| Brand: | P18 |
| Class: | High-speed tool steel |
| Used for rental: | Sections and shapes: GOST 19265-73, GOST 2590-2006, GOST 2591-2006 Calibrated rod: GOST 19265-73, GOST 7417-75 Ground rod and silver: GOST 19265-73, GOST 14955-77 Thick sheet: TU 14 -1-1408-75 Thin sheet: TU 14-1-1706-76, TU 14-1-1408-75 Strip: GOST 19265-73, GOST 4405-75 Wire: TU 14-1-1096-74 Forgings and forged workpiece: GOST 19265-73, GOST 1133-71. |
| Industrial use: | P18 steel is used to make cutters, cutters, drills, cutters, reamers, countersinks, taps, broaches and other cutting tools. |
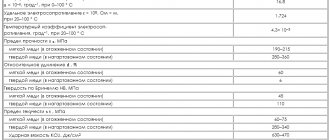
| Material hardness: | HB 10-1 = 255 MPa |
| Critical point temperature: | Ac1 = 820, Ac3(Acm) = 860, Ar3(Arcm) = 770, Ar1 = 725 |
| Forging temperature, °C: | Start 1200, end 900. Cooling in wells at 750-800 °C |
| Cutting ability: | At HB 212-228 Kυ TV. spl. = 0.6 and Kυ b.st. = 0.3 |
| Weldability of material: | Welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment (without restrictions). Good weldability during electric butt welding with steels 45 and 40X |
| Flock Sensitivity: | Not sensitive |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | Less inclined |
| Analogues: | R9K5, R6M5, R6M5K5 |
Chemical composition of P18 steel
| Chemical element | % |
| Carbon (C) | 0,73 – 0,83 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0,2 – 0,5 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0,2 – 0,5 |
| Nickel (Ni) | up to 0.6 |
| Phosphorus (P) | up to 0.03 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 3,8 – 4,4 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | up to 1 |
| Tungsten (W) | 17 – 18,5 |
| Vanadium (V) | 1 – 1,4 |
| Cobalt (Co) | up to 0.5 |
| Sulfur (S) | up to 0.03 |
| Copper (Cu) | up to 0.25 |
| Iron (Fe) | ~73 |
Explanation of steel markings
The P18 quick cutter is marked when using certain standards. In the case under consideration, decoding allows one to determine only the tungsten content, the concentration of which is indicated digitally. The first letter defines the group of high-speed steels. The concentration of other chemical substances is determined by GOST and is not indicated when labeling the alloys of the group under consideration.
Explanation of high-speed steel markings
Physical properties of P18
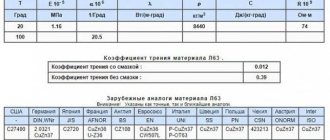
| Test temperature, °C | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 | 900 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity E, GPa | 228 | 223 | 219 | 210 | 201 | 192 | 181 | — | — | — |
| Density, pn, kg/cm3 | 8800 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m °C) | — | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 27 | — | — |
| Electrical resistivity (p, NΩ m) | 419 | 472 | 544 | 627 | 718 | 815 | 922 | 1037 | 1152 | 1173 |
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
Characteristics and Application
When considering the characteristics of the P18 brand, it should be taken into account that it is often subjected to heat treatment. The main qualities include:
- High hardness of the surface layer. If heat treatment is carried out, the hardness reaches 62-65 HRC units. This is quite enough to cut structural metals of ordinary quality at various speeds and feeds. In addition to hardening, tempering is performed, due to which a fine-grained structure is achieved.
- Increased strength determines that the P18 material in question can withstand long-term loads.
- Red resistance allows cutting for a long period. An increase in the temperature of the steel leads to the fact that it begins to lose its performance characteristics.
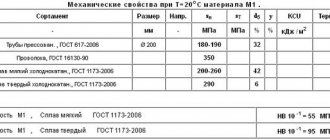
Mechanical properties of P18 steel at elevated temperatures
Mechanical and physical properties of P18 steel
A significant drawback is carbide heterogeneity. When making large tools and using them, the cutting part may become chipped. The problem is solved by increasing the amount of carbide phase. The heat treatment carried out makes the structure fine-grained and more resistant to mechanical stress.
The use of P18 can be associated with the physical characteristics of the material. They are as follows:
- The density is 8800 kg/cm3.
- Elastic modulus 220 MPa.
- Hardness (without hardening) 227 HB.
- Maximum fluidity 450 MPa.
- Tensile strength 830 MPa.
Forging involves heating the workpiece to a temperature of 1200 degrees Celsius. The weldability of the alloy is good; there is no need to heat the material. The surface can be sanded using conventional abrasive wheels.
Hunting knife made of P18 steel
Chainsaw blade made of P18 steel
Self-tapping screws made of P18 steel
The scope of application of P18 steel is very wide. In most cases, it is used in the manufacture of cutting blade tools, which can be used for machining metals of varying hardness.
When using tools that are made from the tool alloy in question, the processing speed increases by 4 times.
The scope of application can be significantly expanded through hardening and tempering; in some cases, forging is carried out.
Mechanical properties of P18 depending on the tempering temperature
| Temperature, °C | 400 | 500 | 550 | 600 |
| Hardening 1280 °C, oil. Vacation three times for 1 hour | ||||
| σв (MPa) | 1370 | 1470 | 2350 | 2210 |
| KCU (J/cm2) | 23 | 19 | 17 | — |
| HRC ∂ (HB) | 61 | 63 | 66 | 65 |
Reviews
Anton, 35 years old: I have long dreamed of a good hunting knife, and my wife finally gave me a gift. We chose it together and was looking for the high-speed metal P18. I’ve already tried it in practice, the knife is comfortable, cuts ropes and branches well, and behaves tolerably when cutting game. So far I like everything.
Evgeniy, 28 years old: I bought a new knife because the one I got from my father broke. I chose for a long time and carefully studied the topic. I settled on a blade made of R6M5 steel because I wanted a knife that would last for decades without requiring weekly sharpening. I'm happy with the purchase, the knife is comfortable, heavy, fits well in the hand. There are no complaints about sharpening - the blade is sharp and cuts everything.
Mechanical properties of P18 steel in a heat-treated state at elevated temperatures
| Test temperature, °C | 200 | 400 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 650 |
| σben. (MPa) | 3570 (180) | 3730 (180) | 3290 (160) | 3060 (150) | 2430 (120) | 2180 (110) |
| H.V. | 815 (10) | 755 (10) | 712 (10) | 661 (10) | 615 (10) | 504 (10) |
| HRC ∂ (HB) | 64 | 62 | 60 | 58 | 56 | 51 |
Production of cutting tools
The price of P18 steel is determined by the type of rolled product, taking into account the weight of the product and the volume of the order. One of the types of finished products is a drill, which is manufactured based on the requirements of State Standard 2034-80. These include the need to ensure a shank hardness of 63-68 HRC.
Grinding is the next stage after heat treatment. For this purpose, special machines are used that can guarantee compliance with the tolerances for the processed product - A1 and B1 according to h8, B - h9.
Return to content
Mechanical properties of P18 steel in the as-delivered condition (after annealing) at elevated temperatures
| Test temperature, °C | 200 | 400 | 600 | 800 | 1000 | 1100 | 1200 |
| σ0.2 (MPa) | 450 (50) | 420 (40) | 300 (40) | 110 (20) | 90 (20) | — | 30 (10) |
| σв (MPa) | 830 (80) | 700 (70) | 480 (50) | 200 (20) | 100 (20) | — | 30 (10) |
| δ5 (%) | 13 (2) | 15 (2) | 31 (3) | 60 (5) | 42 (4) | — | 12 (3) |
| ψ % | 22 (4) | 22 (4) | 55 (6) | 70 (6) | 55 (6) | — | 25 (5) |
| σcom. (MPa) | 1050 (50) | 850 (50) | 620 (40) | 100 (20) | 50 (10) | — | 40 (10) |
| Τk (MPa) | 520 (30) | 450 (30) | 300 (20) | 100 (20) | 50 (10) | — | 40 (10) |
| KCU (J/cm2) | — | — | — | — | 100 (10) | 130 (15) | 45 (5) |
| HB | 227 (6) | 210 (6) | 140 (6) | 30 (4) | 24 (4) | — | 4 (1) |
Features of heat treatment
Heat treatment at a temperature of about 1200 - 1300 ºC, followed by tempering, causes dispersion hardening. During the hardening process, most of the Fe3W3C carbide decomposes and turns into an austenitic or martensitic solid solution. This leads to saturation of the alloy with carbon, tungsten and other alloying elements. Tempering, which is performed at temperatures of 550 - 560 ºC, leads to an increase in hardness to maximum parameters. This occurs as a result of the precipitation of carbides and the decomposition of austenite residues.
Tools of complex shape, incl. thin-edged or operating under variable load conditions, for example, in interrupted turning, must have high strength and toughness.
Heating for hardening of steels of type P18 is carried out at such temperatures and time pauses that will ensure the decomposition of carbides and strengthening of austenite. This is necessary to obtain the required heat resistance.
A thin-bladed tool with cutting part sizes from 3 to 5 mm, the hardening temperature should be 10 - 20 ºC lower than the maximum (1250 ºC).
The high temperatures required for heat treatment can subsequently lead to cracks and excessive stress. In order to avoid these troubles, the material is heated in two stages. The first heating is performed at a temperature level of 400 - 500 ºC, the second at 800 - 850 ºC. Upon reaching the final temperature, which is 1200 - 1300 ºC, the time the part remains in the heating zone is limited. The permissible time is calculated from the ratio of 10 - 15 seconds per 1 mm of thickness (diameter). That is, a drill with a diameter of 5 mm can be in this mode for about 50 - 75 seconds.
The time the workpiece is heated can be doubled compared to peak load. That is, the same drill will be heated for about 100 - 150 seconds.
Preliminary and final heating is carried out in a salt bath. It is filled with a mixture of:
- 78% BaCl2 (barium chloride);
- 22% NaCl (sodium chlorine).
To protect the workpieces from oxidation, the solution is deoxidized with magnesium fluoride.
Steel tempering is also carried out in several stages. The workpieces are kept at a temperature of 550-570 ºC, and it is necessary to carry out two to three sessions lasting one hour each
Chemical composition
The metal contains:
- 73% ferrum;
- 17.75±0.75% tungsten;
- 15% molybdenum;
- 4.1±0.3% chromium;
- 1.2±0.2% vanadium;
- 0.78±0.05% carbon;
- 0.5% each of cobalt, manganese and silicon;
- 0.4% nickel;
- 0.03% each of sulfur and phosphorus.
Compliance of the composition of P18 steel with the specified standards ensures its strength, reliability and durability, allowing it to be used for the manufacture of tools and parts for turning and milling machines, cutting internal and external threads, creating and processing holes. The metal is suitable for machining alloyed, carbon, structural steel with a tensile strength of up to 1 GPa, and non-ferrous metals.
Maintaining operating parameters is ensured at temperatures below 600 C.
Designations
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | R18F2K8M |
| Designation GOST Latin | P18F2K8M |
| Translit | R18F2K8M |
| By chemical elements | — |
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | EP379 |
| Designation GOST Latin | EP379 |
| Translit | EhP379 |
| By chemical elements | — |
What to look for when choosing
A tourist knife, for the production of which 95x18 steel is used, is made with a drop-down blade. Hunting blades are produced with a fixed design. Knives made of steel 95x18 must be selected according to the following criteria:
- Design – it is better to choose a folding design for a tourist knife. It should have a small blade and very compact dimensions. A hunting knife should be of minimal dimensions, but with a significantly larger width and thickness; the blade is fixed with a handle. The product usually comes with a case.
- Size – both tourist and hunting blades must be at least 15 cm in length, but no more than 25 cm for their comfortable use.
- Handle - it should be made of a material that reacts poorly to the environment. The best option would be polymers.
- The quality of the blade - it must be free of chips, nicks, and signs of corrosion.
- Sharpening – the greater the sharpening angle, the rougher the work the knife is intended for.
It is also worth paying attention to other characteristics of the knife:
- blade thickness – optimally 1.5–2 mm;
- the presence of protection on the handle - a lock that prevents the palm from slipping;
- balance between handle and blade.
By purchasing knives from this brand from trusted suppliers or in specialized hunting and tableware stores, you can get:
- product warranty;
- quality certificate;
- professional consultation of your choice.
By following these simple rules, you can be sure that the product will not fail under any operating conditions and will last for many years.
Brand analogues
I would like to leave the last couple of words in case you suddenly find yourself outside the borders of our vast homeland, and you urgently need something fast-cutting. In this case, it is better to familiarize yourself with analogues of P18 in foreign markets.
- United States - T1.
- Europe – 1.3355 or HS18-0-1.
- Japan – SKH2.
- England – VT1.
- China – W18Cr4V.
This list contains only a small part of the known analogues of P18 steel. But even this will be enough to find what you need if necessary.
pros
- High quality . Products made from this steel will almost certainly be free of defects, due to the quality of the raw materials. Therefore, when buying a quick cutter from P18, you don’t have to worry.
- High hardness is very important for any cutting tool. And grade P18 has a hardness on the Rockwell scale from 65 to 64. For a knife, such hardness is considered very high, which classifies such a blade as a high-speed blade. It will very rarely have to be sharpened, because it does not become dull on ordinary materials - it can cut wood almost without hindrance.
- Good elasticity and impact strength due to additives . Usually, hard metal also turns out to be brittle - it is easy to break under lateral loads on the tool. But this alloy, as a rule, will bend, but not break, because some impurities, especially manganese and nickel, make it more flexible and ductile. Carbon and silicon not only add strength, but also protect against breakage. Therefore, saws and cutters are made from P18, which work great.
- The P18 blade has good cutting abilities , does not dull for a long time, and holds an edge well. The admixture of cobalt helps here, which is responsible for the cut. It helps the blade hold an edge, and also allows you to sharpen the blade to a razor sharpness, which it will maintain even during hard work.
- With this knife it will be possible to cut products made of softer materials . This alloy is traditionally used for metal cutting tools.
- In general, this type of steel can be considered almost perfectly balanced - it is distinguished by its hardness, is quite durable, and retains its cutting ability for a long time. Users note that of all high-speed steels, P18 is one of the best. The combination of all these properties makes it an ideal candidate for premium knife steel.
Areas of use
Thanks to the above characteristics and low cost, 95X18 steel has found application in many branches of modern production.
Aviation instrument making uses this steel for the manufacture of critical components of mechanisms that are subject to increased wear resistance requirements. Parts made from 95Х18 are resistant to operation at ambient temperatures up to 500 ºС and moderate exposure to aggressive environments. First of all, this includes seating rings for rolling and sliding bearings.
In mechanical engineering, steel is actively used as a material for parts operating under conditions of abrasive wear. Its applications are extremely diverse and include all kinds of bushings, shafts, axles, hydraulic valves, springs, etc.
In the oil industry, 95X18 is used for the manufacture of roller and ball bearings.
95X18 steel is most widely used in the manufacture of bladed weapons.
The main modern knives used in hunting and tourism are usually made from two grades of steel. These are 95X18 and 65X13. Each of them has its own characteristics. There is still active debate on the forums of hunters’ websites about which one is better.
Steel 95x18 for knives: pros and cons
Advantages:
- First of all, it is worth noting the favorable ratio of the cost of knives and their performance characteristics. Their average price varies between 3,000 rubles.
- With more or less “competent” use, knives keep sharpening for up to 2 months.
- The sharpening process does not require high qualifications from the blade owner.
- These knives are characterized by high resistance to metal corrosion.
- Increased hardness and strength.
Flaws:
- Knives made from steel 95Х18 have a low impact toughness value. This can cause cracks to form when exposed to shock loads, or even split the knife. As a result, such blades are unsuitable for throwing.
- The performance characteristics of the blade strongly depend on the previously performed heat treatment. Steel is sensitive to the slightest deviations from the technology of its implementation. Although we note that in conditions of mass production, this operation is completely entrusted to specialized equipment, which reduces the appearance of low-quality products to nothing.
Minuses
- It is very difficult to forge this steel yourself , because even to melt it you will need a temperature of up to 1280 degrees . After such heating it will have to be processed for a long time, which is also difficult. The finished blade can only be hardened in oil preheated to 200 degrees, after which the blade continues to cool in the open air. Also, after cooling, it has to be released three times at a temperature of 400 degrees, for an hour each time.
- Price : this alloy belongs to the highest class in terms of price. Even a small blade made from it will cost around four thousand. And instruments made from it are produced only by expensive brands.
- P18, despite the chromium content, is easily corroded , so the knife requires care. Protect it from water and other aggressive substances. Knives made of such steel are usually coated with a protective substance at the factory, or undergo protective oxidation. Over time, the coating comes off, especially if the instrument is used frequently, and therefore regular maintenance becomes necessary.
- When using a knife to carry out lateral loads, there is a high risk of breaking it . This happens with all knives made of very hard steel, because with hardness comes brittleness. But for knives made from P18, this risk is noticeably less, because special attention was paid to strength - manganese and silicon were added.
- Sharpening the blade will become very difficult because the alloy has high hardness. The only sharpener that is suitable for such knives is corundum, because corundum is harder than this alloy. The turning process itself will be long and complex. But if you have an electric saw with a rotating whetstone, the process becomes much easier and faster. The knife keeps sharpening for about a year if you do not subject it to extreme loads.
Where is it used?
The metal is widely used in the creation of blade cutting tools intended for machining materials based on iron and carbon with varying degrees of hardness. These include heat-resistant and stainless steels, the hardness of which reaches HRC70. The use of P18 steel ensures an increase in processing speed, eliminates plastic deformation and changes in characteristics as a result of heating.
An increase in the technical parameters of the material is ensured by heat treatment. One of the methods is hardening, which is carried out at a temperature of 1300 degrees. Due to the presence of cobalt in the composition, the temperature increases, at which the internal structure of carbides changes, the main one of which is Fe3W3C. During quenching, most of this substance is converted to hard martensite or austenite.
Low tempering of high-speed steel P18 at t = 550-560 degrees makes it possible to obtain a fine-grained structure. This is due to the decomposition of the residual austenite form and the formation of dispersed carbide compounds.
Alternating heat treatment modes eliminates the risk of cracking. The order most often used is:
- heating up to 500 degrees;
- temperature increase up to 850 degrees;
- setting the temperature to 1300 degrees for a certain amount of time depending on the thickness of the element (1-30 mm, 15 seconds for each millimeter).
After this, stepwise tempering is carried out, which ensures a complete transformation of the residual austenitic structure of P18 steel.
Resistance to corrosion and wear is ensured by additional processing of the cutting part. To do this, one of the methods can be used:
- steaming;
- sulfide coating;
- cyanidation to increase viscosity;
- nitriding to reduce brittleness.
They are carried out after heat treatment, sharpening and grinding, which guarantees increased strength.
Conclusion
P18 steel is well suited for the manufacture of high-speed cutting blades. The blade will not need to be sharpened often, and it will maintain a razor sharpness even during intensive work.
Care should be taken with lateral loads, as the blade is less designed for them.
Such a knife is not suitable as a chopping weapon - a tool made of such steel can only cut, and therefore it is suitable as a kitchen or skinning knife. It can also be used for planing wood, and it will easily cut the hardest species.
You will have to invest a lot of money in such a knife, but you will not have to doubt the quality. In addition, such a blade will almost certainly serve you for a very long time, provided that it is used for its intended purpose and protected from corrosion.
Forging
P18 steel, the characteristics and application of which we have already discussed in detail above, may also be of interest as a material for the manufacture of various household items, in particular knives, chisels, chisels, chisels, in general, everything that is somehow intended for cutting works. And in order to make life easier for blacksmiths and knifemakers, we will consider in detail all the main technological stages of the production of such products.
- The temperature range for forging a product is 1,280–900 °C. However, due to the initial density of the material, steel is very difficult to forge. You will need to spend time and effort on this.
- Hardening will require preheating the blade to 800°C, followed by main heating to a hardening temperature of 1,280°C. P18 is hardened only in oil heated to 200 °C, after which it is cooled in air.
- Tempering is carried out at a temperature of 400 °C for one hour, but three times. The final hardness of the product will be around 62 units on the Rockwell scale.
How to choose a drill?
The purpose of using a drilling tool is to make the necessary holes in various structures. The drills are different:
- device;
- production materials;
- scope of use;
- cost.
One drill is designed to work with aluminum products, the other with thick iron or stainless steel
Therefore, it is important to know exactly what materials are to be drilled, what alloy the selected drill should be made of, so that you can drill a hardened structure. The type of drill is determined by its mechanism
- Spiral ones are the most used. They have the shape of a metal cylinder with 2 to 4 helical grooves, which are designed to remove cut material and reduce friction of the drill against the walls of the hole being made.
- Screw. They differ from screw ones by having only 1 spiral groove and a cutting end equipped with a sharp, centered tip. The threaded tip of the tool allows the drills to go deeper into the structure themselves without applying additional effort.