04/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- How laser cutting works
- Types of laser cutting
- Pros and cons of laser cutting of metal
- The nuances of using laser cutting for some metals
- Laser cutting quality parameters
- How can you improve the quality of laser cutting?
Understanding how laser cutting works is essential to performing or evaluating laser cutting. It is also necessary to know the quality requirements for laser cutting, permissible deviations in size and roughness.
In addition to the above, laser cutting of some metals has its own characteristics, and to carry out this work you need certain knowledge in setting up the equipment. Only all this together will help to obtain high-quality products.
Metal laser cutting services
Laser cutting for metal as a process is based on contact of the surface being processed with laser radiation.
When exposed to a beam during laser cutting of parts, the material at the point of contact reaches the melting temperature. Laser cutting of large thicknesses is usually carried out in this way. Residues of molten metal are removed using gas: nitrogen, oxygen, helium or argon. If laser cutting services in Moscow are required for particularly thin products, the metal is brought to a boiling point, resulting in its evaporation. This is a more labor-intensive operation, so custom laser cutting of metal is more expensive.
What will the cutting price depend on?
The cost of the service depends on several factors: - thickness of the material: the thicker and stronger the metal, the more power and time the master will need to process it; — quality of the cultivated material and equipment: high-quality carbide materials require processing on more expensive equipment; — complexity of the drawing/part: the laser cuts the products according to a given drawing, which is drawn up in advance by a master using a computer program; — work time: urgent work costs more.
| Stages of work: |
| receiving an application |
| processing, cost calculation |
| manufacturing process |
| shipment |
Materials for laser cutting and engraving
Modern laser cutting of materials extends not only to metals and alloys. Plastic, glass and plexiglass, sheets of paper and cardboard, as well as natural wood and products based on it can be laser cut to order according to a sketch. But unlike cutting steel with a laser, the intricacies of which have long been studied, each of the non-metallic materials has its own characteristics. This means that the approach to its processing, especially if laser cutting is required for small parts, must be special.
Price list for cutting stainless steel sheets
| Thickness, mm | Contour length up to 100 m, rub. | From 100 to 500 m, rub. | From 500 to 1000 m, rub. | Cost of one plunge, rub. |
| 0.8 | 58 | 45 | 38 | 1 |
| 1 | 58 | 45 | 38 | 1 |
| 1.5 | 94 | 65 | 50 | 1 |
| 2 | 120 | 85 | 70 | 1 |
| 3 | 160 | 130 | 90 | 2 |
| 4 | 210 | 160 | 120 | 2 |
| 5 | 300 | 210 | 150 | 5 |
| 6 | 400 | 300 | 225 | 5 |
| 8 | 600 | 450 | 350 | 7 |
| 10 | 750 | 600 | 450 | 7 |
The shortest route for your laser cutting order
One of the advantages of our laser cutting of metal to customer sizes is efficiency.
That is why we suggest you use the quick order form on our website, in the “Order and Delivery” section. Specify what type of processing you require: for example, sheet metal laser cutting or laser cutting of small parts. Next, leave your coordinates - phone and email. You can also attach photos of metal products for which you need laser cutting. After sending your message, we will contact you as soon as possible.
What products are produced using laser cutting?
By cutting metal with a laser you can create different types of products. These include sheet panels for finishing work in construction and repair, and threading on tools for working with metal, and all kinds of metal license plates, plates, key rings, engraved souvenirs, industrial metal products for industries and enterprises.
| Full range of products: |
| machine parts |
| radio-electronic equipment |
| elements of metal structures |
| parts of chimneys, fireplaces and containers |
| elements of gates, fences and railings |
| store display details |
| advertising designs |
| fasteners |
| decorative items |
| interior elements |
| vending machine housings |
| racks |
| ventilation grates |
| fire protection products |
How laser cutting is carried out in practice
A production facility offering metal laser cutting must be equipped with the most modern equipment. Any such installation can be divided into three parts:
- active medium, that is, the source of the laser beam;
- a source that creates an environment for the formation of electromagnetic radiation;
- optical system that amplifies the radiation power.
Laser cutting of metal to order according to a sketch can be carried out with solid-state, gas and gas-dynamic lasers. The latter are among the most powerful and are used for laser cutting of corners and other large parts.
What types of lasers are there?
There are several technologies for laser cutting of metal, determined depending on the type of working element - laser, and its power. Today there are three main types of laser systems:
- solid-state with a power not exceeding 6 kW;
- the power of gas installations reaches 20 kW;
- The most powerful are gas-dynamic units, the minimum power of which is 100 kW.
VT-metall offers services:
Industry mainly uses solid-state machines designed for laser metal processing.
Laser radiation in such installations, due to which metal is cut, can be either pulsed or continuous. The working elements (working fluid) in such devices are represented by ruby, glass with an admixture of neodymium or calcium fluorite. The main advantage of this type of equipment is the ability to create a powerful laser pulse in a fraction of a second. Gas laser systems are more suitable for scientific or technical purposes; they are rarely used in industry.
The working fluid in this type of equipment is a mixture of gaseous substances, which is used in the process of laser metal working. The installations operate using nitrogen, carbon dioxide and helium. Electric current, acting on the atoms of these gases, excites them, due to which properties such as monochromaticity and directionality begin to appear. These are the main advantages of gas laser systems.
The most powerful are gas-dynamic lasers, the working substance of which is carbon dioxide.
The process of laser metal working is as follows: carbon dioxide heated to a certain temperature enters a narrow channel, in which its structure expands, after which the gas is cooled. As a result, the necessary energy is generated, due to which laser cutting of metals is performed.
When is plasma cutting effective?
Along with laser cutting of metal and products made from it, customers are offered plasma cutting, when a compressed plasma arc comes into contact with the material. This method is preferable for processing parts of large thickness. Plasma technology allows you to cut metal faster and with less energy consumption. But a better quality cut is still obtained by laser processing, and urgent laser cutting of metal can also be carried out in the shortest possible time.
How is the cost of metal laser cutting calculated?
Working with customers, we prove every day: laser cutting of metal in Moscow (PLC) can be inexpensive. The final cost of the order is affected by:
- material characteristics,
- complexity and precision of execution,
- batch size,
- urgency of work.
Call - and our specialists will advise you on all aspects, and also offer a way to save money and order inexpensive laser cutting of metal.
Order laser cutting
We are waiting for your applications around the clock (online) or by calling the company hotline. After concluding a contract and transferring payment, our specialists immediately begin performing precise laser cutting. By the way, while offering laser cutting cheaply in Moscow, we also take care of delivery. Forget about the hassle of self-pickup: your order will be delivered by reliable and spacious transport.
Low prices for laser cutting: why?
There is no catch in the fact that we offer laser cutting services in Moscow so cheaply.
Our metalworking shop operates on its own premises, not on rented ones. Most custom metal laser cutting operations are automated, which greatly reduces labor costs. Finally, we have been working in the market for a long time and we no longer need to recoup the costs of equipment. Thus, we carry out orders at the lowest prices for the capital and are ready to offer you budget laser cutting for metal without skimping on quality.
Laser cutting and bending of metal in Moscow
Laser processing of workpieces is far from the only operation they will have to endure.
Very often, within the framework of one order, our company solves two problems at once - it performs laser cutting and bending of metal in Moscow. And before starting with them, he carries out mechanical, but also very precise cutting of sheets for future workpieces. The leading metalworking operations - laser cutting, bending - are not necessarily carried out in the listed sequence. Sometimes bending precedes cutting, but consideration should be given to whether the laser beam can process the reshaped workpiece.
Our workshop is equipped with all the necessary equipment to perform laser cutting and sheet bending services in the shortest possible time and without loss of quality. Before executing an order, we compare the physical characteristics of the workpiece and material with the load it can withstand. The possibility of marriage is completely excluded.
After laser cutting, metal bending is carried out as follows:
- the workpiece is carefully clamped in a vice;
- a press is connected to the work, acting on the part with a calculated force;
- finished volumetric products are inspected by inspectors.
Review of machines for laser metal processing
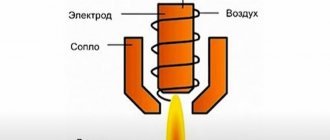
The practical implementation of the achievements of academic physics is laser processing of metal . Discovered in the second half of the twentieth century, a quantum generator, or laser, is a source of monochromatic coherent light and is an amazing optical device that generates photons in an avalanche manner, with the same energy, direction of motion and polarization, i.e. emits a highly focused, high-power light beam.
Physicists and engineers immediately appreciated this discovery, and already in 1962, almost immediately after testing the first laboratory quantum generator, commercial lasers were developed and offered to the market (USA). This is the time of a real revolution in laser technology, as a result of which many modifications and types of lasers were created and are now successfully used: from the smallest, several microns in size, to the giant “Nova” at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the USA, with a length of 137 m and a total power of 1014 W. Laser technology has penetrated into all scientific and industrial areas and is more in demand in metalworking.
The laser has become a highly efficient tool in machine tools due to its unique properties: high radiation power (up to 108-109 W/cm2 in continuous mode and up to 1016-1017 W/cm2 in pulsed mode) at the local processing area, allowing instant heating (burning) and cooling of metal without subjecting the entire workpiece to thermal deformation. Removal of combustion products from the cutting zone is carried out by blowing with oxygen, air, nitrogen or other process gas. In addition, the laser beam is easily controlled, i.e. fits seamlessly into automated systems.
In the 70-80s of the 20th century, lasers began to be successfully used in welding, surfacing, marking, hardening, and cutting metals in the manufacture of parts such as gaskets, brackets, panels, instrument panels, doors, decorative grilles, and circular saws.
After the advent of kinematically complex robotic manipulators and flexible optoelectronic beam guides, laser processing of metals received a “second wind”, i.e. began to be used when cutting spatial metal products. Laser equipment used in cutting is classified according to radiation sources and output power, which in turn determines the processing material. Thus, for processing ferrous metals and stainless steel, solid-state (Nd:YAG neodymium garnet) quasi-continuous and pulse-periodic laser radiation sources with an output power of 100-300 W are used; at the same time, continuous gas CO2 lasers with an output power of up to 2500 W are used to process alloy steels and some types of alloys (as well as ferrous metals).
As a rule, modern equipment for laser cutting of metal consists of:
- laser with cooling and power systems;
- coordinate table for fixing the workpiece;
- computer table control system;
- process gas supply devices;
- ventilation system.
Huge radiation powers lead to overheating of the laser, so double-circuit water systems or refrigeration compressors using freon are used to cool it. Laser power sources are selected based on the technological problems being solved - transformer or pulsed. Where reliability is needed, transformer circuits are used; When minimizing laser installations, pulsed ones are used.
Modern coordinate tables are high-precision equipment and, as a rule, are based on a portal design (“flying optics”), where a stationary metal workpiece is cut by a moving laser beam. There are other schemes. So, when cutting Nd:YAG lasers, the beam moves along one coordinate, and the table with sheet material moves along another.
The coordinate machine is controlled by an industrial computer and, in addition to hardware devices - drives, sensors, etc., includes a package of the following files:
- programs for inputting source data (electronic drawings) in graphic editors AutoCad, CorellDraw, Adobe Illustrator, etc. (*.plt, *.ai, *.dxf, *.cf2 formats);
- control programs for rotating, scaling and reproducing the source file (drawing) across the working area of the table;
- programs for setting parameters of laser processing and insertion mode, automatically taking into account the width of the cut, determining internal and external contours, adjusting the cutting mode directly in the technological process, etc.;
- programs for setting the parameters of the coordinate drive and the operator’s working environment, generating (drawing) the simplest geometric shapes;
- programs for connecting external devices, controlling a laser emitter, communication with an external local network.
In laser cutting modes, different process gases are used, for example, for gentle cutting of ferrous metals, oxygen is used (gas laser cutting), and for stainless steel, a flow of inert gas, usually nitrogen, is used. To remove gaseous and aerosol decomposition products that occur when burning a metal sheet, ventilation is used, which is created by a special device, which is an integral part of all industrial laser processing complexes.
One of the alternative methods to “flying optics” is the use of deformable mirrors, combining the advantages of a stationary and “portal” design. The laser beam changes its trajectory twice, being reflected in a complex of mirrors with a controlled surface shape, before reaching the workpiece. A clear advantage of the method is the absence of complex mechanics; The disadvantages include the difficulty in controlling the surface of the mirrors.
Despite the commonality of the initial ideas, approaches and principles used in equipment for laser cutting of metals, machine tool companies try to produce original equipment so as not to find themselves as outsiders in this very promising market segment - metalworking. Let's focus on the leaders whose machines are widely used.
| Processing range: | |
| TRUMATIC L 3030 | 3000 x 1500 mm |
| Max. thickness of the processed sheet: | 20 mm (steel) |
| 15 mm (stainless steel) | |
| 8 mm (aluminum) | |
| CO2 laser power: | 4000 W |
The German company Trumpf is known for its Trumatic 600L and Trumatic L3030 machines , which use the “flying optics” principle. Everything on these machines is done with German pedantry: impeccable CO2 lasers from FANUC (Germany) will ensure cutting quality at the highest level; the table is equipped with guides made with filigree precision; the drive is carried out by step-by-step single-moment motors and toothed belts, which, together with laser position control sensors, guarantee ideal positioning of the laser head; Computer-controlled pneumatics automate the feeding and unloading of steel sheets.
Technological laser cutting complexes from Tecnology Italiano FPL TRADE claim to be universal in the tasks they perform and, depending on the configuration, are equipped with a 1000, 2000 or 4000 Watt laser. However, unlike most technical counterparts, united by the principle of “flying optics”, the lasers in Tecnology Italiano FPL TRADE machines are fixed. The result is stable radiation generated, and this affects the impeccable quality of the cut. The coordinate table together with the workpiece has an impressive weight and is mounted on a special (without residual stresses in the structure) massive frame. It is controlled by powerful and complex drives. Therefore, this equipment is more likely focused on raster engraving or cutting single or small batches of particularly complex products.
| Technical characteristics of Tecnology Italiano FPL TRADE | |||
| Model | From 1000 | Since 2000 | From 4000 |
| Principle | Fast gas flow excited by 2MHz radio frequency, energy acquisition in a solid. | ||
| Rated power | 1 000W | 2 000W | 4 000W |
| Maximum power at peak heart rate | 1 000W | 2 700W | 5 000W |
| Power stability | +/- 1% | +/- 1% | +/- 2% |
| Wavelength | 10,6 | 10,6 | 10,6 |
| Characteristics of the laser beam | Order in a minimum configuration: guarantees the best cutting result. | ||
| Radiation divergence | less than 2 mrad | ||
| Composition of the gas mixture | CO2 5% | He 40% | N2 55% (+/- 5%) |
| Gas mixture consumption | 10 l/hour | ||
| Coolant flow (water) | 40 l/min | 75 l/min | 160 l/min |
| Recommended cooling outlet | 10,000 kcal/hour | 19,000 kcal/hour | 38,000 kcal/hour |
| Power consumption | 18 kW | 33 kW | 55 kW |
| X-axis machining | 360…3050mm | 360…3050mm | 360…3050mm |
| Y axis machining | -10…1510mm | -10…1510mm | -10…1510mm |
| Head travel along the Z axis | 180mm | 180mm | 180mm |
| Maximum sheet moving speed | |||
| X axis | 100 m/min | 100 m/min | 100 m/min |
| Y axis | 65 m/min | 65 m/min | 65 m/min |
| X+Y | 120 m/min | 120 m/min | 120 m/min |
| Repeatability | +/- 0.03 mm | +/- 0.03 mm | +/- 0.03 mm |
Among the Japanese machine tool manufacturers, traditionally leaders in metalworking, it is worth highlighting the machines of the Ymazaki Mazak group, which are capable of laser cutting of volumetric structures - pipes of various diameters, complex boxes, etc. with various thicknesses up to 25 mm. The equipment is equipped with automatic feeding and unloading systems for products, i.e. can be used in conveyor processing. Of interest in this regard is the automated Fabric Gear complex, designed for laser cutting of profiles of various sections: round, square, rectangular, triangular, and other types. Of course, it belongs to the latest generation of metalworking centers, since it is equipped with an artificial intelligence system and additional tools that allow it to process particularly complex volumetric products in automatic mode. This company produces its machines in six factories in Japan, the USA, England and Singapore.
| Technical characteristics of the main working part of the 3D Fabri Gear 150 / 300 machine | |||
| 8995 mm | 8750 mm | ||
| U axis | 8779 mm | 9100 mm | |
| Axis V | 2315 mm | 2315 mm | |
| Y axis | 985 mm | 1270 mm | |
| Z axis | 370 mm | 370 mm | |
| A-axis | ±99999,999° | ±99999,999° | |
| Axis B | ±135° | ±135° | |
| Travel speed, max. | X, U, V: 1 00 m/min; Y: 36 m/min; Z: 30 m/min; A: 9600°/min; B: 9600°/min; C: 20000°/min | X, U, V: 30 m/min; Y: 24 m/min; Z: 24 m/min; A: 9600°/min; B: 9600°/min; C: 6000°/min | |
| Maximum feed speed during processing | 10 m/min | ||
| Laser cutting head | Equipped with a lens with a focal length of 7'5″ and d2″; (Calculated for a pressure of 1 MPa (10 kgf/cmg)) | ||
| Z axis profiler | Non-contact type (Electrostatic) | ||
| Auxiliary gas switch | There is a choice of three types of gas. Operating pressure range: 0.05 - 0.6 MPa (7.25 - 87.02 psi). Inlet pressure: 0.8 MPa (116.03 psi) | ||
| Software control of auxiliary gas pressure | The auxiliary gas pressure is controlled by software. Maximum set value: 0.6 MPa (6.0 kg/cm2) | ||
Among other companies interesting in this area are Bystronic (Swiss engineering group; AMADA (Japan); SALVAGNINI (Italy); LVD (Belgium).
Among the domestic manufacturers of equipment for laser cutting of metal, it is worth highlighting the products of TekhnoLazer CJSC (Moscow region, Shatura), which produces machines for laser cutting of sheet materials based on technological CO2 lasers with a power of 700 to 5000 W and 2 coordinate tables equipped with a pallet – a loading device, the main function of which is to deliver the workpiece to the laser cutting technological space. An obvious drawback is the manual operation of the pallet. The movement of the laser head is standard, portal type and is carried out by actuators (motor, gearbox, drive gear) by moving two longitudinal trusses connected by transverse beams.
Coordinate table on laser machines TechnoLaser
| Laser | Machine model | ||
| TLV-700 (0.7 kW) | LMC-1200-0.7 | LMC-3000-0.7 | |
| TLV-1000 (1.0 kW) | LMC-3000-1.0 | LMC-6000-1.0 | |
| TLV-1500(1.5 kW) | LMC-3000-1.5 | LMC-6000-1.5 | |
| TL-3 (3.0 kW) | LMC-3000-3.0 | LMC-6000-3.0 | |
| TL-5M (5.0 kW) | LMC-2000-5.0 | LMC-6000-5.0 | |
| TL-6 (TANDEM) (6.0 kW) | LMC-2000-6.0 | LMC-6000-6.0 | |
| Table characteristics | Machine model | |||
| LMC-1200-XX | LMC-2500-XX | LMC-6000-XX | ||
| working area dimensions | x | 1200 mm | 2500 mm | 6000 mm |
| y | 840 mm | 1500 mm | 1500 mm | |
| z | 100 mm | |||
| travel speed | x, y | 50 m/min | ||
| z | 1 m/min | |||
| cutting speed | x, y | up to 20 m/min | ||
| processing accuracy | x, y | 0.1 mm | ||
| positioning accuracy | z | 0.1 mm | ||
Laser technologies (including laser cutting of metal ) are certainly at the very beginning of their evolution and will be improved through the introduction of new economical and high-power lasers, light guides, delivery schemes to the workpiece and other innovations.
Additional features of Proflazermet
The standard deadline for completing work is 5 working days. Of course, laser processing often requires extremely fast order execution, and in this case we are ready to consider the possibility of carrying out urgent work on an individual basis.
We send each client the finished volume in our own branded Proflasermet packaging - so you can be sure that you receive the products without damage during transportation.
Call!,
Discount offers, as well as all the detailed information about the features of the cutting technological process, cutting efficiency, timing and delivery, as well as any questions in related areas, can be obtained from our experienced consultants.
Price list for laser cutting of brass metal
| Thickness, mm | Contour length up to 100 m, rub. | From 100 to 500 m, rub. | From 500 to 1000 m, rub. | Cost of one plunge, rub. |
| 1 | 54 | 42 | 36 | 1 |
| 1,5 | 90 | 70 | 60 | 1 |
| 2 | 112 | 87 | 74 | 1 |
| 3 | 135 | 105 | 90 | 2 |
| 4 | 162 | 126 | 108 | 2 |
| 5 | 198 | 154 | 132 | 5 |
| 6 | 270 | 210 | 180 | 5 |
Pros and cons of plasma and laser
Plasma
Advantages:
- Wide range of cut thicknesses from 0.5 to 50 mm per punch ;
- High cutting speed at large thicknesses;
- Low initial price of equipment
- Well-proven technology for cutting at an angle, as they are now used to calling it, cutting with a bevel.
Flaws:
- It is inappropriate to process metals thinner than 1 mm;
- Edge taper up to 5 degrees (poor quality edge);
- The presence of scale on the holes when turning, so additional processing of the products is required;
- Restriction on hole diameter up to 4 mm;
- High cost of consumables;
- Low accuracy compared to a laser machine;
- Requires post-processing;
- Low cutting speed compared to laser on thin materials;
- Inability to perform many types of cutting available to a laser machine.
Laser
Advantages:
- Edge perpendicularity;
- Small cutting width;
- No scale - you get a 100% finished product;
- The diameter of the hole is less than the thickness of the sheet. You can cut out small parts down to 1 mm;
- Low thermal impact on the edge;
- Cheap consumables;
- Processing of thin metal from 0.2 mm;
- Highest possible cutting speed;
- The materials require no post-processing and are ready to be welded, painted or packaged and then sold.
Flaws:
- You can cut metal only up to 20 mm;
- High initial price of equipment.