- What is a “pipe in polyurethane foam”?
- Types of pipe insulation
- Comparison table for types of insulation for external installation
- Types of pipes in polyurethane foam
- How to choose polyurethane foam pipes
- How to determine the quality of a pipe in polyurethane foam
- Acceptance of pipes based on thermal insulation quality
- Why may the delivery length of pipes be slightly shorter than ordered?
- Can I use used pipes?
- How to lay PPU pipes
- Methods for laying pipes in polyurethane foam
- Who produces polyurethane foam pipes
- Condition of heating networks in St. Petersburg
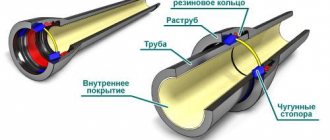
What is a “pipe in polyurethane foam”?
Pipes in polyurethane foam are all pipes for hot water or heating.
They are also called “pre-insulated pipes”, “pipes in polyurethane foam insulation”, “pipes for heating networks”. These are ordinary steel pipes, which are additionally covered with a layer of insulation to reduce heat loss. PPU is an abbreviation that stands for “polyurethane foam”. Pipes without insulation are used only in water supply, gas pipelines or sewerage. The outside of the pipes in polyurethane foam is covered with a black (polyethylene) or gray (galvanized) sheath. And the insulation itself is yellow, with a thickness from 26mm to 90mm depending on the diameter of the steel pipe. Polyurethane foam – yellow. It is very similar to Macroflex foam, but this is not visible in the photographs, because black rubber-bitumen mastic is applied to the end of the insulation so that the foam does not get wet. The ends of the steel pipe stick out from under the insulation to prevent the foam from burning during welding, and they are painted with a primer to protect against corrosion.
At the factory
In the trench
In the context
Why are they needed?
It is clear that for our conditions, heating in the house is the most important component of existence in the winter. But one task is to supply heat to an apartment or house, and a completely different task is to deliver this heat with minimal losses.
PPU pipes insulated
Previously, glass wool was used for these purposes. This is good material, but has its drawbacks. The pipe was wrapped in a layer of thermal insulation. The glass wool was secured with steel wire, and the product was covered with a galvanized steel sheet on top. In the “dashing 90s”, many systems suffered from such insulation. After all, galvanized metal is a valuable material for scrap metal. Therefore, it is increasingly common to use cement mortar instead of such pipeline protection. Nobody needs such material, however, its efficiency is significantly lower than galvanized metal. Therefore, the solution turned out to be relevant - polyurethane foam pipes. In addition, the production of polyurethane foam shells has also begun, which is an excellent thermal insulation material: it performs its functions perfectly and is inexpensive. This is confirmed on the Internet by reviews with photos of those who have had experience installing such a device.
PPU pipe components
Advantages of PPU:
- Installation is very easy, especially when compared with other insulation technologies.
- Heat loss is minimal and does not depend on the level of humidity, as was the case with glass wool.
- Polyurethane foam products with a polyethylene coating can be laid in the ground - no additional insulation is needed.
- Stealing the material is pointless, although the material can be reused if removed correctly.
- Reduces corrosion under a waterproof shell by tens of percent.
Production of polyurethane foam pipes
Thus, polyurethane foam pipes significantly save heat. Due to their technical characteristics, heat loss on factory samples is about two to three percent. And this is confirmed by numerous reviews from those who have used such products.
Types of pipe insulation
Main types of insulation for external installation:
- Pipes in polyurethane foam – in polyurethane foam insulation. Used for heating networks.
- Pipes in VUS insulation. VUS stands for “very enhanced.” Why "very"? Because those who invented this term have little imagination, and also because according to GOST there is a pipe with reinforced insulation (up to 2.5 mm insulation), and there is one with even more reinforced insulation (up to 3.5 mm). Used for water pipes, gas pipelines, and cases. VUS cases are used to protect underground communications. And even heating network pipes in polyurethane foam are sometimes laid under roads inside steel pipes in VUS insulation. VUS insulation – protects the steel pipe from corrosion and mechanical stress. Some network operating organizations allow the use of used pipes in VUS insulation for cases.
- Pipes in PPM insulation – polymer-mineral foam insulation. A relatively new development, very similar to polyurethane foam, but without a shell. Instead of a shell, it has a hard, thin outer layer of polyurethane foam mixed with sand, and is laid directly into the ground without additional protection. A small range of shaped parts due to the complexity of manufacturing (all products are filled with foam in specially made molds) creates limitations for the designer’s imagination and increases labor costs on site. What can be made in polyurethane foam, at the factory has to be done manually on site.
Specifications
| PE d, mm | dy, mm | s, mm | Protective shell pipe | LI, mm | Estimated mass 1 m.p. products, kg | ||
| Dp, mm (PE) | Sp, mm | Sc, mm | PE | ||||
| 32/110 | 25 | 3 | 110 | 2,5 | 0,55 | 150 | 4,1 |
| 38/110 | 32 | 3 | 110 | 2,5 | 0,55 | 150 | 4,1 |
| 45/125 | 40 | 3 | 125 | 2,5 | 0,55 | 150 | 5 |
| 57/125 | 50 | 3 | 125 | 2,5 | 0,55 | 150 | 5,8 |
| 57/140 | 50 | 3 | 140 | 2,5 | 0,55 | 150 | 5,8 |
| 76/140 | 65 | 3 | 140 | 3 | 0,55 | 150 | 7,4 |
| 76/160 | 65 | 3 | 160 | 3 | 0,55 | 150 | 7,4 |
| 89/160 | 80 | 4 | 160 | 3 | 0,6 | 150 | 10,8 |
| 89/180 | 80 | 4 | 180 | 3 | 0,6 | 150 | 10,8 |
| 108/180 | 100 | 4 | 180 | 3 | 0,6 | 150 | 13 |
| 108/200 | 100 | 4 | 200 | 3 | 0,6 | 150 | 13 |
| 133/225 | 125 | 4 | 225 | 3,5 | 0,6 | 150 | 17 |
| 133/250 | 125 | 4 | 250 | 3,5 | 0,6 | 150 | 17 |
| 159/250 | 150 | 4,5 | 250 | 3,9 | 0,7 | 150 | 22,2 |
| 159/280 | 150 | 4,5 | 280 | 3,9 | 0,7 | 150 | 22,2 |
| 219/315 | 200 | 6 | 315 | 4,9 | 0,7 | 150 | 39 |
| 219/355 | 200 | 6 | 355 | 4,9 | 0,7 | 150 | 39 |
| 273/440 | 250 | 6 | 400 | 5,6 | 0,8 | 210 | 58,2 |
| 273/450 | 250 | 6 | 450 | 5,6 | 0,8 | 210 | 58,2 |
| 325/450 | 300 | 6 | 450 | 5,6 | 0,8 | 210 | 69,6 |
| 325/500 | 300 | 6 | 500 | 5,6 | 0,8 | 210 | 69,6 |
| 426/560 | 400 | 7 | 560 | 7 | 1,0 | 210 | 94,1 |
| 426/630 | 400 | 7 | 630 | 7 | 1,0 | 210 | 94,1 |
| 530/710 | 500 | 7 | 710 | 8,9 | 1,0 | 210 | 125,9 |
| 630/800 | 600 | 8 | 800 | 10 | 1,0 | 210 | 150,2 |
| 720/900 | 700 | 8 | 900 | 11,2 | 1,0 | 210 | 193,3 |
| 820/1000 | 800 | 9 | 1000 | 12,4 | 1,0 | 210 | 243,3 |
| 920/1100 | 900 | 10 | 1100 | 13,8 | 1,0 | 210 | 278,1 |
| 1020/1200 | 1000 | 11 | 1200 | 14,9 | 1,0 | 210 | 338,6 |
Comparison table for types of insulation for external installation
| PPU type | PU INSULATION | VUS ISOLATION | PPM INSULATION | MINVATA |
| Max. pipeline temperature | 140 degrees | 60 degrees | 150 degrees | more than 300 degrees |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Reducing heat loss | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Minuses | The maximum pipe temperature is not suitable for steam pipe | Does not reduce heat loss, not suitable for hot water | Small range of shaped products due to the peculiarities of the production process | Impossibility to manufacture pipes and elements in a factory; installation is possible only on site |
| pros | Manufacturing features allow us to minimize labor costs during installation, a “turnkey heating main” and a wetting control system are delivered to the site | Low cost of insulation | Absent, compared to polyurethane foam | Suitable for high temperature pipelines, steam pipelines |
| PU INSULATION | |
| Max. pipeline temperature | 140 degrees |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| PU INSULATION | |
| Max. pipeline temperature | 140 degrees |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| PU INSULATION | |
| Max. pipeline temperature | 140 degrees |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| PU INSULATION | |
| Max. pipeline temperature | 140 degrees |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
| Waterproofing from the environment | Yes |
Purpose of PPU insulation and scope of its application
Scope of application of polyurethane foams:
- Insulation of walls, roofs, window openings, floors in all areas of industrial and civil construction.
- In the manufacture of sandwich panels for the construction of prefabricated buildings.
- In the production of all kinds of refrigeration equipment; stationary refrigerators and cold warehouses, road and railway refrigerators.
- For the manufacture of decorative elements in furniture production, for building decoration parts, lighting equipment.
- For interior trim parts in the automotive industry.
- In carriage building and aircraft manufacturing - as a noise and heat insulating material.
- For insulation of all kinds of pipelines.
- For insulating hard-to-reach places in construction and laying communications.
- For the production of insulated fabrics and synthetic leathers.
- Due to their vibration resistance, rigid polyurethane foam is used in electrical engineering and radio electronics.
- Soft polyurethane foam (foam rubber) is widely used in everyday life - furniture filler, sponges, washcloths, packaging materials.
Types of pipes in polyurethane foam
In a PPU pipe, the metal pipe itself and the polyurethane foam remain unchanged. The wall thickness of steel pipes in heating networks can be from 3mm to 12mm. Foam thickness from 26 mm to 90 mm. The thickness of the polyethylene shell (black) is from 3 mm to 40 mm, galvanized (gray) from 0.55 mm to 1 mm. It all depends on the diameter of the main steel pipe. PPU pipes differ in the type of protective coating. In addition, there is a separate version with a heating cable, which makes it possible to transport liquid in sub-zero ambient temperatures. Pipes in polyurethane foam have special markings, depending on the features:
- PE - polyethylene casing;
- OTs - casing made of galvanized steel;
- PE-U (or PE-B) - the polyethylene shell is reinforced with overhead bandage rings.
- SODC - (operational remote control system) is added after the designation of the casing, which means that two copper wires pass through the insulation (foam), which allow you to connect special devices (megaohmmeter and reflectometer) to the heating main, and find out whether there is water in the insulation and in which one the place got wet, so as not to dig up or open the entire heating main, but to fix the problem locally.
Types of pipes in polyurethane foam
Where are polyurethane foam pipes used?
They are widely used for the arrangement of heating systems for centralized and local heat supply, as well as cold and hot water supply systems. The demand is due to improved performance characteristics. Compared to other similar products, they have the following advantages:
- High thermal insulation properties. The thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam used as insulation does not exceed 0.030 W/m*K. This is the lowest figure among all materials that can be used for pipeline insulation. Therefore, heat loss is reduced to 1-2%. For comparison, in old pipelines heat loss reaches 25-30%.
NB: In old heating networks, reinforced foam concrete was used as insulation, and roofing felt was used as a gyroprotective coating. A metal mesh was laid on top and plastered.
- Durability. The insulation layer and outer casing eliminate the impact of environmental factors on the metal. That is, they provide anti-corrosion protection and protection against mechanical damage, due to which the service life of the products reaches 30 years or more;
NB: The shell of the pipe in polyurethane foam, when laid externally (on the ground), protects the foam from rain, snow, hail, and when laid underground, from groundwater and stray currents, which, if they reach the body of the steel pipe, will cause electrocorrosion. The thickness of the polyethylene shell is many times thicker than galvanized shell, because it also takes on the pressure of the soil. In addition to all the listed misfortunes, the pipe in the ground does not lie motionless, but constantly moves due to the linear thermal expansion of the metal, and over time it wriggles like a snake. The polyethylene shell protects the thermal insulation layer from all of the above.
- Remote diagnostics. The presence of a UEC system makes it possible to detect defects in a timely manner and, thereby, prevent the occurrence of serious emergency situations;
NB: SODK is a system for operational remote control. It consists of two copper wires that are located in the middle of the heat-insulating layer of the pipe in the polyurethane foam. If water gets into the insulation, the contact between the wire and the body of the steel pipe closes. When you connect a megohmmeter, the device will show a short circuit and it will become clear that there is water insulation in this section of the pipeline. In order to more accurately determine the location of wetting, a pulse reflectometer is used. This device measures the wave resistance of polyurethane foam. Using it, you can create a reflectogram of a heating network with a length of more than a thousand meters and determine the location of the defect with an accuracy of less than one meter.
The future of heating networks is as follows: a stationary reflectometer is connected to each heating network, which, using a GPS modem, transmits a signal online to the operator’s console. As soon as the insulation gets wet in any area, the operator’s control light comes on, and he immediately sends the repair team to the track, telling them the specific area of the wetness.
In Russia, in 2022, such systems have already begun to be tested and gradually implemented.
- Quick installation. Channelless installation allows you to reduce the volume of excavation work and do without installing drainage networks. These factors not only reduce installation time, but also reduce the cost of laying the pipeline.
Processes during foaming and mixing PU foam components
When mixing the polyisocyanate and polyol components in the mixing compartment of the casting machine, a fine emulsion is formed. The increase in temperature and increase in viscosity of the mixture is explained by the exothermic reaction occurring in it. When the temperature reaches values greater than 25-28 degrees, intensive foaming of the composition and gas formation begins, which is recorded as the start time when insulating pipes.
Shells for pipes are made by extrusion, but their walls are much thinner than those of conventional pipes, so when pouring foam you must strictly follow the technology
READ ALSO: Rehau pipes or polypropylene pipes, which is better, Petrishin Stroy
The process of gas formation is stabilized by an increase in the viscosity of the polyurethane foam mixture and the presence of an organosilicon foam stabilizer in it. Additional growth of bubbles is also possible due to the reactions of the polyisocyanate and air moisture. Chemical processes lead to the emergence of a polymer structure (three-dimensional). The beginning of its formation is recorded as the gelation time.
Note! After this shaking, mechanical movements, and other influences on the assembly of the structure can cause the polyurethane foam layer of hardening foam to sharply lose quality.
For this purpose, the pipes are kept in thermal insulation on racks. At this time, there are many unreacted groups in the polymer matrix. Further polymerization is characterized by the time the surface of the polyurethane foam loses its stickiness and the time it takes to fill the space between the shell and the pipe. After a few hours, the chemical processes are completed, and after a few days, the mechanical relaxation processes are completed.
How to choose polyurethane foam pipes
The choice of one or another variety depends on the operating conditions. For example, products in a polyethylene sheath (PE) are intended for the installation of an underground pipeline. Where the pipeline runs under a railway, highway, foundation, or in places of increased soil mobility, it is necessary to use pipes with reinforced insulation (PE-U). Laying of above-ground pipelines is carried out using pipes with a galvanized steel casing (OC). Such a shell not only provides protection from climatic factors and mechanical stress, but also gives the main system additional rigidity.
Equally important is the choice of diameter. In main heating mains and water supply systems, pipes with a diameter of 525 to 1020 mm are used. For urban distribution networks, the diameter should not exceed 525 mm. When constructing an autonomous heating and water supply system in private households, a diameter of 50-100 mm is sufficient.
Note! PU foam pipes can be used in heating networks where the temperature of the working fluid will not be higher than 140 degrees and the pressure will not be 16 bar. A short-term temperature jump of 10 degrees is allowed. At the same time, contrary to common sense and the laws of physics, GOST 30732-2006 for pipes and shaped elements in polyurethane foam does not establish a relationship between diameter and pressure, therefore any pipes in polyurethane foam can be used in the specified pressure range.
Polyurethane foam as a material
The PPU PE pipe has a polyurethane foam layer as a heat-insulating material. It is characterized by a low thermal conductivity coefficient (at the level of 19-28 mW/m*K). In general, for pipes (St, PE), polyurethane foam is an infusible thermoactive plastic with a cellular structure.
About 97% of its volume is occupied by pores and cavities filled with gas with very low thermal conductivity (the proportion of closed pores is from 90 to 95 percent). The remaining 3% of the volume of polyurethane foam is a solid material that forms a frame of walls, ribs, and gives it mechanical strength.
Polyurethane foam is a two-component system. It consists of:
- polyol component containing catalysts, polyols, stabilizers, blowing agent;
- isocyanate component containing PMDI (polymer diphenylmethane diisocyanate).
This material is one of the most effective heat insulators used in modern construction of oil, heating, gas pipelines, floors, floors, walls, enclosing structures, etc.
Note! Polyurethane foam is characterized by a significant density range: 40-200 kg/m3. This allows the use of polyurethane foam as thermal insulation for floors.
Polyurethane foam is a dense material that significantly reduces heat loss
Casting rigid polyurethane foam is a foam material. It is obtained in the form of blocks in accordance with the dimensions of injection molds. The shrinkage tolerance value is 4 cm.
How to determine the quality of a pipe in polyurethane foam
The quality of the pipe in polyurethane foam is determined according to several GOSTs, GOST 30732-2006 (for insulation) and GOST for the steel pipe itself.
First of all, it is necessary to determine the compliance of the steel pipe with the manufacturer’s certificate. Pipes above diameter 159 must be marked. In the case of pipes of diameter 159 and below, in the absence of markings, a “tag” from the pipe bundle, or “label,” must be attached to the set of documentation. Sample:
Tag sample
It is imperative to check the data from the “tag” and the quality certificate, and also make sure that the length of the pipe whip corresponds to the length stated in the quality certificate.
Since quality acceptance can occur when insulation has already been applied to the pipes in polyurethane foam and the marking can be hidden under it, it is necessary to carry out inspection before applying the insulation, come to inspect the steel pipe, and if this is not possible, for example, when supplied from another region , ask in advance to send a certificate, tag and photographs of the steel pipe with markings.
Also, steel pipes used in heating networks should not be older than a year from the date of manufacture. GOST 30732-2006 does not have this requirement, but this is an unspoken rule in heating networks, since metal warehouses store pipes in the open air, and they cannot lie like that for more than a year - they have time to rust badly.
Standard for PPU insulation for pipelines
PPU insulation can be carried out simultaneously with pipe production, and can also be installed during pipeline laying. For each case, a special technology is used. Separately manufactured shell pipes are made from grades of polyethylene PE-80 and higher. They are subject to GOST 18599 standards. The surface layer of the coating is black and has a light stabilization characteristic of 2-2.5% soot.
Polyurethane foam insulation is produced in two ways:
- pouring using the “pipe in pipe” method;
- production of shells according to finished sizes.
It is more economical to fill it with polyurethane foam in production. If additional insulation of the system is needed during installation, then the method of installing shells is used. Polyurethane foam has high thermal insulation and protective characteristics. Rigid or elastic varieties are used.
Acceptance of pipes based on thermal insulation quality
GOST 30732-2006 contains a huge number of parameters that need to be controlled, including, the manufacturer of polyurethane foam is required to attach an acceptance test report for each batch of products supplied to them, but the main attention should be paid to the following:
Thermal insulation end: The foam must be dense. If you can stick a knife into it more than 40 - 50 mm without effort, you should think about more accurate methods of controlling this batch or demand to provide an acceptance test report.
At the end, where the thermal insulation adjoins the steel pipe and the shell, there should be no gaps or cracks, otherwise water will get there and the insulation will be damaged.
The end must be covered with waterproofing material, and the free end of the pipe must be painted with a primer. The free end of the steel pipe must have a chamfer at an angle of 30 degrees. The waterproof shell should not have deep scratches or cracks.
If, during a visual inspection, the pipe does not perfectly coincide circumferentially with the shell, it is necessary to check the deviation of the axial lines with a tape measure. Usually this problem is not immediately visible, but when cutting the pipe on site.
Any product in PPU must have a marking indicating:
- product designation;
- trademark or name of the manufacturer;
- batch number;
- date of manufacture.
Marking on products in polyurethane foam
If the pipe in polyurethane foam is made with SODK, it is necessary to check the conductors for breaks and short circuits using a megohmmeter. After checking, it is necessary to make an appropriate entry in the work log.
Not all aspects of pipe quality control in polyurethane foam are listed here, but only the main ones; you can fully accept polyurethane foam insulation only after fully familiarizing yourself with GOST 30732-2006.
Useful tips from the pros
When choosing a company that produces polyurethane foam insulation, pay attention to trusted organizations such as Anta.
A reputable company has the necessary work experience. Also offers a variety of modern thermal insulation coatings, such as galvanized casings.
We can highlight a number of indicators that allow us to call a company truly worthy of attention. So, it is extremely important that the organization has the following factors:
- extensive work experience;
- quality assurance;
- free consultation with specialists;
- no hidden costs;
- execution of the contract;
- use of high quality equipment.
Why may the delivery length of pipes be slightly shorter or longer than ordered?
When issuing an invoice, the theoretical length of the pipe is taken. At metal warehouses, pipes are stored in bundles, and it is not possible to keep track of which pipe is on top and which is on the bottom. After paying the invoice, at the time of loading the steel pipe at the metal depot, the customer is informed how many strands of pipe and what length were loaded for it and clarifies: should the footage be rounded down or up?
When ordering a seamless pipe, everything is even more complicated; according to GOST 8732-78 and GOST 8734-78 it is unmeasured, that is, each rod has an individual length. GOST allows a difference from 4m to 12m. In reality, the difference in a particular batch is smaller, for example, from 9m to 11m. In some cases, when ordering a standard size, the insulation plant may cut it to size and keep the rest of the pipe, but such cases are always agreed upon in advance (before paying the invoice).
Can I use used pipes?
In laying heating networks, used pipes are practically not used. Only as VUS cases, when new pipes in polyurethane foam are laid inside a used large-diameter pipe. In this case, the used pipe only performs the function of additional protection and the requirements for it are, accordingly, much lower.
The laying of heating networks is strictly regulated by state standards; it is almost impossible to use used pipes without damage. The pipe through which water flowed, even for a relatively short time, is no longer suitable for reuse due to corrosion. The pipes through which oil flowed become so saturated with it that, again, they become unsuitable for heating networks where water flows through the pipes. Only gas pipes after sandblasting look almost like new and are generally similar in their characteristics to new pipes that have been lying in the open air at a metal warehouse for a couple of years. But in any case, it is more profitable for pipe factories to take used pipes for scrap and cast new pipes than to try to sell used products.
The polyurethane foam shell after the cycle “production – delivery – laying – operation – digging – delivery back” becomes unusable. It would never occur to anyone to reuse such pipes in a real heating network, since the insignificant savings pale in comparison to the cost of operation that increases tenfold when the insulation begins to deteriorate and become wet.
How to lay PPU pipes
Laying in a trench is carried out on a flat sand cushion with a thickness of at least 100 mm. Pipes and other pipeline elements are first checked for defects. To eliminate the risk of damage to the containment, the pipes must be lowered smoothly, without hitting the bottom and walls of the trench. At the next stage, the joints are welded and the cables of the UEC system are connected. After checking the quality of the weld with a flaw detector, the joints are sealed using heat-shrinkable sleeves.
Important information! Work on insulating joints should be carried out at an air temperature of at least -15 degrees.
In the case of laying a pipeline through a foundation or wall, seals and wall entry collars are used. The standard length of the oil seal is 450mm, but any length can be manufactured. After their installation, concreting is carried out.
When laying a channel, a drainage pipe must be laid next to the heating main, which drains water from the heating network, and collects it in a reinforced concrete well, and a flap valve according to the A-397-80 series is installed at the outlet of the drainage pipe.
If underground installation is not possible (for example, in a wetland), the above-ground method is used. It involves installing pipes on special supports. The technology for connecting joints remains the same.
Pipes are delivered by scow. A scow is a machine 12m or 13.6m long. The machine must be capable of top loading; the pipes are loaded with a crane.
Production of polyurethane foam
The process of manufacturing the substance is mechanical (on an industrial scale, on expensive equipment, certain components of the oil industry are mixed). Currently, there are three known methods for producing polyurethane foam:
- casting;
- extrusion;
- pressing.
Using a press, various structures are made from rigid polyurethane, and from elastic polyurethane, finished products are formed by pouring into special molds.
Methods for laying pipes in polyurethane foam
Ductless pipe laying
Channel pipe laying
Initially, all heating networks were laid without ducts, but then wise people came up with the idea of additionally insulating the pipe in polyurethane foam with reinforced concrete channels (trays). The channels perform the function of additional waterproofing, and also take on the load of the soil in places where heating networks pass under roads, where, in addition to the soil, passing traffic puts pressure on the pipe. For channelless installation in such places, VUS insulated cases are used.
The main problem lies in the method of compensating for the linear expansion of the steel pipe. As mentioned above, the pipe in the ground does not lie motionless, but is constantly moving and bending. When laying without channels, compensation for pipeline expansions is carried out naturally; the route is not laid in a straight line, but makes many turning angles, and it, like an “accordion,” compensates for itself. Soft mats are placed under the turning angles so that the bends have somewhere to “play”. In the case of channelless installation, pipes are laid almost in a straight line, which is definitely a plus, because it is not always possible to design many turns, for example, neighboring underground communications may interfere.
To compensate for linear temperature expansion during channel installation, SKU - bellows compensators are used
Inside the SKU in the PPU there is a KSO - an axial bellows compensator, which is an “accordion” made of stainless steel, which has the ability to compensate for compression and decompression. This device is placed between two fixed supports, and the pipes are mounted on sliding supports (they are called SPOk - Sliding Channel Supports), on concrete pads installed on the bottom of the channel. The bottom of the channel in the places where the pillows are installed is coated with technical petroleum jelly.
Bellows compensator
What do we end up with? Hot water is supplied to the heating main, the pipe expands, “rides” on lubricated cushions along the line of the route, the “accordion” contracts and compensates for the expansion, the pipe does not bend. As the temperature drops, the pipe contracts, the “accordion” expands, and the pipe on the cushions “rides” back along the axis of the route.
Condition of heating networks in St. Petersburg
The heating network system of St. Petersburg is one of the most extensive in Russia. The total length of the pipelines exceeds 4770 km, and the diameter of the pipes varies from 50 to 1400 mm. Heating mains are mostly laid underground. Unfortunately, a significant part of them are in emergency or pre-emergency condition, since these are still Soviet pipes 30 years old. Therefore, the installation of new energy-efficient heating networks is more important than ever for the city.
The information in the article is current as of 06/01/2021.