A welding jig is a device that greatly facilitates the process of welding bulky parts; it is a device for assembling and securing welded parts relative to each other, which are fixed in a certain position. A welding jig is a type of system that allows for volumetric fixation of parts for assembly and welding. A good conductor significantly increases productivity, facilitating the process of manufacturing products, and the quality of the resulting product increases.
The use of a welding jig in production has many other advantages, one of which is high welding accuracy, and in some industries this factor is especially important (for example, in transport engineering). During processing, the part is located either in the jig itself or under it. Another advantage of this device is the ability to process a part in several places at the same time.
To securely secure the workpiece, the jigs are equipped with welding jig clamps. These clamps are capable of holding an object in a “death grip” without being exposed to vibrations from the workpiece. At the same time, the clamps are not prone to deformation of the product being held, since the gripping force can be adjusted. Another advantage of using such auxiliary systems is safety, since securely fastened parts protect workers from injury.
In production, welding jigs are used together with welding robots, which perform welding work. The structure of the conductor is a rigid metal frame, which, in addition to clamps, is equipped with stops and clamps. Stops and clamps are needed to make it possible to adjust the jig to process a part of any configuration. Welding jig clamps come in both manual and mechanical types. From us you can purchase various equipment for welding work: a welding table, a welding jig, as well as clamps for a welding jig. – this is many years of experience in supplying only high-quality industrial equipment.
Source: vector-grupp.ru
It’s annoying when, after carefully calibrating and installing the elements in the desired position, the structure assembled with such diligence falls apart at the touch of an electrode, and you need to assemble everything all over again. It’s even worse when the element is welded, but not in the required position - it has moved imperceptibly or deformed after the metal has cooled. Using universal and specialized welding fixtures helps save time and get a high-quality product at the end.
There are many different devices and mechanisms designed for welding. In industry, where they deal with serial and mass production, specialized mechanized and automated equipment is used - transport devices, mechanisms for laying and tilting products, technological assembly devices, etc. At home, as a rule, manual welding devices of universal action are used, allowing carry out quick assembly of the structure, securely fasten all elements in the desired position and achieve minimal deformation of the part.
Main types of assembly and welding fixtures
Installation accessories
. Installation fixtures are designed to install the part in the desired position - exactly in the position in which it will be in the finished product. Based on their functions and design, they are divided into stops, squares, prisms, and templates.
Stops are used to fix parts on base surfaces and can be permanent, removable or folding (retractable, rotary). Permanent stops, which are most often ordinary plates or bars, are welded or screwed to the base. Removable or folding stops are installed when their constant presence in the part is structurally unacceptable.
Squares are used to install parts at a certain (90°, 60°, 30°, 45°) angle to each other. Squares are easy to use, the edges of which are made rotating and allow you to set any necessary angle between them.
Prisms are used to fix cylindrical products in a certain position. The simplest design welded from corners can be successfully used as a prism. Templates are designed for installing elements of a welded structure in a given position in relation to other previously installed parts.
Fastening devices
. With the help of fastening welding fixtures, the parts, after being installed in the desired position, are firmly fixed in order to prevent their accidental shift or deformation after cooling. Fastening devices include clamps, clips, clamps, ties, and spacers.
Clamp
- a universal tool used for almost any work with metal. For a welder, it is the first most important device, and if it is possible to do without it, then only at the cost of extreme inconvenience and to the detriment of productivity. Clamps for welding can have a variety of shapes and sizes, with a constant throat size and adjustable. Especially convenient are quick-release clamps, in which the clamping occurs using a cam mechanism. In general, it is advisable for a welder to have a set of a variety of clamps, since to assemble one structure, several of them may be needed - of different sizes and configurations.
What is a welding jig?
Reading time: 3 minutes
Welding in a workshop environment is very different from welding in a garage. If in the case of home welding you simply turn on the inverter and weld with piece electrodes, then in production not only special technologies are used, but also special devices. They are designed to simplify the welder’s work and speed up the work. Because often the profit of an enterprise depends on the quantity of products produced.
We will talk about one of these devices in this short article. We will talk about a welding jig, it is not an assembly jig or a welding jig. You will learn what this device is, why it is needed and how to use it.
Equipment for laying and turning of welded products
The stands do not provide tilting and rotation of products during operation, which makes it difficult to weld bulky and heavy components, therefore the welding installations include special equipment, namely: tilters, rotators, roller stands, manipulators and positioners.
Rotators are stationary devices in which the elements to be welded are not only secured, but also rotated around a horizontal or inclined axis in order to install them in a position convenient for welding, and sometimes to move them during welding. Rotators provide marching rotation of the product around a permanently located axis or around a number of axes lying in the same plane. The tilters have a manual or mechanical drive. Depending on the type of rotary device, there are roller, lantern, trunnion (center) and chain tilters.
Rotators are devices for rotating the welded product at working speed or at marching and working speed around an axis that does not change its position in space. There are rotators with a vertical, inclined or horizontal axis of rotation. Rotators with a vertical or inclined axis of rotation VV (vertical rotator) are sometimes called rotary by analogy with rotary lathes.
Welding rotator with a vertical axis of rotation: 1 - faceplate; 2 — bed with a rotation mechanism.
Roller stands or, otherwise, roller rotators or roller beds are designed to rotate and install the product in a position convenient for welding and to rotate the product at operating speed. The rotation of the product is carried out by driven, usually rubber-coated rollers coupled to the product. A significant advantage of roller stands is that the rotation speed of the product, regardless of its diameter, is equal to the peripheral rotation speed of the rollers. A conventional roller stand consists of a system of idle and driven roller supports mounted on a common foundation plate. Olive stands are used not only for welding, but also for assembly.
Manipulators are universal, usually stationary devices designed to rotate a product around an axis during the welding process at different angles of inclination of the rotation axis.
Universal welding manipulator: 1 - main frame; 2 - rotary frame; 3 — faceplate; 4 — faceplate rotation mechanism; 5 — mechanism for tilting the faceplate; 6 - support legs.
The manipulator consists of the following main components: a frame, a rotary table, drives for rotating and tilting the faceplate and a control unit. In most manipulators, all movements are mechanized. In some designs, the table can be tilted and raised manually. Some of them may not have a table lifting mechanism.
Positioners , unlike manipulators, are not designed for welding rotation of the product and serve only to install and rotate (turn) the product into a position convenient for welding. Positioners or installation manipulators are used both to secure the product and to install it in a position convenient for welding. All positioners are similar in design. They have two or three mutually perpendicular axes around which the faceplate with the product can be rotated or tilted.
Positioner setup diagrams
The positioner table rotates and tilts using a manual or electric drive; it has only a marching speed of movement. Positioners for products weighing more than 1.5 tons are usually electrically driven.
general information
A welding jig (welding and assembly jig, assembly jig, assembly jig, welding jig, etc.) is a special device designed for fixing and pre-assembling metal structures with which you will work. With the help of an assembly jig, the parts are securely fixed in one place, it is convenient to weld them and monitor the progress of the work.
The name "welding jig" is colloquial. In professional circles and in stores, this device is called a “welding table-manipulator”. It is often used to fix the rotation of pipes, as well as other large parts. For example, metal beams.
Why are conductors needed? Firstly, they simplify the welder’s work. If he uses a rotating pipe jig, he can rotate the pipe in a given direction without changing its position and welding, in fact, stationary. Secondly, such devices are not just convenient, they also speed up welding work, ultimately increasing the profit of the enterprise. And thirdly, sometimes you simply cannot do without an assembly conductor. For example, in robotic welding.
Technological equipment of welding installations
Flux-holding devices are used to create the necessary layer of flux in cases where this layer is not retained by the edges of the parts being welded. Flux-holding devices can be fixed or movable. Schemes of some of them are shown in the figure.
Flux pads are used to prevent leakage of molten metal into the gap between the edges. A layer of flux is pressed against the underside of the weld, holding the weld pool and forming a back bead.
How to use?
The use of a conductor largely depends on the model of the device itself. But in most cases there is nothing complicated about this, everything is intuitive. If you are using a simple stationary jig table with mechanical clamps, then place the part on it and fix it in the desired position using the same clamps, stops or clamps.
If you use more technologically advanced conductors, then read the instructions for this model. Since each device may have its own nuances of use.
Rules of circulation
They are dictated by the conductor model. Basically everything is clear by default. Working with a manipulator at an ordinary stationary table will not be difficult.
We place the parts of the future structure as required, clamp them with a mechanical vice and get started! To work with conductors at a higher level, it is a good idea to read the attached design. From it you will learn the differences between your favorite model.
If the process is not automated, you will have to “flex your muscles” yourself to firmly connect the parts of the structure. Who else besides you, the performer, knows better how to position the surfaces to be welded.
In production with a high degree of automation, the human factor is almost minimized. The workshops there are equipped with the necessary equipment with high-tech processors.
True, in less advanced industries or in artisanal conditions, craftsmen were also not left alone with soulless metal. Manufacturers of welded equipment produce a considerable range of useful tools for them.
You can get hydraulic, pneumatic, electromagnetic, or even vacuum clamps. Then it will take very little effort to fix the parts of the future structure in the desired position.
Features of welding jigs
Welding jigs vary in size, shape and principle of operation. According to their functional purpose, they are divided into two types:
- Conductors intended only for assembling metal structures using welding tacks. As a rule, their basis is a metal table or plate with rigidly fixed stops, stops, clamps and clamps.
- Conductors for performing assembly and welding work. They combine the functions of a conductor and a tilter. Such models are most often rotatable and provide access to the structure to be welded from any side.
Assembly and welding stands
Stands, racks and plates are the simplest devices for laying and fixing products assembled for welding in a position convenient for welding.
Assembly and welding rack
Assembly stands are structures with a base surface on which products are assembled and welded. When manual welding, universal assembly and welding plates with grooves for various fastening devices or racks are often used.
Stands and devices that combine assembly and welding operations can be stationary, mobile, or overhead.
Various beams are assembled and welded on the trestles of such a rack, installed at a short distance from each other along the entire length, or on a universal stand consisting of a number of fixed posts 2, to which, depending on the configuration of the beam, replaceable supports 1 are attached.
Scheme of a universal stand for welding beams: 1 - support; 2 - stand; 3 - welding tractor.
The listed stands refer to clampless devices. These include tables for welding relatively small parts and plates. A stand or table is usually connected to the arc power source and provides current supply to the product being welded.
If the product is supplied to the welding installation in assembled form, then this installation must have devices for laying and fixing the products in a position convenient for welding. In such cases, universal or specialized stands can be used. A universal device for welding frame structures contains a number of plates with grooves into which, depending on the configuration of the product being welded, various stops, clamps and clamps are attached. Such stands are equipped with a set of universal adjustment devices that can be fixed in various combinations in the grooves of the base plates. For assembly and welding of similar structures, specialized stands for certain products can also be used. They are equipped with a plate on which a number of permanent clamps are mounted, which determine the relative position of the parts assembled for welding. An example of universal stands for assembly and welding of flat sheet structures are electromagnetic stands. Electromagnetic stands can be used to assemble and weld sheets up to 15 mm thick. The disadvantage of this type of device is the negative influence of the magnetic field on the welding arc during the welding process.
A jig is an assembly and welding device equipped with stops, sockets, and fastening devices, which makes it possible to assemble and weld products in the most convenient position. In addition, the stands and devices include devices for holding a bath of molten metal and flux in the welding zone, for forming a sha, etc. Mechanized welding is most often performed in assembly-welding or welding jigs. In these devices, the conductor elements do not interfere with the movement of the welding machine; the jig itself can tilt, giving the seam a position convenient for automatic welding.
Examples of assembly and welding conductors
Clamps are elements that determine the position of the parts being welded relative to the entire device (stand, rack, conductor, etc.). The clamps include: stops (permanent, removable, folding), mounting pins and pins (permanent, removable), prisms (rigid and adjustable) and templates.
Removable stops are used in fixtures that can be adjusted according to the type of part or when welding parts that cannot be removed due to the stops. In the latter case, folding quick-release stops deserve preference. As a rule, stops also serve as support bases, and in some cases they can simultaneously serve as templates for welding mating parts. They can be force (limiting) and guiding (unloaded).
| The emphasis is hard | Removable stop | Folding stop |
Finger or pin type fasteners Prisms, adjustable and non-adjustable, are used for welding pipes, profiles, etc.
| Finger hard | Adjustable prism | Flip finger |
Templates are designed for; fixing the parts installed during assembly along the mating parts of the assembly or along any supporting contours of the products. In this case, the product itself is the load-bearing element of the device.
Clamps are elements of devices that provide clamping of parts to each other, to clamps or load-bearing surfaces of devices. Clamps can be mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic or magnetic.
Mechanical clamps are structurally simple and therefore most common.
| Screw clamps | Eccentric clamp | Spring clamp |
Along with mechanical clamps, pneumatic, hydraulic and magnetic clamps are also used.
Requirements for welding conductors
You can buy jigs for welding of any design and purpose from us. Such products must meet several requirements:
- Ensure strong and precise fastening of parts.
- Prevent their deformation when applying welding seams.
- Have a convenient location of fixing and clamping elements.
- Provide access to all parts of the metal structure for welding work.
- Eliminate the possibility of incorrect assembly of metal structures.
- Be easy to use.
- Ensure the safety of assembly and welding work.
Welding area maintenance equipment
Cradles, stepladders, and special platforms provide a comfortable position for the welder when working on large-sized products. The platforms are designed to accommodate welders and welding equipment, as well as to move them to the welding zone. They are manufactured for one or more welders and can be mobile (self-propelled or non-self-propelled), portable and stationary. The figure shows a universal platform that can move along the workpiece being welded, rise and fall depending on the level of welding, and move in the direction of the workpiece.
Universal platform for a welder: 1 - balcony; 2, 4 — levers; 3, 5 — screw drive; 6 - trolley.
How to order welding conductors
You can order the production of welding jigs in one of the following ways:
- By email
- By phone or...
- Click on the “Cost Calculation” button.
You can order the production of welding jigs from us. We have many years of experience in manufacturing such metal products and offer the best products at an attractive price.
Equipment for fastening and moving automatic and semi-automatic welding machines
Welding with automatic and semi-automatic machines can be carried out both without and with the use of special auxiliary devices, for example, for suspending the apparatus over a movable welded product or for moving the apparatus along a seam or from seam to seam (columns, portals, carts, platforms). Auxiliary equipment of this type is often used for welding with tractors or semi-automatic machines.
Rotary column for semi-automatic welding machine
Jig for drilling holes
A hole drilling jig is equipment to facilitate the process of drilling parts and eliminate defects. It represents a kind of pattern along which the cutting tool moves. Such conductors are widely used on machine tools and are high-precision products. The hole drilling jig is used on various drilling equipment. We are ready to offer the production of jigs for drilling overhead and box-type holes, as well as combined options. The use of jigs for drilling holes allows you to reduce labor intensity and increase the speed of manufacturing parts. In addition, the use of jigs allows you to make holes in several places on the part at the same time.
Conductors are more often used in mass production. We offer production of various types of conductors. Call us, we are ready to offer the best conditions for cooperation.
Source: metallokonstrukciy.ru
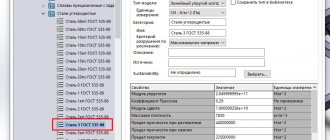
Technical characteristics of the conductor "SLOT-TABLE"
| Conductor type | 4100 | 4200 | 4300 | 4400 |
| Frame size, m. | 3.0 x 1.5 | 3.0 x 1.5 | 3.0 x 2.0 | 3.0 x 2.5 |
| Maximum load, kg | 50 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Vertical rotation range | 360° | 360° | 225° | 225° |
| Load Leveling | — | pneumatic | pneumatic | pneumatic |
| Brake mechanism | manual | manual | manual | manual |
If you follow the operating instructions for assembly and welding tables, the manufacturer guarantees the durability and high wear resistance of assembly and welding tables.