Extruder for feed: drawings and useful recommendations
A simple to use feed extruder makes it possible to independently produce compound feed for animals. This device is considered an indispensable assistant both in large-scale agriculture and in small farms for raising animals and birds. In specialized stores, such equipment costs decent money. To save money, you can assemble the unit yourself; drawings and recommendations from specialists will serve as an auxiliary informant in this matter.
Granulator or extruder?
As you already understood, a granulator and an extruder, although they make granules, are different in their structure and before making any kind of machine you need to understand for yourself what specific machine you need.
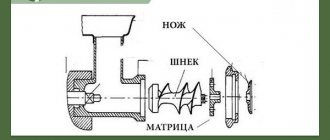
An extruder, or as it is also called a screw press, consists of:
- Auger;
- Matrices;
- Housings;
- Gear motor.
Such a press is usually used, as I already said, at home, to process tens of kilograms of waste. For example, by granulating dry sawdust, you can mix it with coal and reduce the consumption of purchased coal. Or you can pelletize the straw and then make the pellets as a bedding for the animals. There are many use cases and I will not describe them all in this article.
Let's see the differences between a screw press and a conventional granulator:
- Making a screw in a small workshop will be much easier than a granulator;
- A simpler structure means a more reliable design;
- The productivity of such a machine will be much lower, and if granulators start at 300 kg/hour, then screw granulators will have a capacity of up to 300 kg/hour. Of course, it can be done with greater productivity, but it will be a very large machine;
- A much simpler die that can be made more easily on a regular lathe.
What it is
An extruder is used to process grain crops into compound feed, which is much easier to digest in the stomach of animals. Processing is carried out using a press under a pressure of 60 atmospheres and at high temperature. The result is a product shaped like 20-30 mm corn sticks, but with a dense structure.
Apparatuses for preparing feed exist with different power ratings, and the volume of product produced depends on it. For a small farm, a device with a productivity of 25-45 kg/h is perfect - the price of such a device starts from 47 thousand rubles. But a large farm will require more powerful models capable of producing up to 1.5 tons per hour and they cost from 160 thousand rubles.
Extruder device
Due to high prices, equipment for processing products into mixed feed, even second-hand, is available to a narrow circle of consumers. But if you make an extruder for feed with your own hands, you can save a lot. Only in this case you need to study in detail the structure of the unit, the principle of operation, and also have all the necessary spare parts available.
Diagram of a large extruder
The design of the device includes the following elements:
- frame - serves as the basis, all the details are fixed on it;
- drive unit;
- belt;
- loading capacity;
- cuff;
- dosing screw with separate drive;
- gearbox;
- receiving tank;
- motor;
- injection screw conveyor;
- Control block;
- carved blade;
- washer;
- adjustment key.
Operating principle
In a homemade extruder, the main function is performed by the pressing mechanism. The element includes a discharge screw unit mounted in the cylinder. The blade block gives the product the shape of oblong sticks.
The functions of the electrical appliance are not limited to pressing feed. With its help, you can grind grain, carry out heat treatment and disinfection of feed, and mix different components into a single mass.
The design of the injection screw includes:
- outer part;
- internal;
- heating washers;
- outgoing auger.
Each unit is installed on a stud with a left-hand threaded part and covered with a housing made of metal material. Thanks to the keys, the revolutions flow from the main shaft to the combined auger. All components are firmly fixed to the frame.
Detailed extruder design (download)
The housing element is equipped with a hole, and the receiving part is mounted to it. The internal area is equipped with longitudinal grooves, due to which all feed components are mixed along the longitudinal side of the axis.
A pellet regulator is installed on the output part; its design includes:
- matrix block;
- output housing;
- blade pressed by a spring element to the matrix block.
The rotation of the shaft with the blade is carried out by means of a rein. You can monitor the temperature using a thermocouple mounted on the frame. The grain extruder operates from electrical voltage. But there are already modifications that run on fuel.
Making an extruder for feed with your own hands
If you have the necessary material, parts and tools, you can make an extruder with your own hands. Let's look at how to get a low-performance model.
To do this you will need:
- electric motor with a power of 2.2 kW at 3,000 rpm;
- gears from a tractor box - parts from YuMZ would be an excellent option;
- spring 8 mm;
- rod with a cross section of 5 cm;
- welding equipment.
Step-by-step work on making a feed extruder with your own hands:
- To obtain a cylinder, you will need to weld the tractor gears together. As a result, a spare part with a cross-section of 625 mm should be produced. Next, a spring with a diameter of 8 mm is mounted on the hydraulic cylindrical rod. Weld all the parts; if the seam is uneven, treat the area with a grinder.
- Using turning equipment, grind 2 axle boxes that will be used for the auger and gearbox. Weld the auger, shaft element and axleboxes into a single piece, and do not forget to insert a bearing between the last parts.
Blanks in the form of axle boxes
- The equipment head is mounted on the screw; it will act as a regulator of the die to which the nozzles are welded.
Workpiece on auger
- The auger is covered with a housing, all parts are assembled and fixed to the frame, an electric motor, belts and a starting part are also mounted. A loading container is installed on top.
In general terms, a homemade extruder is similar in external and functional characteristics to a household electric meat grinder.
VIDEO: Making a screw granulator with your own hands (Part 1)
How to use a homemade design
A grain granulator assembled with your own hands before large-scale production requires preliminary testing and verification work. Equipment should be tested in a safe environment.
Homemade extruder for the production of animal feed
- The first thing that needs to be checked is the quality of all connections, as well as fasteners and the maximum level of lifting to the stop.
- Then the device is fixed on a flat, stable surface. If the coating is shaky, the device may not perform its functions properly.
- Connect to a power source, start and leave for a few minutes to fully warm up the system. To prevent the elements from rotating in vain, you can check by passing a light product in the form of flour or cake from sunflower seeds through the mechanism. The correctness of the form determines whether the device has warmed up sufficiently.
When the “sausage” shape becomes smooth and dense, then the unit is ready to work with grain
- After the feed comes out in the desired shape, you can add the grain product. The supply of grain must be regular without stopping; the mechanism must not be allowed to function idle. You should also add raw materials in even portions so as not to load the system and create a jam.
- At the output, you need to adjust the feed fraction by periodically tightening the bolt and reducing the hole in the spinneret plate.
- At the end of the productive process, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the internal components from product residues. To do this, you do not need to disassemble the device; just pour the seed shells into the equipment. This raw material is capable of well collecting grain product particles due to the oils it contains.
- Reduce the rotation level to gradually cool the mechanism components. If you need to disassemble the device, you should wear heat-protective gloves, there is a risk of getting burned.
The homemade device is capable of producing up to 40 kg/h of feed. The level of performance depends entirely on the degree of motor power that is included in the design of the equipment. For personal use, such processing efficiency will be sufficient.
Mechanized processing of raw materials makes it possible to fully provide livestock with compound feed, while reducing the cost of purchasing factory-made feed. In the process of preparing feed pellets, you can use a variety of grain products with additives, enriching the diet with various microelements and macroelements, which are so lacking in regular feed.
VIDEO: Making a screw granulator with your own hands (Part 2)
Granulator drawings
Drawings and videos of a granulator from a meat grinder with your own hands show that this is a very simple device. Even beginners can handle its production. It is convenient to use a meat grinder as the basis for the unit precisely because it requires minimal modification. When creating a granulator, you only need to remove unnecessary parts of the device and secure some additional elements.
The advantage of the meat grinder is the presence of a ready-made durable screw mechanism
The dimensions of a homemade granulator are determined in accordance with the dimensions of the meat grinder. The main attention should be paid to the matrix; it should fit tightly and without play into the unit body. During the manufacture of the device, the conformity of all fastened parts to each other is checked. A pulley on one side and a cutting knife on the other must be securely attached to the auger.
The do-it-yourself granulator is compact and suitable for installation on a table in the utility room
Technical features of extruders
The device consists of several parts, and is divided into three sections:
- The first is responsible for receiving raw materials,
- In the second, plasticization and compression occur,
- In the third - pressing.
Grain processing in industrial extruders occurs at high temperatures: from 110 to 180°C, and pressure above 40 atmospheres. Such conditions are necessary for the breakdown of fiber, proteins and starch contained in whole grains. The whole process takes only a few minutes, which means the split protein does not have time to coagulate.
Another advantage of extrusion is the production of clean and safe feed: almost all types of bacteria and fungi die during heat treatment.
The grain extruder is equipped with a special chamber in which the products are pressed. It also contains a shaft with screw pressing, intermediate and feeding elements. The power of the device depends on the engine and rotor, which is responsible for the operation of the cutting unit.
Extruders with barrier type screws
Barrier type augers (Fig. 21) are double-cut augers. This type of screw is mainly used for high-performance extruders.
The operating principle of all barrier augers is largely similar. The barrier zone begins at the point where the barrier flight is placed on the auger. The gap between the barrier turn and the cylinder is larger than the gap between the main turn and the cylinder. The size of the barrier gap should ensure the movement of the polymer melt over the barrier and prevent the movement of solid polymer particles. As a result, the solid material remains on the active side of the barrier coil, and the polymer melt on the passive side. Thus, the barrier coil leads to phase separation, separating the solid material from the melt (Fig. 22). Because solid material can plug the channel, melting must begin before the barrier zone begins to allow the barrier coil to be used.
As the screw moves, the cross-sectional area of the channel for moving solid material decreases, while the cross-sectional area of the channel for the melt increases. At the end of the barrier zone, the melt channel occupies the entire
Rice. 21. Barrier type screw
Rice. 22. Phase separation in a barrier screw
cross section. This geometry ensures complete melting of the solid material. It is permissible for a solid material to cross the barrier gap, but only if its particles are reduced in size so much that they can melt quickly enough. This configuration ensures optimal pellet melting. Another advantage of the barrier design is that flow through the barrier gap occurs at a relatively high shear stress, which ensures active mixing of the melt.
Types of homemade extruders
Industrial models of the device start at 45,000 rubles in price, which is not always acceptable for small farms and private farmsteads. To prepare complete and healthy feed for livestock and poultry, many farmers have learned to assemble the device themselves. There are several ways to make an extruder with your own hands:
- For large volumes of raw materials,
- From spare parts for agricultural machinery,
- From a vacuum cleaner.
Before you start manufacturing, you need to find diagrams and drawings. They will help you understand the intricacies and nuances of fastening and location of the main working units.
A homemade extruder will not only be cheaper. It can be made in a size suitable for the needs of the farm, equipped with additional figured knives or several matrices.
Introduction
As they say, to each his own. Some people make tens of tons of pellets per day in a large modern production facility, while others need an ordinary small granulator for processing straw, sawdust or other waste. This is the small granulator we will look at today.
I would like to say right away that there should be a sieve in front of the press, or at least a mesh and a magnet, which will separate the large fraction from the small one and sort out metal impurities.
There are cases where nuts, keys, and metal objects get into the granulator; pebbles and pebbles may come across during feed processing. This immediately leads to failure of some parts of the extruder, and maybe even to its complete failure. Therefore, it is cheaper to play it safe and reduce the likelihood of getting something that shouldn’t.
Extruder for large volumes of feed
This device consists of:
- Receiving bunker,
- Motor and drive,
- Frames,
- Gearbox,
- cuff,
- cutting unit,
- Dosing screw with drive,
- Cylinder.
The chamber of the pressing unit is a cylinder into which the injection screw is inserted. The auger is divided into three parts: initial, middle and outlet. For greater strength, each of them is secured with a stud with a left-hand thread. The unit is covered with a casing made of steel sheet.
The frame is welded from a corner or pipe sections. The dimensions depend on the planned volumes of processed raw materials and the length of the cylinder. The pressing unit is installed on the frame and secured with several bolts. Next, we begin to manufacture the receiving hopper. Usually it is welded from steel sheets, and a hole is made in the lower part under which a tray is placed. Through it, the raw material flows from the receiver to the supercharger screw. To move the grain, longitudinal recesses are made in the lower part of the body. At the end of the screw section, a cutting unit is installed to regulate the size of the granules. It includes:
The knives are pressed against the matrix by a spring, and the shaft rotates using a drive and a driver. The finished product comes out through the holes in the matrix and is cut with knives according to the specified parameters.
The feed extruder processes grain only at high temperatures created by the operation of the motor and gearbox.
They are connected to the shaft and bow housing by a chain drive and attached to the frame. For safety, the electrical assembly can also be covered with steel cuffs. Temperature regulation is carried out by changing the position of the matrix, and control is carried out with a thermometer. Install it next to the cutting element.
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a homemade granulator
The first thing we need to start with is, like any other event, creating drawings. On the drawings we describe how and what will happen.
What kind of engine will we have, how will it be located, and what do we generally need to make a mini granulator press. We draw everything out on paper so that there are fewer mismatches later.
In addition, do not forget that you will need to make a matrix, a lid and a knife for the meat grinder. To do this, you will need to take the dimensions from the mesh and make a matrix of the same diameter. When making the matrix, you need to take into account that it should fit almost closely to the worm. Therefore, part of the matrix should be recessed. If the ribs in the meat grinder get in the way for this operation, they should be removed.
So we begin assembling the granulator from the place where it will be located. We will need our sturdy table. We firmly attach our future press to it. Durable means bolted, for this you will need to drill holes in the legs.
After this we make the matrix. How to do it correctly is shown in the video below:
Next, you will need to sharpen a new cover for the matrix, since the old one most likely will not fit due to its increased thickness. You need to sharpen the lid with an allowance so that if you decide to increase the thickness of the matrix, you do not need to make a new lid again. After the lid is machined, you can weld pieces of 6 mm wire to it or cut grooves with a grinder. This way it will be easier to twist it by hand.
There are many versions of a pellet knife, and here are just a few of them:
- There is no need for a knife at all;
- You can drill a hole in the screw of the meat grinder and make a screw there, at the end of which a knife will be attached;
- You can weld a thin bolt onto which the knife is screwed.
Ultimately, it's up to you to decide. Our next step is to install the pulleys. Here I think there should be no problems if you are a person with a head.
The last step is to install the engine and tension the belt. We remember that you need to tension the belt so that it can slip if something happens, and the engine does not burn out at this moment.
We carry out commissioning and completion of our mechanism.
Extruder made from spare parts for agricultural machinery
To make this device, you must have:
- Electrical engine,
- Gears from a tractor gearbox,
- Rod, diameter 5 mm, from a hydraulic cylinder,
- Wire, 8 mm thick,
- Sheet metal.
To make a cylinder, several gears are welded together. The result should be a screw with a diameter of about 6.25 cm. Next, a wire is wound onto it at variable pitches. The step width gradually decreases from 2.4 cm to 2 cm. All elements are welded, and the seam is cleaned with a grinding machine.
The next stage: turning the axle boxes on a lathe. One is made for the auger, the second for the gear shaft. When the elements are ready, the parts are welded together in the following sequence: shaft, axle boxes, bearing, auger. The extruder head is attached to the latter using a die.
The assembly of the feed extruder begins with welding the frame on which the motor is mounted. It is connected to the working unit and the starting element using a chain drive. A loading hopper is placed on top: it can be either a bucket or a box welded from iron. At the opposite end, a form is installed to compress the processed mass. Passing through the die, the grain is pressed through the holes and enters the dispenser.
A grain extruder operates on the principle of a meat grinder, and the size of the granules depends on the shape and size of the holes in the die.
What tools and materials will be needed
To make a screw granulator from a meat grinder, you will need to prepare:
- workbench or frame on which the unit will be installed;
- lathe for metal processing;
- grinder;
- welding machine;
- metal mechanical meat grinder - Soviet or modern;
- 220 or 380 V motor;
- knife for cutting pellets;
- two pulleys with dimensions 1 to 2 - for mounting on the engine and on the screw mechanism;
- belt for connecting the motor to the meat grinder;
- drilling machine;
- metal blank for making a matrix.
Important! You will also need fastening elements - bolts and nuts, with which the knife, disk with holes, screw and pulleys will be connected to each other.
Extruder from an old vacuum cleaner
For production you will need:
- Housing and motor from a vacuum cleaner,
- plywood sheet,
- Steel blank for knives,
- Metal disk,
- Wooden pins,
- Fasteners and bushings.
This device is not very powerful, so it is most often used to prepare feed for a small number of poultry, rabbits, piglets or small cattle.
How to make a grain extruder: a square is cut out of a sheet of plywood - a base with a side of 30 cm. A motor is installed on it so that the shaft is 4 cm below the base. For the manufacture of knives, steel grade STZ or higher is used, or they are machined from car holders. The thickness of the knife should not be less than 1.5 mm, and the length and width should not be less than 20 * 1.5 cm. The knife should be sharpened in the direction of the rotating axis. For greater efficiency, the workpiece is shaped like a propeller or the angle of the corner edges is changed.
To attach the cutting element, a hole is drilled on the motor axis, and a regular bushing acts as a fastening element. The working chamber is made of metal sheet. Container dimensions: 70*6 cm. The sheet is bent into the shape of a cylinder, and the upper and lower parts are bent outward. Flanges 1 cm wide should form. They are needed to secure the chamber and hold the sieve. Three pins are installed at the bottom of the cylinder.
The mesh size of the sieve determines the size of the finished granules. The smallest is used to obtain feed flour. A receiving hopper with dampers is welded above the working chamber. With its help, you can regulate the volume of supplied raw materials.
Recommendations for use
The grain extruder is installed on a flat, flat surface. It is advisable to use the device in a room with low humidity and good ventilation. The grain is fed evenly and constantly, otherwise the compartment with the press will be overloaded. To adjust the size of the finished granules, change the sieve or tighten the matrix bolt.
Finish the work by gradually reducing the speed. After each use, the device must be disassembled and washed to avoid clogging of the working and cutting units with particles of dried food.
My books and services
Just recently I published a book. An excellent guide for those who want to organize not just a home press, but a large-scale production of pellets. The book gives tips on the technology that I developed myself, through trial and error. More details about the book can be found in the “MY BOOKS” section.
In addition to the book, I can offer my services in selecting specific equipment for you, I can advise on how and what is best to do to avoid any problems during the operation of the equipment. In order to contact me, you need to contact support (see top menu).
Good luck and see you again, Andrey Noak was with you!
How to make an extruder for feed with your own hands
The life of a farmer is full of worries, as many people know. You can make hard work easier with the help of modern technology or machines. The feed extruder is designed for preparing pet food of different qualities and in different quantities. But not everyone can purchase it for the farm due to its significant cost. A do-it-yourself feed extruder will significantly reduce costs and provide you with an excellent household assistant.
Is it possible to make such a unit with your own hands? Let's try to figure it out.
What is an extruder used for?
Using such a unit, you can process grain into animal feed with high digestibility. Any grain, even not the first freshness, can be processed in an extruder under pressure (no more than 60 atmospheres) and exposure to high temperatures (up to 1600 degrees). The output is products resembling rods or flagella with a diameter of about 3 centimeters . The power may vary depending on the desired quantity of the final product. A productivity of 20-40 kg/hour will be enough for a small farm, and for large farms - a device capable of processing 1-1.5 tons/hour.
Of course, you can prepare the food yourself, steam or boil the grain, adding different components to it. But its quality will be completely different, and animals will need more time to digest it. You need to spend a lot of time, production will produce a lot of waste. All these problems can be avoided by using a feed extruder.
Not everyone can afford to buy such a device, even if it has been used, due to its considerable cost. Many people use their imagination, ingenuity, and their own skillful hands - and creativity begins. Some craftsmen manage to assemble good examples of a household extruder with their own hands. Every owner can try to make one, the main thing is to familiarize yourself with the device and not be afraid to experiment .
Extruder tempering systems
According to the method of maintaining the temperature in the cylinder, extruders with steam, oil and electric heating are distinguished; with water and air cooling.
To prevent premature plasticization of the granulate and its sticking to the walls of the loading funnel and screw, the extruder loading zone is equipped with a cooling “jacket”. Either demineralized water or oil is used as a coolant (used in extruders intended, for example, for processing polyamides or copolymers of ethylene and vinyl alcohol, when it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the loading zone more than 100 ° C). Maintaining the temperature in the loading zone at a given level ensures the stability of the process of feeding and further processing of polymers.
Demineralized water is used to cool the oil in the extruder drive lubrication system.
When processing polymers, extruders with electrical heating are most often used, divided along the length of the extruder into several (5-10) independent temperature zones with individual thermal insulation. Typically, electric heaters - contact or infrared - are used to heat the extruder barrel. Contact electric heaters can be cartridge or tape type. Temperature conditions individually set for each heating zone are automatically controlled by thermoelectric converters and recorded by devices with light or sound alarms when they fall below the lower limit and rise above the upper specified limit.
There are two main sources of energy in an extruder - the mechanical energy of the rotating screw, converted into heat, and
heat from the heaters, with about 80-90% of the total heat provided by the rotating screw. High temperature when the melt is overheated in the melting zone can cause thermal destruction of the polymer. Heating zones in extruders, as a rule, have the additional function of forced cooling, which is necessary due to the self-heating of polymers under the influence of shear deformations in the molten material advanced into the front part of the cylinder when the screw rotates. This function is performed either by air fans or water-cooled cylinder “jackets”.
The water tempering system includes: a pump, a heat exchanger-cooler, an expansion tank, a filter in the soft water circuit, a filter on the cooling water supply pipeline to the heat exchanger-cooler, instrumentation, supply and return pipelines of softened water with solenoid valves for each heated zone extruder. Softened water circulates in a closed circuit (extruder zone - filter - heat exchanger-cooler - pump - extruder zone). An expansion tank is used to replenish the circuit with softened water. Cooling of the softened water after the extruder is carried out in a heat exchanger-cooler, into which chilled water is supplied in the summer, and filtered river water in the winter.
In the new type of extruders of the E10 and E11 series from Oerlikon Barmag, the heating zones can be equipped with cooling fans, which, in combination with aluminum belt heaters, ensures that the melt temperature of high-viscosity PET or PA is maintained at a given level even at maximum extruder performance (Fig. 39).
Rice. 39. Air cooling (a) and tape heaters (b) of the extruder
How the unit works
The extruder is composed of the following elements:
- frame base to which the entire installation is attached;
- drive;
- bunkers for loading grain;
- dosing screw and drive to it;
- injection screw;
- cylinder;
- receiving chamber;
- cutting knife;
- control center/controller;
- engine;
- gearbox;
- cuffs;
- belt;
- washers;
- nuts;
- adjusting key.
The main work is performed by the pressing unit. It is assembled from a forcing screw, which is inserted inside the collection cylinder. Using a matrix with a cutting knife, the resulting mass takes the form of sticks or flagella.
The injection screw consists of three stages:
- entrance part;
- middle part;
- output screw;
- heating washers.
All components are mounted on a stud with a left-hand thread. The part is closed with a metal casing. The keys transmit rotation from the main shaft to the composite screw. The entire structure is attached to the supporting frame using powerful bolts. The case has a window with an attached tray.
Inside the housing itself there are several longitudinal grooves that move components along the axis of the screw. A pellet regulator is located near the exit. It includes:
- bow body;
- matrix (disk), which regulates the process with a handle;
- roller and knife, which are pressed to the matrix by a spring.
Rotate the shaft with the knife through the leash with the fingers. The finished extrudates exit through the nose housing and the hole adjustment dial. The disk is fixed in one position with a bolt; when the position changes, the temperature and pressure level in the apparatus will change. A thermocouple placed on the housing allows you to monitor the temperature.
It runs on electricity, but new models are appearing that run on liquid fuel. Warming up occurs gradually . At the first stage, while the extruder is heating up, cake or flour is loaded into it. The grain is fed only when the system is well heated; it breaks and turns into sticks only at high temperatures and strong pressure.
Extruders with degassing devices
In extrusion lines, mainly two methods of evacuation are used: evacuation of the material in the loading hopper and in the extruder barrel.
There has recently been increased interest in the design of loading vacuum hoppers due to the increase in the production of products made from filled thermoplastics, especially those that are processed in the form of powders.
When processing thermoplastics, water evaporates, which contributes to the formation of a cellular structure in the material and a sharp decrease in the strength of the composition. Air bubbles act similarly, so the use of vacuum loading hoppers for extruders in extrusion lines when processing polyethylene or polypropylene with the addition of 15-40% mica, asbestos, kaolin or soot contributes to a significant increase in the mechanical properties of the resulting products.
In Fig. Figure 28 shows a design diagram of a vacuum system for an extrusion line with two hoppers from Dr. K. Schmidt (Germany).
Rice. 28. Design diagram for vacuuming bunkers
The source material is automatically fed by the loading device 7 through the spool 5 into the upper double-walled hopper 6, where it is mixed with a stirrer 8, heated by an oil heater 2 and an air heater 9. From the upper hopper the material enters the lower double-walled hopper 3, equipped with the same oil heater. Both bunkers are equipped with level regulators 4 and electro-pneumatic valves 10, through which vapors are sucked out by a vacuum pump 12. The lower bunker is equipped with a loading auger 1, rotating from a steplessly variable drive 11. Process monitoring and control devices are installed in the distribution cabinet 13.
Degassing extrusion screws are used to remove volatiles from the polymer in a continuous extrusion process. Extruders with screws of this type have one or more vent holes through which volatile substances are removed. The length of the vacuum zone is usually 2 D or 3 D. During the extrusion process, material particles pass through this section in approximately 2 s. It has been experimentally established that during this time all volatile components can be removed from the melt.
The most common purpose of vented extruders is to remove water from hydrophilic polymers. The permissible moisture content when processing most polymers by extrusion is less than 0.2%. Many polymers have an equilibrium moisture content at room temperature and 50% relative humidity that significantly exceeds this value, for example for PA - 3%, PET - 1%. To obtain high-quality products from such polymers, preliminary drying of the polymer or extrusion with degassing is required, which in many cases is preferable.
In Fig. Figure 29 shows a typical extrusion screw with degassing. The screw consists of five zones. The first three zones - feeding, compression and dosing - are similar to those of a conventional screw. After the dosing zone there is a sharp decompression, followed by an extraction zone, then a sharp compression and an injection zone. To ensure good degassing, two conditions must be met. Firstly, it is necessary to ensure zero pressure in the volume under the ventilation hole, and secondly, the polymer must be completely melted in this area. The zero pressure requirement is to avoid melt leakage through the vent.
The second requirement has several reasons. If the polymer is not completely melted in the dispensing area, a good seal between the vent and the feed area will not be achieved. This will not create a vacuum deep enough to remove volatile products. To increase the rate of gas diffusion and degassing efficiency, the polymer must be in a molten state and at a temperature 20–25 °C above the melting point. In addition, surface renewal occurs in the volume of the molten polymer, which also promotes degassing. Multi-filament screws with a large pitch in the extraction zone have an advantage in terms of degassing efficiency.
There are many options for more or less efficient degassing single screw extruders. Let's look at some of the most common designs.
Rice. 29. Typical degassing extrusion screw: 1 – feed zone; 2 – compression zone; 3 – dosing zone; 4 – decompression; 5 – extraction; 6 – compression; 7 – injection zone
In Fig. 30 shows a conventional extruder with a degassing zone. Volatiles travel with the polymer up to the vent. This type of degassing is called forward degassing. The depth of the channel in the degassing zone exceeds 0.4 D for large-diameter screws, and 0.3 D for small ones. In order to achieve frequent renewal of the surface, the degassing zone is usually made with multi-pass cutting, the angle of inclination of the turns is often increased from the generally accepted 17°66′ (rectangular profile) up to more than 40°.
An extruder with a bypass is often used (Fig. 31). Pushing the melt into the bypass is ensured by a section of the screw with multi-pass, oppositely directed fine cutting located between the dosing zone and the extraction zone. The polymer flows from the bypass to the beginning of the extraction zone. The polymer melt enters the degassing zone through numerous holes. This allows for increased surface renewal and improved degassing efficiency. The bypass has limiters to regulate the flow of material into the dosing area. Degassing through the back of the screw is used in extruders with loading of molten material (Fig. 32). The vent connector is located at least 1 D from the feed hopper to prevent melt from entering it.
Degassing through several holes is used when it is necessary to remove large amounts of moisture, reaction products and polymer decomposition. The most common two-stage extrusion screw is shown in Fig. 33.
Rice. 30. Degassing zone with multi-thread cutting
Rice. 31. Extruder with bypass
Rice. 32. Degassing via rear connector
The system has two ventilation holes. It is used, for example, for the extrusion of polypropylene and crushed polymer waste with the removal of up to 7% of moisture.
A three-stage vacuum process is also possible (Fig. 34, 35). In such cases, the polymer drying step is not carried out. Gases are removed from three zones of the twin-screw extruder 1 through suction pipes 2 with covers 3, ball shut-off valves 4 and electrical heating.
Degassing pipes are connected by pipelines 5 to the evacuation system, and pressure gauges 6 are installed to control the vacuum.
The vapor-gas mixture is sucked off by a liquid ring vacuum pump 2 (Fig. 36) through a preliminary separator 1, compressed in the pump and supplied through a discharge pipeline to the liquid separator (separator) 3, in which the gas is separated from the liquid. The purified gas is discharged to a vortex hydrofilter 4 for additional purification and then released into the atmosphere.
Rice. 33. Two-stage extrusion screw
Rice. 34. Extruder with three vacuum zones
Rice. 35. Extruder degassing tubes
The separated liquid is again supplied as working liquid to the liquid ring vacuum pump. When the set temperature value (15−25 °C) set on control valve 5 is exceeded, softened water is supplied from the network to mix with the working fluid in order to reduce its temperature. Water saturated with NMS is periodically drained into the collector through an overflow system in the liquid separator and enters industrial wastewater tank 6. If there is a small amount of NMS and decomposition products, the vapor-gas mixture can be directly released into the atmosphere.
The company Reifenhauser (Germany) points to the promise of a cascade extruder system. Two separate extruders are used, positioned in series or at an angle (usually 90°) to each other, equipped with individual drives and screws, thereby separating the extrusion process into two stages. One extruder ensures the processes of loading, heating and plasticizing the material, i.e. transition of the polymer from the solid phase to the melt. Another extruder ensures the processes of mixing and dispensing the melt, i.e. used to create pressure.
Rice. 36. Diagram of the extruder vacuum system
The first extruder is often multi-screw, the second is usually single-screw. In such systems (Fig. 37), degassing occurs between the first and second extruders. The efficiency of degassing can be improved by forcing the polymer melt through the holes of the die before entering the second extruder. The main advantage of a cascade degassing system is the ability to control the pressure in the second stage by adjusting the output of the first stage. This system is often used when processing polyvinyl chloride or producing coextruded films from PE, PP and other polymers.
A degassing system design is known in which volatiles are removed through a screw rather than through a vent in the cylinder. The screw has a hollow core connected to a transverse degassing hole in the degassing zone (Fig. 38). Volatile substances are extracted through a rotating nipple on the back of the auger. This scheme is also used in barrier screws. Eastman Kodak (USA) has a patent for a barrier auger with a vent located approximately two diameters from the end of the feed zone, between the main and barrier flights.
Rice. 37. Scheme of cascade degassing
Rice. 38. Ventilation through auger
Provides higher productivity when processing powdered polymers that are prone to the formation of air pockets.
The ventilation hole is positioned in such a way as to avoid clogging it with polymer, which can lead to a complete stop of the process. The plug is removed by air blast by increasing the pressure in the central hole of the screw. This type of degassing is not widely used.
Is it possible to make an extruder yourself?
You can do many useful things with your own hands if you have a set of tools and the necessary parts on your farm. Many drawings can be found on the Internet or by reading the instructions before the factory machines. To create a unit yourself, you cannot do without:
- electric motor (for example, 2.2 kW, 300 rpm);
- gears from the tractor box;
- rod from a hydraulic cylinder (diameter 50 mm);
- wire (8 mm) or springs;
- turning and welding machines.
After preparing the tools and workpieces, they proceed directly to the process of manufacturing the unit .
- To obtain a screw cylinder, two gears are welded together. The result is a part with a diameter of 62.5 mm.
- To make an auger, a wire is wound into three balls onto the hydraulic cylinder rod, each ball must be narrower than the previous one. Wind it as you feel comfortable. The presence of a spring greatly simplifies the task.
- All components should be boiled. If the seam is uneven, you need to trim it using a grinder.
- Turn a couple of axle boxes on a lathe (gear shaft and auger).
- Weld to connect the axle boxes, shaft and auger into one unit, without missing the thrust bearing between them.
- An experienced turner can help you make high-quality parts in a short time.
- The extruder head is fixed to the screw. Its adjustment will be carried out using a die to which the pipes are welded.
- The auger is hidden in a steel casing and is made separately.
- Next, we begin assembling the entire unit. The engine is mounted on the frame and connected by belts to the starting part and the extruder part. At the top there is a bunker for loading grain. Next is the loading part, into which the grain enters after passing through the bunker before entering the three-stage feeding system, gap, and press.
- The spinneret should compress the grain mass to the maximum and dispense the resulting product into the nasal dispenser.
A DIY feed extruder can operate continuously for a long time without consuming too much electricity. The operating principle is reminiscent of a regular meat grinder, only in the end you get not minced meat, but harder sticks. The size of the finished feed depends on how large the spinneret holes are.
Additional equipment for extruders
A number of companies offer additional equipment to equip both new and existing extruder plants. For example, the Expac system from Maag Pump Systems AG (Switzerland) consists of a pump, drive, adapter (coupling device), a set of instruments, a static mixer, a control system, and optionally a melt filter (Fig. 40). The system can be supplied either as individual components or assembled on a mounting frame.
As the main element, the system includes a booster gear pump. The pump installed between the extruder and the filter creates the necessary melt pressure at the outlet, smoothes out possible pulsations and pressure peaks created by the extruder, for example when it wears out or the heterogeneity of the raw materials used, due to its damping effect (Fig. 41). In addition, the melt temperature in the extruder decreases (ΔТ = ΔТ1 – ΔТ2), which increases the service life of the extruder and ensures stable melt quality. The pump transports the melt to the molding tool more evenly, and therefore ensures a higher quality of the molded material. A static mixer in the melt line after the pump homogenizes the melt flow both in composition and temperature.
It is most advisable to use this system in the production of flat and tubular films, composites and extrusion of parts from them.
Rice. 40. Schematic diagram of the Expac system
Rice. 41. Optimizing the extrusion process using a booster pump
506
Some useful tips
The homemade device should be thoroughly checked and tested before use.
- First you need to check the reliability of all connections and fasteners.
- The unit must be installed on a flat surface; any changes will disrupt the operation of the extruder.
- Connect to the mains and let the system warm up. At this time, you can pass a small amount of flour or sunflower cake through the press, observing the shape of the mass that comes out - this way you can understand whether the system has warmed up enough.
- Next is the grain supply. It must be constant to prevent the device from idling. Grain should be poured without excess, otherwise congestion may occur.
- At the outlet, the fraction of the exiting product is regulated by gradually tightening the bolt and reducing the gap of the die part.
- Once recycling is complete, the inside of the mechanism should be cleaned. Use the same flour or cake for this purpose - they will absorb the remaining grain and oil.
- To ensure that the mechanism cools down faster, clean at minimum speed. Disassembly should be carried out only with gloves to avoid burns.
The extruder, made by hand , can process no more than 40 kg of grain per hour. For a small farm this is quite enough. Food prepared by mechanical processing provides complete nutrition for pets, reducing the cost of purchasing food and reducing the time for preparing it.