Knitting wire GOST 3282-74 is a round low-carbon steel wire for general purpose, intended for tying, fencing and other purposes. The production of knitting wire is a priority direction of our company.
To produce knitting wire, we have mastered the annealing of low-carbon, heat-untreated steel wire GOST 3282-74, which allows us to supply it in a wide range. Heat-treated knitting wire GOST 3282-74 has the designation O.
Types and main sizes
Steel wire is divided into two types: with and without zinc coating. This coating is zinc. Also, steel wire is subject to heat treatment and not. After heat treatment, the product turns out to be light and black in color. The thickness of such steel wire ranges from 0.16 mm to 10 mm.
The size range of zinc-coated products ranges from 0.2 mm to 6 mm. The coating itself is divided into two classes: first class and second class. The difference between one class and another is only in the thickness of the coating. All products of the second class have a more dense zinc coating, and therefore thicker. Products of the second class are more durable.
Flexible cable cross-section measurement
For a multi-wire flexible cable, its own method of measuring cross-section is used. This method consists of the following points:
- wrap one vein from the bunch around a pencil;
- measure the length of all turns;
- divide the length by the number of turns and multiply the result by the total number of wires.
The method is quite simple and understandable, so absolutely everyone can use it. To take measurements correctly, you need to perform all actions as carefully as possible.
This procedure is not difficult for professional electricians, but it will not be so easy for beginners to cope with this task. In such a responsible process, the main thing is to do everything carefully and then you can get the most accurate result.
Technical requirements
This wire is made from low-carbon steel grades. All properties comply with GOST provisions. In accordance with this standard, each batch of steel wire must meet the following technical requirements:
- it may or may not be heat-treated;
- the surface of the wire can be coated or uncoated;
- it should not have cracks or scale;
- the presence of scale is allowed only in heat-treated products;
- must comply with the established list of diameters;
- Deviations from the established range of diameters are allowed, but no more than those specified in the standard. For example, for a wire with a diameter of 1.2 mm, the permissible deviation is 0.03 mm, for a wire with a diameter of 3.5 mm, the deviation does not exceed 0.08 mm.
- any sample of thermally untreated wire with a diameter from 0.5 mm to 6 mm inclusive must withstand more than four bending tests;
- the coating is zinc;
- in this case, there should be no uncoated areas on the surface;
- the surface density of the coating must comply with established standards;
- winding is carried out in even layers without entangling and twisting into coils or skeins;
- the weight of a packaging unit must correspond to the accepted GOST (they can range from 500 kg, but not more than 1500 kg).
Wire not heat treated
The given technical requirements are strictly observed by the manufacturer.
Why does the discrepancy occur?
Despite the fact that in the conditions of modern competition, manufacturers are doing their best not to lose their customers, some of them resort to deception. To do this, they save metal by reducing the diameter. It is enough to remove just a couple of square millimeters, and over hundreds of kilometers of cable this will pay off with a significant reduction in cost.
And then the price will be reduced for the buyer, and they themselves will be satisfied. But the consumer ultimately puts himself at risk due to the fact that the conductor resistance is much lower than stated. And in the place where such a wire is laid, there is a risk of fire.
Surface density of zinc coating
In accordance with established standards, such a parameter as the surface density of zinc coating is measured in g/m2. This indicator depends on the diameter of the product and its class. For example, with a product thickness from 0.2 mm to 0.32 mm of the first class, the coating density is 10 g/m2. With a diameter of 6 mm, the density is already 85 g/m2. For products of the second class, zinc coating starts with a diameter of 0.63 mm. For this sample the density is 405 g/m2. More detailed permissible surface density standards are given in the corresponding tables.
What is a cable?
A cable is a long wire, inside of which there are several wires that interact with each other. Several metal cores are required in order to increase the power of the cable. If there are not enough cores, then during voltage surges in the network, this wire will overheat greatly and may burn out.
If you need to determine the cable cross-section, it is enough to pay attention to just one parameter - its diameter. How exactly to use it to carry out the necessary calculations and which tools are suitable for this is worth considering in more detail.
Acceptance rules
There are requirements for accepted products that allow you to monitor their quality. The list of these requirements includes the following provisions:
- wire is accepted in batches;
- each batch must include a product with the same technical characteristics (class, diameter, processing method, type of coating);
- each batch is documented;
- the document includes the following information: name of the product, manufacturer’s details, marking in accordance with GOST, test results;
- weight and size characteristics.
According to the established procedure, the quality of the surface coating is checked on each reel or skein. Checking the diameter and tolerances is carried out selectively on 5% of the finished product. Only three percent of the entire batch is tested for mechanical properties.
Mechanical characteristics of wire
If the results obtained are unsatisfactory, a repeat sample is taken and the tests are repeated again.
The final results are considered acceptable for the entire batch.
Conclusion
You can quickly determine the cable cross-section by diameter. In order to visualize this parameter, a person can use one of several available methods. The main thing when performing the measurement process is to carry out all actions carefully and accurately. To quickly calculate the required indicator, you can use a special table that contains all the data. If a person does not use a table, then he will be able to perform all the calculations using a special formula.
Whatever method a person chooses, all actions should be carried out carefully and carefully. Anyone can take measurements of this nature, taking into account the advice given by professional electricians. Measurements can be taken using special instruments or a regular ruler.
You can measure the cross-section of a cable in just a couple of minutes, finding out whether it can be used for a specific purpose. When choosing a cable, you should always remember this. That the markings on them do not always correspond to reality. That is why it is worth checking the necessary parameters yourself in order to know what quality products are being used. Having calculated the required parameter, a person can verify the quality of the cable and use it to replace the wiring. The main thing is to carry out all the measurements correctly and then the wire used will be as safe as possible for home use; there will be virtually no risk of any short circuits or other troubles.
Test methods
The following methods have been developed for checking the quality of manufactured products:
- weight;
- volumetric gasometric;
- dives.
Their reliability is based on the sampling method of the general theory of statistics. Therefore, as experience shows, it is sufficient to sample one sample from each given batch.
The first method involves visual inspection and weighing. Visual inspection allows you to determine the condition of the selected sample, determine the diameter and depth of detected defects. These parameters are usually measured using appropriate measuring instruments. The diameter and degree of ovality of the steel wire are measured in two planes using a micrometer. Then the obtained data is checked against GOST 6507-78. A prerequisite for such measurements for galvanized wire is the absence of excessive sagging.
Wire quality control
Based on this method, the mass of zinc located on the surface of the sample is determined by calculating the difference in the mass of the sample with zinc and the mass of the sample with the coating removed. Next, the arithmetic mean is calculated using a well-known formula. The error of such estimates, when thoroughly tested, does not exceed 0.001 g.
Next, they begin to evaluate the sample according to the following indicators: bending, stretching, and tearing. If the diameter of the selected sample does not exceed 0.5 mm, it is possible to replace the conventional test with the size of the gap with a formed knot.
Download GOST 3282-74
After this, a test is carried out for the so-called winding. Wind the steel wire onto a rod of the same diameter as the wire itself. If the diameter exceeds 6 mm, then the diameter of the rod should be twice the diameter of the sample. Then the weight characteristics are measured.
It is used in resolving controversial situations and for conducting arbitration analyses.
Volumetric gasometric method.
In preparation for research, the entire zinc coating of the sample is removed down to the steel surface. For this purpose, it is immersed in a special solution.
The final result is calculated as the arithmetic average of several test results.
Heat-treated steel wire
The order in which this method is implemented is determined by the following sequence of operations:
- from the presented sample, several pieces of wire of the same length are selected (the difference in length should not exceed 0.5 mm);
- each section is thoroughly degreased (degreasing solutions can be: alcohol, gasoline or other suitable chemical solutions);
- then, using the chemical properties of zinc, they dissolve it (they try to catch all the hydrogen released);
- in laboratory conditions, the volume of hydrogen produced is measured;
- using a well-known formula, the surface density of zinc is calculated;
- In sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, the so-called zinc stripping is performed.
Immersion method
In this method, the selected sample is immersed in a solution of copper sulfate. The density of the solution should be 1.116 g/cm3. At a temperature of 18 °C.
In this case, the following order is followed to obtain the results:
- prepare several test steel bars of the same length (usually 150 mm);
- carry out degreasing with washing with distilled water;
- each steel sample is thoroughly wiped from traces of liquid and dried;
- then dipped into the prepared solution (it contains copper sulfate);
- the distance from the location of the bars to the surface of the solution should be 100 mm, immersion time - 60 seconds;
- six steel samples are tested simultaneously;
After the test, the remaining copper coating on the surface of the bars is checked. If there are areas with remnants of copper coating on the surface of at least one steel bar, the sample did not pass the test. The assessment is made visually.
Determining cable cross-section using a ruler
It is possible to measure the cable cross-section by using a simple ruler. This is a very old method of taking measurements, but it is no less effective than carrying out the same actions using special instruments. To take a measurement using a regular ruler, follow these instructions:
- carefully strip the core of insulation;
- tightly screw the core onto a regular pencil;
- measure the total length of the winding using a ruler;
- divide the winding length by the total number of cores present in the cable.
When winding a core around a pencil, you need to make sure that you get at least 15 turns. The coils should be pressed very tightly against each other, so that there is no free space between them. It is necessary to take measurements not just once, but several times in order for the result to be as accurate as possible.
It is important! This method is only suitable for determining the diameter of thin wires. If the cable is thick, it will be very difficult to wind it, which will not allow you to do everything efficiently and take accurate measurements.
Packaging, labeling, transportation and storage
After producing steel wire and checking its quality, it is necessary to solve important logistical problems. They can be successfully resolved only with strict adherence to established standards for packaging, labeling, storage, and transportation.
The following requirements apply to the packaging of such a specific steel product:
- finished products are packaged in coils, skeins, coils;
- to give strength, each skein is tied with the same steel wire (attachment points must be distributed along the length);
- all packaging units are carefully wound, the ends are brought out in such a way that they are accessible for unwinding;
- coils of thin steel wire (for example, 0.8 mm and thinner) are tied with steel wire of the same diameter;
- the end of the wire should be brought up on the reel and have a fastening loop;
- if a whole batch of skeins of the same name is being prepared for shipment, they are combined and tied into coils;
- Preservation of shipped steel products is carried out only at the request of the customer.
Wire packing
As required by the standard, finished products can be packaged and preserved as follows:
- coils of 0.5mm wire wound ready for transportation must be wrapped in special paper and placed in boxes;
- skeins with larger diameter wire, in addition to the paper layer, are wrapped in polymer film;
- in addition to polymer film, the standard allows the use of non-woven materials;
- coils of thick wire with a total weight of 500 kg to 1.5 tons are not packaged.
Based on established standards, it is allowed to use the following as packaging material for wire:
- paraffin-impregnated thick paper (in one or two layers);
- various types of film;
- certain types of nonwoven materials (for example, the so-called container stitched canvas, in several layers, impregnated with a special composition);
- special types of fabric: chemical fibers, synthetic fabrics, packaging fabrics;
- It is allowed to use various types of technical tapes for tying and fastening.
Preparing wire for transportation
Finished and packaged steel wire can be sent to the consumer by any type of transport: rail, road, water. When sending a finished order, special attention is paid to the length of the transport arm and the geographic location of the customer. If transportation involves moving a finished order several thousand kilometers, to areas with a cold and humid climate, then, with the approval of the customer, the sender can additionally take measures to protect against corrosion on the road. The main limitation when transporting such cargo is the limit on the weight of a single shipment. It should not exceed 1.5 tons. The consumer can reduce this norm to a value convenient for him, for example, 100 kg.
When moving the ordered steel wire by covered transport, the weight limit of the cargo package is 1250 kg. Transportation by rail can be carried out: in wagons, gondola cars, on open platforms, special and universal containers. In all cases, there are procedures and rules for securing such cargo on railway transport. These rules are established by order of the Ministry of Railways.
Before shipping, markings are applied to the finished items. As required by the standard, it must include the following information:
- information signs;
- transport markings;
- special manipulation signs;
- If necessary, additional inscriptions can be applied.
Marking of finished products
This information is printed on a label and attached to each reel, regardless of its size or weight. Typically, this label is made in a typographical way and has columns for the following information: trademark or company logo, symbol of the product type, main characteristics. The label contains a stamp from the technical control service. It confirms the compliance of shipped products with standards. Manipulative signs are applied to this label. They indicate what actions are allowed to be performed with this cargo
The storage of such products, made of low-carbon steel, does not require special conditions. These conditions are determined by the manufacturer and the consumer himself.
Advice from professional electricians
Experienced electricians already know how to determine the cable cross-section correctly even by eye. For those who do not understand this matter very well or are taking measurements for the first time, professionals are ready to give some useful tips. And so, experts advise people who want to take cross-section measurements to follow these rules:
- you need to pay attention to the quality of the metal from which the core is made (the aluminum or copper core must have a rich color, otherwise a low-quality metal alloy was used, and this can be dangerous for use);
- the section should be performed exclusively along the core, because the insulating material should not be taken into account;
- If you doubt the size of the conductor, you need to take a thicker cable, since then there is definitely a guarantee that it will withstand a certain load.
Using these tips, everyone can independently deal with electrical cables and calculate the required value.
Areas of application of steel wire
The use of the steel wire in question is widespread in many industries: industry, construction, agriculture. In particular, it is used:
- for the production of a wide range of hardware products (nails, self-tapping screws, fastening brackets)
- production of various shapes of fencing;
- steel wires for power transmission systems, communications;
- bundling wires and attaching them to insulators;
- in printing for stitching finished products;
- production of steel mesh for various purposes;
- in winemaking for the production of steel muzzles;
- at construction sites and house-building factories for reinforcing reinforced concrete structures;
- wire steel fiber, which allows you to eliminate cracks in concrete structures.
The most popular range of knitting wire
Of the variety of products produced, the most popular is the following range of tying wire:
- For the construction industry, products with a diameter of 1.2 mm and 1.4 mm. With its help, a bundle of the most common steel reinforcement 8 and 12 mm is produced.
- In printing, steel wire of 0.3 and 0.5 mm is used.
- For electrical networks, a diameter of 3 to 5 mm is used.
In each specific case, the required diameter and length of the steel wire is calculated.
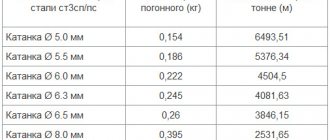
Calculation of section parameters using a table
Having made the necessary measurements, you can determine the cable cross-section using the indicators in a special table. By measuring the thickness of the core diameter using a special table, you can determine the cross-section.
The cable cross-section calculation table is as follows:
Thanks to this table, you can find out the necessary information very quickly and without unnecessary problems. The table shows the cross-sectional area of different cables and allows you to significantly simplify the calculation process, because some novice electricians, using only a formula, find it difficult to determine this indicator.