Factors in the location of ferrous metallurgy are determined mainly by the geography of mineral deposits necessary for the metallurgical process. From the standpoint of economic feasibility, metallurgical plants appear in the vicinity of iron ore deposits. This is a general rule.
However, there are exceptions to this. The absence of coal basins and powerful power plants near iron ore deposits excludes the possibility of building a metallurgical plant in such an area. Ideal conditions are considered to be the concentration of all factors in one place: the presence of ore, coal and electricity.
The choice of area for the construction of a metallurgical plant plays an important role, because new cities grow around the new enterprise, infrastructure develops, and the economic activity of small businesses increases. Most metallurgical plants play a city-forming role in their locations.
The importance of metallurgy for economic development
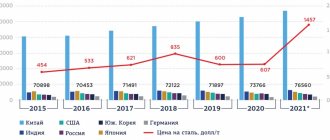
Russia is one of the world leaders in steel production. The metallurgical industry of the Russian Federation constitutes a significant part of the country's gross domestic product. According to this indicator, it is second only to the oil and gas sector.
The export of metal products provides stable foreign exchange earnings to the Russian economy.
The metallurgical complex consists of ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy. Products produced by metallurgical plants are used in a huge number of sectors of the economy. Ferrous metallurgy indirectly creates jobs in related industries.
Rolled metal is the basis of mechanical engineering and construction. In the production of many parts, housings, reinforcing elements and fasteners, steel is simply irreplaceable in terms of performance characteristics.
To understand the principles by which the location of new metallurgical plants is selected, you need to understand the features of steel production technology.
Features of the metallurgical process
A metallurgical plant is an enterprise with a full metallurgical cycle, including all three stages of the metallurgical process: iron smelting, steel production, rolling.
There are two types of metallurgical plants:
- plant producing steel and rolled products;
- a plant where iron and steel are produced.
The technological process for the production of steel and rolled products is a complex sequence, the stages of which are as follows:
Mining of iron ore, coking coal and limestone;
- ore dressing at mining and processing plants;
- coal coking;
- smelting cast iron in blast furnaces;
- steel production in oxygen converters or open-hearth furnaces;
- rolling steel ingots on crimping mills;
- rolling of blooms and slabs on section rolling, sheet rolling and pipe rolling mills.
The production of rolled metal is impossible without the presence of powerful energy resources. This factor stimulates the development of the electric power industry and other related sectors of the economy. Russia's electric power potential ensures the production of steel and rolled metal at dozens of factories and mills.
The blast furnace process requires specific carbon-containing fuel. This need is met by coke production.
The factors for locating ferrous metallurgy enterprises are determined by its basis – raw materials.
Raw material base
Domestic metallurgy is developing thanks to the wealth of minerals that fill the bowels of the state.
Numerous deposits of coking coal fully satisfy the needs of metallurgists. Most Ural plants operate on coal supplied from the Kuznetsk coal basin (Kuzbass).
In terms of iron ore reserves, the Russian Federation is now in first place in the world. Its territory contains about 19% of the world's reserves of this mineral. Large deposits of iron ore are called an iron ore basin. The largest examples of them in the post-Soviet space are:
- Krivoy Rog iron ore basin;
- iron ore basin of the southern Urals;
- Kursk magnetic anomaly.
Experts develop iron ore deposits using open (quarry) and underground (mine) methods.
The feasibility of developing deposits of coal or ferruginous quartzite is determined by the depth of the deposits, transport accessibility of the deposit, as well as technological parameters.
Having considered the factors (not only raw materials) influencing the choice of location for metallurgical plants.
Aluminum industry in Russia
Deposits of bauxite, from which aluminum is obtained, are located in:
- Ural;
- North;
- North-West;
- in Eastern Siberia.
The bulk of the aluminum industry is located in:
- Central Federal District;
- Northwestern Federal District;
- Southern Federal District;
- Volga Federal District west of the Urals.
| Locality | Raw materials used |
| Boksitogorsk | Tikhvin bauxite |
| Volkhv, Pikalevo | Khaba nephelines |
| Kamensk-Uralsk, Krasnoturinsk | North Ural bauxites |
Criteria for choosing the location of metallurgical enterprises
The greatest economic effect is achieved when enterprises and interrelated industries are concentrated in one territory. This gives metallurgical plants significant savings on transportation costs.
It also greatly simplifies the organization of production management:
- Metallurgical plants, due to their technology, require large volumes of water resources. This makes it mandatory for them to be located near bodies of water.
- The environmental factor is also important. Metallurgical plants cannot be built near environmental protection zones. Their design must take into account the wind rose of each specific area.
- Electrometallurgical plants require large amounts of electricity and scrap metal to operate. Such enterprises are usually built near powerful hydroelectric power stations.
Industrial zones with metallurgical plants should be located at a reasonable distance from residential areas. Under the influence of these factors, design institutes are developing new metallurgical enterprises that comply with all environmental protection standards.
Among the many factors for the location of ferrous metallurgy, a special place is occupied by its proximity or distance from large river and sea ports. Export deliveries are most feasible when products are shipped by sea, which is the cheapest. Proximity to the river system is one of the main requirements for the construction site of a metallurgical plant.
Ferrous metallurgy
Metallurgy development centers in Russia
Most Russian metallurgical enterprises are located in the Urals. This region accounts for up to half of the total volume of steel produced. The main industry giants are located in Magnitogorsk, Chelyabinsk and Nizhny Tagil.
In the European part of Russia, large plants are located in Lipetsk, Cherepovets and Stary Oskol. In the latter, by the way, there is the only electrometallurgical plant in Russia.
In the West Siberian region, metallurgical production is represented by two large plants in Novokuznetsk. The factors for the location of metallurgy in Siberia are determined by the presence of cheap Kuzbass coal in this territory.
The geography of the location of metallurgical enterprises is quite extensive. The general rule for the three named centers of metallurgy is the attraction to sources of raw materials and fuel.
Metallurgy of non-ferrous metals has its own characteristics.
How does this industry differ from ferrous metallurgy in terms of its location factors?
Ferrous metallurgy
Ferrous metallurgy is an important industry, specializing in the production of ferrous metals. A wide range of products are used in various fields of activity. Russia ranks 5th in the production of steel and rolled metal (the main types of metallurgical products). The production of ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy throughout the world is constantly increasing. This is due to the fact that the demand for products is rapidly increasing.
Companies that operate in the iron and steel industry are classified into several categories:
- Full cycle. Enterprises of this type carry out all stages of production, from the extraction of raw materials to the sale of finished products.
- Conversion. One of the stages is separated into a separate production. These may be subsidiaries of a large concern or plant.
- Small ones. This type represents metallurgical workshops, which are components of large complexes.
There are several regions producing ferrous metallurgy. Each of them has its own characteristics. In each of these regions there are enterprises that specialize in the extraction, processing of raw materials and production of ferrous metals.
Volumes and features of production
The total production is about 9.8%. The ferrous metallurgy industry includes more than 1.5 thousand organizations and enterprises. The dynamics of product exports is increasing every year. Metallurgical plants are traditionally located at a relatively short distance from the places where iron ore lies.
The production volumes of ferrous metallurgy products are quite large. There are more than 34 enterprises located in Russia. The largest plants are:
- Oskolsky;
- West Siberian;
- Novolipetsk;
- Cherepovetsky;
- Magnitogorsk.
Features of ferrous metallurgy production:
- consumption of large quantities of raw materials;
- high labor intensity of the process;
- high energy consumption;
- variety of products;
- high production costs.
Despite these difficulties, the industry is developing, because the demand for metal products is not decreasing. Russia produces metal that is not only used within the country, but is also exported.
Placement factors
Factories are located either in close proximity to sources of raw materials. The main factors for locating ferrous metallurgy enterprises are:
- proximity to factories where ferroalloys and electric steel are produced;
- availability of fuel and natural resources.
Most production sites are located in the Moscow region. Ferroalloys are produced in special furnaces or in factories using the electrothermal method.
Mining and processing companies are located near sources of raw materials. Coke and gas enterprises operate as part of full-cycle metallurgical concerns. Full cycle enterprises are based where there are fuel and raw materials resources, as well as sources of electrical energy.
Geography of ferrous metals metallurgy
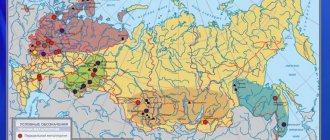
Let us consider the geographic features of the ferrous metallurgy industries in Russia and the areas of development. Our country is well supplied with raw materials for ferrous metallurgy, but the distribution of deposits across the territory is uneven.
- The Russian Federation has large reserves of iron ore.
- In Yakutia, promising deposits are located in the Aldan province, as well as in the Olekmo-Amgun region.
- Deposits of chromium and manganese are insignificant. Manganese occurs in the Sverdlovsk and Kemerovo regions, and chromium occurs in the Perm region.
The dominant producer of steel and cast iron is the Ural Metallurgical Base, which has been operating since the 18th century.
Source
Impact of ferrous metallurgy on the environment
The main substances that enter the air and pollute it include products formed during the combustion of fuel. Iron oxide emissions also have a negative impact. Dust is generated as a result of loading and unloading, as well as during batch preparation. Gas formation and dust emission occur during the production of rolled metal and limestone roasting.
The trends and strategies for the development of the iron and steel industry are thought-provoking. The impact of this industry on the environment is enormous. It is necessary to develop effective measures to protect the environment and introduce technologies that would reduce the harmful impact on nature.
Industry development prospects
The demand for metal products is not decreasing. Metal today is used in various branches of human activity. Raw materials and finished metal products are used not only within the Russian Federation, but are also supplied to other countries. The industry will develop. Already, technological processes associated with the extraction and processing of raw materials are being modernized.
Source
In order to assess the market situation as accurately as possible for 2022 and the next two years, experts have put forward three forecast scenarios.
- Optimistic. The global pandemic will be stopped approximately by the end of 2022. First, world markets will recover, prices will stabilize, the Russian market will show a slight drop (about 5%), but after that it will continue to grow again.
- Pessimistic. If quarantine is forced to be extended, the market decline will become more severe and amount to 15%. A long production shutdown could even cause a financial crisis. And in this case, the market will begin to grow only in 2022.
- Base. This type of scenario is close to pessimistic. It also provides for a market decline of 10% by 2022, after which slow growth will begin.
According to experts, under such circumstances, large holdings that have a certain margin of safety and a wide range of products will have a great advantage.
Features of non-ferrous metals production
A distinctive feature of non-ferrous metal smelting plants is the high level of environmental pollution from their activities and the high energy intensity of the technological process.
Non-ferrous metals are distinguished by the diversity of their deposits. The geography of non-ferrous metal deposits is very extensive. “Give examples,” the majority of the population will say. These are mountains, rivers, and large ore deposits on the ground and underground. Gold and rare earth metals “live” in the sands. People can provide examples of some copper mines in the Urals, where copper is extracted from groundwater.
The metallurgical process for the production of non-ferrous metals is similar to the same process in ferrous metallurgy, although it has its own characteristics. The technological chain for the production of non-ferrous metals is as follows:
- ore mining and beneficiation;
- smelting in high temperature furnaces;
- pressure treatment.
Tin industry in Russia
A distinctive feature of this industrial sector is the territorial dispersion of the stages of the technological process.
Tin reserves are located in:
- Yakutia;
- Primorsky Krai;
- Chukotka Autonomous Okrug;
- Khabarovsk Territory;
- Sherlovogorsk field;
- Irkutsk region;
- Omsukchan and Khingan fields.
Almost all Russian tin, more than 95%, is smelted at NOC OJSC.
Metallurgical processing is focused on areas of consumption and routes for concentrates.
Criteria for choosing the location of non-ferrous metallurgy facilities
The geological factor is the main criterion influencing the location of plants for the production of non-ferrous metals. Due to the low proportion of useful components in non-ferrous metal ores, their transportation is not economically feasible.
This requires the location of factories in this industry in mining areas. Nickel production, for example, is strictly tied to the place of its extraction.
Such factors lead to the fact that production is located in unfavorable climatic conditions - in the Arctic Circle (Norilsk).
The development of non-ferrous metal deposits is often associated with a number of difficulties. Access to useful minerals is often blocked by a shield of waste rock and must be blasted. Such development requires the use of a large amount of equipment: excavators, conveyors, electric locomotives.
Aluminum production
The aluminum industry occupies one of the leading and unique positions in non-ferrous metallurgy. This fact is explained by the fact that higher quality raw materials (bauxite, nepheline) are used for metal production. The central territories where bauxite production is carried out are considered to be Boksitogorsk, Severouralsk and the Severo-Onezhskoye deposit.
Nepheline deposits are located in Kirovsk on the Kola Peninsula and in Goryachegorsk, which is located in Eastern Siberia. The difference between the minerals is that nephelines have a more complex composition. Main stages of the aluminum industry:
- alumina production;
- production of metal aluminum.
Such activities can occur both in one area and in different territories. Enterprises producing alumina try to locate as close as possible to the deposits, since this production is considered more material-intensive.
Aluminum plants are located closer to sources of mass and cheap electricity. Russia is second only to the People's Republic of China in the production of this metal. Comparative table of aluminum production in thousands of tons by countries for 2012 and 2016.
| Place | A country | 2012 | 2016 |
| 1 | China | 21500 | 31000 |
| 2 | Russia | 3950 | 3580 |
| 3 | Canada | 2900 | 3250 |
| 4 | India | 1700 | 2750 |
| 5 | UAE | 1800 | 2400 |
Areas where limestone and cheap fuel are found along with aluminum raw materials are considered optimal for the production of alumina. Such areas include Achinsk-Krasnoyarsk in Siberia and Severouralsko-Krasnoturinsky in the Urals. Enterprises for processing metals and alloys are located closer to consumers and are usually located in large industrial centers.
Problems and prospects for the development of metallurgy in Russia
A common problem of the Russian metallurgical complex is the need for modernization and technical re-equipment.
Domestic metallurgical enterprises are faced with the task of reducing the energy intensity of their production. The rapid growth of metallurgy in China requires Russian manufacturers to take effective measures to reduce costs.
Reducing costs while maintaining the quality of products is the only way to be competitive manufacturers in the global steel parts market.
Metallurgy in the Far East will develop thanks to iron ore deposits in the Aldan province and the discovery of coking coal deposits in Yakutia. The construction of full-cycle metallurgical enterprises in the Far East is due to the need to reduce the cost of metal for the local machine-building plants.
Railroad deliveries significantly increase the cost of rolled steel. This factor plays a negative role in the competitiveness of metal-intensive enterprises in the Far East.
Metallurgy of the Far East and Siberia
This territory accounts for 13% of ferrous metal production. Centers:
Novokuznetsk – Novokuznetsk Metallurgical Plant – produces railway rails. Until 2011, it bore the name KMK and supplied products not only throughout Russia, but also abroad. OJSC West Siberian Metallurgical Plant is located 20 km from the city. It ranks 5th in size among Russian metallurgical plants. Issues:
- wire;
- Common consumption goods;
- coke, rolled, metallurgical products.
Iron ore comes from:
- Khakassia,
- Mountain Shoria;
- Angara-Ilimsk basin.
Pipe metallurgy enterprises:
- Petrovsky iron and cast iron plant;
- JSC Amurstal – rolled steel;
- Krasnoyarsk Metallurgical Plant.