Before carrying out work, it is recommended to check the humidity, air and substrate temperatures, as well as the dew point.
Option 1 – application by airless spray (optimal).
If necessary, dilute the primer with an appropriate solvent to working viscosity (but not more than 5% by weight of the material).
Optimal pressure is 100-160 bar, nozzle diameter is 0.013-0.017″.
Option 2 – application by pneumatic spraying:
If necessary, dilute the primer with an appropriate solvent to working viscosity (but not more than 10% by weight of the material).
The optimal pressure is 2.5-4 atm, the nozzle diameter is 1.4-2.5 mm.
Option 3 – application with a brush or roller.
If the soil is too thick, it can be diluted with an appropriate solvent for more convenient application (but not more than 5% by weight of the material).
Use only brushes and rollers that are resistant to organic solvents!
Safety precautions:
Use personal protective equipment (overall clothing, gloves, goggles, respirators). If the material comes into contact with exposed skin, immediately wash it off with clean water and soap, or remove it with a solvent. In case of contact with eyes, rinse them with plenty of water and consult a doctor immediately!
When carrying out work indoors, it is important to ensure good ventilation; do not use open flames or use welding equipment!
More detailed information regarding compliance with safety measures when working with the material can be obtained from specialists upon request.
Advantages of the method
Using the cold galvanizing method has a number of undeniable advantages:
- independence from the size of the product being processed;
- permissibility of galvanizing welds on site;
- ability to work in a wide range of ambient temperatures: from -20°C to +40°C ;
- high adhesion of the zinc-containing layer to paints and varnishes;
- obtaining an elastic coating resistant to mechanical and thermal deformation.
The undoubted advantages of protection include ease of use, relative cheapness and quick payback.
The cold galvanizing method has found wide application in the anti-corrosion protection of a wide variety of objects:
- building metal structures;
- bridges;
- hydraulic structures;
- reservoirs, cisterns;
- pipelines made of steel and ferrous metals;
- oil and gas pipelines;
- railway and water transport;
- agricultural machinery, etc.
Note:
All of the above information regarding technical characteristics and recommendations for applying LCM POLYMER materials is based on our theoretical knowledge and practical experience in using the products subject to the conditions of transportation and storage. The company is not responsible for damage caused by using the material for other purposes or in violation of the instructions for use, storage, transportation and subsequent operation of the coating. The material is intended only for professional and industrial use by specialists with the necessary theoretical knowledge and practical experience. You always have the right to request more up-to-date technical data by contacting our hotline.
Paints and primers for cold galvanizing of metal
Cold galvanizing is the process of applying zinc-containing paints and primers to the metal surface. They are compositions with polymers, binders and a maximum zinc content (up to 96%). Such coatings provide double protection: active and passive. During active (cathode) electrochemical contact occurs between the coating and the metal, the zinc “sacrifices” itself to protect the metal. Therefore, corrosion will not occur until all the zinc is used up. Passive protection involves the creation of a durable, uniform coating that is impermeable to moisture and aggressive substances.
Anti-corrosion paints and primers for cold galvanizing are inexpensive and easy-to-apply compositions. Hot-dip galvanizing is an expensive procedure, especially for large structures. It is performed by immersing products in liquid zinc. Cold galvanizing paints can be applied to metal structures without dismantling them directly at the place of use (outside or inside). When applied, zinc-rich primers are not inferior in their properties to hot-dip galvanizing.
Advantages of paints with zinc
- Versatility.
The compositions are used as independent or auxiliary coatings. Suitable for external and internal work. - Efficiency.
Zinc-rich compounds provide double protection with increased protective action (from 10 to 50 years). - Economical.
Depending on the choice of paint and the method of its use, you can reduce galvanizing costs by at least 2-3 times. - Fast drying.
Paints with zinc harden in the shortest possible time (from 15 minutes), which simplifies the application of repeated layers or topcoats. - Practicality.
After cold galvanizing, it is possible to weld metal structures and decorative painting in any color, including weld seams. - All-weather.
Metal processing is carried out in a wide temperature range (from -30°C to +60°C). - Ease of use.
Paints and primers with zinc can be applied independently without the involvement of specialists. Available in buckets and aerosol cans.
Areas of application of zinc-containing compounds
- Metalworking enterprises.
- Automobile, ship and carriage building.
- Agricultural and harvesting equipment.
- Construction of roads, bridges and power plants.
- Protection of roofs and external fences.
- Manufacturing of artistic forging products.
Choosing paint and primer with zinc
When choosing a zinc composition, you need to pay attention to its main characteristics: 1) type (paint, primer); 2) purpose; 3) zinc content; 4) conditions and method of application; 5) drying time. Primers provide reliable protective protection for metals and are suitable for subsequent painting. For large metal structures, liquid paints are usually used in buckets of different sizes. For local processing of products - aerosol cans.
DO YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS?
Ask them by phone: 8
or email:
[email protected]
General principles of cold galvanizing
Hot galvanizing allows you to protect the metal from corrosion for the next 40-50 years, and no additional measures will be required. A technologically complex and costly process in everyday life has been replaced by cold galvanizing, which allows you to obtain a high-quality protective coating with minimal effort, but it will have to be renewed periodically.
The cold galvanizing process is similar to simple painting of metal structures, only zinc-rich paints (ZNC) are used instead of conventional paints. They contain at least 94% zinc, the rest are binding additives. CNC should not be confused with zinc-containing paints: the proportion of zinc in them is lower, and the density of the composition is always less than 2.2 kg/l.
The nature of cold galvanizing
To better understand the features and advantages of the method, you need to remember the school chemistry course. The process of protecting iron-containing alloys with zinc is possible due to the unique physical and chemical properties of this element.
Zinc very easily enters into chemical reactions with various types of substances, and when interacting with water, it forms a practically insoluble hydroxide, which covers the surface of the metal and prevents further interaction of zinc and water. By the way, aluminum behaves in a similar way.
If you cover a steel structure with a layer of zinc, the zinc in air will begin to oxidize over time. The reaction product is zinc oxide, which does not react with water and forms a durable film on the surface of the structure.
That's it, further reaction is impossible, since zinc oxide and zinc bicarbonate (formed in smaller quantities) are inert towards water. This is protection based on the barrier principle .
It is worth noting that iron also reacts with water to form oxides, which we call rust, but these compounds do not form a continuous dense film, allowing moisture to pass deep into the metal and provoking the development of corrosion.
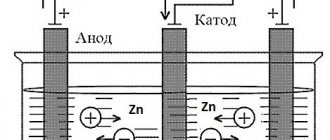
In addition to barrier protection, zinc also provides electrochemical protection. Let us recall the electrochemical voltage series of metals, in which zinc comes before iron.
This means that zinc is chemically more active and in a zinc/iron pair it will react first. In the presence of atmospheric moisture, an electrochemical reaction can occur to form zinc carbonate. This compound is also insoluble in water and stops the further development of the corrosion process.
The principle of “working” of zinc coating remains the same, despite the method of its application:
- hot galvanizing;
- electrolytic galvanizing;
- diffuse galvanizing;
- gas-dynamic galvanizing;
- shopping;
- cold galvanizing.
Immediately after protecting a metal structure using the cold galvanizing method, mainly electrochemical protection works: while the coating has not yet reached maximum strength, moisture particles can penetrate through it and reach the steel.
At this point, an electrochemical zinc/iron couple is formed. In the future, the protection is built according to the barrier type, but if the integrity of the paint is damaged and moisture penetrates into the structure, then the electrochemical protection is activated again.
Advantages and disadvantages of cold galvanizing
Cold galvanizing of metal is a simple, reliable and one of the most popular ways to protect it. In everyday life, the technology has become widespread, as it has many advantages :
- the compositions used have good adhesion both to the base and to decorative paints and varnishes, so the structure can be easily painted in the desired color;
- the coating can be applied to a product of any size and any geometry, and if it is already installed and in use, then there is no need to dismantle it - all work can be performed on site;
- surface preparation before cold galvanizing is relatively simple;
- metal parts protected by this method are easily welded together;
- Easy to apply, no special skills or tools required. For painting, spray guns, paint rollers and ordinary brushes are used;
- work can be performed in almost any weather (permissible air temperature -20...+400C);
- low financial and time costs.
The main disadvantage of cold galvanizing is the low resistance of the coating to mechanical damage. Simply put, the paint can simply be scratched, exposing the steel structure. On the other hand, updating the coating is not so difficult and expensive, so the minus cannot be called very significant.
General information
As you know, galvanizing provides the most durable protection of metal against corrosion. The duration of this protection is 20-25 years. However, it is not always possible to perform galvanizing using traditional methods - “hot” or electrochemical deposition.
For example, this is difficult to achieve when finishing large metal structures. Moreover, it is impossible to apply the coating yourself at home. The way out of this situation was the use of zinc paint or, in other words, cold galvanizing.
This technology has properties that are practically not inferior to hot-dip galvanizing, but at the same time it is distinguished by a simple and affordable method of forming a protective coating. The composition is applied in the same way as other paints and varnishes.
Diagram of the difference between conventional coating and cold galvanizing
Disadvantages of the method
All galvanizing methods have both advantages and disadvantages. The main disadvantage of cold galvanizing compositions is the high requirements for thorough preparation of the metal before applying the zinc-containing layer, compliance with all requirements for surface preparation and application and curing of the coating.
The cold galvanizing compositions themselves are distinguished by excellent protective characteristics and a long service life. But violation of the rules for surface preparation and painting specified in the technical specifications for the composition for cold galvanizing entails a deterioration in the quality of the coating and a reduction in its service life.
For example, if the quality of cleaning and degreasing is poor, dust, oil or grease stains may remain on the metal surface. In such areas, the adhesion of the protective layer will be low, and the coating will peel off over time.