Water and gas pipes are widely popular when laying various communications in the field of housing and communal services. Where are VGP pipes mainly used? What distinctive qualities are they characterized by? What assortment is produced by manufacturers? The answers follow.
HSV pipes
The relevance of using pipes of this category
The high popularity enjoyed by VGP pipes made from steel alloys can be explained very simply. No matter how exceptional the characteristics of today's popular pipes made of polymeric materials may be, their use in many cases is simply not possible. Such cases, in particular, include installation of a pipeline in the open air, where it will be affected by a lot of negative factors.
The demand for such products is also explained by the fact that, according to generally accepted requirements, pipelines for transporting gas and supplying it to consumers can only be made of steel pipes. That is why VGP pipes are simply an irreplaceable material in any gas industry.
Gas supply to a private home is a typical example of using VGP pipes
This is interesting: How to attach an anchor bolt: video, photos, nuances, tips
Briefly about VGP
All that remains is to clarify the very concept of a VGP pipe: what it is, and how the product differs from other steel pipes. In principle, a water and gas pipe is a special case, one of the widely used varieties, of electric-welded metal, produced in accordance with GOST 3262 standards. Its main difference from its “brothers” is the reinforced seam, a feature that allows it to withstand greater pressure than other materials. In addition, the VGP pipe is distinguished by increased anti-corrosion qualities, which is also an important factor in the technical operating conditions.
Measurement systems
The table shows the sizes of different types of pipes. Data shown in millimeters and inches.
Steel pipes are not losing ground and are still the main material for laying gas and water mains.
In this work, pipe diameters indicated in inches are used. With this approach, there are no difficulties during pipeline installation.
What do you know about the sizes of plumbing hatches for the bathroom and toilet? Which ones are installed on the wall and which ones are installed on the floor under the tiles is written in a useful article.
A heating diagram with a solid fuel boiler and a heat accumulator is published here.
But when replacing or installing a combined system , situations arise that require matching the sizes of products made from different materials, for example, with fiberglass-reinforced polypropylene pipes (read GOST here).
In such cases, tables of steel pipe sizes come to the aid of designers.
The standard shows the exact metric size of steel products and compliance with polymer pipes.
The standard range of diameters used in most countries (mm): 6, 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 100, 110, 125, 200 and so on.
Dimensions in inches are also used when designing. When translating, take into account that one inch is 2.54 centimeters.
Large-sized products are used when laying sewer lines (the depth of laying pipes in a private house is indicated on this page).
Steel grades and tolerances
The classification given above is quite incomplete. It can be continued almost endlessly. Such a huge range is due to the large number of applications for steel pipes.
Among other classifications, there is another one - by diameter. Naturally, thinner or thicker pipes are used for different purposes. Today, the industry produces steel products with a diameter from 17 to 114 mm. In this case, the following indicators are considered normal error:
- For products with diameters from 17 mm to 48 mm, the normal error (tolerance) can be considered 0.4-0.5 mm;
- For materials with diameters from 60 to 114 mm, the normal error is considered to be 0.8-1% of the diameter.
On the wall this figure is 15%.
Water and gas pipes of various diameters
It must also be said that these tolerances are typical only for the following grades of steel:
- 0.8ps and 0.8kp;
- 10;
- 15, 15ps, 15kp;
- 20, 20ps, 20kp;
- St1ps;
- St2ps;
- St3ps and St3kp.
Dimensions
Water and gas pipes are manufactured in accordance with GOST, which sets clear requirements for their sizes and basic characteristics:
- the wall thickness should be 2.5-4.5 mm, the permissible deviation is minimal and only on the condition that it does not reduce the reliability of the product and the quality of the product;
- the conventionally accepted DU for steel VGP pipes is 6-150 mm, while with a length of more than 20 mm, a deviation from the established standard of 2 mm is allowed; if the length is less, then the deviation should not exceed 2 mm;
- the outer diameter of the water and gas pipe can be from 10 to 165 m, the total number of standard sizes is 14, and the basic classification of products is carried out precisely on this basis;
- the length of the pipes varies from 4 to 12 meters, while for each linear meter a two-millimeter curvature of the pipe is allowed;
- Pipe threads must be applied with a aligned cylindrical or knurled end.
This is interesting: Stainless steel marking: subtleties of stainless steel designation
Directory of rolled metal products
There are two types of water and gas pipes - black water and gas pipes and galvanized water and gas pipes. Their main difference is the presence/absence of a galvanized coating, thanks to which the water and gas pipe acquires amazing anti-corrosion properties and becomes more resistant to aggressive external factors. Practice shows that non-galvanized pipes are lighter than galvanized pipes by an average of 3 percent.
Possessing high strength, excellent performance characteristics and a relatively simple manufacturing procedure, water-gas pipes are widely used today not only in construction for heating distribution and supplying household gas, but also in mechanical engineering, aircraft manufacturing, the automotive industry, the agricultural industry, and in the construction of various types of metal structures.
As a rule, water and gas pipes are used together with such additional products as bends, tees, valves, bends, transitions, barrels, plugs and other pipeline fittings.
Depending on the length, the water-gas pipe can be of measured length or unmeasured in the range from 4 to 12 meters. If we are talking about measuring pipes, then an allowance of 5 millimeters is allowed for each cut and a longitudinal deviation over the entire length of about 10 millimeters. In the case of unmeasured pipes, subject to an agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to have up to 5 percent of pipes in one batch, the length of which ranges from 1.5 to 4 meters.
The accuracy criterion also affects the classification of water and gas pipes. And here there are two types of pipes:
Water and gas pipes of standard precision (manufactured from steels that comply with GOST 1050 and GOST 380).
High precision water and gas pipes (made from steel that complies with GOST 1050).
Products of the first group are in most cases used for the construction of gas pipelines, water pipelines and heating systems. The latter find their application in the production of parts for gas and water supply structures.
This is interesting: Slings
The letters after the word “pipe” in the symbol deserve special attention.
Thus, a water-gas pipe with a length of thread is designated by the letter “D”, a water-gas pipe going under thread rolling is marked by the letter “N”, and the letter “P” placed after the size of the nominal bore indicates a pipe with increased manufacturing precision.
When producing water and gas pipes, small deviations in weight (maximum 8 percent) and curvature are allowed. At the request of the consumer, maximum mass deviations for a batch should not exceed 7.5 percent, and for an individual pipe - 10 percent. If we talk about curvature, then it does not go beyond 2 millimeters per meter of pipe length (if there is a nominal bore up to 20 millimeters inclusive) and beyond 1.5 millimeters if the nominal bore exceeds 20 millimeters.
| Name | Diam. mm. (int.) | Thickness Art. mm. | Length mm. | Unit change | Weight 1m, kg |
| Water and gas pipe | 15 | 2,5 | 6000-8500 | tn. | 1,16 |
| Water and gas pipe | 15 | 2,8 | 6000-8500 | tn. | 1,28 |
| Water and gas pipe | 20 | 2,5 | 6000-8500 | tn. | 1,5 |
| Water and gas pipe | 20 | 2,8 | 6000-8500 | tn. | 1,66 |
| Water and gas pipe | 25 | 2,5 | 6000-8500 | tn. | 1,39 |
| Water and gas pipe | 25 | 2,8 | 10000 | tn. | 2,12 |
| Water and gas pipe | 25 | 3,2 | 10000 | tn. | 2,39 |
| Water and gas pipe | 32 | 2,8 | 10000 | tn. | 2,73 |
| Water and gas pipe | 32 | 3,2 | 10000 | tn. | 3,09 |
| Water and gas pipe | 40 | 3 | 10000 | tn. | 3,38 |
| Water and gas pipe | 40 | 3,5 | 10000 | tn. | 3,84 |
| Water and gas pipe | 50 | 3 | 10000 | tn. | 4,22 |
| Water and gas pipe | 50 | 3,5 | 10000 | tn. | 4,88 |
| Water and gas pipe | 65 | 4 | 6000 | tn. | 7,05 |
| Water and gas pipe | 80 | 4 | 6000 | tn. | 8,34 |
| Water and gas pipe | 100 | 4 | 10000 | tn. | 10,65 |
| Water and gas pipe | 100 | 4,5 | 10000 | tn. | 12,15 |
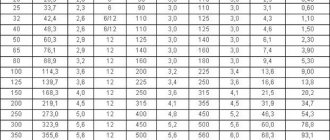
Parameters of water and gas pipes (GOST 3262-75)
| DU Symbol. | Outer diameter, mm | Lungs | Regular | Reinforced | ||||||
| Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1m, kg | Meters per ton | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1m, kg | Meters per ton | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1m, kg | Meters per ton | ||
| 6 | 10,2 | 1,8 | 0,37 | 2681,8 | 2,0 | 0,40 | 2472,5 | 2,5 | 0,47 | 2106,4 |
| 8 | 13,5 | 2,0 | 0,57 | 1763,0 | 2,2 | 0,61 | 1631,1 | 2,8 | 0,74 | 1353,4 |
| 10 | 17,0 | 2,0 | 0,74 | 1351,6 | 2,8 | 0,98 | 1019,8 | 2,8 | 0,98 | 1019,8 |
| 15 | 21,3 | 2,5 | 1,16 | 862,7 | 2,8 | 1,28 | 782,8 | 3,2 | 1,43 | 700,1 |
| 20 | 26,8 | 2,5 | 1,50 | 667,5 | 2,8 | 1,66 | 603,4 | 3,2 | 1,86 | 536,9 |
| 25 | 33,5 | 2,8 | 2,12 | 471,7 | 3,2 | 2,39 | 418,2 | 4,0 | 2,91 | 343,6 |
| 32 | 42,3 | 2,8 | 2,73 | 366,6 | 3,2 | 3,09 | 324,1 | 4,0 | 3,78 | 264,7 |
| 40 | 48,0 | 3,0 | 3,33 | 300,4 | 3,5 | 3,84 | 260,3 | 4,0 | 4,34 | 230,4 |
| 50 | 60,0 | 3,0 | 4,22 | 237,1 | 3,5 | 4,88 | 205,1 | 4,5 | 6,16 | 162,4 |
| 65 | 75,5 | 3,2 | 5,71 | 175,3 | 4,0 | 7,05 | 141,8 | 4,5 | 7,88 | 126,9 |
| 80 | 88,5 | 3,5 | 7,34 | 136,3 | 4,0 | 8,34 | 120,0 | 4,5 | 9,32 | 107,3 |
| 90 | 101,3 | 3,5 | 8,44 | 118,5 | 4,0 | 9,60 | 104,2 | 4,5 | 10,74 | 93,1 |
| 100 | 114,0 | 4,0 | 10,85 | 92,2 | 4,5 | 12,15 | 82,3 | 5,0 | 13,44 | 74,4 |
| 125 | 140,0 | 4,0 | 13,42 | 74,5 | 4,5 | 15,04 | 66,5 | 5,5 | 18,24 | 54,8 |
| 150 | 165,0 | 4,0 | 15,88 | 63,0 | 4,5 | 17,81 | 56,1 | 5,5 | 21,63 | 46,2 |
Water and gas pipes are widely used in the installation of water supply, gas and heating systems in residential buildings. Galvanized water and gas pipes are used for installation in aggressive and humid environments, as well as for the manufacture of various structures, machines and mechanisms.
In fact, this type of pipe has become the basis for the work of not only the entire gas service, but also the entire public utility sector. Without them, today it is impossible to put into operation either residential or industrial facilities. All pipes have a specified service life, after which they are replaced with new ones as planned. This is due to the peculiarity and enormous importance of the media transported through them for the life support of residential areas.
Any damage to the integrity of the pipe can lead to a leak of natural gas, hot or cold water. Of course, these accidents differ from each other in terms of the level of danger, but the way to prevent them is the same: timely replacement of water and gas pipes with new ones.
At the same time, old dismantled pipes often do not have any external damage, and their level of wear allows for further use in less critical areas of the national economy. For example, in agriculture for the construction of irrigation systems, or in the manufacture of various landscape structures, gazebos, benches and fences.
Water and gas pipes are made from metal blanks, called strips, by special molding and further welding of the seam. For this purpose, ordinary carbon steel is used without further heat treatment. All water and gas pipes are manufactured using electric welding and mandatory quality control of the weld. It is the seam, as a source of increased danger to the integrity of the entire pipeline, that receives increased attention. To do this, an X-ray examination of its surface is carried out.
Water and gas pipes vary in size. In construction and public utilities, almost the entire range of products of this name is used at the same time. By the way, prices for pipes are based on their weight, or rather per ton.
The dimensions of water and gas pipes are determined by the nominal diameter, expressed in millimeters or inches. In this case, the external size of the pipe remains unchanged, and only the size of the nominal diameter and the wall thickness of the product change. The length of finished products can range from four to twelve meters. In this case we are talking about the measured length. If the pipes have a length from 1.5 meters to 11.5 meters, then we are talking about an unmeasured length. In addition, pipes can have a length that is a multiple of the measured length with a seam allowance of 5 mm. All this allows you to select pipes in accordance with the intended further use. It is more convenient to use ready-made pipes without cutting them specially.
All products are manufactured in accordance with GOST. For ease of installation, cylindrical threads are applied to both ends of the pipe. The pipes are connected using special couplings or welding.
Our country not only produces water and gas pipes in quantities sufficient for domestic consumption, but also supplies them to the foreign market. When choosing such pipes, you should know that a galvanized water pipe weighs three percent more than a black pipe of the same diameter.
In the production of water and gas pipes, a distinction is made between products of normal precision and products with an increased level of precision. In the first case, we are talking about the installation of water supply or heating systems, and in the second case, about the use of pipes in the manufacture of various structures. When marking finished products, the letter “P” must be added, which means increased accuracy of the pipe diameter. These pipes also differ in wall thickness. Accordingly, there are products with a thin wall, called light, or with a thick wall, called reinforced pipes.
Some technical requirements
All steel water and gas supply materials are manufactured according to technical standards and have GOST 3262-75, as noted earlier. Production is carried out from types of steel (GOST 380 and GOST 1050) without standardization of the chemical composition and all mechanical qualities.
If necessary, the ends of the pipes can be chamfered at an angle of 40 degrees at the manufacturer's factory. With this type of work, an end ring is left, the width of which lies in the range from 1 to 3 mm.
It must be said that chamfers are removed from products whose wall thickness is more than 5 mm.
In addition, at the customer's request, threads can be applied to both ends. The condition is a conditional passage, which should not be less than 1 cm.
Among other things, individual water and gas supply elements can be equipped with couplings (GOST 8944,8954,8965 or 8966). In this case, each water and gas steel pipe must be equipped with one coupling.
The surface of the products must not have cracks, blisters or dents. There should be no delamination, chips or burrs at the ends.
The following defects are allowed:
- Risks;
- Individual dents;
- Traces of stripping;
- A layer of scale that does not interfere with inspection;
- Some manufacturing defects, but only if they do not reduce the wall thickness to the minimum value in some places.
Below is a table of correspondence of some parameters of water and gas products.
table of correspondence
| Outer diameter, mm | Conditional passage, cm | Wall thickness, mm | ||
| ordinary | lungs | reinforced | ||
| 17 | 1 | 2.2 | 2 | — |
| 21.3 | 1.5 | — | 2.35 | — |
| 21.3 | 1.5 | — | 2.5 | — |
| 26.8 | 2 | — | 2.35 | — |
| 26.8 | 2 | 2.8 | 2.5 | — |
| 33.5 | 2.5 | — | 2.8 | — |
| 42.3 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 2.8 | — |
| 48 | 4 | — | 3 | — |
| 60 | 5 | 3.5 | 3 | — |
| 75.5 | 6.5 | 4 | 3.2 | 4.5 |
| 88.5 | 8 | 4 | 3.5 | 4.5 |
| 101.3 | 9 | 4 | 3.5 | 4.5 |
| 114 | 10 | 4.5 | 4 | 5 |
TEST METHODS
4.1. For quality control, one sample is cut from each selected pipe for each type of test.
The tensile test is carried out in accordance with GOST 10006. Instead of the tensile test, it is allowed to control the mechanical properties by non-destructive methods.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 6).
4.2. The surface of the pipes is inspected visually.
4.3. Hydraulic testing is carried out in accordance with GOST 3845 with exposure to test pressure for at least 5 s.
4.4. The bend test is carried out according to GOST 3728. Galvanized pipes are tested before coating.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.4a. The expansion test is carried out according to GOST 8694 on a conical mandrel with a cone angle of 6°.
Testing on a mandrel with a taper angle of 30° is allowed.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4).
4.4b. The flattening test is carried out according to GOST 8695.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3).
4.4v. Weld inspection is carried out using non-destructive methods according to regulatory and technical documentation.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
4.5. The thickness of the zinc coating on the outer surface and in accessible places on the inner surface is controlled according to GOST 9.301 and GOST 9.302, as well as with devices of the MT-41NTs, MTZON or Impulse type according to the normative and technical documentation.
4.6. The thread is checked using thread ring gauges in accordance with GOST 2533 (third accuracy class).
In this case, the screw-in of the no-go ring gauge onto the thread should be no more than three turns.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4).
4.7. The curvature of the pipes is controlled using a straight edge in accordance with GOST 8026 and a set of probes in accordance with NTD.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 5).
4.8. The right angle of the pipe ends is controlled with a 90° square measuring 160´100 mm, class 3 GOST 3749, plate probes set 4 according to NTD or an inclinometer GOST 5378. The bevel angle of the chamfer is controlled with an inclinometer according to GOST 5378.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 6).
4.9. The outer diameter is checked using smooth micrometers in accordance with GOST 6507, clamp gauges in accordance with GOST 2216 or GOST 18360.
The wall thickness, the height of the internal burr and the height of the burrs are measured with a micrometer according to GOST 6507 or a wall gauge according to GOST 11358 at both ends of the pipe.
The length of the pipes is measured with a tape measure in accordance with GOST 7502. The threads are controlled with gauges in accordance with GOST 2533.
The mass of a batch of pipes is controlled on scales of no more than 10 tons with a division value of no more than 20 kg.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 3, 4, 5, 6).
4.10. Weld inspection is carried out using non-destructive methods according to technical documentation.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 4).
What to look for when choosing pipes
For the end user, who needs such steel pipes to solve specific problems, certain operational characteristics of these products are of interest, allowing them to be selected optimally.
In order to make the right choice of such pipes and use them in accordance with their main purpose, it is important to understand the classification of products. The criteria by which such classification is carried out are stipulated by the provisions of GOST 3262-75.
Important criteria for sorting pipes of the VGP category are the material and method of their manufacture, as well as the method of their processing. So, depending on these parameters, pipes are distinguished:
- made of ferrous metal, the surface of which is not protected in any way;
- pipes whose surface is galvanized.
Tubular products, on the inner and outer surface of which a thin layer of zinc is applied, even differ in appearance from ordinary ones, as can be seen by comparing their photos. Such surface treatment of pipe products is necessary in order to reliably protect them from the aggressive influence of the external environment. Pipes coated with a thin layer of zinc, due to the chemical properties of this metal, perfectly resist corrosion and can be successfully operated even in the most difficult conditions for a long period of time.
Important parameters of such pipes, regardless of whether they are galvanized or not, are their geometric dimensions: nominal diameter, which is denoted by the abbreviation DU, as well as their wall thickness.
All geometric parameters of pipes of the VGP category, including their diameter, must comply with the requirements specified in GOST. All geometric dimensions of pipes produced by modern industry can be selected using the appropriate tables.
From the production line, water and gas pipe products can be produced in two modifications:
- without thread;
- with ready-made threads on both ends, which are applied by rolling or cutting.
Decoding the numbers in the designation allows you to find out the exact diameter of the product. Thus, products for which their DU is designated by the number 50 (VGP pipe DU50) have a diameter equal to two inches. And for pipes of the VGP category, the designation of which includes DU25, the diameter is equal to one inch. Accordingly, the markings of water and gas pipes indicate their diameter in millimeters, and converting it into inches is not difficult.
Certification
The product quality certificate is a guarantee for the purchased product. Products must comply with established quality standards; GOST of VGP pipes is very important when choosing a quality product.
- A quality certificate is issued to products that have been subject to research and passed laboratory tests.
- The certificate specifies the galvanizing method; it can be done hot or cold.
- The product can also be subjected to sanitary and hygienic tests, after which the VGP pipe receives a hygienic certificate.
A product that has all the necessary certificates is in greater demand than a non-certified product.
Scope of application
The primary purpose of VGP pipes is to transport water (both hot and cold) and household gas to the end consumer. When installing a network of water and gas steel pipes, either welding, threaded adapters, or other additional parts and segments are used for connection. Most often, these products are present in household communications. A huge percentage of modern and private housing constructions and high-rises built in the past are equipped with VGP steel pipes for consumers to receive gas, heat and water.
In addition to their direct purpose, pipes are widely used for the construction of metal structures of various types and sizes: shelving and cabinets, scaffolding, fences and small architectural forms. But this is already a separate area of their application, into which we will not delve too deeply.
For gas pipeline
Installation features
When installing VGP metal products, specialists use the following methods:
- The pipeline is connected with couplings on special machines. This method is used only on ordinary pipes.
- The connection is made by electric welding.
To summarize, let's say that although polymer products are widely used today, water and gas pipes are not replaceable, and continue to be used everywhere, especially in the housing and communal services sector.
Water and gas pipes produced by Severstal Distribution
Extra options
For the convenience of those who are going to purchase water and gas pipes and use them for certain purposes, the length of such products is also standardized and may correspond to one of the following categories:
- interval 4–12 meters - measured length;
- length of pipes, a multiple of their measured value;
- unmeasured length, which, nevertheless, must be within the limits of the measured value.
Consumers of such products should keep in mind that the price is set not per unit of pipe length, but per unit of its weight. It is also important to take into account that the weight of galvanized pipes is 3% higher than the weight of products made from unprotected steel.
Steels from which high-precision galvanized and non-galvanized pipe products are produced must comply with the requirements of GOST 1050, while the chemical composition and mechanical characteristics of the manufacturing material are not subject to standardization. The welds with which water and gas pipe products are connected after they are formed must be of a reinforced type.
Mechanical properties of rolled products used for pipe production
The range of water and gas pipe products made of black steel involves their production with several options for wall thickness. Depending on this parameter, such products are:
- light class;
- ordinary category;
- reinforced type.
The wall thickness of such products, which can be selected according to the assortment according to the table, is standardized by the requirements of GOST 3262-75. Based on this regulatory document, a range of pipe products is formed; it also stipulates a number of other parameters that such products must comply with: nominal diameter, outer diameter, theoretical weight of one linear meter.
Dimensions of light series pipes intended for thread rolling
Pipes of various classes are designed for operation under different operating pressures. Thus, pipes corresponding to the light category can be operated at a pressure not exceeding 25 kgf/cm2, and reinforced type products - 32 kgf/cm2.
At the request of the customer of a batch of water and gas pipes, long or short threads can be applied to their ends. Galvanized pipe products can be supplied to customers not only with threads, but also equipped with couplings for their installation.
Thread Requirements
Kinds
The main types of VGP pipes, their weight and dimensions are indicated in the current GOST 3262-75.
In accordance with the standards, the entire range of pipes is conventionally divided into two types depending on the method of their manufacture:
- galvanized;
- non-galvanized (black).
Galvanized ones have the highest performance characteristics:
- do not corrode;
- are characterized by high strength and strength;
- show resistance to mechanical damage;
- when transporting liquid inside galvanized pipes, deposits form 10 times slower than in non-galvanized products;
- have an aesthetic appearance.
The disadvantages include:
- high cost - galvanized pipes are much more expensive than non-galvanized ones;
- in case of deformation, the galvanized layer is destroyed first;
- When moving cold water, condensation often forms;
- For smooth operation and stable use, an uninterrupted water supply is required.
This is interesting: Copper ore - copper mining, refining, deposits
The advantages of non-galvanized pipes include:
- high strength and resistance to mechanical damage;
- the ability to transport liquid and gaseous media under high pressure;
- vibration resistance:
- the possibility of steel deformation under the influence of high temperatures is completely eliminated;
- low cost compared to galvanized models.
Not without its drawbacks:
- susceptibility to corrosion;
- the occurrence of condensation during transportation of cold liquid;
- low throughput;
- the need for constant coloring and maintaining appearance;
- The service life of such models is much lower than galvanized ones.
In addition to this classification basis, in the production of rolled pipes, indicators such as nominal bore and wall thickness are also taken into account and varied - all these parameters must necessarily comply with GOST.
Depending on the resistance to hydraulic pressure, HSVs are divided into:
- light – used in conditions where the pressure does not exceed 25 kg/cm2;
- conventional - the pressure is at the same level of 25 kg/m2, but periodic hydraulic shocks are possible;
- reinforced - withstand pressure up to 32 kg/cm2; upon individual requests, pipes with a maximum pressure of 50 kg/cm2 can be produced.
Based on the type of readiness, the following are distinguished:
- pipes with threaded ends (cut or knurled);
- ordinary - without thread.
According to the accuracy class, several typical modifications of VGP are also distinguished.
- The first group includes standard precision products. In the production of such pipes, the chemical composition and mechanical characteristics are not standardized in any way. The products have found application in the arrangement of water and gas utilities for domestic purposes.
- The second category includes high-precision products, which also includes galvanized pipes.
In the manufacture of these varieties, VGP strictly follows the requirements for the composition of the material and the mechanical characteristics of the finished products. Pipelines for industrial use are made from such pipes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The water and gas pipe is characterized by high strength and good wear resistance.
The rigidity indicators of such products are equal to the quality characteristics of solid metal timber with similar diameter parameters.
The use of VGP pipes is in demand when constructing not only main lines, but also household pipelines, for example, when replacing polypropylene water supply pipes reinforced with fiberglass (the characteristics are written here), where gas or water is used as the working medium.
The main advantages of water and gas pipelines are presented:
- low coefficient of linear expansion, which prevents deformation of the structure under the influence of high temperatures and as a result of freezing of the working environment;
- high strength compared to polypropylene and other materials, as well as the possibility of use in creating pressure-type structures;
- good thermal conductivity , which has a positive effect on the long-term preservation of temperature indicators of the transported working medium (read reviews about a hot water meter with a temperature sensor on this page);
- tightness , allowing the delivery of gaseous and volatile substances, as well as acids and other chemically active components.
It is important to remember that high thermal conductivity can cause cooling of the transported working medium, therefore the use of VGP pipelines with the additional use of thermal insulation materials is considered optimal.
What do you know about the design and repair of a water ball valve? Read this useful article for instructions on how to disassemble and restore the tightness of shut-off valves for water supply inside buildings.
Watch a video on how to make a heat accumulator for heating boilers with your own hands on this page.
Manufacturing technology
Galvanized and non-galvanized pipes are made of carbon steel, according to the strict requirements of GOST 1050. They are produced on automated lines, so the products are of high quality.
There are two manufacturing methods:
- seamless - by rolling or pressing;
- with a seam - a seam is made using electric welding.
Seamless types - there is no seam on them. They are made in two ways - cold or hot. Hot-deformed models are obtained from a solid billet by hot deformation.
Cold-formed ones are produced using the following methods:
- cold roller method;
- by pulling.
All cold-rolled models are subjected to hydraulic testing, chemical and heat treatment. They have increased strength, reliability, and durability compared to types produced using the hot method.
The production technology for welded types is as follows:
- preparation of steel blanks (strips) - long metal strips manufactured in accordance with GOST, using the hot rolling method;
- bending steel strips into pipes using specialized equipment;
- electric welding of the resulting joint.
For welded water and gas models, the seam must be reinforced, since this is the most fragile place. Therefore, it must be examined by radiography.