What is kerosene
Being in the aggregate state of liquid, it is a mixture of various hydrocarbons. The main raw material for the production of kerosene remains oil, as the main source of various combustible and lubricating fractions. On a modern industrial scale, fuel is obtained by classical distillation or rectification. The main use of kerosene is determined by its physical and chemical properties. The boiling point is in the range from 150 to 250 degrees, more resistant to detonation, safe for use at high altitudes. The range of applications is quite wide: it is used in lighting fixtures, garden equipment, diesel power plants, aircraft engines and rockets.
Kerosene appears to be a clear, oily liquid. It may have a yellowish tint, which depends on the method of production (area of application).
Who discovered kerosene
The invention of this hydrocarbon liquid is attributed to the ancient scientist from Persia - Razi Muhammad. The discovery of kerosene occurred as a result of simple distillation, when one of its fractions was actually evaporated from crude oil. Taking into account the development of exact sciences at that time, it was not possible to accurately determine the composition of kerosene. For this reason, the liquid was used until the 19th century for its elementary property - flammability as part of lighting architectural elements.
The use of kerosene as a patented substance dates back to 1854. During this period, the era of inventions began, so Abraham Gesner hastened to secure a patent for the light oily substance.
Why is this liquid called kerosene?
Kerosene owes its name to the ancient Greeks. The translation of the word Keros sounds like wax. This is exactly how the distant ancestors of humanity perceived that substance. A fairly simple method of production made it possible to accumulate impressive reserves of oily liquid. The fuel oil produced in parallel, however, has not found such wide application as kerosene in terms of combustion temperature in lamps or simple heaters. Often, excess “ancient wax” was burned directly in storage. This happened until the chemical structure of the substance was thoroughly studied.
Rules for storing gasoline
Flammable and combustible substances are stored taking into account all safety rules for premises with flammable liquids:
- pouring flammable substances from one container to another must be done under strict control over the filling of the container;
- all storage containers must be technically tested and certified;
- containers with gasoline are prohibited from being placed near open flame sources and heating devices;
- Do not heat containers with a kerosene lamp or gas burner.
The speed and correctness of initial actions is the key to effective fire suppression in the future. Knowing how to use fire extinguishing agents as intended can save your life.
Source
Kerosene composition
Given the possibility of being obtained by distillation, this liquid occurs in nature in its pure form. In a simple structure, it is a mixture of hydrocarbons in varying percentages. The volume of components depends on the oil field.
Liquid composition:
- Hydrocarbons: Aliphatic. In a volume from 20 to 60 percent;
- Aromatic – up to 25%;
- Naphthenic – up to 50%.
- Nitrogenous;
Depending on the percentage of one or another component, kerosene’s chemical composition may show the predominance of certain qualities. That is why, when used responsibly, laboratory tests are carried out and the quality of the raw materials is taken into account. In modern conditions, in order to obtain a liquid with a precise component composition, the fuel manufacturing technology is modified.
Kinematic viscosity
When characterizing kerosene according to GOST, this position will also be relevant. It must be said that the viscosity of the hydrocarbons included in this product changes significantly with a decrease/increase in its temperature. The higher the latter is, the lower the viscosity becomes.
This is a very important characteristic. The viscosity of kerosene has a great influence on a number of operational features of aircraft fuel systems, as well as combustion and mixture formation processes in the engine.
Thus, the viscosity of kerosene at 20 °C is 1.2 - 4.5 mm2/s.
Method for producing kerosene
Currently, the liquid used as fuel is produced from petroleum. On a small scale, the traditional distillation method is used. When heating raw materials in special cubes, hydrocarbon compounds begin to actively separate from the fuel oil base. The method is based on the physical properties of kerosene, when lighter fractions are separated from heavier ones when heated. The method is not secret, so it can be easily reproduced at home.
With the growing need for advanced fuels and the imposition of quality requirements, industrial methods for producing a mixture of hydrocarbon compounds are emerging. So, starting in 1866, the cracking (or splitting) method appeared. In fact, the promising American used a slightly modified pressure distillation. True cracking, which laid the foundation for the production of kerosene grades, appeared in 1981 thanks to the Russian engineer Gavrilov. From this moment, the industrial production of fuel begins its countdown, in which the depth of processing has significantly increased (the volume of waste has decreased).
How to prevent detonation
Fuel oil products are explosive substances, but you can avoid an emergency by following simple rules.
They are as follows:
- the engine must be operated at high speeds;
- use an intercooler to cool the charge air emerging from the front of the cylinder;
- choose the right candles;
- switch to high octane fuel.
Drivers of tanks transporting flammable substances must strictly comply with the requirements of GOST R 52734.
What is kerosene used for?
Today this type of fuel is used for its intended purpose. Application directly depends on the brand, variety, and area of demand. When purchasing for industrial needs, the mixture’s compliance with current standards for consistency, density, hydrocarbon composition and other physical and chemical properties is checked.
In addition to technical purposes, certain brands of kerosene are known to be used for medical purposes. The liquid is used to remove lice, as a basis for lotions and ointments for the treatment of skin diseases. With a certain component composition, it is used as part of drugs for the treatment of diseases of the lungs, nervous system or gastrointestinal tract.
Precautions when extinguishing
When extinguishing LV on your own, follow the rules to avoid injury and damage:
- do not start putting out a fire if you are wearing oily clothes or your hands are dirty with gasoline or other flammable liquid;
- When extinguishing a fire, make sure that there are no people within 10 meters of the fire;
- It is not recommended to extinguish the LV using water, this can lead to an explosion;
- It is advisable to extinguish LV fires in special clothing: hands should be protected with gloves, there should be no bare areas on the body.
Main types of kerosene
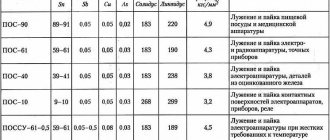
A flammable viscous liquid obtained from petroleum, classified by application. There are technical, lighting, missile and aviation types of factions. If they say that kerosene is a fuel for cars, this is not entirely true. Diesel is used to refuel cars.
Technical
One of the most popular types of substance. It is known to use kerosene according to its chemical formula as a raw material for the production of certain groups of hydrocarbons. These are propylenes, ethylenes and more complex chains, on the basis of which solvents, plastics, plasticizers, and powder compositions for waterproofing are produced. Kerosene is often used as technical fuel for heating industrial premises, workshops, and workshops. The main difference from other varieties remains the content of aromatic hydrocarbons. Their volume should not exceed 7 percent of the total mass.
Missile
As the main combustible fuel, kerosene, almost in its pure form, is used to launch space and military vehicles. The specific heat of combustion parameters provide effective thrust sufficient to impart impressive kinetic force to various objects. At the same time, the sufficiently high ignition temperature of kerosene creates safe conditions in critical piloting conditions.
Aviation
Civil, military and special types of communications on manned aircraft operate on this type of fuel. Various brands of jet fuel are used for refueling and as a technical fluid. Known to be highly resistant to ignition from accidental electrical discharges. If conditions are met, it can be stored as emergency reserves (defense industry, remote sites).
Lighting
Due to the unique physical properties of kerosene during combustion (at temperatures ranging from 35 to 75 degrees), a minimal amount of by-products is released. High-quality raw materials are especially valued, providing an effective and long-lasting glow.
Temperature
The flame temperature depends on the nature of the combustible substance and the intensity of the oxidizer supply. For example:
- The ignition temperature for most solid materials is 300 °C.
- The flame temperature in a burning cigarette is 250-300 °C.
- Match flame temperature 750-1400 °C; while 300 °C is the ignition temperature of wood, and the combustion temperature of wood is approximately 800–1000 °C.
- The combustion temperature of propane-butane is 800-1970 °C.
- The flame temperature of kerosene is 800 °C, in an environment of pure oxygen – 2000 °C.
- The combustion temperature of gasoline is 1300-1400 °C.
- The flame temperature of alcohol does not exceed 900 °C.
- Magnesium combustion temperature – 2200 °C; a significant part of the radiation is in the UV range.
Highest known combustion temperatures:
- dicyanoacetylene C4N2 5260 K (4990 °C) in oxygen and up to 6000 K (5730 °C) in ozone;
- cyanogen (CN)2 4525 °C in oxygen.
Since water has a very high heat capacity, the absence of hydrogen in the fuel eliminates heat loss due to the formation of water and allows the development of high temperatures.
Main indicators of the physical properties of kerosene
Suppliers of fuel for various needs are leading petrochemical companies. Often the supply is carried out by private industries working in the direction of unique developments. When forming industrial reserves, a number of characteristics and properties of kerosene are taken into account. Physical parameters are most often studied in combination with chemical formulas. In this regard, the following mixed properties are distinguished:
- Density;
- Viscosity;
- Heat released during combustion;
- Flash points, boiling points;
- Liquid color. It happens without color, yellowish or light brown tint;
- Chemical composition. Depends on the raw materials;
- Concentration limit of ignition. By analogy with natural gas, the volume of a substance in nearby air mixed with kerosene vapor is studied;
- Acidity
Kerosene density
This physical quantity directly depends on the temperature of the liquid. To compile a density table, measurements are taken at various degrees of heating of the sample taken for research. An increase in the parameter is achieved through the use of various production technologies and increasing the content of heavy hydrocarbons. When heated, a direct dependence of density is observed; it begins to decrease. For example, at a temperature of 20 degrees, the density is at the level of 819 kg/m3, then rushes to a value of 618 kg/m3 when heated to 270 degrees. This property should be taken into account in practical applications. The initial density of the substance is less than water, which is why almost all oil derivatives form a continuous film on the surface of reservoirs.
Approximate properties depending on where kerosene is used:
- Aviation brands TS-1 -780 kg/m3, TS-2 – 766 kg/m3;
- Lighting – 840 kg/m3.
Kinematic viscosity of kerosene
In practice, this indicator is obtained by calculation. The initial data for calculations are density and dynamic viscosity. The parameter is used to determine the lubricating properties of a substance when used as a technical fluid in industry and aviation. The kinematic viscosity indicator is taken into account when filling storage tanks, tanks, reservoirs and other types of containers.
The parameter remains directly dependent on the degree of heating, the initial value is taken as 1.819·10-6 m2/s, maintained at a temperature of 20 degrees. Kinematic viscosity decreases less actively than dynamic viscosity (in a ratio of 4.8 versus 5.7).
Flash point of kerosene
This parameter is often studied as the flammability of a liquid. By definition, this is the starting temperature at which vapors above the tank (container, pipeline) ignite. However, the flash level does not indicate detonation of the entire volume of kerosene used. The initial parameter used for industrial supply purposes is 28 degrees. If there is a downward deviation from this parameter, fuel is not allowed for sale. In practice, active ignition of kerosene occurs when heated (for example, with compressed air) to 300 degrees. In this case, the flash point takes into account unauthorized fire (from extraneous sources).
Heat from burning kerosene
The starting value is 43 MJ per kg of fuel. The parameter is taken into account when burning raw materials for space heating. The level of influence on adjacent mechanisms during active combustion of fuel in jet engines is also being studied.
Algorithm of actions when burning gasoline
If you witness the ignition of fuel, including gasoline, follow the instructions:
- Immediately notify the fire department about the fire or ask people nearby to do so.
- If a car is on fire, use the built-in fire extinguisher, directing the active substance from the edge to the middle of the fire.
- If there is a fire under the hood of the car, carefully open the lid using a stick or iron objects at a distance of 1-2 meters. Cover the fire with a cloth, use a fire extinguisher, or try to cover the flame with sand.
- If you are unable to extinguish the fire, move 10 meters away from the fire and wait for rescuers to arrive, and also follow what the fire service recommends.
- In cases where there are cars or construction objects nearby, warn others about the danger.
- Oil facilities and large enterprises must have an automatic fire safety system. If it does not work, staff must turn it on manually.
| Emergency services | Landline number | Cell number |
| Fire Department | 01 | 101 |
| Police | 02 | 102 |
| Ambulance | 03 | 103 |
| Single help service | 112 | 112 |
Is kerosene dangerous for humans?
As with any technical fluids, it all depends on the quantity. Considering the fact that kerosene is obtained from oil as a natural resource, it is harmless in small quantities. The substance is often used for medical purposes, but mostly for external use. If they enter the esophagus, heavy fractions can cause deterioration of health and allergic reactions. In such cases, decontamination elements should be adopted.
Speaking about what kerosene is, we should remember about an extremely interesting set of chemical elements and active compounds to study. Practical properties as a fuel, technical fluid, and feedstock for various types of industry keep this substance at the level of global consumer demand.
Types of fuel
It varies. But petroleum products and other fuels are easily flammable.
The classification is as follows:
| What state of aggregation is it in? | Origin of combustible materials | |
| Natural | Artificial | |
| Liquid | Oil. | Gasoline, diesel fuel, tar, kerosene. |
| Gaseous | Natural and industrial. | Generator, lighting, water. |
| Firm | Coal, shale, firewood and peat. | Coke, pulverized fuel and briquettes. |
The combustion temperature of kerosene and other products is different. It is quite difficult to measure it. The rules for extinguishing also vary. People who have a boiler naturally use solid materials to heat rooms.
Area of use
Kerosene is used for lighting in lamps. Regardless of the name, this is its main, but not only, area of use.
It is also used in household appliances for heating or cooking. This may include:
- Kerogas is a heating device that used to be widespread. During its operation, there is no direct combustion of kerosene, it simply evaporates. Due to this, soot formation does not occur.
- A kerosene stove, which differs from the previous type in that kerosene already burns in it. Therefore, it is impossible to use other types of kerosene due to the possible formation of soot.
- Primus, which is similar to a gas burner. It differs only in a different type of fuel. Tourists and fishermen often take it with them.
Another area of use is in machines that cut metal. The prevalence in these areas is mainly due to the fact that the flame does not smoke when burning kerosene.
In addition, this type of kerosene can be used as a solvent. It is used in the production of glue, paints and varnishes, rubber, and in everyday life (for cleaning clothes, leather goods, and so on).
Characteristics of the substance
Russia has developed a clear system of standards that determine the basic properties of all materials and substances. Kerosene for lighting is no exception. GOST 11128-65 and GOST 4753-68 set the basic parameters that a given flammable liquid must comply with.
If kerosene is used for lighting, it is important to consider the dead flame height, sulfur content, flash point and cloud point. The latter indicator characterizes the ability of a hydrocarbon to burn at low temperatures. In addition, kerosene for lamps must contain the maximum possible amount of light fractions (that is, saturated aliphatic hydrocarbons).