Features of the operation of rolling machines
Purpose
The equipment allows us to produce various types of products:
- Long products. These include rods and strips of various geometric shapes, as well as shaped parts, spring and rhombic.
- Special purpose profile. Metal products in the form of angles, channels, I-beams, as well as combined blanks with a variable cross-section.
- Rolled products in the form of thin sheets up to 4 mm, as well as thick sheets more than 4 mm.
- Pipe profile with connection using welding and seamless joints.
Design and principle of operation
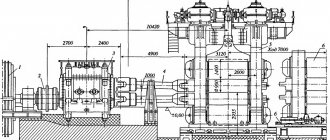
The rolling press consists of three main parts:
- The cage is working. The design of these elements includes rolling rolls, installation plates, a base frame, and wiring.
- Electric motors for transmitting movement to working elements.
- Mechanisms of distribution and transformation of motion. Consists of a spindle, couplings and gears.
The units differ in the number of stands and work roll sizes:
- Machines for thick metal have up to two working compartments with rollers ranging from 3 m to 5.5 m in length. In addition, vertical rollers can be installed, which are used for processing side edges.
- Broadband equipment contains up to 15 stands, rolls have a length of up to 2.5 m.
- Universal rolling presses consist of 5 compartments, and the length of the shafts is up to 1.5 m.
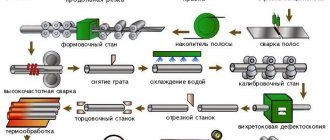
In industry, there are three methods for processing metal raw materials until they acquire the required geometric shape:
- In the first case, a rolling device is installed on the casting unit, and the initial contour of the part is obtained until complete crystallization. The disadvantage of this method is the need to maintain a high temperature until the end of processing, as well as additional precise running-in.
- As a result of rolling through furnaces with temperatures inside the chamber up to 1350 C, the edges are independently welded. At the exit of the equipment, a finished pipe profile is obtained.
- The third method involves manufacturing parts at a workpiece temperature corresponding to the environment. To prevent defects, the units use a large number of rollers that rotate in the opposite direction.
Specifications
Rolling machines have characteristics that distinguish them from analogues:
- the type of profile produced in a particular installation can be pipe, section, as well as thin and thick sheet;
- the range of metal thickness intended for rolling is from 0.4 mm to 200 mm;
- necessary raw materials for rolling;
- performance indicator, the choice of machine before purchase, as well as the preparation of raw materials, depends on this factor;
- number of working cells with rolls for the required profile;
- the diameter of the working shafts for rolling, as well as their useful length;
- rated voltage - 220 V / 380 V;
- the power indicator of the electric motor used is from 2.2 kW and above;
- assembled installation dimensions;
- total weight of all equipment in the complex;
- presence of reversal in the rolling mill.
Varieties
Based on the number of rolls located in the working stand and their placement, rolling machines are divided into the following types:
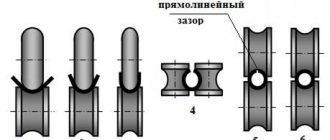
- double-roll - the design has paired mechanisms for pressing, which can rotate in different directions;
- three-roll - contain three shafts in each stand;
- four-roll - consist of two pairs of working parts;
- multi-roll - have a design of 4 or more rolls, and in universal ones they are used in a vertical position, sometimes they are installed in the spaces between horizontal ones;
- rolls mounted at an angle to the surface of the metal workpiece.
Rolling presses are distinguished by the location of the stands:
- equipment with working mechanisms arranged in one line is called linear;
- in stepped installations, the stands are installed in several lines parallel to the main flow;
- equipment for continuous and semi-continuous rolling; with the help of such machines, industry achieves high productivity.
Depending on the type of product produced during the process of pressing blanks, installations are divided into the following types:
- Crimping equipment. Allows the production of steel ingots weighing up to 25 tons. A piece of square or rectangular cross-section comes out of the working stands.
- Continuous pressing machines for blank material. As a result of the operation of such mechanisms, steel plates are modified into a special profile and sheets.
- Rail and beam machines roll blooms into rails, channels and large beams. In industry, step and sequential mills are used.
- Sectional machines are used to produce metal parts of different grades.
- In the process of manufacturing wire, wire mills are installed in the workshop; they are divided into stepped, semi-continuous and continuous.
- Slabs are processed using a sheet rolling machine. Thick-sheet, wide-strip, and also with winders are used.
- Pipe rolling equipment produces seamless and welded pipes. During the rolling process, two levels of processing are used. Initially, a hollow sleeve is made from a round bar, then a pipe of the required diameter is made from it.
Selection principle
When purchasing equipment, pay attention to the following:
- Productivity of finished products, process automation, reliability and profile quality.
- The use of additional installations to ensure automatic rental.
“Made with us” and on Yandex.Zen
A unique device was put into operation in Gatchina: an experimental automated rolling mill “Kvatro-800 Mill” for testing new types of metal. It was developed and built in the workshops of the Prometheus Research Institute of Structural Materials, and on September 18 it was demonstrated in operation for the first time.
This is the last stage of a very complex technological chain. Scientists first create new types of steel in theory, then smelt prototypes, which are then fed to a rolling mill. There they are processed, the behavior of steel under heavy loads and high temperatures is recorded, the process is completely controlled by a computer.
The rolling mill allows you to simulate the production chain of any steel production in Russia - this is a way to seriously save money when starting to produce new steel on an industrial scale, Prometheus employees say.
Following the grand opening of a new unique device in Gatchina, Prometheus employees and the co-creators of the project - the heads of the Polytechnic University and the Rubin Central Design Bureau - observed the spilling of steel and the rolling of steel sheets. “The mill closes the chain of equipment for the creation of nanomaterials,” explains Prometheus General Director Alexey Oryshchenko.
For two years, scientists built theoretical models of new types of steel and smelted prototypes, which on a rolling mill acquire special properties due to the formation of nano-sized structures. The process of processing steel sheets under heavy loads and high temperatures is carried out by a computer. “An industrial sample of a nanostructured material has already been obtained. This is the only steel in the world,” the general director clarifies and exclaims, “Kulibins still exist today!”
At this rolling mill, Prometheus employees will simulate the production processes of structural nanostructured materials at Russian steel mills.
Alexey Oryshchenko is confident that “in the near future, nanotechnology will become the basis for the modernization of the entire economy.” The scientist is optimistic about the prospects for life on earth. He believes that thanks to the introduction of technologies for the production of materials with new properties, “our world made of iron” can change for the better. “There will be no need for huge metallurgical plants.” New materials will not corrode and will become durable and ductile. As a result, the world will be able to live without landfills. Harvests will be produced by the land, not greenhouses. Automatic production management will free up people who will engage in science, culture and medicine, but as prevention.
Although the equipment has just been launched, there is already a result: Izhora plants are starting to produce nanotech pipes with a guaranteed service life of at least 25 years.
Sources:
Rolling mill
A machine for pressure processing of metal and other materials between rotating rolls, i.e., for carrying out the rolling process, in a broader sense - an automatic system or line of machines (unit) that performs not only rolling, but also auxiliary operations:
- transportation of the original billet from the warehouse to the heating furnaces and to the mill rolls,
- transfer of rolled material from one caliber to another,
- edging,
- transportation of metal after rolling,
- cutting into pieces,
- marking or branding,
- edit,
- packaging,
- transfer to the warehouse of finished products, etc.
Classification and design of rolling mills
The main feature that defines a device is its purpose depending on the range of products or the technological process being performed.
According to the range of products, mills are divided into:
- billets, including mills for rolling slabs and blooms,
- sheet and strip,
- varietals, including beam and wire,
- pipe rolling
- rolling parts (tires, wheels, axles, etc.).
According to the technological process, they are divided into the following groups:
- foundry and rolling units (units),
- crimping (for crimping ingots), including slabs and bloomings,
- reversible single-cage,
- tandems,
- multi-cage,
- continuous,
- cold rolling.
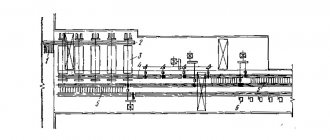
Main equipment of rolling mill
The size of a rolling mill intended for rolling sheets or strips is characterized by the length of the roll barrel, for billets or long metal - by the diameter of the rolls, and for a pipe rolling mill - by the outer diameter of the rolled pipes.
Mill equipment used to deform metal between rotating rolls is called main equipment, and auxiliary equipment for performing other operations.
The main equipment consists of one or more main lines, each of which contains 3 types of devices:
- working stands (one or more) - these include rolling rolls with bearings, frames, installation mechanisms, plates, wiring;
- electric motors for rotating rollers; transmission devices from electric motors to rolling rolls, consisting mostly of a gear cage, spindles and couplings.
A gearbox is often installed between the gear cage and the electric motor. If each roll has its own electric motor, the transmission devices consist only of spindles. The most widespread are mills with horizontal rolls:
- two-roll (duo),
- three-roll (trio),
- four-roll (quarto),
- multi-roll.
To compress metal along the side surfaces, stands with vertical rolls, called edgers, are used. Mills in which vertical rolls are located near horizontal rolls are called universal.
They are used for rolling wide strips and I-beams with wide flanges. In screw rolling mills, the rolls are located in the working stand obliquely - at a feed angle. Such mills are used for rolling pipes, axles, balls, etc.
The number and location of working stands are determined by its purpose, the required number of metal passes between the rolls to obtain a given profile and the specified productivity. On this basis, the camps are divided into 8 types.
Single-stand mills include most blooming mills, slab mills, ball rolling mills, and cold rolling mills for sheets, strips and pipes.
In cases where it is not possible to accommodate the required number of calibers in one working stand or when high productivity is required, mills with several working stands are used. The most advanced multi-stand mill is a continuous one, in which metal is simultaneously rolled in several stands.
Continuous mills are used for hot rolling of billets, strips, sections of metal, wire, pipes, as well as for cold rolling of sheets, tin, strip and other profiles.
Rolling speeds are very different and depend mainly on the required productivity, the range of rolled products and the technological process. In crimping, billet, plate, and large-section mills, the rolling speed is about 2-8 m/sec.
The highest speeds are typical for continuous mills:
- when rolling long metal 10-20 m/sec;
- strip 25-35 m/sec;
- wires 50-70 m/sec;
- during cold rolling of sheet metal 40 m/sec.
Data on the productivity, drive power and weight of equipment of some rolling mills, which are most widespread in the USSR for the production of hot-rolled steel.