The process of measuring the main types of fasteners has its own characteristics. Helpful tips: the reliability and quality of fastening two or more parts together depends on the correctly selected sizes of fasteners. This question often presents difficulties, because even wrenches are calculated taking into account the indicators of all fasteners. An important selection of necessary hardware.
The main indicators for selecting a bolt with the required nut:
- Product diameter.
- Part thickness.
- Length of hardware.
- Information on the surface of fasteners.
The manufacturer shall display data in accompanying documents for bolt shanks with metric threads in MdxPxL
. Take into account important nuances when selecting the necessary hardware. Determining the correct sizes of bolts and nuts.
Letter designation
Decoding the meanings of the letters:
1. M - metric thread.
2. D - diameter of fasteners.
3. P - indication of a very small thread pitch, just small in size, large, especially large ones are not added.
4. L - this letter indicates the length of the part.
The literal value is written in capital and small characters (D is abbreviated as “diameter”). Length - denoted by “L” from the word “lenght”. Thickness - “stoutness” - “S”. The height is designated by the symbol “H”, the word “high”.
Numerical values near letters are indicated in mm. To measure the correct indicators (take bolts), you should find out the required type of fastener. It is allowed to use the rules of the domestic GOST, the European ISO quality standard, and the requirements for DIN (Nemetchina) standards.
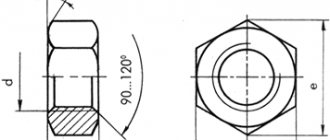
Relative bolt parameter values:
1. d - nominal bolt thread diameter.
2. D = 2d - bolt head along the diameter of the circumscribed circle.
3. h = 0.7d - bolt head height.
4. lo = 2d + 6 - thread length, c = 0.15d - chamfer size.
5. l = m + n + Sm + H + K - bolt length.
Metric size chart.
| Metric thread diameter | Key size | ||
| main S, mm. | reduced S, mm. | increased S, mm. | |
| M1 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.2 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.4 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M1.6 | 3.2 | — | — |
| M2 | 4 | — | — |
| M2.5 | 5 | — | — |
| M3 | 5.5 | — | — |
| M4 | 7 | — | — |
| M5 | 8 | — | — |
| M6 | 10 | — | — |
| M7 | 11 | — | — |
| M8 | 13 | 12 | — |
| M10 | 17 (16) | 14 | — |
| M12 | 19 (18) | 17 | 21 (22) |
| M14 | 22 (21) | 19 | 24 |
| M16 | 24 | 22 | 27 |
| M18 | 27 | 24 | 30 |
| M20 | 30 | 27 | 32 (34) |
| M22 | 32 (34) | 30 | 36 |
| M24 | 36 | 32 | 41 |
| M27 | 41 | 36 | 46 |
| M30 | 46 | 41 | 50 |
| M33 | 50 | — | 55 |
| M36 | 55 | 50 | 60 |
| M39 | 60 | 55 | 65 |
| M42 | 65 | 60 | 70 |
| M48 | 75 | — | 75 |
| M52 | 80 | — | 80 |
| M56 | 85 | — | — |
| M60 | 90 | — | — |
| M64 | 95 | — | — |
| M68 | 100 | — | — |
| M72 | 105 | — | — |
| M76 | 110 | — | — |
| M80 | 115 | — | — |
| M85 | 120 | — | — |
| M90 | 130 | — | — |
| M95 | 135 | — | — |
| M100 | 145 | — | — |
| M105 | 150 | — | — |
| M110 | 155 | — | — |
UNC/UNF inch thread table wrench
| Thread diameter (key size), inch | Wrench nut size, inch | Wrench nut size, mm |
| 1/4 | 7/16 | 11.11 |
| 5/16 | 1/2 | 12.7 |
| 3/8 | 9/16 | 14.29 |
| 7/16 | 5/8 | 15.88 |
| 1/2 | 3/4 | 19.05 |
| 9/16 | 13/16 | 20.63 |
| 5/8 | 15/16 | 23.81 |
| 3/4 | 1 1/8 | 28.58 |
| 7/8 | 1 5/16 | 33.34 |
| 1 | 1 1/2 | 38.10 |
| 1 1/8 | 1 11/16 | 42.86 |
| 1 1/4 | 1 7/8 | 47.63 |
| 1 3/8 | 2 1/16 | 52.39 |
| 1 1/2 | 2 1/4 | 53.15 |
| 1 3/4 | 2 5/8 | 66.68 |
| 2 | 3 | 76.20 |
| 2 1/4 | 3 3/8 | 85.73 |
| 2 1/2 | 3 3/4 | 95.25 |
| 2 3/4 | 4 1/8 | 104.76 |
| 3 | 4 1/2 | 114.30 |
What nuts are needed?
To navigate the huge variety of nuts, it is best to consult reference books or study the issue online. Each type of fastener has its own production technology and operating requirements. Accordingly, for quality control, there are separate markings for each type.
- Spline nuts - GOST 11871 88.
- High nuts - GOST 15523 70.
- Low nuts - GOST 5916 70.
- Increased fasteners - GOST 22354 77.
- Standard hex nut - GOST 5927 70.
What classes of strength and accuracy, what size of nuts - these regulatory documents will be able to answer all the basic questions that relate to these hardware.
Methods for calculating the parameters of a bolt with a nut
When determining the diameter of a fastener, various tools are used, which include a caliper, a template ruler, and a micrometer. An accurate measurement of the result is obtained when using the decoding caliber “pr. - Not.". This type is called “passes - does not pass.” The first part is determined when the nut is tightened without force, in the second - when the elements being tightened do not match.
It is recommended to measure the length using a ruler or caliper. The thread pitch of fasteners can be measured with a special tool. It's called a pedometer. If the necessary device is not available, then measure the distance from one turn to another using a caliper.
The accuracy of the result with this tool is achieved only when measuring large diameter threads. Indicators are considered accurate if you check them not two turns, but take 5 times more. The result obtained is divided by the number of turns used during measurements.
The coincidence of the numbers with the number of the threaded series obtained during verification refers to the reference true value. If this does not happen, then this can be attributed to the inch type of thread. To accurately determine the step, additional testing is necessary.
Information about bolted connections must be indicated by the manufacturer in the accompanying documents. Not all consumers have access to such documents. Let's consider possible ways to determine the parameters of hardware.
How not to make a mistake?
Calculating fasteners sometimes seems complicated. To select suitable hardware without wasting effort, you need skill and knowledge. Important indicators that influence fastening hardware and their types include length, thickness, diameter, sometimes taking into account height.
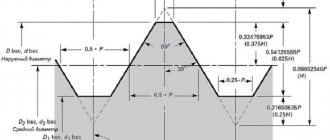
The thread of any standard product must be suitable for the diameter of the fastening material of a certain working profile - the main (normal), reduced and increased in value. A modified bolt head is almost never seen, or is rare. It is not difficult to calculate the required parameter of wrenches that will fit a certain bolt size from M1.6 to M110. Modern ISO standards have established modified dimensions for hex heads; these data are marked in brackets in the table.
Independent method for calculating sizes
The available sample should be examined from all sides. Sometimes markings are visible on the surface of the product. This fact will speed up the selection of fastening hardware. It is impossible to read anything on a damaged bolt head.
How do you measure indicators yourself? You need to proceed from the key dimensions, taking into account the thread pitch and bolt diameter. When using the basic technical indicators of hardware, the right tools are selected.
Scope of application and features
Nuts are used in many branches of modern production. First of all, we are talking about work related to the assembly of various structures, for example, in the automotive industry. And in order for the connection to be durable and reliable, during the production process the surface of this type of fastener is covered with a protective layer that has anti-corrosion properties.
There is another type of part used to fasten various objects, and also has a hole. This is a puck. The differences are as follows:
- there are threaded threads on the inner surface of the nut, while the washer is smooth;
- the nut is used as a direct fixation of the element to be fastened, while the washer plays the role of a gasket, and in some cases, insulation.
Even the round nut, or rather, its side surface, has notches that make tightening easy. And the puck is absolutely even.
About using the tool
The head is measured using a caliper. This leads to a more accurate determination of the length of the gap between the two faces on the head. The results obtained from measurements should be recorded on a millimeter measuring tape.
When determining the size, inspect the length of the fastening hardware. You can take measurements with a regular ruler. The head should be measured by the length of the hardware from the bottom to the chamfer.
Calculation of the wrench size for a bolt with internal hexagons
In addition to hexagonal fastening hardware, the mechanical engineering and instrument-making industries widely use bolts that have cylindrical, reliable heads. The work of screwing them is done using a hexagonal corner wrench. The manufacture of bolts complies with the requirements of DIN 912 and GOST 11738 - 84 rules.
Size chart for bolts and hexagon screws
| Thread, M | M4 | M5 | M6 | M8 | M10 | M12 | M14 | M16 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M33 | M36 |
| Key size, mm | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 17 | 19 | 19 | 22 | 24 | 27 |
Bolt sizes are determined using a micrometer, sometimes using a template ruler. Recommendations require working using a template. Using the device allows you to get the desired result.
The caliper determines the thread pitch with high accuracy on large parts. The pitch of small parts is determined by checking at least 10 turns at once. The existing system allows you to calculate an M10 bolt in inches, where 1 inch is equal to 25.4 mm. CIS markets use indicators in accordance with GOST.
The type of bolts is determined by the geometric shape of the hardware. There are different measurement methods:
- Check the protruding shape of the head, where the length of the part for fastening is carried out without taking into account its measurement.
- Concealed head types.
These include:
1. Hexagonal heads of fasteners, in accordance with the requirements of GOST 7805 - 70, 7798 - 70, 15589 - 70, 10602 - 94.
2. Hexagonal reduced head, produced according to the rules 1559 - 70 of GOST 7808 - 70, 7796 - 70.
3. High-strength fastening products, according to GOST 22353 - 77.
4. Hexagonal parts with high-strength increased dimensions corresponding to GOST R 52644 - 2006.
Method for determining the number on a wrench
High popularity is observed when purchasing hex nuts. They differ in sizes - M6, M8, M10, M12, M 16, M 24, M20, M30, M27, M 36, M 52, M 48, M 42. The bolt and nut are connected using wrenches. Information about working profile wrenches is applied to the body of the handle, examples: 7 x 8 or 17 x 19. Using the table, you can easily find the required wrench and calculate the appropriate working bolt from M1.6 to M110.
Certain work is performed with wrenches with different profiles. When the need arises, they work with the use of: gas, cap, cylinder, combined, hexagonal, spark plug - when replacing a spark plug, end, open-end, adjustable. Sometimes fastening hardware with non-standard sizes is used. In such cases, GOST and OST parts are used or orders are prepared strictly according to the drawings.
Universal wrenches are often used; they work well with hardware of various diameters. They are convenient to work with. Such products have an intermediate length located between two parallel edges. You can accurately measure it without using other tools by finding out the thread diameter indicated in the documents supplied with the fasteners.
Suggested options
Nuts are a type of fasteners that are needed for threaded connections. The key difference between a nut is the thread. They are used for bolted connections in conjunction with other parts. To do this, use special devices or tools to determine the diameter of the thread. As an option, use technical documentation.
The intermediate length between two parallel faces of the head diameter varies and must be calculated. Correct measurements are taken using a ruler, then the bolt head will be clearly placed in the selected wrench. It is recommended to obtain an accurate result of the parameters by working with a caliper.
When determining the length of the bolt shank, the height of the head is not taken into account. If there is an M16 rod, a thread with a diameter of 16 mm is provided. In an automobile bolt with a pointed end, its length is calculated taking into account the direction of the magnitude.
Using a wrench taking into account threading
Many fastening hardware is made for a bolt that has a metric thread. Determining the parameters of a nut with a similar diameter is performed with additional steps. It is not the nut parameters that need to be checked, but, for example, the threads of screws or the bolt shaft.
The wrench has different lengths. The thread size affects the nut, and is determined by the dimensions: from M1 to M110. The intermediate length between the jaws on the wrench is allowed - 3.2 - 155 mm. The length of the handles remains 150 - 500 mm.
A combination inch wrench is used when assembling fastening hardware on foreign cars that do not have the metric system. The tool has two grips for fastening materials on both sides of the handle: one end is equipped with an open-end wrench and the other with a spanner. The combined device is convenient to work with.
Definition of spanners
An inch parameter is expressed in inch measurements. The width of the key's mouth has nothing to do with the name, but is determined by the thread of the fasteners. It is intended for this category. If you compare the metric system, you will notice the existing difference in the hexagonal working profile of nuts and bolts in inches by fractions of mm.
This is the reason for the discrepancy with the wrench with metric threads: either there is a loose fit with the edges of inch fasteners, or it does not screw on at all. The task should be performed using an inch wrench with a socket head. Determining the accuracy of a suitable element will require clarifying whether the outer inner diameter of the bolt matches the specific nut.
You will need to use a special table. You should check the height of the nut, as this indicator may change, affecting the size of the height of the part. To accurately determine the pitch, you need to use a thread gauge.
If there is no such tool, then it is necessary to count the number of turns of a particular gap. With a correctly selected nut for the bolt, it is easy to determine the parameters of the wrench. With sufficient force, the connection can be securely fixed.
Nut size and main types of nuts
There are several main types of nuts:
- Hex or Flat Nut: A versatile, general purpose part.
- Lock nut: Used for enhanced safety when the nut should not come loose due to
vibration or other constant loads.
- Cone Nut: Used to center objects.
- Groove or Castle Nut: Used in conjunction with a cotter pin on objects that turn or twist.
- Cap Nut: Used to create a finished look by capping the end of the thread.
- Wing Nut: Used when tightening a joint by hand.