HEX BOLTS AND HEX NUTS UP TO 48mm DIAMETER
Design and dimensions
Official publication
Moscow
Standardinform
2010
ATTENTION READERS!
The Federal State Unitary Enterprise "Russian Scientific and Technical Center for Information on Standardization, Metrology and Conformity Assessment" prepared for publication in 2010 collections of national standards, compiled according to an industry (thematic) principle.
The collections include official publications of standards with all changes and amendments approved (adopted) as of the date of publication of the collection.
In 2010, collections of standards will be published on the following topics:
Leguminous crops. Technical specifications Cereal crops. Technical specifications for confectionery products. Analysis methods
Potatoes, vegetables, melons. Technical conditions Cereal products. Technical conditions. Analysis methods
Margarines, fats for cooking, confectionery and baking industries Stone fruits. Technical specifications Meat products. Analysis methods
Processed products of fruits and vegetables. Analysis methods
Wheat processing products. Pasta. Technical conditions. Analysis methods
Food products, canned food. Microbiological analysis methods
Live fish, chilled and frozen. Specifications
Fish and fish products. Methods of analysis. Marking. Package
Oilseeds
Juices. Technical conditions. Analysis methods
Raw materials and food products. Methods for determining toxic elements Unified System of Design Documentation (ESKD)
Unified System of Program Documentation (USPD)
Unified System of Technological Documentation (USTD)
System for developing and launching products
Hex bolts and hex nuts up to 48mm diameter. Design and dimensions
Oil and petroleum products. General rules and regulations
Metal pipes and connecting parts to them. Part 2. Threaded pipes. Metal pipes and connecting parts to them. Part 4. Cast pipes made of ferrous metals and alloys and connecting parts for them. Basic dimensions. Technological testing methods for pipes
© STANDARDINFORM, 2010
GOST 7798-70
INTERSTATE STANDARD
Hex BOLTS
Benefits of 10.9 Strength Bolts
The main advantage of this product is the ability to optimize the metal consumption of the final structure and its weight while simultaneously increasing the resistance indicators, as well as the strength of threaded connections. In other words, it is allowed to use high-strength bolts that have a smaller diameter and, accordingly, weight compared to fasteners of the same type, but lower strength, all other things being equal. For clarity, let us give a specific example for a bolt with M20 thread. Ultimate breaking load for:
- class 5.8 is 13 t or 126 kN;
- class 10.9 is equal to 26 t or 254 kN.
The difference is obvious.
Other advantages of using high-strength fasteners include:
- developers have additional options for designing metal structures by reducing the dimensional characteristics of mating components (for example, the same flanges);
- possibility of: - using pre-stressed spatial metal structures; — place increased loads on the designed interface. That is, effective solutions are available using less material- and financially-intensive methods;
- the use of high-strength fasteners is an excellent opportunity to increase the service life of production equipment. We are talking about scheduled audits, restoration and repair work. Such fasteners can be reused many times in updated connections.
ACCURACY CLASS B
DESIGN AND DIMENSIONS
Official publication
Moscow
Standardinform
2010
INTERSTATE STANDARD
HEX BOLTS, ACCURACY GRADE B
Design and dimensions
Hexagon bolts, product grade B. Construction and dimensions
GOST
7798-70
MKS 21.060.10 OKP 12 8200
Date of introduction 01/01/72
1. This standard applies to hex head bolts of accuracy class B with a thread diameter from 6 to 48 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).
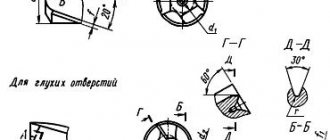
2. The design and dimensions of the bolts must correspond to those indicated in the drawing and in the table. 1.2.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 2-6).
3. Thread - according to GOST 24705. Thread run-out and undercut - according to GOST 27148. Bolt ends - according to GOST 12414.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 5).
Behind. The radius under the head is according to GOST 24670.
36. Tolerances of dimensions, deviations in shape and location of surfaces and control methods not established by this standard - in accordance with GOST 1759.1.
Sound Allowable bolt surface defects and control methods are in accordance with GOST 1759.2.
For—Sv. (Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 4).
(Deleted, Amendment No. 4).
5. The head design options are determined by the manufacturer.
5a. It is allowed to produce bolts with a diameter of the smooth part of the rod dv approximately equal to the average diameter of the thread.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 3).
56. To apply markings, it is allowed to manufacture bolts of versions 1 and 2 with a hole on the end surface of the head with dimensions that do not reduce the strength of the head, while the depth of the hole should be no more than 0.4 k.
(Introduced additionally, Amendment No. 5).
6. Technical requirements - according to GOST 1759.0* *.
Design and manufacturing technology
A bolt is a metal rod with a thread on it. At one of its ends there is a head, most often a hexagonal configuration with dimensions for a specific wrench. The parts are connected by screwing the nut until it stops. Uniform load distribution is ensured by the use of washers.
Bolts with a strength class of 8.8 and higher are considered high-strength. For their manufacture, alloy steels or carbon steels with a carbon content not exceeding 0.5% are used. The production of blanks is carried out on high-quality equipment using hot and cold stamping. The video shows the first version of this technology. At one stage, to prevent the hardware from being susceptible to corrosion and reducing its strength, it is subjected to heat treatment. The thread is applied on special automatic machines.
Screw classification
Let us now consider the screws available in the TsKI assortment. The largest group of them are general purpose screws. We meet them every day in everyday life and at work. They all have a fully threaded shaft (although there are exceptions) and different shaped heads. The heads have slots or recesses for different types of keys.
Another large group of screws are set screws. The name comes from their purpose. For the most part, they are designed for precise installation and fixation of parts in mechanisms. To do this, they have various protrusions or recesses at their ends.
According to GOST 12414-94 (ISO 4753:1999): “Ends of bolts, screws and studs. Dimensions" the following setscrew ends are provided:
The torque is driven by the following elements:
The summary table shows the actual, most common combinations of setscrew heads and ends, indicating the DIN standard.
Unit of measurement – millimeters
To form the connection, nuts are used that have similar thread and accuracy characteristics - B (domestic GOST 5915 or DIN 934 standard).
The following raw materials are used in the production of bolts with strength 10.9:
- structural alloy steel grades: St.35XGCA, St.30XGCA, St.40XSelect, St.40X, St.40G2, St.45G, St.38XA, St.35X;
- Stainless austenitic steel A1 and .
Types of tests
In order to confirm the quality of manufactured fastening products, certain tests are carried out. Their methods and methods are recorded in GOST R 52627-2006. Tests can be carried out in any laboratory, including a factory one, which has successfully passed certification in a center operating under Rosstandart. Tests are carried out on:
- hardness . The ability of the manufacturing material to resist various types of deformation;
- torsion _ Such tests are carried out in accordance with the requirements of the international standard ISO 898-7: The torque at which the bolt breaks is established;
- stretching _ As a result of these tests, material indicators such as relative elongation, yield strength and tensile strength are determined.
Product properties are determined by the results of tests.
Similarities and differences between DIN 931 and DIN933 standards
Standards DIN 931 and DIN 933 are the closest analogues of GOST 7805 and GOST 7798, respectively. However, there is one important aspect here. As you know, each domestic standard normalizes the production of bolts of only one precision level. So, the first of the above is valid for class “A” fasteners, and the second is for fasteners made with accuracy corresponding to class “B”. In German regulatory documents the situation in this regard is somewhat different.
- The requirement to produce bolts with accuracy class “A” applies to products with threads up to M24 and a length not exceeding 150 mm.
- The dimensional characteristics of such fasteners must meet the requirements of class “B” if their thread diameter is greater than M24 and their length exceeds 150 mm.
There are also differences in the limit values of the thread diameter. It was said above that GOST 7805 has more nomenclature items compared to GOST 7798 due to the addition of seven diameters, the size of which is less than 6 mm (minimum -1.6 mm). And the upper values of this indicator are identical – M48.
In German standards, everything looks exactly the opposite. That is, the minimum thread there is the same - M1.6, but the maximum is different. In DIN 931 it is M39, and in DIN 933 it is M52. Accordingly, all maximum values of other parameters, starting from the height of the head and ending with the holes in the rod, also differ.
Bolt materials
| Product Type | Strength class | Possible steel grades |
| Bolt | 3,6 | StZkp, StZsp, St5kp, St5sp, |
| 4,6 | St5kp, 10.09G2.09G2S and 09G2SD | |
| 4,8 | 10, 10kp | |
| 5,6 | 30,35 | |
| 5,8 | 10, 10kp, 20, 20kp | |
| 6,6 | 35,45 | |
| 6,8 | 20,20kp,45, 40Х | |
| 8,8 | 35,45,35Х,38ХА,45Г,40Х | |
| 10,9 | 40Khselect, 30KhZMF, 30Kh2NMFA | |
| 12,9 | 20Х2НМТРБ |
Fastener properties
Hardware produced by various enterprises differ from each other in geometric parameters, shape, material, and purpose. In addition, they can be distinguished by the type of coating and a number of others. In addition to the mentioned properties, bolts of the same type differ in strength parameters.
For example, an M16 bolt can be used to fasten parts of a fence or fence, and the same bolt can be used to assemble a bridge or crane structure. Accordingly, for the first option, a bolt with lower strength parameters can be used than for the second application option. Bolts used to assemble cranes and similar equipment are called crane bolts. They are distinguished by higher strength and especially strong steels are used for their manufacture. In the Russian Federation, GOST 7817-70 is in force, which normalizes the requirements for fasteners used in particularly critical structures.
Hardware has several forms - bolts, nuts, screws, etc. Each of these products is used to solve specific problems. Various steels and different technologies are used for their manufacture. The marking that will be applied to the surface of the fastener also depends on this.