There are hundreds of steel grades in the world. Only one domestic stamp book describes more than 700 grades of this alloy. But, we can say that out of this entire quantity, only a few are in deserved demand among manufacturers of various types of metal structures. The characteristics of 09G2S steel make it possible to attribute it specifically to this minority. Why does this happen and where is it used?
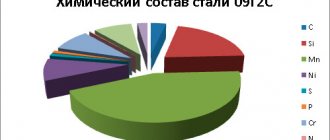
09G2S - chemical composition
The steel is classified as silicon-manganese. In accordance with the requirements of GOST 27772-88, it fully complies with C345 steel. The latter is used for the manufacture of building structures.
In accordance with the labeling system adopted in our country, composition 09G2S is deciphered as follows:
- carbon (C) - 0.09%;
- manganese (Mn) - 2%;
- silicon (Si) - no more than 1%.
The amount of alloying components in the steel is not so high, which is why 09G2S steel is classified as low-alloy. This alloy forms the basis of a whole family of steels. For example, - 09g2, 09g2dt, 09g2t, 10g2s and many others. The characteristics of alloys of this family are approximately similar.
09G2S - properties
The composition of the alloy provides this material with the following basic properties:
- density 7.85 g/cu. cm.;
- the yield strength, when heated to different temperatures, lies in the range from 255 to 155 MPa.
Parts made of 09G2S alloy can be welded together by any known type of welding used in industry. In this case, there is no need to carry out any additional preparatory operations, for example, preheating the welding site.
This type of steel has found its application in the creation of welded structures. The good weldability of this material is ensured by the low content of carbon atoms.
Many years of experience show that a higher amount of carbon leads to the formation of various defects, for example, porosity, lack of penetration. Moreover, when carbon burns out, hardened micro-sections are formed in the structure of the weld and this leads to a decrease in the quality of the weld.
Among the many advantages of this steel is the fact that it does not acquire additional brittleness after tempering. In addition, its structure makes it possible to ensure resistance to excessive heating and, as a consequence, the appearance of cracks in the weld area.
Several methods are used to produce this grade of steel:
- open hearth;
- electrothermal;
- converter
Cast iron is used as the main raw material. In accordance with GOST requirements, the melt is optimized, that is:
- raise the amount of carbon;
- alloying components are introduced.
Thanks to these measures, the finished product receives the required properties.
Assessment of weldability of steels. Carbon equivalent formulas
Assessment of the weldability of steels includes such indicators as:
1. The tendency of steel to form cold and hot cracks when welding in the weld metal or heat-affected zone.
2. Tendency to form hardening structures and change the structure of the metal in the heat-affected zone. In this area, there is a strong enlargement of grains, and, as a result, a decrease in strength.
3. Physical and mechanical characteristics of the welded joint
4. Compliance of special parameters of the welded joint (such as heat resistance, wear resistance, etc.) with the specified requirements.
Range of products made from steel 09G2S
The metallurgical enterprises of our country produce the following rolled products:
- 19281-73 Long and shaped rolled products;
- 19282-73 Sheets and strips.
That is, on the metallurgical products market, consumers can purchase a channel, angle, sheet, etc. We can safely say that such a wide range of products is ensured precisely by the properties and, of course, the price of this material.
For comparison, we can say that on average the price of a hot-rolled sheet of 09G2S steel is 43,000 rubles per ton, while a sheet of ordinary steel costs approximately 41,000 - 43,000. But the properties of the material described cover all the costs associated with its acquisition and processing.
Steel 09G2S - low-alloy structural steel for welded structures
Analogues and substitutes
IMPORTANT. The possibility of replacement is determined in each specific case after assessing and comparing the properties of steels
Type of delivery
Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 19281-73, GOST 2590-88, GOST 2591-88, GOST 8239-89, GOST 8240-89. Thick sheet GOST 19281-89, GOST 5520-79, GOST 5521-93, GOST 19903-74. Thin sheet GOST 17066-80, GOST 19903-74, GOST 19904-74. Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71.
Purpose
Parts of apparatus and vessels operating at temperatures from -70°C to +475°C under pressure. In steam and hot water pipelines - parts made of sheet metal - up to a temperature of 450°C, pipes - up to a temperature of 425°C, in boilers - sheet parts operating at temperatures up to 450°C, in all cases without pressure limitation. Fasteners in boilers and pipelines are used up to temperatures of 425°C and pressures of up to 10 N/mm2.
Steel grade 09G2S must be tested for tension at elevated temperatures.
As a result of such tests, the yield strength at 320 °C for sheets of steel grade 09G2S with a thickness of 60 mm and more should be at least 18 kg/mm2
Interpretation of steel 09G2S
The two-digit number 09 indicates the approximate carbon content in steel in hundredths of a percent, i.e. The carbon content in steel is approximately 0.09%.
Beech G means that the steel contains manganese in an amount of about 2%.
The letter C means that the steel contains silicon.
Chemical composition, % (GOST 19281-2014)
| C, carbon | Mn, manganese | Si, silicon | P, phosphorus | S, sulfur | Cr, chromium | Ni, nickel | Cu, copper | As, arsenic | N, nitrogen |
| no more | |||||||||
| 0,12 | 1,3-1,7 | 0,5-0,8 | 0,035 | 0,040 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,08 | 0,008 |
Application of steel 09G2S for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| Sheets GOST 5520, categories 7, 8, 9 depending on the wall temperature | -70 to 200 | For welded fittings assemblies operated in a macroclimatic region with a cold climate | |
| Category 6 | -40 to 200 | ||
| Categories 3, 5 | -30 to 200 | ||
| Category 12, 17 | -40 to 475 | ||
| Category 15, 17 | -70 to 475 | ||
| Sheets GOST 19281, category 3 | -30 to 200 | ||
| Category 4 | -40 to 200 | ||
| Category 12 | -40 to 475 | ||
| Categories 7, 15 | -70 to 200 |
Application of steel 09G2S for reinforcement fasteners (GOST 33260-2015)
| Steel grade, according to GOST 1759.0 | Material standard or specification | Application options | |||||
| Bolts, studs, screws | Nuts | Flat washers | |||||
| Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||
| 09G2S | GOST 19281 | -70 to 425 | 16 (160) | -70 to 425 | 16 (160) | -70 to 450 | Not regulated |
Maximum permissible temperatures for the use of 09G2S steel in environments containing ammonia
| steel grade | Steel application temperature, °C at ammonia partial pressure, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||
| St. 1(10) to 2(20) | St. 2(20) to 5(50) | St. 5(50) to 8(80) | |
| 09G2S | 300 | 300 | 300 |
NOTE The conditions of use are established for a corrosion rate of the nitrogen layer of no more than 0.5 mm/year.
Maximum permissible temperature for using 09G2S steel in hydrogen-containing environments
| steel grade | Temperature of steel application, °C at partial pressure of hydrogen, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||||||
| 1,5 (15) | 2,5 (25) | 5 (50) | 10 (100) | 20 (200) | 30 (300) | 40 (400) | |
| 09G2S | 290 | 280 | 260 | 230 | 210 | 200 | 190 |
Temperature of critical points, °C
Yield strength σ0.2 (GOST 5520-79)
Mechanical properties
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa, | σв, MPa, | δ5 (δ4), % |
| no less | |||||
| GOST 19281-2014 | Long and shaped rolled products | To 10 | 345 | 490 | 21 |
| GOST 19281-2014 | Sheet and strip (transverse samples) | From 10 to 20 incl. | 325 | 470 | 21 |
| From 20 to 32 incl. | 305 | 460 | 21 | ||
| St. 32 to 60 incl. | 285 | 450 | 21 | ||
| St. 60 to 80 incl. | 275 | 440 | 21 | ||
| St. 80 to 160 incl. | 265 | 430 | 21 | ||
| GOST 19281-2014 | Sheet after quenching and tempering (transverse samples) | From 10 to 32 incl. | 365 | 490 | 19 |
| From 32 to 60 incl. | 315 | 450 | 21 | ||
| GOST 17066-94 | Hot rolled sheet | 2 — 3,9 | — | 490 | (21) |
Mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
Note : Normalization at 930-950 °C.
Mechanical properties depending on tempering temperature
| tref., °C | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5, % | Ψ, % |
| 20 | 295 | 405 | 30 | 66 |
| 100 | 270 | 415 | 29 | 68 |
| 200 | 265 | 430 | — | — |
| 300 | 220 | 435 | — | — |
| 400 | 205 | 410 | 27 | 63 |
| 500 | 185 | 315 | — | 63 |
Impact strength KCU
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | KCU, J/cm2, at temperature, °C | ||
| +20 | -40 | -70 | |||
| GOST 19281-89 | Long and shaped rolled products | From 5 to 10 From 10 to 20 incl. From 20 to 100 incl. | 64 59 59 | 39 34 34 | 34 29 — |
| Leaf and strip | From 5 to 10 From 10 to 160 incl. | 64 59 | 39 34 | 34 29 | |
| Sheet after quenching and tempering (transverse samples) | From 10 to 60 | — | 49 | 29 | |
Categorization of steel 09G2S
Technological properties
Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1250, end 850. Weldability - weldable without restrictions. Welding methods: RDS, ADS under submerged arc and gas shield, ESW. Cutting machinability - Kv tv.spl = 1.0 and Kv b.st = 1.6 in the normalized, tempered state at σв = 520 MPa. Tendency to temper brittleness - not prone. Flock sensitivity - not sensitive.
Find out more
Steel St0 - carbon steel of ordinary quality...
Steel grade 20: explanation, characteristics, chemical...
Stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т
Some foreign analogues of steels and alloys...
09G2S - scope
Products made from steel 09G2S are used for the production of structures for various purposes. This is facilitated by high strength, which allows the use of thinner structural components. That is, where the thickness of the material from ordinary steel is 5 mm, then from low-alloy steel it will be 1.5 - 2 times less, and we must remember that the cost of these different steels is approximately the same.
The characteristics inherent in the 09G2S alloy make it possible to use it in the manufacture of parts and assemblies that will operate in the temperature range from -70 to +450 degrees Celsius. Weldability, which is significantly higher in comparison with other steels, makes it possible to create complex engineering structures used in shipbuilding, mechanical engineering, and railway transport. After certain types of heat treatment, this steel is used for the production of pipeline fittings. By the way, the ability of this steel to operate at temperatures of -70 degrees made it possible to use pipes made from this material for transporting hydrocarbons in the north of our country.
This steel, with its high weldability and excellent mechanical parameters, is ideal for the production of shaped products, such as beams or channels. In addition, this steel is used to produce components for the machine tool industry, transport, construction and chemical industries.
In construction, a square pipe made of 09G2S steel is widely used. Various fences are made from it, including decorative ones, advertising structures and small architectural forms are erected. This material also plays an important role in the production of boiler equipment, most of which is made from it.
It should be noted that the use of structures made of 09G2S steel allows the functioning of municipal facilities, transport systems, and industrial complexes located in regions with a harsh northern climate. For example, products such as flanges are in wide demand. Experience shows that 09G2S steel is the optimal material for their production. The fact is that they can be used both indoors and when working at various temperatures, including low ones.
The wide applicability of 09G2S steel and its analogues is explained not only by its exceptional technological properties, but, from the point of view of cost reduction, for the production of specific products. In fact, structures welded from this material are easier to process, have less weight and have good strength and wear resistance parameters.
Strength class is. What is Strength Class?
Strength class – arm. the standardized value of the yield strength established by the standard, N/mm2.
The strength class of reinforcing steel is the standardized value of the physical or conditional yield strength of steel established by the standard.
Category: Types of reinforcement
Encyclopedia headings: Abrasive equipment, Abrasives, Highways, Automotive equipment, Motor transport, Acoustic materials, Acoustic properties, Arches, Reinforcement, Reinforcement equipment, Architecture, Asbestos, Aspiration, Asphalt, Beams, Uncategorized, Concrete, Concrete and reinforced concrete, Blocks, Window blocks and doors, Logs, Beams, Cables, Ventilation, Weighing equipment, Vibration protection, Vibration technology, Types of reinforcement, Types of concrete, Types of vibration, Types of fumes, Types of tests, Types of stones, Types of bricks, Types of masonry, Types of control, Types of corrosion, Types of loads on materials, Types of floors, Types of glass, Types of cement, Water-pressure equipment, Water supply, water, Binders, Sealants, Waterproofing equipment, Waterproofing materials, Gypsum, Mining equipment, Rocks, Combustibility of materials, Gravel, Lifting mechanisms, Primers, fiberboard, Woodworking equipment, Woodworking, DEFECTS, Ceramics defects, Paint defects, Glass defects, Concrete structure defects, Defects, woodworking, Material deformations, Additives, Concrete additives, Cement additives, Dispensers, Wood, chipboard, Railway transport, Factories, Factories, production, workshops, Putties, Concrete fillers, Concrete protection, Wood protection, Corrosion protection, Sound-absorbing material, Ash, Lime, Wooden products, Glass products, Tools, Geodesy tools, Concrete testing, Testing equipment, Cement quality, Quality, control, Ceramics, Ceramics and refractories, Adhesives, Clinker, Wells, Columns, Compressor equipment, Conveyors, Precast concrete structures, Metal structures, Other structures, Corrosion of materials, Crane equipment, Paints, Varnishes, Lightweight concrete, Lightweight concrete fillers, Stairs, Trays, Mastics, Mills, Minerals, Installation equipment, Bridges, Spraying, Firing equipment, Wallpaper, Equipment, Equipment for the production of concrete, Equipment for the production of binders, Equipment for the production of ceramics, Equipment for the production of glass, Equipment for the production of cement, General, General terms, General terms, concrete, General terms, woodworking, General terms, equipment, General, factories, General, aggregates, General, quality, General, corrosion, General, paints, General, glass, Fire protection of materials, Refractories, Formwork, Lighting, Finishing materials, Test deviations, Waste, Production waste, Panels, Parquet, Lintels, Sand, Pigments, Lumber, Feeders, Plasticizers for concrete, Plasticizing additives, Plates, Coatings, Polymer equipment, Polymers, Flooring, Floors, Pressing equipment, Devices, Devices, Purlins, Design, Production, Anti-frost additives, Fire-fighting equipment, Others, Others, concrete, Others, putties, Others, paints, Others, equipment, Types of wood, Destruction of materials, Mortar, Crossbars, Piles, Piling equipment, Welding , Welding equipment, Properties, Properties of concrete, Properties of binders, Properties of rock, Properties of stones, Properties of materials, Properties of cement, Seismic, Warehouses, Hardware, Dry mixtures, Resins, Glass, Construction chemicals, Building materials, Superplasticizers, Drying equipment , Drying, Drying, woodworking, Raw materials, Theory and calculation of structures, Thermal equipment, Thermal properties of materials, Thermal insulation materials, Thermal insulation properties of materials, Thermal and damp treatment of concrete, Safety precautions, Technologies, Concreting technologies, Ceramic technologies, Pipes, Plywood, Trusses, Fiber , Foundations, Fittings, Cement, Workshops, Slags, Grinding equipment, Putties, Veneer, Plastering equipment, Noise, Crushed stone, Economy, Enamels, Emulsions, Power equipment
Welding steel
As noted above, welding 09G2S steel does not require preliminary preparation, but there are methods that use additional heating up to 120 C. Welding parts can be performed using any electrodes, for example, E42A or E50A. The technology and welding techniques are no different from those used when working with other grades of steel. But there are also small exceptions, for example, GOST requires cutting edges with a steel sheet thickness of 5 mm or more. Good weldability of 09G2S allows you to work without cutting edges up to a thickness of 40 mm.
When semi-automatic welding of sheets, the typical mode is the following:
- welding current strength - from 200 to 230 A;
- shielding gas pressure - from 2 to 2.2 atm.
Structures made of this steel do not require special conditions for cooling after welding. Cooling down in the open air, it gains the necessary seam quality parameters.