Copper pipes are used in the installation of hot water supply, hot water supply, air conditioning, heating, and gas supply systems. They are expensive, but durable, flexible, and resistant to corrosion. But in order for engineering communications from them to last for decades, the connection of copper pipes must be done correctly.
We will tell you how to install copper pipelines that ensure the tightness of the transported medium or circulating coolant. The article presented for review describes installation technologies in detail. Taking into account our advice, the construction of the systems will be completed perfectly.
Copper pipe soldering process
The time needed to solder copper pipes will be helped by markings on the fitting itself with recommendations for the required solder size.
Before soldering begins, the outer part of the pipe end and the inner fitting are sanded to bare metal. Next, a thin layer of solder paste or flux is applied to the cleaned end of the pipe. These materials, in a molten state, dissolve oxide films on the elements being connected, protecting their surfaces from further oxidation, which is caused by high temperatures.
However, given the fact that flux destroys the surface of the metal, when soldering with your own hands, it must be applied just before starting work and only on the area that will go into the fitting. After hardening, the flux forms a film that does not require removal.
Next, the pipe is inserted into the socket of the capillary fitting until it stops. Places are heated evenly with the flame of a gas burner or a hot air gun. For this purpose, it is advisable to use a lamp equipped with two burners or nozzles with sprayers.
If the flux used contains tin, then when it is heated to the required temperature, silvery drops will appear. In other cases, you can make sure that the desired temperature has been achieved by touching the solder to the heated surface - the solder should spread. The molten solder must be injected into the joint immediately. Moreover, it does not matter at all from which side it will be introduced. Thanks to capillary action, the solder will evenly fill the entire joint. Remains of flux from the fitting are removed using a rag.
The use of a variety of fittings in which the manufacturer has applied a bead of solder of the required size inside will help reduce soldering time. The fitting is placed on a pipe coated with flux and heated with a torch or hot air gun until the solder becomes liquid. After cooling, the water supply and heating pipeline structure is ready for operation.
Assembling a pipeline using fittings
Copper pipes are connected using fittings only in places accessible for inspection. This rule is due to the fact that the connection is not completely sealed and leaks may form over time.
The advantage of a threaded connection is that, if necessary, repairs can be made without additional effort, since the resulting connection is detachable.
Tools and materials
To assemble the pipeline, you will need the following materials and tools:
- copper pipes of suitable diameter;
- connecting crimp or press fittings;
Special devices for pipeline assembly
The types and number of fittings are selected in accordance with the pipeline diagram.
- pipe cutter or hacksaw for metal;
- pipe bender for copper pipes. The device is used to organize a pipeline with fewer connections, which increases the strength of the system;
- file for processing pipes after cutting (before joining). Additionally, you can use fine sandpaper;
- FUM tape for sealing threads. In addition to FUM tape, you can also use linen thread, Tangit Unilok thread or any other sealing material;
- wrench.
Assembly instructions
Assembling a copper pipeline with your own hands using fittings is done in the following way:
- cutting pipes for pipelines. The length of each pipe must fully comply with the diagram drawn up during the development of the system;
- removal of the insulating layer. If pipes with insulation are used for a pipeline system being installed for any purpose, then the insulating layer is removed for a durable connection. To do this, cut the desired area with a knife and clean the pipe;
- The cut edge is processed with a file and sandpaper until a smooth surface is obtained. If burrs, potholes or other irregularities remain at the end of the pipe, the connection will be less tight;
Cleaning the pipe before connecting to the fitting
- if necessary, pipes are bent;
- a union nut and a ferrule are put on the prepared pipe;
Installation of fitting elements for connection
- the pipe is connected to the fitting. Initially, tightening is done by hand and then with a wrench. During the tightening process, the crimp ring completely seals the connection, eliminating the need to use additional sealants. However, when connecting a copper pipe to a pipe or fitting made of a different material, additional sealing with FUM tape is required.
Fixing the fitting
It is important not to overtighten the threads, as soft copper is easily deformed.
Varieties
Fittings of different sizes and shapes (carbon, arc, tees, plugs, couplings) are available to consumers. Thanks to such a wide range, any potential buyer can find components that meet all requirements. The method of fastening is one of the factors influencing the type of fitting. Connectors come in several types.
Capillary
Capillary (solder) fittings are used to fix metal pipes. The connection occurs as follows: a copper pipe is inserted into the fitting sleeve, then the remaining space is filled with flux and solder. After this, they are melted with a special torch (soldering iron), ensuring the reliability of all the formed connections. Then wait for the pipe to cool and thoroughly clean its surface.
Compression
They are usually called crimp or collet, since their installation requires a special crimp ring. No soldering is used for installation. They have an undeniable advantage: these products can be used in places where the installation of other types of fastenings is impossible (for example, due to a high fire hazard).
Crimping parts are used not only for household work, but also when installing communications on the street, even for transporting toxic chemical compounds. They are easy to install, provide a high-quality, tight connection, but periodically all joints need to be checked and tightened. For this reason, pipelines using push-in fittings cannot be sewn into floors and walls.
Crimping models are produced in the following two versions:
- press;
- with fixing rings.
Press fittings
Such products are designed for permanent connection; they are used in cases where soldering is not possible. They are used extremely rarely for copper pipes. To install them, you need to use a special tool - a press machine. The connection with press fittings is durable and impenetrable. Installation does not take much time.
Press fittings can be used to connect pipes in thick walls. The connection with these elements is more durable (compared to a compression fitting), but due to the need to use special equipment, it is more financially expensive. Press fittings are used, as a rule, in mass construction.
Press fittings are:
- triple;
- bypass;
- straight;
- transitional - for connecting pipes with different diameters;
- corner.
Self-locking
Self-locking fittings are a new product on the market today. These elements are mechanical devices with a system of internal rings, where one of them has small teeth. When pressing on the ring with a special key, these teeth fix the structure. This type of connection is considered very reliable and durable; a self-locking fitting can be used several times. They are removed as easily as they are installed - by pressing the key.
Threaded
Threaded models are the most commonly used copper pipe fasteners because they can be easily replaced or reused if necessary.
Because of this distinctive feature, an important requirement is put forward to the joint: free access to the joint so that nothing interferes with repair or dismantling work. Fittings of this type have external or internal cylindrical threads
The process of connecting with threaded fittings is quite simple. The fitting is screwed onto the pipe, observing the requirement for complete tightness of the joint. This requires special materials: fum tape, thread, rubber or polymer gasket.
The connection with a threaded fitting is reliable and durable, the main thing is to carry out all installation work correctly, and we must not forget about the sealing material. Typically, threaded fittings are used in residential buildings and cottages, garden farms and private buildings, where it is not always convenient to weld. Based on external characteristics, threaded fittings are divided into the following types:
- couplings;
- squares;
- nipples;
- plugs;
- bends.
Sealed joining of copper pipes without soldering
Additionally, it is worth noting that, despite the fact that connecting pipes by soldering is considered the most reliable method in most cases, there are still situations when it is not possible to use this method. In such cases, you can resort to connecting copper tubes without soldering. Special fittings will be required that will ensure a reliable connection due to the clamping effect that is formed by the threaded connection.
In this case, the connection is made in the following sequence:
- First, the fittings are disconnected, which often have two components.
- One of the elements is put on the pipe. As a rule, this is a nut and a clamping ring.
- Next, thread the pipe into the fitting and tighten the nut.
It is worth noting that before connecting copper tubes without soldering, you should be aware of all the risks, since it is quite difficult to obtain a high-quality connection. Minimal distortions of the connected parts are not allowed at all, otherwise the technology is grossly violated. To make the threaded connection extremely tight, it is advisable to additionally seal it with special threads. At the same time, it is worth making sure that they do not end up on the inside of the pipe, since subsequently water may not pass through the system properly.
How to choose?
In order to properly install the system, it is necessary to take into account the features of threaded fittings. You must focus on the purpose of the pipes; if you use high-quality materials and carefully follow all the rules, you are guaranteed a high-quality connection for many years. Find out what the sizes and purposes of fittings are, use this when designing.
Selection of fittings
If you need to rotate the structure, you will need corners; if you plan to branch, be sure to purchase tees, crosses, and manifolds. If you just need to connect two pieces of pipe (of the same diameter or of different diameters), stock up on couplings, and, of course, don’t forget to buy plugs.
Pipe connections made of various materials
How is a steel pipe connected to a copper pipe? For this, a fitting is used, at one end of which there is a thread for fixing to a steel pipe. There are no threads on the other end; it is completely smooth, since the copper pipe will be attached by soldering.
When installing a pipe into such a fitting, the threads should be wrapped with plastic sealing tape, after which the coupling is screwed onto the pipe. Such a sealing tape is necessary to prevent corrosion from starting in the area where two types of metal are joined.
Steel and plastic fitting
Another example is a fitting made of steel and plastic. It is also made of two parts. The first part looks like a nut with a threaded segment that screws into a steel pipe. The other part is plastic, with a gasket and nut also made of plastic.
Standard fitting consisting of steel and plastic parts
The nut is screwed onto another extension of the first part, which has an external thread. Next, a special solvent is used to attach the plastic insert to the plastic pipe.
Plastic and copper fitting
There is also a popular fitting made of plastic and copper, which also includes two components. The first component has two ends. One is made of copper and has a thread, but the other end is completely smooth - it is this that is attached to the copper pipe by soldering.
Plastic fitting with copper thread
The other component is a plastic nut with a spacer. The nut is screwed onto the copper thread, and its other end is glued to the plastic pipe.
Main conditions for carrying out welding work
Before carrying out important work, it is recommended to become familiar with the following points:
- It is undesirable to use the lead version in the manufacture of water supply, because it is a material that has very high toxicity.
- A suitable water supply flow should not be more than 2 m/s. Otherwise, solid impurities will begin to show up poorly on the functioning of the structure.
- During the installation process, the use of flux is a priority; in the final step, the entire system is cleaned first. Otherwise, corrosion forms on the copper walls.
- There should be no overheating at the connecting points of the structure. In another case, the strength of the system is lost, as is the impermeability at the joints.
- It is supposed to perform soldering using other metals, connecting a copper pipe with a brass or bronze fitting first, otherwise the pipe will lose its own strength.
- If irregularities or burrs appear during pipe cutting, they must be smoothed out before soldering. This is due to a decrease in operating time, the occurrence and increase in the area of deformation.
- The use of abrasive compounds is absolutely prohibited. Residual particles lead to iron defects or fistula formation.
When in contact with other substances during work using additional types of material, the water flow must be directed from them to the copper structure. If this rule is violated, chemical reactions occur. pipeline reaction.
Fig 2. Water direction
The metal is highly flexible, making it easily subject to deformation during the cutting process.
Capillary soldering method
Before you begin laying the water supply, you need to cut the copper pipes to the required sizes.
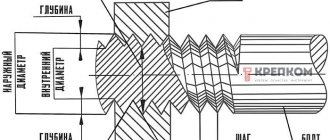
This method is based on the capillary effect, which promotes uniform distribution of solder throughout the entire cross-section, regardless of the position of the pipe. To create a capillary effect, special fittings are used, the diameters of which must differ from the diameters of the pipe by a strictly defined value. For soldering over an open fire, a gap of 0.1-0.15 mm is recommended.
Connections using capillary soldering are carried out using special fluxes and solders - thin wires made of metal alloys with a low melting point, usually tin with small additions of copper and silver. Soldered joints are used in cases where water supply is carried out with one’s own hands in the floor or walls, or in other cases when visual control of the integrity of the joints is impossible.
There are two soldering methods: high temperature and low temperature.
High-temperature soldering, otherwise known as hard soldering, is used where the operating conditions of copper pipelines involve high temperatures. Such soldering is carried out using special fluxes and hard solders. For do-it-yourself pipeline installation, this type of soldering is practically not used.
Low-temperature, or soft, soldering is used for pipelines used for transporting liquid and gaseous media, the operating temperature of which does not exceed 110ºC. When doing low-temperature soldering with your own hands, the joints are heated to a temperature of approximately 300ºC.
Why is it better to crimp (crimp) wires?
Wire crimping is one of the most reliable and high-quality mechanical connection methods currently used.
Using this technology, cables and wires are crimped into a connecting sleeve using clamping pliers, ensuring tight contact along the entire length. The sleeve is a hollow pipe and can be made independently.
For hoses up to 120 mm², mechanical grippers are used. For large sections, products with a hydraulic hammer are used. In the compressed state, the bushing usually has the shape of a hexagon; sometimes a local recess is made in some sections of the pipe. When crimping, electric copper bushings GM and aluminum tubes GA are used. This method allows you to crimp wires made of different metals.
This is largely facilitated by the treatment of the constituent components with a lubricant based on quartz petroleum jelly, which prevents subsequent oxidation. Combined aluminum-copper hoses or GAM and GML tinned copper hoses are available for joint use.
The crimp connection is used for cable bundles with a total cross-sectional diameter between 10 mm² and 3 cm².
Communications made of copper pipes and fittings
High-quality copper pipes and fittings, the technical and operational characteristics of which comply with international standards ISO 9002, BS2 and DIN, are today produced by both foreign and domestic companies. Such pipes, as well as connecting elements for them, successfully withstand the high pressure of the media transported through them, high and low temperatures, and mechanical stress to which they may be subjected during operation, transportation and storage.
Unlike polymer pipes that are popular nowadays, copper pipe products do not deteriorate from exposure to sunlight; they are not afraid of corrosion, which is a real scourge for products made from ferrous metals. The service life of copper pipes and fittings cannot be compared with any similar product made from another material. It is noteworthy that copper products are practically eternal; the service life of communications from them is at least 100 years.
Heating and water supply system made of copper pipes in a private house
Pipe products, as well as fittings made of copper, are used for arranging utility networks for various purposes:
- heating systems;
- air conditioning;
- cold and hot water supply;
- gas communications.
Those consumers who decide to use copper pipe products and copper fittings primarily use them to build reliable and durable water supply networks. Fittings made from copper are more compact in size and look much neater than products made from ferrous metals. This is explained by the fact that when designing and manufacturing copper fittings, there is no need to make their walls thicker, taking into account their further corrosion, since they are simply not susceptible to it.
DIY installation of copper pipes in the heating system
There are several reasons explaining the high popularity of pipes and connecting elements for them made of copper:
- copper, as is known, has antiseptic properties, therefore, pathogenic microorganisms do not develop in water pipes made from this metal, and the quality of the water transported through them even improves;
- installation of pipelines for which pipes and fittings made of copper are used is much simpler than communications made of black pipes;
- due to the high ductility of copper, pipes made of this metal, when water freezes in them, do not burst, but simply deform; in order to destroy a copper pipe, it is necessary to apply an internal pressure of 200 atm to it, and such pressures simply do not exist in household communications.
What nuances exist?
To organize the creation of a pipeline system, pipes made of durable plastic are used. Stainless steel belongs to the expensive price segment, but reliability covers this nuance. For major repairs, a copper pipe can be a full-fledged alternative.
Such a system favorably tolerates sudden temperature changes and is not afraid of large amounts of chlorine or ultraviolet radiation. To avoid the development of corrosion, special devices are installed inside. If there are no compositions of heavy metals and other substances in the liquid, then nothing will prevent such pipes from serving for even a dozen years.
Among the significant disadvantages are the following aspects:
- Softness.
- High price.
The last drawback is considered completely justified due to the long service life.
Applications of copper pipes
Installation of copper pipes in heating systems is possible due to their high resistance when working with high-temperature liquids. This property is especially relevant for a single-pipe heating scheme, in which to ensure the coolant temperature in the last radiator is about 70ºC, it is necessary that in the first it is equal to approximately 120ºC
Connecting pipes with compression fittings does not provide an absolute guarantee of reliability and requires constant monitoring during operation.
The maximum temperature that polymers used in heating systems can withstand does not exceed 95ºC, and media with temperatures up to 300ºC can be transported through copper pipes. An important property of a pipeline made of this metal is its ability to withstand pressure of 200-400 atm, while the soldered connection of copper pipes, made by hand, remains sealed. At the same time, metal-plastic products can withstand, on average, a pressure of 6 atm with a possible operating pressure in the system of 6 - 8 atm. Heating pipes made of soft copper can easily withstand 3-4 freeze-thaw cycles.
Thanks to its antibacterial properties, copper can resist the infiltration of contaminants in urban water supplies. Plumbing copper is resistant to chlorine. Moreover, chlorine, being a strong oxidizing agent, promotes the formation of a protective oxide film on copper, which extends the service life of the pipeline. However, it should be remembered that hidden laying of copper pipes with your own hands can only be done if there is a polymer shell on the pipes, which protects the copper from stray currents.
Copper pipes are universal: in addition to water supply and heating systems, they are used to transfer gases and refrigerants in refrigeration systems, and are used in air conditioning systems.
Connecting pipes using soldering
Let's consider connecting copper tubes with fittings followed by soldering, which can be low- and high-temperature. In the first method, soldering is carried out at a temperature of 300 ºC. The second method is used when installing systems with high loads for industrial purposes.
Couplings are used as connectors for copper pipes; tin-lead solder and flux are additionally needed.
The pipe soldering technology will be as follows:
- First of all, a pipe of a certain size is cut. This process must be carried out carefully, taking into account the size of the existing fittings.
- The ends of the pipes must be inspected - there should be no defects such as chips, cracks or burrs. If they are not eliminated, there will be problems with the tightness of the connection after all the work is completed.
- After making sure that the ends are clean, you can start connecting. Due to the fact that several pipes will be connected, and they can be of different sections, the fittings must be selected accordingly.
- Next, the end of the pipe and the inner walls of the couplings should be treated with flux, which will degrease the surfaces to obtain the highest quality connection.
- Now the end of the pipe is threaded into the copper tube connector and heated. It must be selected so that the cross-section is 1-1.5 cm larger than the cross-section of the pipe. The pipes are heated with a gas burner. The gap between the pipe and the coupling is filled with molten solder. Currently, you can find any type of solder on the market to suit your needs, so there should not be any problems with the choice.
- After the solder is evenly distributed around the circumference, the parts to be joined must be left until it has completely hardened.
At the final stage, you need to check the connectors for the copper pipes and the entire system by running water into it. At this moment, not only the system will be checked, but it will also be cleaned of flux residues, which over time can cause metal corrosion.
Capillary method for connecting copper pipes
Soldering copper pipes, which is rightfully considered the most reliable and durable method of connecting copper parts, is carried out based on the principles of capillary technology. In accordance with this effect, which is based on the laws of physics, liquid can rise through a capillary, overcoming the force of gravity, if there is a certain distance between the lower and upper points of its rise.
Solder fittings
This physical effect allows copper pipes to be soldered in such a way that the solder melted by a gas torch is evenly distributed over the entire area of the joint being created. In order to effectively perform such soldering, the pipes can be placed in any spatial position, the main thing is that the molten solder is supplied from the bottom of the joint being formed.
In more detail, the capillary soldering process is as follows:
- Using a gas burner, the site of the future connection is thoroughly heated;
- molten solder is supplied into the gap between the ends of the pipes being connected or between the pipe and the fitting used, which completely fills it due to the capillary effect;
- the resulting compound is allowed to cool completely;
- After the formed joint has completely cooled, its elements are thoroughly cleaned using a special cleaning composition.
Using soldering, based on the capillary effect, pipeline elements not only made of copper, but also of ferrous metals are connected. If a steel fitting is used as a connecting element for copper pipes, then a layer of special flux is applied to the site of the future connection. When soldering using capillary technology, very current wire is used as solder, which can be made of tin, copper, and in some cases even silver.
Installation of copper pipes
In the process of installing plumbing systems with your own hands, it often becomes necessary to connect copper pipes with products made from other materials. In heating systems, cold and hot water supply, copper connections with steel, plastic and brass are safe from the point of view of corrosion processes. But the contact of copper with galvanized steel is dangerous for galvanized pipes and leads to their destruction due to electrolytic processes. To avoid pipeline failure, the connection must be made using, and the water flow must be directed from steel to copper.
Before starting work, it is necessary to prepare a tool for installing copper pipes of a heating system or hot or cold water supply. To do this you will need: a pipe cutter or a hacksaw for metal, a file or scraper, and if there are areas of complex configuration - a pipe bender, a gas torch or a hot air gun.
Laying a copper pipeline with your own hands begins with sections of a pre-calculated length. Then it is necessary to clean the outer and inner parts of the pipe from burrs, and if necessary, level the cut. Using a pipe bender will prevent the pipe from flattening and the formation of creases, which can cause a decrease in the performance of the pipeline in these places.
If the diameters of the pipes do not exceed 15 mm, then their bending radius should be at least 3.5 diameters, and if more than 15 mm, then four diameters. When bending by hand, a high-quality bend can be obtained only with a radius equal to 8 diameters.
Despite their resistance to corrosion, copper pipes, due to violations of manufacturing technology, improper soldering and severe contamination of water with abrasive inclusions, can be subject to very dangerous pitting corrosion. The pipe corrodes where the oxide film is destroyed. One way to avoid this process is to install filters on water supply and heating pipelines.
In the modern construction market, copper pipes, due to their unique performance qualities, quite successfully compete with products made from steel, plastic and metal-plastic, despite their high cost.
Even taking into account the fact that polymer pipes are being used more and more often, metal products are still enjoying considerable success. Typically, the metal used is copper, brass and steel. Copper is superior in terms of resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. Actually, the connection of copper pipes will be discussed in this article.
Even though copper pipes are expensive, taking into account all the characteristics of the material, their use is quite justified.
First of all, before connecting copper pipes, you should decide how to connect them, by soldering or another method.
Selection of installation equipment
In work, two types of installation of a copper piping system are very often used. At the beginning of work, everyone decides for himself which pipeline will be: detachable or one-piece.
The following connection methods are distinguished:
- welding using an electric apparatus,
- by pressing,
- using a gas burner or an electric soldering iron.
All methods can be selected during production, regardless of the pipeline option. The main thing is to decide whether fittings will be used additionally or not. If the system must be light and accessible in terms of performing construction work or adding related elements, it is better to make the pipeline detachable. The connector can be selected:
- compression,
- threaded,
- with automatic fixation.
For DIY creation, this is the best variety; there is no need to use soldering. You don’t need to have extensive experience or knowledge to make a dismountable system on your own in everyday conditions. Sometimes you will have to tighten the nuts to avoid leaks. Constantly adjusting the pressure leads to a decrease in the strength of the fasteners.
The option without including connectors is important in a situation where it is intended to be closed with a concrete screed. Here welding will be the first priority procedure. It differs from the first option in its very long service life and reliability. The thread should not be on a copper product. The connection takes place exclusively using connectors. Additionally, soldering or pressing will be required.
Figure 8. An example of a one-piece system
Necessary materials and equipment: tin and others
The following tools are required for working with copper pipes:
- pipe cutter, hacksaw or grinder with a thin disk;
- chamfer;
- pipe expander (expander);
- soldering flux;
- solder;
- soldering iron for copper, for example, a propane torch for soldering copper pipes;
- rubberized gloves;
- paper napkins.
Pipe cutters of various sizes are used to cut pipes. Larger samples have a large turning radius and are inconvenient to use in hard-to-reach places, so if there is a need to cut off a section of a finished installed water supply, use a small pipe cutter. You can cut the pipe with a hacksaw or a grinder with a thin disk, but a better cut can only be achieved using a pipe cutter.
After the pipe is cut, the burrs are removed. This is necessary to ensure that there is no turbulence in the fluid flow in the system. When there are no obstacles, the water supply does not experience stress and works like a clock.
Before welding the copper, the ends of the pipe are polished with fine-grained sandpaper, which can be purchased at hardware stores. They clean both surfaces that are preparing for soldering. Sometimes small brushes with a diameter of Ø 22 mm are used for these purposes; they are suitable for almost all pipes. For cleaning, the stem of the brush is inserted into a screwdriver or drill, with the help of which the process is carried out faster and with better quality.
Flux is applied to the cleaned, smoothed outer surface - a composition that prevents the oxidation process of copper.
Flux can be used from various manufacturers, for example, Sanha
Rubberized gloves are used to protect hands, since when cutting copper and burrs, many small metal elements are formed that dig into the skin like splinters. In addition, when cleaning the surface with a drill, the rotating brush chews on rag gloves.
To solder copper correctly, you need to take into account that from the moment of stripping and applying flux to soldering, no more than half an hour should pass, otherwise the stripping must be repeated again. If the flux is applied with a brush, there should be no bristles or hairs from it left on the surface - otherwise the connection will not be tight and the pipeline will leak after water is supplied.
After inserting the pipe into the socket, the remaining flux is not completely removed with a napkin, it remains on the connection in the form of an edge of 1–2 mm, and when soldering, the solder is drawn inward - the capillary effect is triggered. First, the joint is heated with a burner, and the moisture between the walls is evaporated. Then the burner is brought up a second time, the copper gradually heats up, and the flux takes on a tin appearance. At this moment, solder is placed on the front side, soldering occurs, and the molten alloy flows down to the back side, solidifying as it moves. The excess metal overhangs that form below are separated on their own. Soldering copper can be done in different ways.