Laying underground engineering systems is carried out in different ways. The HDD puncture method, which requires a drilling rig and more, is considered promising and universal. Features of the puncture method
Horizontal directional drilling is a relatively new technology that does not involve digging trenches. It allows you to maintain the integrity of the landscape and reduce financial costs for the project. The installation time is also reduced.
Advantages of laying pipes without trenches
Most often, pipeline systems are laid using dug trenches. This method has some significant disadvantages:
- Disturbance of the fertile layer due to opening of the soil.
- Removal of vegetation, including trees and shrubs.
- High tariffs for work performed.
- Long preparation.
In addition, a channel passing through the roadway cannot be laid without disturbing the asphalt surface, which inevitably leads to reconstruction of the road after the work is completed. And blocking a busy section of the highway can cause certain difficulties. The solution to problems in this case is trenchless or closed installation of communication lines, including the installation of HDD pipes.
This method has many advantages:
- Lower material costs to complete the process.
- Accelerated installation process.
- Minimum labor costs, including the number of workers.
- Environmental safety.
- All-season work (frozen soil makes it difficult to openly lay pipes at low air temperatures).
- Ensuring the safety of the work being carried out.
The installation process, carried out in a short area, for example, under the roadway, does not require the use of special equipment. The installation process is quite simple. To perform it, a cylinder of a certain size and a rod with extension elements are required. This device allows you to manually remove soil, but first you need to dig small pits on the sides of the road, that is, at the entrance and exit of the pipe. If installation involves work over a long section, then special equipment must be used.
Equipping the construction site before the start of HDD puncture
3.1. Before starting the main construction work, the following preparations must be carried out:
- underground communications discovered in the work area must be opened with pits. This is done to determine the depth of their laying. They are then marked with warning signs;
- work areas are fenced off with a standard fence, with the simultaneous installation of the necessary road signs;
- a strip along the route is cleared, accompanied by cutting down and replanting green spaces, if any.
- temporary access and internal roads are being built;
- general-site warehouses are created;
- The construction site is provided with water supply and fire-fighting equipment, alarm and communication equipment.
3.2. Construction mechanisms are mounted on a leveled, stable base, which should not have a slope greater than that allowed by the technical data sheet. Near the protruding parts of construction mechanisms, a free passage of at least 1 m in width must be left.
3.3. The pit under construction must be fenced with railings no less than 1.1 m high. In the dark, the fence must be illuminated.
Closed gasket options
The trenchless method of laying pipes is used for various communication systems:
- Communication cables.
- Pipelines transporting oil, gas and thermal resources.
- Sewage, as well as cold and hot water supply.
- Repair work on certain sections of the pipeline or replacement of individual sections of the pipe.
Closed pipeline installation currently involves many execution methods. In particular, the following options stand out:
- Replacement of obsolete pipe products with new elements (rehabilitation).
- Piercing the soil.
- Soil punching.
- Horizontal directional drilling.
The first option (rehabilitation) is used when it is necessary to carry out repair work or a complete replacement of individual pipeline elements is required. Other options involve direct laying of pipe elements. Trenchless installation is widely used because this method helps prevent many problems that arise when laying open pipelines.
Scope of application of HDD
The level of comfort in modern cities has evolved over many years. Water supply, electrical networks and telephone lines are laid underground and are thereby protected from possible damage.
At the same time, the networks wear out and require repair or replacement. At a certain stage of technical development, special services had to dig a trench and lay new pipes or cables in it to replace those that had expired. Today, trenchless installation of communications makes it possible to carry out this work without disturbing the surface layer of the earth.
Long-term practice shows that the underground space of large cities and even medium-sized settlements is maximally filled with various routes. A significant part of these communications were transferred many times from the balance sheet of one company to the ownership of another. Most of the technical documentation has been lost. The excavation of each new trench carries the risk of damaging an existing communication line or water supply.
In such situations, trenchless laying of pipelines using the puncture method becomes the only available way to complete the task.
Laying communications to newly built areas or additional communication lines in old areas requires overcoming serious obstacles. These include roads and railways, reservoirs, and avenues with heavy traffic.
The only solution in such cases is a horizontal puncture under the road. The work is carried out without the slightest damage to the surrounding nature or nearby buildings.
Using the sanitation method for repairing and laying pipelines
Rehabilitation is a closed pipe laying, which involves replacing old elements with new pipe products. There are two ways to perform the process:
Relining
This method involves saving the old system and using it as a capsule for the new pipeline. Before carrying out work, preliminary high-quality cleaning of the pipe from excess debris is required. Then a new pipe element with a smaller diameter is inserted into it. Despite the fact that modern pipes are made from materials with excellent quality characteristics, the old design can act as additional protection, reducing the risk of accidents.
Relining work can be performed in several ways, in particular by retracting the pipe. This process begins at the end of the old communication and before the beginning of the pipe. During the work, the section is disconnected from the general system, then a new element made of more technologically advanced materials is inserted into the pipe being repaired in this section. Relining allows for slight destruction of some sections of the old pipeline.
Process economics
Every adequate specialist strives to ensure that any production process, any technological operation is carried out with minimal costs.
Many years of practice have proven that the price of HDD puncture is lower than all other methods of performing this type of work. This is especially noticeable when drilling is carried out in densely populated areas. And HDD puncture under the road is just an illustrative example of the advantages of this technology over all others that are used in this industry.
Installation of pipes using the puncture method
The puncture method is most often used on clay and loamy soils. In this way, pipes with a diameter of no more than 600 mm can be laid. The maximum distance over which pipes can be laid using soil puncture is 60 meters. This wiring involves compacting the soil around the pipe. A puncture can only be performed using special equipment, since this requires a force of 3000 kN. The most common option is to puncture and use a hydraulic jack.
To reduce the coefficient of friction and resistance in the soil, you can use a cone-shaped tip. The base of this element should be 2 cm wider than the pipe itself. Pipelines with a small diameter can be laid without using a tip; the puncture is carried out directly by the pipe.
Using a cone tip on a pipe reduces passing accuracy. Since when passing through the ground, this element may encounter an obstacle and deviate from the intended puncture line.
Puncture is performed at a speed of 4-6 meters per hour, depending on the complexity of the soil and the equipment used. Vibration helps increase the speed of pipe movement with this trenchless installation method. Together with the efforts of the jack, it allows movement through the ground at a speed of 20-40 meters per hour.
Puncture under railway and tram tracks
To carry out drilling work in the specified area you will need:
- Permission from the local branch of JSC Russian Railways;
- Creation of design documentation with accurate calculations;
- Agreements on technical control and installation of insurance packages;
- Coordination of all plans by representatives of JSC Russian Railways.
Piercing under railways and tram tracks is carried out under technical supervision by Russian Railways employees and only in accordance with the work plan.
Soil punching method
Laying pipelines using the trenchless method also involves using the soil punching method. This option is more effective when laying large-diameter steel pipes, up to two meters. The process is similar to the piercing method, but the piercing is done with the open end. The resulting soil is removed.
The required degree of force for pushing is created by hydraulic jacks installed around the entire circumference of the pipe. Work of this type can be carried out on soil with a high content of clay, loam and sand. The optimal diameter of the pipes used can range from 60 cm to 172 cm. Pipelines can be laid by pushing soil in areas no more than 100 meters wide. This method is often used to lay a pipe in a ditch for a drive-in, as this is a fairly effective method.
Soil punching is performed as follows:
- First you need to dig a pit.
- Then a thrust wall is installed on which the jacks are attached.
- Connect one end of the pipe and jacks located on the wall. The other end remains open.
- The forces created by the jacks are transferred to the pipe, its free end is pressed into the soil layer.
- The movement of the part in the ground leads to the formation of an earthen column inside. It is removed using shovels with long and short handles, as well as using pneumatic impact devices.
Road puncture within cottage villages
In the cottage, country and private sectors, laying pipes using the horizontal puncture method is often the only way to carry out communications painlessly for the landscape. The advantage of this method is that any communications can be carried out. The road surface, landscaping and the sites themselves remain untouched. The main part of the work is carried out deep in the ground; only the starting and ending points are located on the surface.
In cases where pipes run under privately owned plots, it is necessary to conclude an agreement and consent with each of the owners. You will also need permission from employees of the administration, partnership or other organization that manages the cottage community or the private sector.
Dismantling and removal of equipment
8.1. When the case is in the receiving pit, the installation is disassembled. The expander and pilot rods are removed from the receiving pit, and the drilling rig is removed from the starting pit.
8.2. Between workers who are in the starting and receiving pits, reliable communication in both directions must be ensured.
8.3. After completion of construction and installation work, all equipment is disassembled and removed from construction sites. Then the terrain is graded and the pits are filled.
Drilling using the HDD method has many advantages:
- The work can be completed in 1 day, up to 3-5 people will be required.
- You can make a puncture under obstacles that are difficult to get around (for example, under a highway).
- The landscaping of the local area - road surface, flower beds, etc. - is not disturbed.
- It is possible to lay communications in those places where ground work is prohibited or impossible.
Thus, horizontal drilling technology is the most economical solution in terms of both time and financial costs.
Set of equipment for HDD
To create inclined or horizontal wells you will need:
- drilling rig;
- locating device;
- additional tools: rods, swivels, adapters, staples, etc.
Now let's look at each of these tools in more detail to find out what role it plays in HDD drilling technology.
Drilling rig - there are both high-power industrial machines for horizontal inclined drilling, and more compact mini-rigs that can be used in the construction of a private house. All of them run on diesel fuel and consist of a body, a device for supplying water to the drilling zone, a chassis and a control panel.
Main characteristics of this equipment:
- maximum pulling force (indicated in tons);
- diameter and maximum puncture length (depending on the parameters of the drill rod);
- average bentonite consumption (how many liters are consumed per minute);
- the angle of rotation of the drill rod (determines at what angle an inclined well can be drilled).
Of these, the most important are the first two characteristics - when choosing a car, you should pay attention to them first.
Mini-units, which are used to perform relatively small punctures using horizontal directional drilling, are not only smaller in size, but also have a simpler design. They only include the engine and the working part with the drill rod. It is not difficult to learn how to operate such a machine, and even 1 person can handle it.
Geolocation system is a probe and data recording device with which the operator can control the drilling process. Since it is impossible to observe the operation of the drill itself, the probe provides information about the presence of solid inclusions or important objects (for example, existing communications) in the working area. The use of a location system makes punctures using HDD technology controllable and completely safe, and also minimizes the risk of equipment breakdown.
Additional tools - this category includes all devices and accessories that facilitate the drilling process and laying communications. For example, these are lighting fixtures, clamps for casing pipes, pumps for pumping bentonite from the working area, brackets, adapters, etc.
HDD technology: stages of work
The entire drilling process can be divided into preparatory and actual drilling work. The preparatory part includes studying the soil and site features, preparing the site for installing the drilling machine, planning the depth and trajectory of the puncture, preparing the necessary tools, etc. The importance of this work is difficult to overestimate - the success and safety of the puncture largely depends on them.
Preparatory stage
Approximate list of works:
- Investigation of the territory for the presence of underground facilities, pipelines and other communications.
- Determination of soil characteristics: soil type, water saturation, presence of rock inclusions, etc. Depending on these factors, horizontal directional drilling technology may change.
- Outlining the optimal puncture trajectory - not only the entry and exit points are important, but also the route itself, taking into account the type of soil and the location of underground obstacles.
- Preparing a site for installing a drilling machine: it is necessary to level and sometimes compact the site, provide lighting, create conditions for drainage of water, excess bentonite, etc.
- Placement of the drilling rig at the starting point, delivery of the necessary tools and bentonite.
Well drilling stage
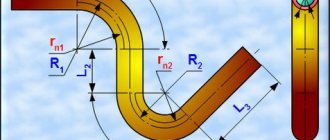
Horizontal directional drilling technology, which is used to obtain tunnels at an angle, involves the creation of a pilot well. This is a small puncture with a diameter of up to 10 cm, which is usually performed with an inclination of 10 to 20 degrees. After the puncture reaches the desired depth, the angle of inclination changes - up to horizontal drilling.
Depending on the shape and trajectory of the well, the direction of movement of the drill can be changed repeatedly in all planes. For example, if you need a well in the shape of an arc, which allows you to go around any obstacle (a pond, a building with a foundation), immediately after the lowest point of the trajectory, the drill is gradually directed upward. Thus, closer to the finishing point, the track receives the desired angle of inclination.
Important: the HDD puncture technology involves tracking the movement of the drill using a location probe. Sounding allows not only to identify unknown obstacles, but also to track the position of the drill, the direction of its movement, temperature, etc. This helps to avoid overheating, breakdowns, and deviations from the given trajectory.
After the puncture is completed, the well must be expanded to a given diameter. To do this, instead of a drilling head, a reamer is mounted on the HDD installation and the reverse stroke is turned on. Thus, the reamer moves in the opposite direction - from the finishing point to the starting point, expanding the hole. Most often, it is not possible to achieve the desired tunnel diameter in one pass, then 2-3 passes are necessary. Each time a larger reamer is used. This is the final stage of performing a well using the horizontal drilling (HDD) method.
Use of bentonite in drilling
During drilling operations, a bentonite solution is supplied into the tunnel - it facilitates the advancement of the drill (working as a lubricant), and also facilitates easier extraction of soil. Mixing with water, bentonite forms a gel-like composition that envelops the walls of the hole, making the soil more stable and preventing landslides.
The quality of this solution plays a decisive role and determines the efficiency of the entire process. The composition of bentonite may vary depending on the type of soil on the site, but in any case the addition of sand should not exceed 1%.
Limitations of the HDD technique:
- Drilling, especially inclined drilling, cannot be carried out on monolithic rocky areas or in soil with a high concentration of solid inclusions, as well as in soil with high water saturation.
- Underground barriers can become a serious obstacle to laying communications using this method.
- Using a horizontal drilling installation, it is impossible to change the direction of the tunnel two or more times in one short section (up to 5 meters). The bending of the drill rod is not sufficient for this.
In other cases, the HDD method is optimal and the most economical for creating wells, tunnels, pipelines, and laying underground communications on both a domestic and industrial scale.
Leave a request for an estimate. For free!
Send a request
Return to list
Laying the pipeline
7.1. A string of the pipeline being laid is attached to the expander by gripping the pipe through a swivel.
7.2. Next, the pipeline is pulled, which goes into the previously created well. The puncture process is under the control of the HDD operator. Upon completion of the broaching process, excess bentonite is removed in both pits, the initial and final ones.
Advantages of GNP
Laying utility lines using the puncture method has undeniable advantages:
- Directly for the work you will need a small team of specialists (2-3 workers);
- The cost of GNP work is more than 2 times lower than laying communications using a drilling rig;
- Using GNP, you can lay new pipelines and replace old ones; when using a drill, replacement is not available;
- There is no risk of soil collapse in the puncture, even if work is carried out in unstable soil;
- Less equipment is required and no additional solutions are needed.
With GNP, resources, finances and labor are saved.
What problems does the technology solve?
Increasingly, situations arise when the classic (with digging of trenches) laying of communications is undesirable or impossible. In these cases, the HDD method comes to the rescue with its special drilling rigs, which make it possible not to disturb the top layer of soil. The technology is used to lay the following types of communications:
- Water supply (including for transporting drinking water).
- High pressure gas pipeline.
- Heating networks.
- Gravity sewerage.
- Electrical cables.
- Cases for communication cables, telephone and fiber-optic communication lines.
- Replacement of outdated communications.
- Formation of underground passages of any degree of complexity.
Schematic representation of a puncture (gasket) Source forward-gnb.ru