gas cloud at the welding site. The process itself is very similar to conventional electrode welding.
The main advantage of this method is the absence of the need to carry gas cylinders with you, a huge selection of materials with different types of chemical compositions, with the help of which you can form the necessary arc properties and change the characteristics of the seam.
Since semi-automatic welding is similar to conventional electrode welding, slag from the burnt flux gets into the welding zone, so it is necessary to ensure sealing of the welding surface. To do this, you need to put a few more new ones on top of the finished seam.
Flux-cored wire has low rigidity, so it must be fed to the welding zone with a slight increased pressure; bends in the semi-automatic welding hose are simply unacceptable.
It is extremely necessary to observe the polarity conditions of the phase wire and the “ground”
On the left you see the polarity of welding without using gas, and on the right with using gas when welding.
In order to start the process, you need to connect the power source in the following way: minus to the torch holder, and plus to the surface to be welded. In the case of welding using shielding gas, the connection occurs in the reverse order.
This method of power connection provides a high temperature for melting the flux and the formation of a protective gas environment.
The main advantages of gasless welding:
- Easy welding process
- No need for a gas cylinder
- Fast speed of work
Types of semi-automatic gas shielded welding
One of the most popular types of semi-automatic welding is gas shielded welding (MIG/MAG welding). This technology is suitable for joining parts made of any metal, while you can work freely both outdoors and indoors.
The device has a special device that feeds wire into the welding torch at a certain speed. The mechanism of the device consists of an electric motor, a gearbox, pressure and feed rollers and a cassette with the wire itself. The feed mechanism can be open or closed. There are also simple (contain one or two pairs of rollers) and complex systems (four or more roller units).
Wire feeding, controlled by a control panel of ten meters or more, is possible with intermediate mechanisms. Thanks to them, the welding area is increased. All additional mechanisms clearly interact with the main ones. This is how the semi-automatic device and gas device operate continuously.
Stages of this type of semi-automatic welding:
- preparation of welded edges;
- selection of welding materials;
- setting the operating mode of the device;
- the welding process itself, performed using special equipment;
- evaluation of work, checking the resulting seams.
The welding technology depends on the type of connection: butt, lap, corner “boat”, tee. In this case, the location of the seams is taken into account. So, horizontal seams should go at an angle back and from left to right without transverse vibrations. Vertical seams go from bottom to top for small metal thicknesses and from bottom to top for products with a thickness of 4 mm or more.
To fill the groove, transverse oscillatory movements are performed. When working, before a new welding approach, remove the directional ball at the end of the wire.
The described type of semi-automatic welding is simple and efficient. The only inconvenience is the constant use of a gas cylinder. If you need to constantly move from place to place, you can use a cart. The advantage of the technology is the low cost of gas (the cheapest option is argon gas). The method is also distinguished by high quality seams.
Semiautomatic welding machine for gas environment
Semi-automatic welding machine designed to work in a protective gas environment is a new type of welding that is gaining popularity. Over the past 20 years, the use of this type of welding has reached a large scale.
This type of welding involves two types of work:
MIG (Metal Insert Gas) - welding occurs under the influence of an inert gas, for example argon, as well as other types of gas mixtures.
MAG (Metal Active Gas) is a process of welding metal using an active gas, for example carbon dioxide.
The use of gas cylinders does not allow mobile welding in any conditions, however, when used stationary, this type of welding is the best and has no analogues.
The welding process is carried out by feeding electrode wire, which contains silicon and manganese, into the welding zone together with carbon dioxide.
This creates a protective environment for the electrode and welding surface from the effects of the environment.
The advantage of this welding is the ability to control the process; also the advantages of welding in a gas environment include saving time, because when gasless welding it is necessary to change the electrodes and clean the welding seams from slag.
The quality of work using a protective gas environment is much superior to gasless welding, but there are small nuances here too.
Let's look at them using the example of seam quality. When using CO2 active gas, the seam will have a scaly appearance and burrs, i.e. effect of stuck balls. At the same time, when using a mixture of argon gases in the amount of 80% and carbon dioxide 20%, respectively, the seam has a smooth and even surface that does not require additional processing.
In recent years, for the operation of semi-automatic welding machines, the use of inverter types of power sources instead of an alternating current source has become widespread. This is due to such advantages as:
- Light weight of the device
- Smooth voltage regulation, which means safe work performance
- Low load on the electrical network, which in turn leads to uninterrupted operation of other electrically consuming devices in the room.
Design and purpose of a semi-automatic device
In semi-automatic welding, you do not need to supply the electrode yourself and replace it in the holder. A special wire is installed in the machine device instead of an electrode. It automatically enters the welding zone. The welder adjusts the required feed and, maintaining a certain distance to the metal, completes the work.
Various types of semi-automatic welding are easy to perform and do not require special knowledge. All equipment and parts are relatively inexpensive. It is the cost advantage that makes this type of welding popular both in large industries and in maintenance or repair companies.
Also, semi-automatic welding machines are widely used by private craftsmen, as well as non-professionals when working at home or in the country. Before purchasing equipment, you need to study the basics of this technology, determine the desired application, then select a specific device model.
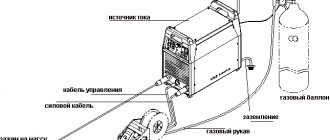
The mechanism of semi-automatic equipment is universal for all types of welding. Main details of the device:
- power supply, control unit, display panel and manual adjustment elements;
- a hose cable for supplying wire, gas and current to the welding area (otherwise - a welding hose), a cable for connecting to ground;
- welding torch;
- mechanism for automatic wire exit;
- container with inert or active gas, special gas equipment.
In addition to the listed basic elements, some types of semi-automatic welding may require additional devices. For example: unwinders, pipe connection equipment, hose stands, restrictive screens, hoods, etc.
How to choose a welding machine
Like any equipment, the welding machine has its own design and it consists of:
- Burner, differing in type of power and cooling methods
- Wire feed mechanism. It includes feeding method, speed regulation and number of pinch rollers
- Hose that varies in diameter
- A gas reducer, which must have two pressure gauges.
When choosing a semi-automatic welding machine, you should take into account the thickness of the metal that will be exposed to welding, the length of the seam the machine produces, as well as the conditions for performing welding work.
Before purchasing, you need to clarify all the above parameters, as this will help you choose the device that is right for you.
It is necessary to select a welding machine using the following method:
- The choice begins with clarifying the tasks for which the device is purchased
- When choosing, pay attention to the quality of the welding machine, read information about the manufacturer and study reviews about it and the machine. Also pay attention to the cost, which cannot be lower than average.
- If you choose a low-power device, then you should take into account that it is capable of processing only small surfaces.
- At the place of purchase, find out the specifics of the warranty, the availability of service centers and the availability of consumables and spare parts for the device, such as conductive tips, torch nozzles, insulating sleeves, feed spirals and rollers.
How is semi-automatic welding carried out?
As in other types of welding, before starting work, you need to make sure that the parts have been pre-treated - degreased and cleaned. Before starting work, connect the ground cable to the welding table and check the extension of the welding wire. If the wire is longer, you need to cut it off with side cutters.
HELPFUL ADVICE.
It is important that the tip of the wire is sharp - then it will be easier to light the arc. During the welding process, before each new seam, the tip (or the resulting ball) of the wire will need to be bitten off - this will make the start of the new stage easier.
Like any type of welding, semi-automatic welding begins with ignition of the arc. To do this, the welding wire must touch the surface of the part being welded. We press the torch button - the supply of welding wire and shielding gas begins simultaneously.
The arc is ignited. The welding process is taking place. To extinguish the arc, you need to release the button and move the torches away from the work being welded.
The torch can be operated with one hand, but when using two hands the seam will be more accurate and control over the process will be more confident. You need to grab the burner with one hand, your index finger should be at the bottom of the start button. You can lean on your other hand with your leading hand - this will make it easier to control the distance to the surface to be welded and the angle of inclination, as well as make the necessary movements with the torch.
There is no universal welding torch angle that must be observed when welding. If we cook parts in the same plane and both parts are of the same thickness, then the burner can be held vertically. If the parts are different in thickness, then the tilt should be made towards the part with a smaller thickness. When welding two parts at an angle, it is more convenient to hold the torch at an angle of 5-25% degrees (from the vertical). The distance from the nozzle to the surface to be welded is from 5 to 20 mm.
The movement of the burner can be either forward or backward. When welding at an angle backwards. With this method, the depth of penetration and the height of the seam increases, its width decreases. When welding at an angle forward, the edges are better fused, the penetration depth is reduced, but the seam is wider. This method is good for welding metal of small thickness.
During the welding process, you will choose the most convenient and comfortable welding style for you - from the way you hold the torch to the parameters of the machine. Also pay attention to the sound of the arc - it will help you adjust the settings. Thus, a correctly installed arc has a smooth hissing sound. If you hear a cracking sound, then most likely there is an imbalance between feed speed and voltage, or poor contact in the welding area.
The influence of torch speed on seam quality
The quality of the weld also depends on the welding speed - the speed at which the electric arc passes along the welding site. The speed of the welding torch is controlled by the welder and affects the shape and quality of the weld. Over time, you will learn to determine the speed by looking at the thickness and width of the seam during the welding process:
- Too high a speed is accompanied by increased metal splashes. The seam is thin and intermittent.
- A speed that is too slow will produce a wide, blurry seam.
How to move the welding torch during semi-automatic welding?
There are many ways to move the torch to form a seam:
- For metals 1-2 mm thick, you can move the torch in a zigzag pattern to act with an arc on both sheets being welded - then the result is strong and airtight. In addition, with this method, the electric arc does not penetrate the metal.
- If you have some experience, use a straight seam, without any oscillatory movements. This weld can be used to weld metals of any thickness, but here it is important to feel that the arc evenly covers both workpieces.
- When you need to make a long seam, in order to prevent overheating of the metal and thermal deformation, you can weld in small segments from one or the other end of the parts being welded. This will allow the entire segment to be welded without thermal deformation of the sheet metal.
Preparing the welding machine for work
Like any type of activity, carrying out welding work requires compliance with the rules of preparation for the process, this will ensure the safety and quality of the process itself.
Before starting work, you need to prepare the welding surface to avoid the appearance of pores. To do this, you need to remove dust, debris, dirt, moisture, oil, as well as rust up to 30 mm from the edge of the gap from the surface.
The surface can be cleaned with a metal brush, a steel brush for metal, rags, or a sandblaster, then it must be degreased and etched.
It is also necessary to prepare the welding machine; for this, the following preparation steps must be followed:
- Check the grounding of the device. Any cooking equipment must be checked for connection to the grounding conductor. Missing or malfunctioning jeopardizes the safety of the welding process.
- Checking the network voltage. Many devices are sensitive to power surges and may fail. Therefore, the voltage in the network must be stable.
- Select the welding machine mode. Modern semi-automatic machines have many welding modes and its adjustment. With their help, you can adjust the welding to the material being welded and the nature of the welding.
- Before starting work, you need to adjust the diameter of the tip; it should be several millimeters larger than the size of the wire.
- Check the adjustment of the tip and feed mechanism. If these elements are upset and configured incorrectly, this can lead to operational errors or damage to the material being welded.
- Checking the quality of the wire. It should be smooth without burrs, dents and various kinds of scratches.