Steel 09G2S
| Profile | Size(mm) | NTD |
| Circle | GOST 19281-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006 | |
| Calibrated circle | GOST 19281-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006 | |
| Square | GOST 19281-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006 | |
| Forging | GOST 1133-71 |
Characteristics of steel 09G2S
The operational and technical characteristics of products made from steel 09G2S are regulated by GOST 19281-73.
This alloy contains 11 elements. The percentages of all components of the substance are presented in the table below and in the diagram.
| Cr | Mn | Ni | Mo | C | Fe | P | S |
| up to 0.3 | 1,3 – 1,7 | up to 0.3 | 0,25 – 0,4 | up to 0.12 | 96-97 | up to 0.035 | up to 0.04 |
Steel 09G2S , whose Brinell hardness is 450-490 MPa, is one of the most popular grades of steel for buildings in construction. But this is not the only advantage of steel. With a specific gravity of 7.85 g/cm3 after processing and obtaining a 2-phase structure, the steel acquires a high level of endurance limit while simultaneously increasing (3.0-3.5 times) cycles until structural failure.
Structural steel 09G2S is capable of maintaining its original characteristics at high pressure in the temperature range from -70 ˚С to +425 ˚С. Steel 09G2S is resistant to loads with a variable force vector, durable and responds well to heat treatment.
Steel 09G2 is divided into categories depending on the requirements for impact bending tests. The characteristic is the impact strength of KCU - the ability of the material to absorb mechanical energy during the process of deformation and destruction under the influence of load.
The category is indicated along with the steel grade. For example, steel with category 12 is designated as 09G2S-12 . Category 15 - 09G2S-15. The difference between them is the impact strength temperatures.
Strength class 09G2S is described by GOST 19281-2014.
Interpretation of steel 09G2S
- 09 – quantitative fraction of carbon content in the alloy (0.09%);
- G2 is manganese and its part in the entire volume fluctuates around 2% (the exact figure ranges from 1.3 to 2%);
- C – denotes silicon, the absence of numbers after the symbol indicates that it is less than 1%.
Advantages of steel 09G2S
- High mechanical strength
- Durability – the service life of parts made from this steel is more than 30 years
- Wide operating temperature range – from -70°С to +425°С
- No tendency to temper brittleness
- After tempering, the viscosity of steel does not decrease
- Does not lose ductility and does not change grain size when welding elements
Application of steel 09G2S
- Heating and steam boilers;
- Welded complex structures
- oil industry - pipe laying in the far north of Russia, installation of complex welded parts;
- mechanical engineering – production of steam boilers and other equipment for working at high temperatures;
- In simple street structures
The specific gravity of this alloy is 7.85 g/cm3. The weldability of this steel is not limited.
Welding methods:
- manual arc (RDS)
- argon-arc (AS) submerged arc and gas protected
- electroslag (ESS)
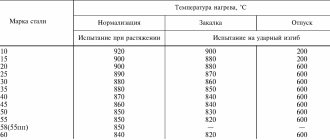
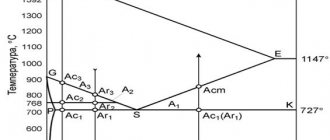
The critical point temperature is:
- Ac1 = 725°
- Ac3(Acm) = 860°
- Ac3(Acm) = 860°
- Ar1 = 625°
The material has no flake sensitivity and no tendency to temper brittleness.
Forging temperature:
- start – 1250°С
- end – 850°С
Cutting machinability is available in the normalized tempered state δB = 520 MPa, Kυ b.st = 1.0 K υ tv. spl=1.6
Modulus of elasticity of steel
The elasticity of solids is the ability to return to its original shape after the cessation of deforming influences. For example, a block of plasticine has zero springiness, while rubber products can be compressed and stretched. When various forces are applied to objects and materials, they become deformed. Depending on the physical properties of the body or substance, two types of deformation are distinguished:
- Elastic - the consequences disappear after the action of external forces ends;
- Plastic - irreversible change in shape.
The modulus of elasticity is the name of several physical quantities that characterize the tendency of a solid body to deform elastically.
The concept was first introduced by Thomas Young. The scientist suspended weights from metal rods and observed their elongation. Some samples doubled in length, while others were torn during the experiment.
Today the definition combines a number of properties of physical bodies:
Young's modulus : Calculated by the formula E= σ/ε, where σ is the stress equal to the force divided by the area of its application, and ε is the elastic deformation, equivalent to the ratio of the elongation of the sample from the beginning of deformation and compression after its cessation.
Shear modulus (G or μ) : the ability to resist deformation while maintaining volume when the direction of loads is tangential. For example, when hitting the head of a nail, if it was not made at a right angle, the product becomes distorted. In sopromat, the value is used to calculate shifts and torsion.
Bulk modulus or bulk modulus (K): changes caused by the action of a confining stress, such as hydrostatic pressure.
Punch ratio (Ⅴ or μ) : the ratio of transverse compression to longitudinal elongation, calculated for material samples. For absolutely fragile substances it is zero.
Lamé's constant : the energy that provokes a return to its original form, calculated through the construction of scalar combinations.
The modulus of elasticity of steel is correlated with a number of other physical quantities. For example, when conducting a tensile experiment, it is important to take into account the tensile strength, exceeding which results in destruction of the part.
- Ratio of rigidity and ductility;
- Impact strength;
- Yield strength;
- Relative compression and tension (longitudinal and transverse);
- Strength limits under shock, dynamic and other loads.
The use of a number of approaches is determined by the requirements for the mechanical properties of materials in various industries, construction, and instrument making.
Determination of steel sensitivity to cold cracking
Cold cracks form after welding due to tensile residual stresses. Their strength depends on the rigidity of the resulting structure and the thickness of the seam. Its value can be determined by the stiffness intensity coefficient - K. It characterizes the applied force, which opens the gap by 1 mm, which is also 1 mm wide in the welded joint. It is calculated like this:
where Kq is a constant, which is considered to be equal to 69, S is the thickness of the steel sheet (in mm)
It is important to note that the ratio is only valid if the sheet thickness does not exceed 150 mm
How steel can be susceptible to cold cracking can be determined by the parametric equation:
where Рш is the “embrittlement” coefficient (this is the name for the process when a metal goes from a viscous state to a brittle one), H is the amount of diffusion hydrogen, K is the hardness intensity coefficient.
The value of Psh is found by solving the Bes-Sio equation:
The results of repeated studies helped to establish the threshold value at which the sensitivity of steel to the formation of cold cracks manifests itself. This happens if the Pw value exceeds 0.286.
Thermophysical properties of steel depending on temperature
The following thermophysical properties of steel of various grades are presented:
- steel density, kg/m3;
- specific (mass) heat capacity of steel, kJ/(kg deg);
- thermal conductivity of steel, W/(m deg);
- coefficient of thermal expansion of steel, 1/deg.
What does the transcript look like?
Knowing the labeling makes it possible to directly understand what exactly is offered by the manufacturer and what features the product has. From a technical point of view, the marking 09g2s means the following:
- 09 - exact proportion of carbon in the total alloy;
- G2 - presence of manganese and its fluctuation in the total volume - 2%;
- C—presence of silicon, the proportion of which does not exceed 1%.
However, one should not think that the composition of steel includes only those elements that are indicated in the marking.
In addition to manganese and silicon, the overall composition is supplemented by sulfur, nitrogen, nickel, copper and phosphorus. However, the share of additional components rarely exceeds 1%, so they are not mentioned in the labeling.
Also, decoding concerns not only doping, but also other criteria. For example, the following should be included here:
- Structure and changes after the hardening process;
- Main purpose;
- Manufacturing method;
- Chem. composition of the material.
As a result, there are analogues for these indicators on the domestic market. You can often hear that 09g2s is steel 345. However, the second indicator is intended for builders and does not mean the chemical composition, but the fluidity indicator, which corresponds to the steel standard.
Elastic modulus of different steel grades
Spring steel alloys have the greatest ability to resist deformation. These materials are characterized by high yield strength. The value shows the stress at which the deformation increases without external influences, for example, when bending and twisting.
The elasticity characteristics of steel depend on alloying elements and the structure of the crystal lattice. Carbon imparts hardness to the steel alloy, but in high concentrations it reduces ductility and springiness. The main alloying additives that increase elastic properties: silicon, manganese, nickel, tungsten.
Often, the desired indicators can be achieved only with the help of special heat treatment modes. In this way, all fragments of the part will have uniform fluidity indicators, and weak areas will be eliminated. Otherwise, the product may break, burst or crack. Grades 60G and 65G have such characteristics as tensile strength, viscosity, wear resistance, they are used for the manufacture of industrial springs and musical strings.
The metallurgical industry has created several hundred grades of steel with different elastic moduli. The table shows the characteristics of popular alloys.
Table of strength moduli of steel grades
| Name of steel | Young's modulus of elasticity, 10¹² Pa | Shear modulus G, 10¹² Pa | Modulus of bulk elasticity, 10¹² Pa | Poisson's ratio, 10¹²·Pa |
| Low carbon steel | 165…180 | 87…91 | 45…49 | 154…168 |
| Steel 3 | 179…189 | 93…102 | 49…52 | 164…172 |
| Steel 30 | 194…205 | 105…108 | 72…77 | 182…184 |
| Steel 45 | 211…223 | 115…130 | 76…81 | 192…197 |
| Steel 40Х | 240…260 | 118…125 | 84…87 | 210…218 |
| 65G | 235…275 | 112…124 | 81…85 | 208…214 |
| X12MF | 310…320 | 143…150 | 94…98 | 285…290 |
| 9ХС, ХВГ | 275…302 | 135…145 | 87…92 | 264…270 |
| 4Х5МФС | 305…315 | 147…160 | 96…100 | 291…295 |
| 3Х3М3Ф | 285…310 | 135…150 | 92…97 | 268…273 |
| R6M5 | 305…320 | 147…151 | 98…102 | 294…300 |
| P9 | 320…330 | 155…162 | 104…110 | 301…312 |
| P18 | 325…340 | 140…149 | 105…108 | 308…318 |
| R12MF5 | 297…310 | 147…152 | 98…102 | 276…280 |
| U7, U8 | 302…315 | 154…160 | 100…106 | 286…294 |
| U9, U10 | 320…330 | 160…165 | 104…112 | 305…311 |
| U11 | 325…340 | 162…170 | 98…104 | 306…314 |
| U12, U13 | 310…315 | 155…160 | 99…106 | 298…304 |
Modulus of elasticity for metals and alloys
| Name of material | Elastic modulus value, 10¹² Pa |
| Aluminum | 65—72 |
| Duralumin | 69—76 |
| Iron, carbon content less than 0.08% | 165—186 |
| Brass | 88—99 |
| Copper (Cu, 99%) | 107—110 |
| Nickel | 200—210 |
| Tin | 32—38 |
| Lead | 14—19 |
| Silver | 78—84 |
| Gray cast iron | 110—130 |
| Steel | 190—210 |
| Glass | 65—72 |
| Titanium | 112—120 |
| Chromium | 300—310 |
Elasticity of steels
| Name of steel | Elastic modulus value, 10¹² Pa |
| Low carbon steel | 165—180 |
| Steel 3 | 179—189 |
| Steel 30 | 194—205 |
| Steel 45 | 211—223 |
| Steel 40Х | 240—260 |
| 65G | 235—275 |
| X12MF | 310—320 |
| 9ХС, ХВГ | 275—302 |
| 4Х5МФС | 305—315 |
| 3Х3М3Ф | 285—310 |
| R6M5 | 305—320 |
| P9 | 320—330 |
| P18 | 325—340 |
| R12MF5 | 297—310 |
| U7, U8 | 302—315 |
| U9, U10 | 320—330 |
| U11 | 325—340 |
| U12, U13 | 310—315 |
Application
Steel 09g2s is actively used in the shipbuilding, transport, oil and chemical industries. On its basis, welded joints of complex configurations are made and fasteners are manufactured. Examples of using:
- Laying of main pipelines
- Construction of residential and industrial facilities
- Production of household and household appliances
Other examples of the use of such steel include the manufacture of technical equipment, boilers and ships, etc. It is worth noting that the wide temperature range of this steel allows it to be used where other materials have a risk of deformation over a long service life, in particular, for the production of boilers that are constantly used at high temperatures.
The feasibility of purchasing this or that steel directly depends on its qualities. With them, as you have already seen with the help of this article, everything is in order, so it is better to buy 09g2s metal than to buy its cheap substitutes.
You can purchase steel of this grade wholesale and retail. The final cost in any case will depend on the volume of the purchased batch. Therefore, it is always better to check with the supplier’s managers for more detailed consultations on price issues.
2007 - 2022 "Intechmet" Manufacturing of metal products and metal structures to order. Cutting and chopping of metal. Rolled metal wholesale and retail.
Moscow, Nizhnie Polya Street, building 31, building 1, office 404.
Contact us, we will be happy to help you within 15 minutes.
Tensile strength
Solids are capable of withstanding limited loads; exceeding the limit leads to destruction of the metal structure, the formation of noticeable chips or microcracks. The occurrence of defects is associated with a decrease in performance properties or complete destruction. The strength of alloys and finished products is checked on test benches. The standards provide for a number of tests:
- Prolonged use of deforming force;
- Short-term and long-term shock impacts;
- Tension and compression;
- Hydraulic pressure, etc.
In complex mechanisms and systems, the failure of one element automatically causes increased loads on others. As a rule, destruction begins in those areas where stress is maximum. The safety margin serves as a guarantee of equipment safety in emergency situations and extends its service life.
Source of the article: https://e-metall.ru/blog/uprugost-stali/