Bench cutting
TO
category:
Metal cutting
Bench cutting
Next: Bench straightening
Cutting is the process of dividing a workpiece into parts of specified sizes and shapes. Cutting is used to produce workpieces of specified sizes and shapes from rolled products and sheet metal, as well as slots and holes in the workpieces. Modern cutting methods provide high-performance processing of workpieces of almost any size and from materials with any physical and mechanical properties.
The following technological cutting methods are distinguished. 1. Sawing with hacksaws, band saws and circular saws. Used for cutting long products. 2. Cutting with scissors. Used for cutting sheet metal. 3. Cutting on metal-cutting machines (lathes, milling, etc.). 4. Anode-mechanical, electric spark and light beam (laser) cutting. These methods are used in cases where other methods do not provide sufficient productivity and the required quality. For example, they are used for cutting high-strength materials along complex and precise contours, etc. 5. Oxy-acetylene cutting. It is used for cutting workpieces of considerable thickness made of carbon steel. It does not provide high accuracy and leads to changes in the structure and chemical composition of the material at the cut site. However, it is widely used in single production environments due to its simplicity, high productivity and versatility.
Rice. 1. Sawing (a) and cutting workpieces with scissors (b): 1 - workpiece, 2 - knives; y - rake angle, a - rear angle, P - sharpening angle, 8 - cutting angle
Cutting can be done either manually or mechanically.
The physical essence of cutting is based on various methods of destruction of the workpiece material at the cutting site.
When sawing and cutting on metal-cutting machines, the force F applied to the cutting wedge is directed at an acute angle to the surface being processed. Therefore, the cutting wedge cuts the material and turns it into chips. When cutting with scissors, the force F applied to the cutting wedge is perpendicular to the surface being processed. Therefore, the tool cuts the material without creating chips.
Electric spark cutting is based on electrical erosion (destruction) of the workpiece material. Capacitor C, included in the charging circuit, is charged through resistor R from a direct current source with a voltage of 100-200 V. When the voltage on the electrodes (tool) and (workpiece) reaches the breakdown voltage, a spark discharge with a duration of 20-200 μs occurs between their nearest microprotrusions. The discharge temperature reaches 10,000–12,000 °C. At the point of discharge on the workpiece, an elementary volume of material instantly melts and evaporates and a hole is formed. The removed material in the form of granules remains in the dielectric medium (oil) in which the processing process takes place. Discharges that follow each other continuously destroy all the workpiece material located from the tool at a distance of 0.01-0.05 mm. To continue the processing process, the electrodes must be brought closer together, which is done automatically.
Rice. 1.6. Electric spark cutting of workpieces: 1 - wire-tool, 2 - workpiece
When using oxygen-acetylene cutting, the workpiece metal at the cut site is first heated with an oxygen-acetylene flame to its ignition temperature in oxygen (for steel 1000-1200 °C). Then a stream of oxygen is directed into this place and the metal begins to burn. This generates so much heat that it is sufficient to maintain a continuous cutting process.
Anodic-mechanical cutting is based on the combined destruction of the workpiece material - electrical, chemical and mechanical. Direct current passing at the cutting site between the workpiece and the tool causes electrical erosion of the workpiece surface. The resulting molten particles of material are removed from the processing zone by a rotating tool - a disk. At the same time, the electrolyte supplied to the processing zone, under the influence of an electric current, forms oxide films on the surface of the workpiece, which are removed by the same rotating tool.
Cutting tools. When sawing, hacksaw blades (for manual and mechanical hacksaws), band saws and circular saws are used as cutting tools. Hacksaw blades and band saws are a thin strip of high-speed or alloy (Х6ВФ, В2Ф) steel with fine teeth in the form of wedges on one or two sides. Band saws are made by bending a strip into a ring and soldering its ends with high-temperature solder. A circular saw has teeth located on the periphery of the blade. The cutting teeth are hardened to a hardness of 61 - 64 HRQ. To prevent the tool from jamming in a narrow cut, its teeth are spread apart.
When choosing a sawing tool, you should first take into account the length of the cut and the hardness of the material being processed.
When making long cuts, it is necessary to choose blades with a large tooth pitch, and when processing thin-walled workpieces - with a fine one. At least three teeth must be involved in cutting simultaneously.
The higher the hardness of the material being processed, the larger the sharpening angle should be. The chips formed in this case have the shape of a comma and fit tightly into a small space. When machining soft materials, use tools with a large chip space. A positive rake angle improves productivity because the tooth cuts rather than scrapes the workpiece material.
To process high-strength materials, hacksaw blades with synthetic diamonds on the working surface are used.
To cut sheet material, cutting tools in the form of knives are used, which are most often removable. Knives come with straight, curved and round (roller and disk) cutting edges.
In anodic mechanical cutting, thin discs made of mild steel are used as a tool. On an electric spark machine, a continuously moving wire is used as a cutting tool.
Equipment and accessories for cutting. In a tool shop, small workpieces are cut with a hand saw. The hacksaw blade is mounted in a frame so that the teeth are directed away from the handle.
Manual lever shears are designed for cutting sheet material. Tool shops use small, portable shears. They can cut sheet steel up to 4 mm thick, aluminum and brass up to 6 mm thick.
Hand scissors are designed for cutting sheet material, making workpieces with a curved contour, cutting out holes with a complex contour in workpieces. For straight cuts, scissors with straight, wide knives are used. If the upper cutting edge is located to the right relative to the lower one, then the scissors are called right-handed, and if it is on the left - left-handed. To obtain external curved cuts, use hand scissors with curved wide knives. Cutting out internal curved contours is done with scissors with narrow curved knives.
Mechanical cutting of sheet material is carried out using manual electric shears, vibrating shears, as well as roller, multi-disc and sheet shears.
Sequence and techniques of work when cutting. Cutting is preceded by marking. Then the cutting method, equipment and tools are selected.
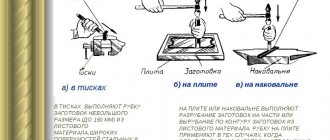
Correct execution of cutting techniques is of great importance for quality processing. The location of the workpiece and tool during manual cutting must be such that the marking line is constantly accessible for observation. When the cutting length is large, the pressure on the hacksaw is increased, and when the length is short, it is reduced. Since the teeth of a hacksaw break especially easily at the beginning and end of a cut, at these moments the pressure on it should be minimal.
When cutting, hand scissors should be opened to 2/3 of the length of the cutting edges. In this case, they easily grip the workpiece and cut well. The cutting plane should always be perpendicular to the surface of the workpiece being cut. Misalignment leads to jamming, crushing of edges and the appearance of burrs.
Correct adjustment of the tool is of great importance. So, with a weak tension on the hacksaw blade in a hand hacksaw, the cut is oblique. A large gap between the knives leads to the formation of burrs. The appearance of burrs with correctly adjusted knives is a signal that they have become dull.
When cutting with a hand saw, you should stand freely and straight, half-turned towards the vice.
Topic 5: “Metal cutting”
Cutting is a metalworking operation in which metal is separated into parts.
Hand scissors are used for cutting steel sheets with a thickness of 0.5-1.0 mm and non-ferrous metals with a thickness of up to 1.5 mm.
Depending on the design of the cutting knives, scissors are divided as follows: straight - with straight cutting knives, designed mainly for cutting metal in a straight line or in a circle of large radius; curved - with curved knives; finger - with narrow cutting knives for cutting holes and surfaces with small radii in sheet metal.
Cutting scissors.
According to the location of the cutting knives, scissors are divided into right and left. For right scissors, the bevel of the cutting edge of the lower knife is on the right, for left scissors, it is on the left.
Chair shears differ from ordinary hand shears in their larger sizes and are used for cutting sheet metal up to 2 mm thick.
Lever shears are used for cutting sheet steel up to 4 mm thick (non-ferrous metals up to 6 mm).
When working with thick sheets of strip or profile metal, and also if you do not need to saw the metal, but cut a groove or slot, scissors can be replaced by a hacksaw. But before you start working with this tool, you must first configure it correctly. First, you need to choose a blade for your hacksaw. It is selected depending on the type of metal. Secondly, the blade must be properly tensioned in the hacksaw frame; The degree of tension can be easily checked by lightly pressing on the side of the canvas: if it does not bend, then the tension is sufficient. The most comfortable position of the hands when working with a hacksaw is as follows: the end of the handle rests in the middle of the palm of the right hand, and the fingers of the left hand clasp the tension screw of the movable head.
Movements with a hacksaw should be made smoothly, without jerking; frequency of movements – 30–60 double moves (pull-pull) per minute; in this case, at least 2/3 of the length of the canvas should work. The hacksaw blade must be strictly perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece being processed.
Special mention should be made about cutting metal pipes. When cutting them with a hacksaw, there is always a fear (especially if the mechanic is not experienced enough) that the blade of the hacksaw will “go” to the side and the cut will turn out to be not a circle, but an oval. To avoid this, it is preferable to cut pipes not with a hacksaw, but with a special device - a pipe cutter
Safety precautions when cutting metal with scissors:
1. When cutting thin sheets with scissors, the cut part is strongly bent; at the cut site the edges of the sheet become very sharp. Care should be taken not to injure your hands. Students are advised to use mittens.
2. When cutting, you should carefully ensure that the fingers of your left hand do not get caught under the cutting part of the scissors, and the fingers of your right hand are not pinched by the handles or levers of the scissors. The left hand should never be on the cutting line when supporting the material being cut.
3. Chair scissors must be rigidly and securely fastened to their bases. If you use hand scissors secured in a vice, then their fastening must also be done very firmly and quite reliably. If the scissors break, it is easy to injure not only yourself, but also a friend.
4. When the scissors approach the end of the cut, you should move the workpiece closer to the middle of the cutting part of the scissors so as not to cut with the edges of the blades. In addition, when finishing the cut, it is necessary to slightly reduce the force, making it as smooth and calm as possible, so that the scissors do not break.
To mechanize the difficult and labor-intensive process of cutting sheet metal, as already noted, electric shears, guillotine shears, and a powered hacksaw are used.
Guillotine shears
Cutting is a metalworking operation in which metal is separated into parts.
Hand scissors are used for cutting steel sheets with a thickness of 0.5-1.0 mm and non-ferrous metals with a thickness of up to 1.5 mm.
Depending on the design of the cutting knives, scissors are divided as follows: straight - with straight cutting knives, designed mainly for cutting metal in a straight line or in a circle of large radius; curved - with curved knives; finger - with narrow cutting knives for cutting holes and surfaces with small radii in sheet metal.
Cutting scissors.
According to the location of the cutting knives, scissors are divided into right and left. For right scissors, the bevel of the cutting edge of the lower knife is on the right, for left scissors, it is on the left.
Chair shears differ from ordinary hand shears in their larger sizes and are used for cutting sheet metal up to 2 mm thick.
Lever shears are used for cutting sheet steel up to 4 mm thick (non-ferrous metals up to 6 mm).
When working with thick sheets of strip or profile metal, and also if you do not need to saw the metal, but cut a groove or slot, scissors can be replaced by a hacksaw. But before you start working with this tool, you must first configure it correctly. First, you need to choose a blade for your hacksaw. It is selected depending on the type of metal. Secondly, the blade must be properly tensioned in the hacksaw frame; The degree of tension can be easily checked by lightly pressing on the side of the canvas: if it does not bend, then the tension is sufficient. The most comfortable position of the hands when working with a hacksaw is as follows: the end of the handle rests in the middle of the palm of the right hand, and the fingers of the left hand clasp the tension screw of the movable head.
Movements with a hacksaw should be made smoothly, without jerking; frequency of movements – 30–60 double moves (pull-pull) per minute; in this case, at least 2/3 of the length of the canvas should work. The hacksaw blade must be strictly perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece being processed.
Special mention should be made about cutting metal pipes. When cutting them with a hacksaw, there is always a fear (especially if the mechanic is not experienced enough) that the blade of the hacksaw will “go” to the side and the cut will turn out to be not a circle, but an oval. To avoid this, it is preferable to cut pipes not with a hacksaw, but with a special device - a pipe cutter
Safety precautions when cutting metal with scissors:
1. When cutting thin sheets with scissors, the cut part is strongly bent; at the cut site the edges of the sheet become very sharp. Care should be taken not to injure your hands. Students are advised to use mittens.
2. When cutting, you should carefully ensure that the fingers of your left hand do not get caught under the cutting part of the scissors, and the fingers of your right hand are not pinched by the handles or levers of the scissors. The left hand should never be on the cutting line when supporting the material being cut.
3. Chair scissors must be rigidly and securely fastened to their bases. If you use hand scissors secured in a vice, then their fastening must also be done very firmly and quite reliably. If the scissors break, it is easy to injure not only yourself, but also a friend.
4. When the scissors approach the end of the cut, you should move the workpiece closer to the middle of the cutting part of the scissors so as not to cut with the edges of the blades. In addition, when finishing the cut, it is necessary to slightly reduce the force, making it as smooth and calm as possible, so that the scissors do not break.
To mechanize the difficult and labor-intensive process of cutting sheet metal, as already noted, electric shears, guillotine shears, and a powered hacksaw are used.
Guillotine shears
Scissors
Sheets of galvanized steel, copper, brass and aluminum up to 1 mm thick can be cut easily and cleanly using special scissors. Cutting high-strength steel sheets requires more effort and therefore more time.
Hand scissors with straight knives make straight cuts; with knives slightly rounded, curved cuts are made. There are also universal scissors for cutting metal sheets. But no matter what shape the scissors have, it is advisable to use the back of their blades, since the lever action is maximum there. Thanks to this, you will waste significantly less energy.
For specialists
For normal work, it is enough to have standard hand scissors. As in any other case, the higher the quality of the instrument, the more expensive it is. If you do a lot of sheet metal work, you might want to consider purchasing hand-held lever (parallel blade) or die cut shears.
To cut along a curved line, it is better to use scissors with a slight bend in the blades. With this simple tool you can cut thin sheets without much effort.
Pipe cutter
It is quite difficult to cut a pipe with a hacksaw accurately and accurately at right angles. And if these are thin-walled copper pipes, which are usually used when installing kitchen and plumbing equipment, then cutting them with a hacksaw is generally undesirable, since under the action of the spread saw teeth they are easily deformed, which, in turn, makes it impossible to tightly connect such pipes, which is usually done with a roller welding with crushing of edges.
Cutting roller
For cutting pipes - especially thin-walled ones - it is better to use a pipe cutter. Using a cutting roller, the pipe is brought with slight pressure to the guide roller, then a full turn is made with a pipe cutter. With each revolution, the cutting roller is carefully pressed. Repeat this operation until the pipe is cut.
Deburring
When cutting pipes with very thin walls, you should be extremely careful in adjusting the feed of the cutting roller: there is a risk of pushing through the wall. It is better to feed the roller to a shallow depth in a few revolutions than to try to cut with great force. A cut pipe will have burrs on the inside. They need to be carefully cleaned with a finely cut round file.
After each revolution of the tool around the pipe, it is necessary to adjust the position of the cutting roller using a manual spindle. Then cutting continues.