Methods of protection against metal corrosion are relevant. Because metal is one of the most popular materials used in the automotive industry. And although it has been successfully replaced in some areas, the main problem associated with the use of metal products is corrosion. Types and methods of protecting metal corrosion differ from each other.
Corrosion, destruction of metal as a result of electrochemical action. This is the dissolution of an electrolyte or chemical action in a moisture-containing or airy environment, as a result of which metals combine with chemical elements located in an airy or aqueous environment. Rust is the corrosion of iron and its alloys; the corrosion of other metals comes down to oxidation, the formation of oxides. Chemical corrosion occurs as a result of exposure to dry gases and liquids that react chemically with the metal.
Types of metal corrosion:
- processes are chemical and electrochemical
-by the nature of destruction, uniform and not uniform
- by type of corrosive environment: gas, liquid, atmospheric, soil
Chemical corrosion
Based on the reaction between metal and an aggressive environment. The result of this corrosion is the formation of scale on the metal, or in the case of copper, a green coating. This type of corrosion spreads evenly over the entire surface of the metal. Chemical corrosion does not affect metal as strongly as electrochemical corrosion.
Electrochemical corrosion
This is a process in which metals and alloys lose some of their electrons, they pass into an electrolytic solution formed on the surface of the metal in the form of ions, and the electrons replacing the metal atoms pass into the metal with a negative charge, a galvanic reaction is formed, resulting in the destruction of the metal . Metals used in construction are usually subject to electrochemical corrosion due to the presence of moisture on the surface of the metal, this is caused by a constant change in temperature, resulting in the formation of condensation.
Atmospheric corrosion
Atmospheric corrosion of metal is similar to the occurrence of electrochemical corrosion, due to the presence of air humidity. When humidity rises above 70 percent, intense loss of steel occurs. The corrosion process is also affected by the presence of aggressive elements in the environment such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide,
uniform across the surface , but it does not pose a great danger if it does not reach critical levels of metal damage. Uneven is the most dangerous because it can form separate areas of damage to the metal, which will lead to a significant weakening of the elements of the metal structure.
It is impossible to completely avoid corrosion processes, but it is possible to reduce the impact of these processes.
There are several types of corrosion control measures.
Technology for creating protection stations
Another technology for creating cathodic protection is connecting the element to external current sources. In most cases, for these purposes, special cathodic protection stations (CPS) are built, which consist of several elements - the main current source, anode grounding, various cables and wires connecting individual structural elements and auxiliary points with mechanical or computer control, which allow you to control the parameters .
Most often, this technology is used for objects located near power lines - these can be pipelines, various factory buildings, and so on. VCS can operate in multi-threaded mode - in this case they will serve several protection systems at once. On pipes, a practice has become widespread in which several separate blocks are placed on the pipes to distribute the current more efficiently. The thing is that in the case of long pipelines, in the places where the pipes are connected to current sources, special points with an increased level of electric field voltage are formed - because of this, damage to the pipes can occur. The use of such blocks allows electricity to be distributed evenly throughout the entire protective circuit.
Automation
Checkpoints can operate both manually and automatically:
- In the case of manual control, the change in voltage parameters is regulated by the operator. At the physical level, regulation is carried out by switching the operation of the transformer. The operation of the winding is regulated, which allows you to change the parameters of the electric current.
- In the case of automatic control, the change in voltage parameters is regulated by the device itself based on the parameters that were once set by the operator. At the physical level, control is carried out using special semiconductor thyristors. They turn on or off when the electric current parameters deviate from the specified parameters.
Methods of protection against metal corrosion
Methods of protection against metal corrosion are divided into technological, active and passive.
Active methods
Methods of protection against corrosion of metals involve constant exposure to the metal, these include methods of changing the corrosive environment. This is a decrease in soil acidity, a decrease in chlorine content in water. Protective protection also belongs to the active method; it consists of binding the metal to a contact material that is more susceptible to oxidation, it is called a protector and is essentially a lightning rod. Takes over electrolysis processes that affect metal rusting.
Technological techniques
This is when, during the production of metal, chromium, titanium, manganese, and nickel are added to the steel alloy, which help to obtain steel with anti-corrosion properties. For example, when chromium is added, a high-density oxide film is formed on the metal surface.
Passive methods
The metal is insulated using various coatings that prevent the formation of corrosion. Cathodic and anodic coatings are used.
Anodic coating
When applying anodic coating, a metal is coated with another metal with a large negative potential. This is usually zinc or cadmium. Currently, it is common to protect metal by applying a layer of zinc.
Cathodic coating
produced by metals with a more positive potential. When cathodic coating of metal, mechanical protection of the metal is observed. Tin-copper is used as a cathode coating. nickel. To coat metal, the hot method, spraying, metallization, galvanization are used. With the hot method, steel is placed in molten metal, which is coated with a thin layer. The hot method is used for tinning, coating metal with tin, and galvanizing.
Oxidation
Chemical methods of coating the metal are also used, this is oxidation, an oxide film is formed that protects the metal from corrosion, this process is also called steel bluing. You can also treat steel with anodization, which is the electrolysis of aluminum. Also through phosphating and nitriding.
Application of enamels and primers
The most accessible method of protecting metal is the use of special enamels and primers.
They provide barrier protection from the effects of harmful environmental factors; it consists of mechanical protection of the surface. Damage to the coating occurs when microcracks form, resulting in under-film corrosion. To prevent this, passivation of the metal surface is carried out using special paint and varnish coatings.
The composition includes special chemical agents. Such paint and varnish coatings include primers and enamels containing phosphoric acid and other inhibitory elements that slow down the corrosion process. More effective paint and varnish materials are those that provide protective protection. This is achieved by adding metals that create donor electron pairs to paint coatings, these include zinc, magnesium and aluminum.
To protect metal structures that are operated in an industrial atmosphere, special enamels are being developed that form moisture-protecting urethane coatings. To protect against constant contact with an aqueous environment, enamels are produced that can be applied to zinc, copper and other surfaces.
Currently, a wide range of anti-corrosion enamels are available on the market. One of the innovations is the coating of metal with fluoroplastic; it is chemically inert to almost all aggressive environments. Enamels based on it are applied with a brush, air or airless spray, to a cleaned metal surface. When using a particular material, it is necessary to take into account factors such as the type of metal, the conditions of its operation, production capabilities and the feasibility of use.
Corrosion treatment agents are used depending on the type of metal, the operating environment, and the loads acting on it. For each area of operation of the structure, standards are provided. The optimal method is metal processing in a factory. That is, the application of transport primer.
Before he gets to the construction site. The application of anti-corrosion materials provides only 20 percent of metal protection; the main factor influencing the quality protection of metal is its pre-treatment from dirt. rust, as well as any other substances that will interfere with the painting of the surface.
Components of cathodic protection
There are mandatory components without which protection simply will not function.
Cathode and anode
The cathode in our protection circuit is the car itself, it will serve as a minus. An anode can be any metal structure, plate, or any surface that is capable of conducting electric current, even wet asphalt. Without these two components, the electrochemical protection of a car against corrosion simply will not function.
From some experts you can hear about the potential difference and the degree of protection, which is determined by this indicator. Iron will be protected from corrosion at potentials in the range of 0.1–0.2 V. In fact, the distance between the anode and cathode can reach several centimeters and even meters. The greater the distance between the electrodes, the greater the potential difference should be. And the air will not conduct a small voltage current; the potential difference should be at the kilovolt level.
What really affects the effectiveness of a car's protection is the area of the anode. The larger it is, the better the car’s cathodic protection against corrosion will be.
Electricity
For the circuit to work properly, no electric current is needed between the two electrodes. Even if it does arise, it will be in the nature of a by-product. Such a current can be generated by a wet anode, wet car wheels, etc. And it will appear on the battery, which will discharge faster than usual.
To ensure that the installation of cathodic protection does not cause harm to the car, but works in the direction we need, we will need to connect the on-board system to the anode using an additional resistor. Such a device will limit the discharge of the battery if the anode is short-circuited to the cathode. The reason for this situation may be an incorrectly assembled circuit, failure of the anode, for example, complete oxidation up to decomposition.
Metal corrosion treatment
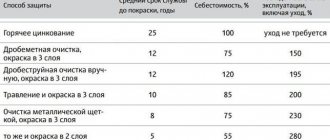
Mechanical cleaning of the surface using brushes, scrapers, as well as using power tools with various attachments
Sandblasting is the most effective method for cleaning surfaces, but it has a number of disadvantages, such as low productivity, the creation of dust, which disrupts working conditions at the construction site.
Hydrojet cleaning increases productivity, and the use of abrasive materials improves cleaning quality.
Chemical cleaning . It involves the use of special materials that are divided into washable and indelible.
Rinse-off chemical cleaning methods
Washable materials include a 5% solution of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, but when using these materials it is necessary to use a substance that slows down the chemical process, the so-called inhibitor. If you do not slow down the chemical reaction, in addition to rust, the metal itself will be destroyed. You can use a 15-30% solution of orthophosphoric acid; as a result of its use, rust turns into a solid structure, which is protection against subsequent corrosion. A mixture of 50 g of lactic acid per 100 ml of petroleum jelly helps well. Acid converts rust into salt, and petroleum jelly dissolves it.
Leave-in chemical cleaning methods
Consider the use of soil converters; rust is converted into soil and does not require further rinsing. If it is not possible to completely get rid of rust, it is necessary to pre-paint the metal using a primer with special anti-corrosion properties. Final surface treatment is carried out using varnishes, paints, and enamels with special properties.
Typical types of rust damage
The following characteristic types of corrosion damage are distinguished:
- The surface is covered with a continuous rusty layer or individual pieces.
- The part has small areas of rust penetrating into the thickness of the part.
- In the form of deep cracks.
- One of the components in the alloy is oxidized.
- Deep penetration throughout the entire volume.
- Combined.
Types of corrosion damage
Due to their occurrence they are also divided into:
- Chemical. Chemical reactions with active substances.
- Electrochemical. Upon contact with electrolytic solutions, an electric current arises, under the influence of which the electrons of the metals are replaced, and the crystalline structure is destroyed with the formation of rust.
Stages of anti-corrosion work
- Preparation of necessary materials.
- Applying a primer to ensure better adhesion of the enamels.
- Application of enamels with protective coating
- Drying the coating or heat treatment.
The most effective method of applying paint and varnish coatings is considered to be the airless spraying method. Since it allows for painting with the highest quality. Existing metal irregularities.
A less effective way is to paint with a brush. It is not advisable to apply paint coatings with a roller.
Areas of application of anodic coatings
Anodic protective coatings are generally suitable for titanium, steels, iron and aluminum. For example, our company has products made of anodized aluminum. We offer both delivery and installation.
This includes:
- pavilions for swimming pools. Anode layers are applied to their frames and rails;
- arenas, hangars and sheds (including trade);
- structures for sports needs (for example, hockey stands);
- advertising profiles;
- railings, handrails and fences;
- elements of windows and doors.
Quality control of work performed
The methods used to protect against metal corrosion are subject to quality control. Performed to verify previously performed production controls. Defect prevention. Development of measures to eliminate detected defects. Quality control of anti-corrosion work begins with checking the documentation. Documentation on the anti-corrosion protection facility, the materials used, and product quality certificates must be provided. Upon completion of the quality control of the work, a report is drawn up containing information about the location of the work, the state of the work performed, the materials of their grade and consumption used. Information about the organization that performed the work, and the signatures of the persons who carried out the work. The commission conducting quality control checks the following parameters:
— type of anti-corrosion coating, there should be no areas that have not been treated.
— the thickness of the coating layer is checked by measuring in various places where poor quality processing is presumably possible.
— the adhesion of the paint and varnish material to the metal surface is controlled.
Products by topic
- Choose …
View
Street bars
27950 ₽ – 41600 ₽
- Choose …
View
Horizontal bar
17550 ₽ – 39000 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Bench with stops
26950 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Swedish wall
35900 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Inclined bench for abdominal exercises
27950 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Workout complex VK-003
151500 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Workout complex VK-001
132500 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Workout complex VK-002
82200 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Workout complex VK-004
137800 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Workout complex VK-005
98800 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Single handle bar
54500 ₽
- Add to cart
View
Parallel bars
9750 ₽
Violations detected during quality control of work.
After completing the work, rusting occurs on the surface of the treated metal, this is due to the fact that the temperature regime was not observed or the moisture was not completely removed. It is also possible that the metal is not sufficiently cleaned of oxides, which leads to subsequent corrosion. Insufficiently removed various contaminants, oil, soap, salts, all this will lead to damage to the paintwork and further rusting of the metal. The presence of dust on the surface being treated reduces adhesion. Which leads to peeling of the paintwork. Failure to maintain the time allowed for the metal to remain untreated leads to its rusting; interlayer holding must also be observed; the solvent does not have time to dissolve and it leaks through other layers. Which leads to disruption of the coating in the form of bubbling. All these violations identified during quality control must be corrected immediately.
Powder coating
An alternative to paint and varnish compositions was powder coating, invented in 1950.
Externally, the application process is similar to spraying with compressed air. However, the absence of “fog”—a suspension of paint in the air—is immediately striking. The part itself seems to attract paint, which settles on it in an even layer.
The attraction provides electricity. The part itself is charged with a positive charge, and the paint with a negative high-voltage charge. And since unlike charges attract, the paint sticks to the metal, just as pieces of paper stick to a comb rubbed against hair.
Then the part is heated to a temperature of 200-250 degrees. The paint melts and, spreading, forms the thinnest, only a few tens of microns, but durable dense layer.
Strict technological requirements and expensive equipment dictate a cost that is one and a half to two times higher than that of conventional paint. However, the high quality of monolithic polymer coatings allows them to compete on equal terms with traditional ones, but even displace them in some cases.
Today, the application of powder coatings has become commonplace; it can even be ordered via the Internet https://oooprofpokraska.ru/metall/.