The transition to modern production is largely due to the introduction of automatic machine tools at enterprises. Drilling machines help create holes, recesses, and complex recesses in workpieces made of any material. The highlight in the operation of such devices is the chuck for the drilling machine.
Thanks to the high power of equipment, modern computer precision and the highest speed of operation, machine tool production today occupies a leading place among alternative production methods.
General information
The use of drilling machines necessitates the creation of holes of the desired size in workpieces of various sizes. This filigree work is produced by drilling. The structure of a drilling machine is simple, but even the configured equipment cannot function without a drilling machine chuck. Its task is to securely secure the drill itself and uniformly transfer the engine force to it.
The products are used not only on stationary drilling equipment, especially large ones; craftsmen encounter them in conventional drills; even a miniature screwdriver is equipped with this fastener. According to the standards, before work, the selection of a product is carried out by comparing its properties with the following points:
- choose the correct rigidity of the product, this will ensure reliable fastening of the drill;
- check whether the standard size corresponds to the radial runout;
- the thickness of the drill used largely determines the choice of chuck;
- The drill and chuck used must be suitable for the workpiece material.
If you neglect the rigidity of the material, the load on the drill during operation will increase, this will lead to its breakage, overheating and damage to the integrity of the chuck. In the worst case, this will lead to a malfunction of the device itself.
Drilling machine device
Mounting features
Before turning on any drilling machine, it is necessary not only to ensure that the workpiece itself is securely fixed, but also to check the fastening of the chuck and the drill being used. Complete staticity ensures better and more accurate work results.
According to the type of machine fasteners, products are divided into the following types:
- elements secured using a cone, it corresponds to the existing machine hole on the cone-type device;
- the product is attached to the machine using a regular thread.
Depending on the method of attaching the product to the machine, each fixing element for the drill has its own internal structure. If the outer surface is framed by a Morse taper, then the internal mechanism will correspond to the cone type. The internal part of Morse is marked according to GOST standardization.
The type of product is selected based on the need to create a specific hole, ease of use due to the quick change of attachments or the drill holder itself.
Morse taper cartridge
Drill chuck design
Examine the drill chuck design in the diagram below. The device includes:
- a body having a cylindrical shape;
- a cage rotating on its outer surface;
- cam mechanism.
Image No. 1: Cam drill chuck design
Now we will tell you how to remove such chucks from drills and drilling machines, and we will also present the technology for disassembling clamping devices.
Classification of fasteners
Any drilling master has a multifunctional machine; it is equipped with a variety of cartridges, unique drills, and spare parts for the most vulnerable parts of this equipment. The design of the product is divided according to the type of clamp into the following types:
- fasteners with a key locking mechanism;
- cartridges where fixation is ensured by a clamping nut.
Additionally equipped with a clamping ring for this nut, this element is sometimes missing.
According to regulatory standards and other documents that provide strict requirements in the manufacturing process of chucks, independent modification and modernization of the fixing element is allowed, this further increases the accuracy of drill fixation.
The ideal fit of the drilling tool leads to a reduction in possible errors during the work process, while the quality of the result strives to be maximum.
Chucks for securing drill bits are divided into the following types:
- quick-change elements;
- three-jaw;
- self-clamping;
- collet.
Quick-change parts are equipped with a replaceable sleeve; conical drills are suitable for it. Three-jaw elements clamp the drill bit with internal hooks with an additional locking spring. This type is used if the drill is thin and the load on the nozzle does not exceed the minimum values. Fastening a self-clamping type drill does not require additional operations to ensure fixation.
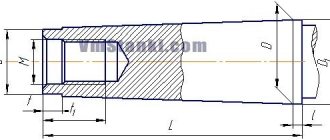
Chuck for drilling machine 2m112, Morse taper B18
The structure of a drill and types of cartridges for it
The cartridge is a seat. He holds the main working element of the tool - a drill, a drill, a screwdriver. There are special attachments for grinding or cleaning surfaces. They are fixed on a round or multifaceted pin, which is also placed in the device.
Depending on the design features, the following types of products are distinguished:
- conical;
- gear-crown;
- quick-clamping
Why do you need to disassemble the cartridge?
The clamping fixture must provide high precision hole drilling. However, after some time the seats wear out. This causes the cartridge to start hitting.
This means that the working area of the drill shifts in different directions during operation. In this case, the formation of the hole has certain deviations in location and diameter. Wear of the cams makes it impossible to properly fix the drills, which causes them to stop under load. The solution is to replace the worn element with a new one.
Collet chucks for drilling
A fastening feature in the design of any drill is the presence of two grooves. Installation of the nozzle into the chuck is accompanied by its rotation, while the locking balls fall into special recesses in the shank. The replacement of the mandrel ends here. When you stop a running machine with this type of fastening mechanism, the spindle is automatically locked.
This fastening of the clamps ensures reliable fixation of the drill in a minimum time. The unique structure of the collet eliminates the possibility of gaps appearing inside the fastening mechanism; this completely eliminates vibrations of the nozzle during operation.
Jaw chucks
The structure of the cam fastener has 4 important components: a strong body, a bushing, special cams and a ring. The big advantage of this mechanism is the absence of plastic internal parts, but there is also a drawback - a special key is used for fixation. It significantly slows down the process of replacing nozzles and their alignment. By the way, the centering accuracy of this type of fastener is insufficient, which leads to loosening and weakening of the drill.
jaw chuck
Disassembling the cartridge
Like any tool, in order to continue its normal operation, the cartridge may require cleaning , for which it will be necessary to disassemble . Disassembly can be done in several ways.
If the cartridge is not a monolithic part consisting of a single piece of any metal or alloy, then disassembly can be carried out using the impact method by tapping a hammer on its back side (the outer ring in this case slides off the internal gear rim, which allows for complete disassemble the part).
The thermal method involves a step-by-step disassembly process.
- 1. it is imperative to remove the holding cams inside (so that they are flush with the surface of the cartridge itself),
- 2. then install the chuck with a rotating ring in a vice
- 3. Then you should heat the clamped ring with a hair dryer (or some kind of burner) , after carefully placing a cold, damp bandage (or gauze) inside.
- 4. After the ring has warmed up well, the base of the chuck must be knocked out (the ring itself will remain in the vice) towards the jaws.
You should pay attention to the thickness of the metal so that upon impact the part does not deform.
Reassembly of the cartridge must also be done under heat. The use of a cloth soaked in cold water is mandatory, as it helps cool the part from the inside; If heating takes too long, an external water supply should be provided.
Use of fasteners
Among the most common fastening structures used in production are the B16 model, the slightly larger B18, and the Morse cone. The digital indicators in the model name do not correspond to the dimensional values of the chuck; for example, the cone-shaped mount for B16 drill bits is characterized by a diameter of 27 mm.
Chucks for drilling equipment may differ from each other in the following ways:
- according to the external shape and individual length of the working area;
- on some models, a protective plastic casing is sometimes present or absent;
- the method of fastening the components of the cartridge differs in different models;
- the alloy from which the machine part is made differs in color.
To expand the capabilities of the drilling device, it is equipped with additional adapters with a cone. Thanks to this improvement, it is possible to install cartridges with a reduced or significantly larger Morse cone.
The most functional and durable type of fastener is also distinguished - quick-clamping, it is ideal for highly efficient equipment operating at high speeds. Thanks to the tapered shanks, the part is characterized by high versatility. But the cost of this piece of equipment is unattainable.
Choosing the type of cartridge among the modern variety of these parts is not difficult if you give preference to universal varieties. But professional activities associated with high-precision and complex drilling require a scrupulous analysis of the parts of the chuck; this is not carried out by every specialist in this field.
Types of drill chucks
Today, there are several classifications that divide existing drill chucks into groups: in the first, the main feature of the division is the method of changing attachments , in the second - the method of fastening the chuck on the machine , in the third - the accuracy class . Of course, foreign manufacturing companies offer their own methods of dividing these parts, but the ones listed are universal and allow you to select the cartridge necessary for specific tasks without any problems.
Classification of cartridges according to the method of changing nozzles
According to the first classification, the following groups are distinguished:
- Key chucks , which have a shank in their rear part and allow you to install replaceable attachments through the use of special keys . Similar chucks are installed on modern hand drills;
- Collet chucks require drills to be secured using adapter collets , which are elongated steel adapters of two diameters. This type of chuck is used to provide fastening for small diameter tools (up to 40 mm) equipped with a shank. Usually supplied complete with Morse taper and adapter collets;
- Keyless chucks differ in that they allow the operator change the attachment on the tool without using any keys (hence the name). This group is further subdivided into two others.
- Fastening of quick-change chucks is carried out through their fixation using a conical shank. In addition, such parts are always equipped with a special replaceable sleeve for attachment drills;
- Precision chucks differ from those described above in that they are designed to work on the corresponding drilling machines and provide reductions in radial runout to a value of 0.6 mm (and modern models can boast an even smaller value of 0.04 mm).
Classification of cartridges, method of fastening the cartridge
According to the method of mounting the chuck on the machine, the division is very simple:
- Installation can be carried out using a shank and a Morse cone , which are literally put on each other, performing coupling. In some cases, matching threaded holes may be made in them to ensure good quality fasteners;
- Also, fasteners can be based on threaded coupling with the machine.
Operators of some enterprises can independently change the factory part as follows: a thread is cut on the outer part of the Morse taper, which must match the size of the shank, plus an additional nut is applied so that it is possible to remove the clamping tool using a regular replacement wrench. Such operations must be coordinated with senior management.
Classification of cartridges by accuracy class
According to the accuracy class, drill chucks on the market are divided into two groups: there are products of class I and class II . Before release for sale, the class is assessed by measuring the radial runout exerted on a control mandrel, which is in a fixed state in the clamping elements of the cartridge. Cartridges of the second class allow a slightly larger deviation than products of the first (for example, for a mandrel with a diameter of 2-4 mm and a length of 40-50 mm, the radial runout values for the first and second classes are 0.05 mm and 0.1 mm, respectively).
By the way, tests on the control mandrel are carried out three times , and the arithmetic mean of the resulting deviation values is taken as the result (this is necessary for a comprehensive check of the operation of the part). If the results are borderline, another set of tests is carried out; with the remaining “floating” values, the part is assigned the worst class.
You can fully familiarize yourself with the permissible values of classes in the regulatory document GOST 15935-88.
It should be noted that previously absolutely all chucks used on drilling machines were clamping self-clamping chucks, which are tightened by spindle rotation, are becoming increasingly popular in industry Clamping chucks are gradually fading into the background and are actively used only in everyday life in ordinary hand drills. By the way, the use of self-clamping chucks on a non-industrial scale is not recommended by specialists.