The compressor is a reliable assistant for a small home workshop, car service center and large production. Piston models require constant lubrication of the moving parts of the piston group. The oil is changed periodically, following the manufacturer's recommendations. Between servicing it must be topped up as it is used up.
Oil for air piston compressor
Oil in a piston compressor is the main consumable. It is designed to solve the following problems:
- lubrication of moving parts, reduction of friction;
- cooling of piston group parts;
- anti-detonation;
- additional sealing of working chambers.
If a decrease in tightness only reduces the performance of the unit, then insufficient lubrication or overheating can lead to failure of the unit, costly repairs, or even an accident. Therefore, the owner is obliged to monitor the level and replenish its supply as it is consumed.
Functions of compressor oil
The lubricant material solves a number of problems aimed at ensuring stable operation of the compressor:
- lubricates rubbing parts, thereby extending their service life;
- cools the piston group, which heats up during operation;
- seals gaps;
- reduces detonation;
- ensures the tightness of the working chamber.
Insufficient oil level or absence of oil leads to a decrease in the tightness of the compression chamber and a deterioration in compressor performance.
Oil change: rules and recommendations
Manufacturers of compressor equipment always indicate in the user manual which brands of oils can be used for replacement in a given model. Global brands even produce brands of lubricant under their own name.
Important! Automotive compressor lubricants can be used for replacement in the compressor crankcase in case of extreme need. It is intended for other operating modes, temperature, pressure.
Prolonged use may damage the compressor. After short-term use, you should immediately change the oil to the recommended one.
In the manual, in addition to the main recommended brand, one or two compatible ones must be indicated for replacement. If it is not available, you can replace it with a lubricant for compressors of any global brand. It will cost more, but is guaranteed not to harm the unit.
When changing the compressor oil, follow the instructions in the owner's manual for your specific model. Experts have formulated several general recommendations:
- Be sure to turn off the power to the device before starting replacement;
- relieve pressure.
- Unscrew the plug and drain the old grease into the prepared container. It is better to take a flat cuvette with a capacity 1/3 larger than the rated oil volume.
- Some models are recommended to be tilted towards the drain hole.
- After the oil has completely drained out, carefully tighten the plug. Wipe off any splashes that might get on the body.
- Fill with new lubricant to the normal level.
A slightly increased amount of oil must be poured into piston compressors - part of the lubricant will be distributed over the surfaces of the parts.
The waste must not be poured onto the ground or down the drain; this will lead to serious environmental pollution. It must be submitted for recycling to specialized receiving organizations.
Be sure to completely change the oil in the compressor. A mixture of clean lubricant with contaminated lubricant, especially of different types, leads to increased wear of unit parts. It is strictly forbidden to mix synthetic and mineral varieties.
Compressor oil compatibility table
| Ether* | PAG | PJSC | Group III synthetic oil | Mineral oils of group I and group II | Silicone base oil | |
| Ether* | Yes | No | Maybe | Maybe | Maybe | No |
| PAG | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| PJSC | Maybe | No | Yes | Maybe | Maybe | No |
| Group III synthetic oil | Maybe | No | Maybe | Yes | Maybe | No |
| Mineral oils of group I and group II | Maybe | No | Maybe | Maybe | Yes | No |
| Silicone base oil | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
It is impossible to answer for sure whether one oil will be compatible with another, since it is always worth considering incompatibility with additives and the degree of contamination of the oil during operation. When changing oil in compressors, we strongly recommend draining the old oil and flushing the system, regardless of what base oils are included in the old and new oils, since there is always the possibility of incompatibility. This conservative recommendation is also based on a risk-benefit model when it comes to tank size; tanks tend to be small in size. So, due to the fact that the container contains a small volume of oil, i.e., its loss in the process of removing its residues will be minimal, draining the oil and flushing the system should be carried out taking into account all risks and compatibility aspects.
This procedure not only reduces risks, but also improves equipment performance.
In some cases, the services of technical specialists may be required. If the question arises about removing carbon deposits and varnish deposits, it is worth thinking about the incompatibility of oils. In this case, it is necessary to flush, possibly using solvents, replace seals, etc.
We bring to your attention recommendations for washing. These can be used as requirements to complement OEM requirements.
What kind of oil to pour into a piston compressor
To avoid breakdowns, the choice of lubricant should be taken seriously. High-quality products will ensure full rated performance, operational stability, as well as a long service life of the unit. One of the most important indicators of lubricant quality is its viscosity. It is measured in laboratories and determines the ability of a material to linger on lubricated surfaces. Viscosity should not be less than seven conventional units. Such a lubricant will envelop the parts and components of the unit, primarily the piston rings and crankshaft bearings, reducing friction between them.
Read also: DIY mercury antenna for TV
The next indicator is the pour point. In summer and in heated rooms, it is quite acceptable to use cheaper varieties with high temperatures. If the compressor will be used outdoors in winter, it should be replaced with low-temperature lubricants.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Thanks to people who are not sufficiently competent in the design and operation of piston compressors, a wide variety of myths hover around the operation of this equipment. Dispelling the main ones is the task of this article.
Main characteristics taken into account when choosing compressor oils
The main properties of lubricants for compressors running on an electric motor or internal combustion engine:
- Viscosity. Characterized by values 1-15. The optimal value is 10-12. This composition is well retained in the lubrication zone. A product with a lower viscosity is consumed very quickly. Viscosity also characterizes the tendency of a lubricant to lose performance at high temperatures. The higher the viscosity value, the more resistant the product is to heat.
- Availability of additives. High-quality lubricants from well-known manufacturers always contain additives that increase valuable performance properties - anti-oxidation, anti-foaming, anti-corrosion, temperature stability. In domestic labeling, the presence of additives is indicated by the letter “P”, in foreign labeling – I.
- Self-ignition temperature. For air compressors, lubricants with this parameter not lower than +350 °C are recommended.
- Pour point. This is an important quality taken into account when it is necessary to operate compressor equipment in winter conditions.
Myth #1: Receiver size matters.
Often, in a literal interpretation, this myth says: a good receiver is a great receiver. This statement is supported by the opinion that a large receiver provides higher compressor performance. This is not true.
The size of the receiver has nothing to do with the performance of the compressor, which depends solely on the engine power and the characteristics of the compressor group. The volume of the receiver provides the compressor with optimal operating mode by adjusting its switching in each unit of time.
To calculate the optimal compressor volume, it is enough to perform a simple calculation of two indicators: the operating time in the discharge mode (t1) and the time of pressure drop in the receiver (t2) using the formulas: t1 = Vр * (Рmax – Рmin) / (Qк – Qexp) t2 = Vр * (Рmax – Рmin) / Qexp where Vp – receiver volume Pmax and Pmin – switch-off and switch-on pressure Qk – volume of air produced (compressor performance); Qflow – air flow.
By summing the operating time in the pumping mode and in the falling mode, one can obtain the duration of one compressor operating cycle. By comparing the calculated indicators of several equipment models, you can choose the best option.
Helpful information
Content
One of the conditions for the uninterrupted operation of a screw compressor is timely oil change. This equipment is characterized by an optimal balance of ease of use and durability. The working part of the unit consists of a compression chamber, a pair of specially shaped screws and a motor.
Lubrication value for screw compressor
The service life of a screw compressor depends on the quality and regularity of oil changes more than in other types of devices. Increased requirements for the properties of the lubricating fluid are due to the specific operation of the equipment. Air injection is carried out by a pair of screws, during the rotation of which the cavity between them moves from the suction point to the compression chamber. The screws do not touch, leaving a microscopic gap between them. During operation, this gap is filled with an oil film, so air leakage is excluded. During compressor operation, the oil composition gradually changes. Wear products from parts, dust and moisture from the incoming air enter the process fluid. A change in composition leads to a deterioration in technical parameters. For screw compressors, timely oil change is one of the most important operating requirements.
How often does a screw compressor require an oil change?
The standard service life of the lubricating fluid is from 2500 to 3000 working hours, but at least once a year. It is not recommended to exceed this time. For some models, the developer may set other deadlines, which must be reported in the instruction manual.
External factors also influence the period of permissible work:
level of pollution and humidity of captured air.
ambient temperature.
The reason for the reduction in oil life may be a malfunction of the air filter or another structural element of the screw compressor.
When operating a new screw compressor, the first oil change should be carried out at shorter intervals. As a rule, the oil product needs to be completely replaced after 500 hours of operation. This is due to the fact that during the running-in stage of the unit, moving parts are ground in and wear products are released.
Also, residual molding sand gets into the oil, which can remain on the surfaces of new parts made by casting. All these factors lead to the fact that the composition of the lubricating fluid in a new compressor unit changes faster than in a run-in and well-tuned unit.
Procedure for changing oil in a screw compressor
Make sure that the pressure in the system and receiver is “0” and disconnect from the power supply.
Remove the compressor housing wall.
Visually check the absence of oil leaks, the condition of the radiator, the strength of fastening of the components, the tension of the belts, and the clogging of the air filter. If problems are identified, fix them.
Completely drain the entire volume of lubricating fluid. The old grease is drained through the oil drain valve. The operator should ensure that the system is empty.
Replace the oil filter and filter separator (oil separator). As a rule, during this maintenance the air filter is also changed.
After this, new oil is poured in the quantity recommended by the manufacturer.
Check the oil level through the oil indicator sight glass
After checking that the oil filler holes are closed, turn on the compressor for a few minutes. Then you need to recheck the oil level and add if necessary.
Important! You can fill only those brands of oil recommended by the manufacturer. You cannot mix different brands. If the compressor has not been used for a long time: before starting after changing the oil, it is necessary to add a portion of oil to the screw pair (through the air filter pipe or otherwise).
Tags: procedure for changing oil in a screw compressor, changing oil in a screw compressor, changing oil in a screw compressor step by step
www.compressor-mash.ru
Myth No. 2: Oil for internal combustion engines is also suitable for compressors.
This is one of the most common misconceptions that exists in many car services. Its logic is based on a similar principle of operation of a piston compressor group and an internal combustion engine. But this is not a reason to use motor oil instead of compressor oil. All self-respecting manufacturers of automobile oils have products for compressors in a separate product group. It is easy to make sure that compressor oil differs from other types of oils - just compare the characteristics of different types of products.
Compressor oils are superior to automobile oils in terms of kinematic viscosity and flash point in an open crucible. In addition, it is strictly forbidden to mix oils of the same type and with similar characteristics if they are produced by different manufacturers. Compressor oil must be completely drained and replaced with new oil when switching to a new brand of product.
Classification of compressor oils and their scope
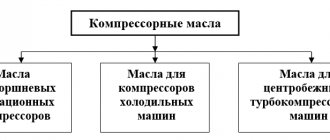
All modern compressors are divided into two main types, differing in their design and operating features. These include:
- Volumetric. In such equipment, the distilled gaseous substance is sucked into the working chamber, compressed and thrown out under pressure by the forward-return movement of the piston system;
- Dynamic. The compression of the medium they distill is carried out using turbine mechanisms. The intake gas is accelerated by the turbine rotors, after which it suddenly slows down, causing it to be dynamically compressed.
In volumetric piston compressors, oil provides lubrication of moving parts - piston group, valves, bearings. Traditionally, such models use mineral oil that meets international certificates DIN-51506-VGL, VDL. The viscosity class for them corresponds to ISO/VG standards from 68 to 150. In positive displacement rotary or screw compressors, the moving parts are lubricated using an oil bath. As a result, the oil is constantly mixed with the forced air, heating to a temperature of about 90-100ºC.
At the outlet of the compressor chamber, a filter device is installed that separates the oil from the gaseous substance. Therefore, for use in rotary and screw compressors, oils with increased deaeration and demulsification characteristics are used.
Special requirements are also imposed on increased anti-corrosion properties and the maximum amount of deposits during operation. Most manufacturers of such equipment provide instructions in the accompanying instructions regarding the selection of a suitable lubricant.
In dynamic modifications of compressor units, lubrication is provided through a forced supply circuit: gears, shaft seals, bearings. It is recommended to use the same type of oil for the compressor operating mechanism and its drive system. It is recommended to use special turbine oils of the following grades in dynamic installations that comply with the ISO/DP-6521 standard:
- DIN-51-515 TDL-32;
- TDL-46;
- TDL-68;
- TDL-EP with extreme pressure additives.
Conventional motor oils are classified according to their flash point.
Compressor lubricants are divided, unlike motor lubricants, according to the temperature of the pumped substance.
In Russia, along with the international classification of compressor oils, the domestic classification adopted by Gostekhnadzor back in Soviet times is still often used.
According to it, all compressor oils are divided into 4 groups:
- Lubricant intended for operation under moderate loads. The temperature of the discharge gas does not exceed 160ºC.
- The second group is intended for operation under moderate loads, but with a discharge gas temperature of up to 180 degrees.
- Compressor lubricant of the third group is designed for mechanisms operating under increased loads and temperatures up to 200ºC.
- The last group includes oils intended for operation in extremely difficult conditions, with increased pressure and temperatures up to 200ºC.
Each group has a special list of operational and technical properties that must be taken into account when choosing the type of oil for the compressor.
It should be noted that foreign manufacturers have not developed a unified classification for operating temperature, and each large company uses its own standards.
Myth #3: An industrial compressor can be used in a continuous production cycle.
Even an industrial compressor is not designed for continuous use. Even more durable screw-type devices will not withstand such a load.
The classification of piston compressors into industrial, semi-professional and household is based not on their ability to withstand certain loads, but on design features. Industrial compressors differ from household and semi-professional compressors by a belt drive and can only be oil-powered, while lower-class devices can also be oil-free with a direct drive. This is what allows industrial compressors to be used more intensively, but this does not mean that they can work around the clock.
Compressor maintenance requirements
Before carrying out work, you must make sure that the compressor is disconnected from the power supply and that the pressure gauge shows zero pressure.
The optimal maintenance schedule is every 500 hours of equipment operation. In addition to standard EO work, maintenance includes:
- checking the oil level and the formation of dust or oil deposits - if this is detected, it is necessary to clean the equipment;
- cleaning or blowing out the radiator with compressed air;
- checking the cleanliness of the oil (there should be no intense darkening);
- checking the functionality of electrical equipment, wiring and terminal connections.
Please note that the first change of oil and, accordingly, the oil filter should be carried out after the first 500 hours of operation of the equipment, that is, after its “break-in”. If the installation has not been put into operation (“equipment downtime”), then the oil must be changed one year from the date of manufacture of the compressor.
The oil change is carried out according to the following scheme:
- you need to remove the right wall of the compressor;
- turn on the equipment so that the oil warms up to a temperature of 70 degrees;
- turn off the compressor;
- remove the plug and gradually open the oil drain valve (to receive the waste liquid, prepare a container in advance);
- remove the old oil filter and replace it with a new one;
- turn the screw block pulley approximately 3-5 turns (the direction is indicated by the arrow on the end surface);
- close the tap and then pour oil through the oil filler neck, monitoring the fill level using the oil indicator;
- close the filler hole with a plug;
- turn on the compressor and leave it running for 1-2 minutes until the oil temperature approaches 70 degrees, then turn off the installation and add oil if necessary;
- mount the right wall of the installation.
It is better to invite an experienced specialist to change the oil in the compressor.
To ensure correct operation of the installation, you should use oil for screw compressors with the following technical indicators:
- viscosity - 46 cSt at a temperature of 40 ° C;
- minimum pour point temperature - from -8 to -10 ° C;
- flammability point temperature is more than 200 °C.
It is not recommended to mix oil from different manufacturers and brands.
After every 2000 operating hours, it is necessary to replace the air filters, check the belt tension and, if necessary, adjust it, and also check the tightness of the pipeline.
After every 4000 hours of operation of the unit, it is necessary to change the oil separator filter, change the oil and oil filter, check the safety valves, clean the radiator, check the condition of the belts and, if necessary, replace them with new ones, and also check the condition of the receiver.
If the compressor is installed in a dusty room, it is recommended that maintenance operations be carried out more frequently, paying the greatest attention to cleaning the radiator.
Additional recommendations when changing oil:
The oil drain valve is located at the bottom of the oil sump and is used to drain used oil. If necessary, condensate is also removed through this tap. The valve of the oil removal valve should be opened and closed only if the installation is turned off and there is no pressure inside the housing.
The oil level is monitored visually; the maximum oil level should not be higher than the upper cut of the inspection window, the minimum should be the lower cut (under the condition of a “cold” installation).
Maintenance operations:
- Replacing the air filter (after every 2000 hours of operation) - if the replacement frequency is not observed, the service life of the screw unit is reduced.
- Oil change (after every 4000 hours of operation, but at least once a year) - the first oil change is carried out after a “trial” period of operation after (500 hours). Oil is poured into the unit through the oil filler hole located on the oil sump body and closed with a special cap. The lid can only be opened if there is no pressure in the housing.
- The oil separator filter is replaced after every 4000 operations of the unit, but at least once a year.
- Oil filter replacement - carried out after every 4000 hours of operation, but at least once a year, the first replacement should be carried out after 500 hours of operation.
- Belt replacement is carried out after every 4000 hours of operation. After the first 50 hours, and then every 2000 hours, it is necessary to check the belt tension level and tighten them using a special adjuster.
To replace the belts you need:
- remove the protective fence;
- relieve the tension from the two bolts and two nuts with which the plate is attached to the screw block;
- using the tensioner screws, carefully move the plate along with the screw block down;
- remove the straps;
- using the tensioner screws, move the plate with the screw block up so as to create the desired tension level;
- fix the plate with bolts and nuts;
- put the safety guard in place.
Additional recommendations for belt tension:
- Belt tension should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations described above.
- For normal operation of the unit, it is necessary to regularly check the cleanliness of the contact area between the belt and pulleys, adjusting the degree of belt tension if necessary.
- The degree of belt tension must be periodically monitored; a mandatory tension check must be performed after a break in the operation of the equipment for a week or more. Belt deflection is determined using a dynamometer, ruler and cord.
PREVIOUS POST TO TOP NEXT POST
www.pst.ru
Myth No. 4: How much compressed air a compressor consumes is equal to its performance.
This statement is completely false. Performance does not depend on the volume of air consumed, but on temperature conditions and ambient pressure, that is, on suction conditions.
The characteristic of a piston compressor is its suction performance (theoretical), which actually corresponds to the volume of air that the device can consume in a certain unit of time. However, in reality this value will be significantly less - real performance is approximately 1/5 lower than theoretical.
Read also: Drl 250 lamp technical characteristics
Myth No. 5: many cylinders are good, more are even better
The principle “more is better” does not work when it comes to the number of cylinders in a piston compressor. It is much more important to know about the number of compression stages, depending on which one-, two- and multi-stage piston groups are distinguished.
If, for example, we compare two-cylinder compressors with one- and two-stage groups, then the second option can easily detect the following advantages:
- productivity is higher;
- cylinder heating is lower;
- reliability is higher.
It should also be noted that a compressor group of two cylinders with two stages is superior in performance to a group with three cylinders but one stage.
Some useful tips
When to change the oil? How often should this be done? Is it possible to change compressor oil to oil for piston internal combustion engines? How to properly drain old compressor oil? Where to put used oil? This is a list of the most frequently asked questions by compressor equipment owners. We offer you some tips and recommendations to help answer these questions.
- After purchasing a compressor, carefully read the accompanying documentation, paying special attention to the section where the rules for operating the equipment are indicated.
- The frequency of oil changes (an indicator based on the number of hours worked) is indicated in the operating documents. Strictly follow these recommendations, this will significantly extend the life of the compressor. When starting work, check the oil level in the inspection window each time; it is important to ensure that it is at the proper level.
- In the operating instructions, the manufacturer must indicate the brand of oil that can be poured into a specific type of compressor. If you do not have the opportunity to purchase just such an oil, you can use oils from other manufacturers, but with absolutely identical characteristics.
- Under no circumstances should you fill a piston compressor with oil for piston internal combustion engines! This is a recipe for equipment failure.
- The container, after draining the compressor oil, will be unsuitable for further use. Therefore, you can use a simple plastic bottle for this.
- Pay attention to the color of the used oil; if it is very dark, then it is safe to say that the equipment has regularly overheated.
- Do not throw away used compressor oil, it is quite toxic! It can be handed over to a collection point without any problems, after which it will be processed.
- There is no need to mix used oil with new oil, this can negatively affect not only the operation of the compressor, but also lead to an emergency. To be sure that the used oil has completely drained out, tilt the piston head. This will avoid mixing new oil with used oil.
- Try to use the same base oil, choosing, for example, “synthetic”; in the future, you should not change its base.
- Do not neglect flushing the unit with special flushing liquids. This will increase the service life of the compressor and help, despite the intensity of work, to maintain its performance characteristics. The frequency of such a procedure should be indicated in the accompanying instructions.
Myth #6: Compressor pressure is related to the pressure required for pneumatics.
Determining compressor pressure based on information about the pressure required by air consumers is a fundamentally wrong approach. Optimal selection of a compressor based on pressure criteria requires taking into account two points:
- it is necessary to add 2 bar to the pressure required by consumers (the difference between the maximum operating pressure and the switching pressure), this will ensure optimal compressor operation;
- The longer the air path, the greater the pressure drop.
Therefore, in addition to pressure, it is necessary to think through the design of the pipeline, the diameter of the pipeline and select the optimal equipment.
Myth No. 7: A compressor that does not pump air is broken.
If the compressor does not work as usual, or has stopped pumping air altogether, this does not mean that it is broken. The reason for downtime may be low voltage in the electrical network or shutdown after reaching maximum pressure. An alarming symptom in such a situation is the characteristic hum of the engine. The equipment must be switched off immediately to avoid serious damage.
Connecting an extension cord may interfere with the normal operation of the compressor. The longer the wire, the higher the risk that the compressor will not work, although technically it will be fully operational. Therefore, to connect equipment, it is better to use extension cords of no more than 2-3 meters.
Particular care should be taken when connecting to a three-phase network and ensure that the electric motor and pulleys on the compressor group rotate in the direction indicated.
How to clean a compressor
Sooner or later, this equipment becomes heavily clogged with street dirt or dust. Also, storing it in a dusty trunk or closet contributes to the operation of the device. But a car compressor can be easily cleaned by first disassembling the entire structure.
Do the following on the compressor:
- unscrew the four screws on the roof and open it, check the condition of the bearing;
- Next, remove the radiator, head, as well as the valve in it, pay attention to the presence or absence of a very large gap: if there is one, then the compressor will not be able to work properly for a long time;
- examine the condition of the piston and cylinder: pistons wear out very often and quickly, therefore they must be constantly replaced in a car compressor;
- look at the compressor grilles, through which dust and dirt can get into the device, clean the insides: blow them with a vacuum cleaner and make sure that next time the compressor is not located near dusty places;
- assemble the device and check its operation.
After maintenance, the equipment should work perfectly. It is important that air flows freely through the car tire pump. Then the pumping process will be carried out much faster.
Myth #9: Moisture and oil in compressed air are a sign of trouble.
The presence of moisture and oil in compressed air is not a sign of a compressor malfunction.
The volume of oil gradually decreases due to natural entrainment; this is a completely normal process. The presence of moisture in compressed air is also normal, unless the compressor operates next to a dryer. And installing a moisture separator or cyclone separator still will not ensure complete removal of moisture.
An oil-free compressor, contrary to popular belief, does not produce air of a higher degree of purity. Of course, there will be no oil in it, but moisture will still be released. At the same time, it will come into contact with the internal working surfaces and lead to the formation of rust. Only expensive medical compressors equipped with an anti-corrosion coating are protected from this.
In any garage, an air compressor should occupy the most honorable place, because after it appears on the farm, its owners remember with horror the times when they had to manually unscrew soured nuts and blow out the carburetor using their lungs. But, with the advent of this most useful device, life changes for the better. The most common air compressors come in two designs: screw and piston. A screw compressor consists of a housing, inside of which there is a compression chamber, two worm shafts and a motor. The basis of this design is the shafts through which air is pumped.
Read also: Machine for cutting gas blocks
They are located almost right next to each other, but do not touch - tightness, due to which the compressed air does not “leak” out, is achieved using an oil film on their surface. A piston compressor can have many more components and parts than a screw compressor. A piston is used as a supercharger, which during movement draws in air using an inlet valve, and during the translational movement of the piston, air is supplied through the injector to the receiver.
In both cases, system lubrication plays an important role, since without a good oil film, compressor performance decreases sharply .
Oil change is shown in the video
How much oil should there be in a refrigerator compressor?
The Nord refrigerator has broken down with symptoms - it is trying to start, silence and humming, after 10 seconds there is a click and silence. And so on in a cycle. In principle, it became clear immediately that the problem was in the compressor, it was jammed, and with a click the thermal protection relay turned it off. The compressor itself was removed from the refrigerator before disposal (repair was considered impractical):
On the table, the compressor was started every other time, without developing pressure, without creating a vacuum. Therefore, it will be used for dissection for educational purposes, which I hasten to share.
This device is wonderful for many reasons.
Firstly, the compressor is completely sealed, and the motor is located inside a sealed space, and does not enter the shaft through an oil seal or some other seal. This greatly simplifies the seals, making leaks uncritical - everything stays inside.
Secondly, the lubrication system - the motor and cylinder work in an oil bath, are lubricated with oil, and cooled with it.
Thirdly - a resource - at our department we have a refrigerator that has been working for more than 50 years, of course it knocks when starting up until it collects oil, but it works and freezes.
Fourthly, quiet operation due to tightness and installation of the engine on spring suspensions. Anyone who has heard how piston compressors work knows that there is nothing to do with them at home.
According to the principle of operation, it is a piston pump, similar to a car pump, which is used to inflate wheels.
The motor contains two windings - starting and working. The motor is asynchronous, and to operate it requires a rotating magnetic field, which is created by a pair of windings (they have different inductances, so there is no need for an additional capacitor, as when starting three-phase motors from a single-phase network). The starting winding is connected during startup, and overload protection is provided by a starting protection relay.
The posistor starting relay contains a washer made of a material that increases its resistance when heated by the current passing through it and turns off the winding. Overload protection - bimetallic strip at the bottom of the relay
External view of the compressor without a cover:
To make it clearer, I made an animated picture:
The piston does not contain sealing rings; the tightness of the cavity is ensured by a small gap and oil. Freon and oil inside are not separated and are in free contact.
And here is the reason for the lack of pressure - the oil has coked and settled on the petal valves
The reason is overheating.
Why are there 4 pipes? This compressor model has additional oil cooling - tropical version.
Even the winding band burst due to overheating:
Actually, why do you need a refrigerator compressor in a household? After certain manipulations (adding a receiver, filter, oil separator, pressure switch, housing) you can get a compact, and most importantly silent source of compressed air - for operating an airbrush, burner, etc. There are special silent compressors, and since the performance of one compressor from a refrigerator is small, they use them in packs:
Since the compressor has a suction pipe, it can receive vacuum, but that’s a completely different story.
Features of choosing a lubricant
To avoid this kind of trouble, you need to be as careful as possible when choosing lubricants . Much depends on the quality of the oil that will be used in the engine and system - the stability of the drive and its service life. If the oil that is poured for the operation of screw or piston compressors is of high quality, then its operation will be stable and will not bring unexpected surprises.
The oil used for a piston compressor, as for screw types, should first of all be recommended by the manufacturer themselves, since air compressors have high requirements for what you are going to put inside. The first mandatory requirement that must be met is the viscosity of the oil.
This value should be no lower than seven units, since it is involved in the lubrication of many parts and should adhere to them well . Operating temperature is also important, but it depends on the season and the characteristics of the compressor itself. Basically, it will have to be replaced with the change of season. But if you prefer a universal one, then a new one will need to be filled only during maintenance, after a certain time of engine operation.
The user talks about his experience using the compressor and the choice of oil
Examples of oil labeling
- K-19, KS-19 are low-sulfur oils that can be used in medium and high pressure compressors.
- K3-10 – compositions that maintain performance characteristics up to +200 °C.
- K2-24, K3-20, K4-20, K2-220 - such oils can be poured both into compressor engines and into the piston area.
- VB, VB-I, DAG – are designed for use in any type of compressor equipment in which the temperature does not exceed +140 °C. The presence of the letter I in the designation indicates the presence of special additives that increase the performance properties of the lubricant composition.
- VC, VC-I, DAA. They are in demand in permanently installed units with a temperature limit of +160 °C, and in mobile units operated in open space, +220 °C.
- VD, VD-I, DAB. Such oils are poured into powerful air piston compressors with a temperature limit of +220 °C, regardless of the location of operation of the equipment.
Oil change, rules and recommendations
Many manufacturers indicate specific requirements in the operating instructions and give recommendations on what kind of oil is poured into the compressor.
But some nuances are not described in the instructions. It is best to pour a little more than the maximum oil level into a piston compressor, since they do not have a separate lubrication system - it comes by capturing a certain amount of it directly from the crankcase. But a similar system is provided in the design of an oil-free piston compressor. In turn, if replacement is necessary in such a compressor, it is necessary to flush the entire tank. To do this, you need to fill in oil with a very low viscosity level and let the compressor run for about 15 minutes. Then it must be completely removed by slightly tilting the piston head. Do not pour processed products, especially on the ground. It is better to hand it over to a collection point for further processing.
Also, do not mix several types of products. No matter what the condition of the air compressor, even the most worn and old one needs to be filled with good and fresh material. The reason for this increased attention may be the occurrence of an emergency.
Fire is especially dangerous when the compressor is running. Over time, it wears out and loses all its properties; in addition, in most structures it evaporates, its level decreases, and the density of pollution increases. To avoid the consequences of such operation, regularly change the oil in accordance with the recommendations.
Foreign standards, but not alien
The existing range of compressor oils is wide. Its increase is due to the growing demand for compressed air, the development of compressor designs, and tightening requirements for their performance, reliability and energy efficiency.
Compressor oils of various viscosity classes are offered by the main players in the Russian oil industry (compressor oil LUKOIL, ROSNEFT).
As foreign trade liberalized, foreign-made products appeared on the domestic market, manufactured taking into account the latest advances in oil refining technologies (SHELL compressor oil, MOBIL compressor oil).
It is not surprising that today in Russia brands of compressor oil have become widespread, the production of which is regulated by European standards (DIN 51506-2017, ISO 6743-3A).
In DIN 51506-2017, compressor oils are classified into groups depending on the final temperature of the compressed air:
- VB, VB-L – up to 140°C;
- VC, VC-L – up to 160°C;
- VD, VD-L – up to 220°C.
They differ in their aging resistance (VDL compressor oil is especially resistant). “V” means compressor oil, “L” indicates the presence of additives.
Manufacturers, in order for their products to be easily recognizable on the market, give them their own names (SHELL CORENA compressor oil, MOBIL RARUS compressor oil, LUKOIL STABIO compressor oil). If the name contains (or implies, ─ as indicated by the reference to DIN 51506-2017) a combination of the letters VD, VDL (VD-L), VB, VBL (VB-L), VC, VCL (VC-L), present in Brand numbers in most cases indicate the kinematic viscosity of the oil at 40 OC. It is equal to the ISO viscosity grade with relatively small deviations (± 10%).
Examples: compressor oil 32, compressor oil 46, compressor oil 100 (for example, compressor oil VDL 100 or compressor oil VG 100), compressor oil 150.
The brand of compressor oil may contain a direct reference to its ISO viscosity ─ compressor oil ISO 100. Or a more specific example ─ Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 100.
Mannol Compressor Oil
Compressor oils Mannol Compressor Oil ─ one of the products of the company Sudheimer Car Technik-Vertriebs GmbH ─ is represented in Russia by the company BITECH (https://bi-teh.ru/). The German manufacturer produces a wide range of products, including lubricants and oils ─ industrial, motor, and transmission. Including compressor oil brands:
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 46;
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 100;
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 150.
Mineral compressor oil Mannol Compressor Oil based on paraffin oils is used to lubricate piston, screw, and centrifugal air compressors, and Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 46 is also used for pneumatic tools. Its effectiveness is enhanced by the presence of ashless additives.
Mannol Compressor Oil has vital properties for compressors:
- thermal stability;
- oxidation resistance;
- anti-corrosion properties;
- low volatility;
- leaves a minimum of deposits.
All of them help to guarantee stable, reliable operation of the equipment.
Buying compressor oil Mannol Compressor Oil means making the right choice for the correct operation of compressors.
Compressor oil manufactured in northern Germany is distinguished by high quality and compliance with the requirements set by consumers for this type of product.
A few lines below about the requirements, but now we list the main functions of compressor oil.
Compressor oil functions:
lubrication;
lubrication of rubbing surfaces reduces abrasive wear of parts, reduces energy losses caused by friction, ensures the cleanliness of rubbing surfaces, helps prevent scuffing, jamming and other defects fraught with serious breakdowns and rapid wear;
cooling;
removal of excess heat is a necessary condition for the functioning of the compressor;
- corrosion protection;
- sealing gaps;
Having several orders of magnitude less fluidity than air, oil fills gaps, promoting better sealing of cavities.
The piston compressor lubrication system includes a pump, oil filter, thermostat, and oil cooler. Compressor oil for reciprocating compressors lubricates pistons, valves, bearings and crank mechanism. It forms a stable liquid layer between the rubbing surfaces (cylinder liner and piston ring).
Compressor oil for screw compressors lubricates shaft bearings, screws and gears (or just gears), helps reduce the temperature in the compression chamber, and seals the gaps between rotors.
Oil review - brief description of oils from different manufacturers with prices
Compressor oil is a rather specific material, designed specifically for narrow-profile use. Manufacturers strongly recommend using only high-quality, certified product to achieve the best performance of their products. Among the high-quality and inexpensive oils, the following names can be distinguished:
Unlike the ones above, the following oils are more common and can be purchased online from the comfort of your home.