Designations
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | 45G17Yu3 |
| Designation GOST Latin | 45G17Ju3 |
| Translit | 45G17Yu3 |
| By chemical elements | 45Mn17Al3 |
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | Yu3 |
| Designation GOST Latin | Ju3 |
| Translit | Yu3 |
| By chemical elements | Al3 |
| Name | Meaning |
| Designation GOST Cyrillic | EI839 |
| Designation GOST Latin | EI839 |
| Translit | EhI839 |
| By chemical elements | — |
Welding steel 45. Practice
If work is carried out outside equipped workshops, then it is difficult to ensure strict adherence to the technology. In this case, you can use the following method:
- Preparing parts for welding : cleaning, forming edges for welding seams.
- Warming up parts using a gas (propane, acetylene) cutter or torch . To determine the temperature, you should use an infrared pyrometer; thermal pencils are also used, which begin to melt when certain values are reached.
- Welding is carried out as quickly as possible ; if necessary, the parts can be additionally heated during the process.
- Upon completion of work, the product must be placed in a container with sand so that the cooling process occurs as slowly as possible.
- If the part is too large and cannot be removed into the sand, then you can heat the welding area with a cutter or torch , gradually reducing the temperature.
In some cases, it is possible to use the “cold” welding method. For this, it is recommended to use a semiautomatic device or argon, since the heating zone in this case will be smaller than when using coated electrodes.
Welding is done as follows:
- elements of the product are assembled onto small tacks - 5-7 mm with a pitch of about 150 mm;
- The structure should be scalded with small seams , it is important not to let the metal get too hot;
- If possible, the seams should be placed unevenly on different sides of the product..
Important: this method cannot be used when welding critical structures.
When using the cold method, it is necessary to conduct a thorough visual inspection of the seams and check the strength of the joints, since the likelihood of cracks is high.
Description
Steel 45G17Yu3 is used : for the production of rolled sheets up to 60 mm inclusive and strip bulbs used in various metal structures and equipment in shipbuilding; long and shaped rolled products; forgings and stampings; light-loaded structures of ship hulls, ships and marine equipment products (sheet and profile parts of surface ship hulls, forgings welded into the hull, chains and chain devices, winches, capstans, axles, drums, bolts, nuts, studs, gears and worms for low-speed mechanisms , frames, casings, hatch covers, rescue devices, doors, cable hangers, pilot post spools (in a nitrided state, ballasts, ship engine housings); transformer parts.
Note
Low-magnetic steel of austenitic class. Magnetic permeability μ ≤ 1.01 gs/e. Cold forming, as well as mechanical cutting, slightly changes the magnetic permeability of steel, but the value of this characteristic after these technological operations does not exceed 1.01 gf/e, if the cold deformation does not exceed 50%. The magnetic field of products increases sharply in the presence of scale, which is ferromagnetic. Scale must be completely removed. Steel cannot be used for friction parts and parts operating in aggressive environments.
45G17Yu3 (Yu3, EI839)
- Products made of steel 45G17Yu3 (Yu3, EI839) in stock:
Circle - Sheet
- Square
to make a request
Steel 45G17Yu3 (Yu3, EI839) for shipbuilding, low-magnetic austenitic class
Steel 45G17Yu3 is used: for the production of rolled sheets up to 60 mm inclusive and strip bulbs used in various metal structures and equipment in shipbuilding; long and shaped rolled products; forgings and stampings; light-loaded structures of ship hulls, ships and marine equipment products (sheet and profile parts of surface ship hulls, forgings welded into the hull, chains and chain devices, winches, capstans, axles, drums, bolts, nuts, studs, gears and worms for low-speed mechanisms , frames, casings, hatch covers, rescue devices, doors, cable hangers, spool valves of pilot posts (in a nitrided state, ballasts, ship engine housings); transformer parts. Magnetic permeability μ ≤ 1.01 gf/e. Cold forming, and Also, mechanical processing by cutting slightly changes the magnetic permeability of steel, but the value of this characteristic after these technological operations does not exceed 1.01 gf/e, if the cold deformation does not exceed 50%. The magnetic field of products increases sharply in the presence of scale, which is ferromagnetic. The scale must be completely removed. Steel cannot be used for friction parts and parts operating in aggressive environments.
Specifications
| Chemical composition in% |
| NTD | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | Si | Ni | Fe | Al |
| TU 14-1-607-73, TU 14-1-906-74, TU 14-1-774-73, TU 14-229-278-88, TU 14-1-780-73 | 0,40-0,50 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,040 | 16,0-18,0 | ≤0,50 | ≤0,60 | ≤0,50 | — | 2,40-3,60 |
| RD 9257-76 | 0,40-0,50 | ≤0,030 | ≤0,040 | 16,0-18,0 | ≤0,50 | ≤0,60 | ≤0,50 | Ost. | 2,40-3,60 |
| Mechanical properties |
| Mechanical properties at 20°C |
| Delivery status | Section (mm) | t test (°C) | holiday temperature (°C) | sТ | s0.2 (MPa) | sB (MPa) | d5 (%) | d4 | d | d10 | y (%) | KCU (kJ/m2) | HB | H.R.C. | HRB | H.V. | HSh |
| Hot rolled sheets in delivery condition | ||||||||||||||||
| TU 14-1-774-73 | 5-6 | 390-635 | ≥610 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||
| TU 14-1-774-73 | 7-40 | 390-540 | ≥610 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||
| TU 14-1-780-73 | 3; 4 | 392-657 | ≥608 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||
| TU 14-1-906-74 | 3-40 | ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | ≥1960 | |||||||||||
| TU 14-229-278-88 | 6-30 | ≥343 | ≥610 | ≥26 | ||||||||||||
| Forgings. No heat treatment | ||||||||||||||||
| KP-30 | ≤250 | ≥294 | ≥589 | ≥40 | ||||||||||||
| KP-35 | ≤150 | ≥343 | ≥608 | ≥35 | ||||||||||||
| KP-40 | ≤100 | ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||
| Group A hot-rolled bars in the delivered condition without heat treatment | ||||||||||||||||
| ≥343 | ≥589 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||||
| Shaped hot-rolled steel (angle, strip-bulb, channel) | ||||||||||||||||
| ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | ||||||||||||||
| Additional Information |
| Rolled products and forgings made from steel grade 45G17Yu3 (Yu3) are, as a rule, not subjected to heat treatment (except for annealing to remove excessive hardening). Annealing at a temperature of 400-600 °C reduces the corrosion-static strength, and at a higher temperature it increases. You can heat rolled steel and forgings (without reducing the yield strength below 40 kgf/cm2 (392 MPa)) up to a temperature of 800 °C. |
| Technological properties |
| Machinability | Turning, milling and gouging are possible at lower speeds compared to conventional structural steels. Drilling, cutting and cutting internal and external threads with conventional tools is difficult. |
| Weldability | It welds satisfactorily with each other and with conventional ferromagnetic body steels, as well as with corrosion-resistant steel such as grade 12Х18Н9Т by manual welding with coated electrodes, automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding and semi-automatic welding with thin wire in carbon dioxide. Materials for welding: austenitic electrodes grade EA-606/11 - for manual welding of steel with each other and with steel 12Х18Н9Т; electrodes of the EA-48M/22 brand - for manual welding with AK type steel and other ferromagnetic steels; wire grade Sv-08G35Yu6M2 + flux 48-OF-11 - for automatic and semi-automatic welding of Yu3 steel to each other and to AK type steels and ferromagnetic steels. Heat treatment after welding is not recommended. |
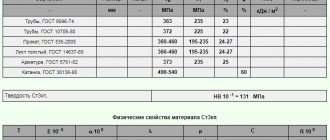
| Physical properties |
| Test temperature, °C | 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 800 |
| Modulus of normal elasticity (E, GPa) | 171,6 | ||||||||
| Modulus of elasticity under torsional shear (G, GPa) | |||||||||
| Density (r, kg/m3) | 7600 | ||||||||
| Thermal conductivity coefficient (l, W/(m °C)) | 15,49 | 17,58 | 18,84 | 21,77 | 23,86 | 25,54 | 28,89 | ||
| Ud. electrical resistance (R, NΩ m) | 900 | ||||||||
| Linear expansion coefficient (a, 10-6 1/°С) | 15,37 | 16,81 | 17,91 | 18,59 | 19,24 | 19,57 | 19,93 | 21,79 | |
| Specific heat capacity (C, J/(kg °C)) | 481,5 |
| Foundry properties |
| Temperature of the beginning of solidification, °C | 1395 |
| Melting point, °C | 1425 |
| Designations |
Mechanical properties:
|
Standards
| Name | Code | Standards |
| Castings from non-ferrous metals and alloys | B84 | RD 9257-76 |
| Blanks. Blanks. Slabs | B31 | TU 14-1-2403-78, TU 14-1-607-73 |
| Sheets and strips | B33 | TU 14-1-2633-79, TU 14-1-774-73, TU 14-1-780-73, TU 14-1-906-74, TU 14-229-278-88 |
| Long and shaped rolled products | B32 | TU 14-1-779-73, TU 14-1-985-74 |
Checking Welded Joints
In production, effective control methods are used: scanning of seams with x-rays or ultrasound. This allows you to detect most defects: lack of penetration, cracks, fistulas.
If possible, then weld test samples from 45 steel, cut the seams with a grinder and inspect them visually. There should not be:
- pores - small bubbles that significantly worsen the properties of the seam. A small number of pores is allowed;
- cracks - during the operation of the structure they can increase and cause destruction of the connection;
- fistulas - also affect the strength of the suture.
In cases where the product is intended to operate under loads, it is recommended to check the connections mechanically. To do this, the part is subjected to loads. For example, if a weld must withstand a load of 10 tons, the test should be carried out with a weight 30% higher - 13 tons.
Chemical composition
| Standard | C | S | P | Mn | Cr | Si | Ni | Fe | Al |
| TU 14-1-780-73 | 0.4-0.5 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.04 | 16-18 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.5 | Remainder | 2.4-3.6 |
| RD 9257-76 | 0.4-0.5 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.04 | 16-18 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.5 | Remainder | 2.4-3.6 |
Fe is the basis.
Analogs of steels. Corrosion-resistant steel
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| 1.4003 | X2CrNi12 | — | — | — |
| 1.4512 | X2CrTi12 | 409 | SUH 409 | — |
| 1.4000 | X6Cr13 | 410S | SUS 410 S | 08Х13 |
| 1.4002 | X6CrAl13 | 405 | SUS 405 | — |
| 1.4006 | X12CrN13 | 410 | SUS 410 | 12Х13 |
| 1.4024 | X15Cr13 | (410) | SUS 410 J1 | — |
| 1.4021 | X20Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J1 | 20Х13 |
| 1.4028 | X30Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J2 | 30Х13 |
| 1.4031 | X39Cr13 | — | SUS 420 J2 | 40Х13 |
| 1.4034 | X46Cr13 | (420) | — | 40Х13 |
| 1.4016 | X6Cr17 | 430 | SUS 430 | 12Х17 |
| 1.4520 | X2CrTi17 | — | — | — |
| 1.4510 | X3CrTi17 | 439 | SUS 430 LX | 08Х17Т |
| 1.4113 | X6CrMo17-1 | 434 | SUS 434 | — |
| 1.4509 | X2CrTiNb18 | 441 | — | — |
| 1.4521 | X2CrMoTi18-2 | 444 | SUS 444 | — |
| 1.4589 | X5CrNiMoTi15-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.4310 | X10CrNi18-8 | (301) | SUS 301 | — |
| 1.4318 | X2CrNiN18-7 | 301 LN | SUS 301 LN | — |
| 1.4301 | X5CrNI18-10 | 304 | SUS 304 | 08Х18Н10 |
| 1.4303 | X4CrNi18-12 | (305) | SUS 305 | 12Х18Н12 |
| 1.4306 | X2CrNi19-11 | 304 L | SUS 304 L | 03Х18Н11 |
| 1.4541 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | 321 | SUS 321 | 08Х18Н10Т |
| 1.4550 | X6CrNiNb18-10 | 347 | SUS 347 | — |
| 1.4401 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | 316 | SUS 316 | — |
| 1.4404 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | 316 L | SUS 316 L | — |
| 1.4571 | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 | 316 Ti | SUS 316 Ti | 10Х17Н13М2Т |
| 1.4561 | X1CrNiMoTi18-13-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.4435 | X2CrNiMo18-14-3 | 316 L | SUS 316 L | 03Х17Н14М2 |
| 1.4439 | X2CrNiMoN17-13-5 | S 31726 | SUS 317 | — |
| 1.4539 | X1NiCrMoCu25-20-5 | N 08904 | — | — |
| 1.4565 | X3CrNiMnMoNbN 23-17-5-3 | S 34565 | — | — |
| 1.4462 | X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 | S 31803 | SUS 329 J3L | — |
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| 10 X2 M | 10CrMo9-10 | 1.7380 | F22 |
| 13 XM | 13CrMo4-4 | 1.7335 | F12 |
| 14 HMF | 14MoV6-3 | 1.7715 | — |
| 15 M | 15Mo3 | 1.5415 | F1 |
| 17 G | 17Mn4 | 1.0481 | — |
| 20 | C22.8 | 1.0460 | — |
| 20 G | 20Mn5 | 1.1133 | — |
| 20 X11 MNF | X20CrMoV12-1 | 1.4922 | — |
Mechanical characteristics
| Section, mm | sТ|s0.2, MPa | σB, MPa | d5, % | kJ/m2, kJ/m2 |
| Hot rolled sheets in delivery condition | ||||
| 5-6 | 390-635 | ≥610 | ≥30 | — |
| 7-40 | 390-540 | ≥610 | ≥30 | — |
| 3; 4 | 392-657 | ≥608 | ≥30 | — |
| 3-40 | ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | ≥1960 |
| 6-30 | ≥343 | ≥610 | ≥26 | — |
| Forgings. No heat treatment | ||||
| ≤250 | ≥294 | ≥589 | ≥40 | — |
| ≤150 | ≥343 | ≥608 | ≥35 | — |
| ≤100 | ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | — |
| Group A hot-rolled bars in the delivered condition without heat treatment | ||||
| — | ≥343 | ≥589 | ≥30 | — |
| Shaped hot-rolled steel (angle, strip-bulb, channel) | ||||
| — | ≥392 | ≥608 | ≥30 | — |
45G17Yu3: circle, sheet, square, hexagon
Steel grade 45G17Yu3 is produced on the basis of C-Fe-Mn-Al alloying and has low magnetic permeability. This property allows this grade of steel to be used in electrical engineering, in particular in the manufacture of transformers. Characteristics of steel 45g17yu3
The austenitic structure of steel under normal temperature conditions does not change under deformation loads. The welding properties of the metal and its malleability to machining contribute to the widespread use of steel 45G17Yu3:
- in shipbuilding, for the manufacture of sheet and profile parts of hulls, as well as many other parts and mechanisms of ships, including ship engine housings;
- in the mining industry, for trays used in the transportation of minerals;
- in construction, as the use of various metal structures.
physical characteristics
| Temperature | E, GPa | r, kg/m3 | R, NOM m | C, J/(kg °C) | l, W/(m °С) | a, 10-6 1/°С |
| 20 | 1716 | 7600 | 900 | 4815 | — | — |
| 100 | — | — | — | — | 1549 | 1537 |
| 200 | — | — | — | — | 1758 | 1681 |
| 300 | — | — | — | — | 1884 | 1791 |
| 400 | — | — | — | — | 2177 | 1859 |
| 500 | — | — | — | — | 2386 | 1924 |
| 600 | — | — | — | — | 2554 | 1957 |
| 700 | — | — | — | — | 2889 | 1993 |
| 800 | — | — | — | — | — | 2179 |
Technological properties
| Name | Meaning |
| Weldability | It welds satisfactorily with each other and with conventional ferromagnetic body steels, as well as with corrosion-resistant steel such as grade 12Х18Н9Т by manual welding with coated electrodes, automatic and semi-automatic submerged arc welding and semi-automatic welding with thin wire in carbon dioxide. Materials for welding: austenitic electrodes grade EA-606/11 - for manual welding of steel with each other and with steel 12Х18Н9Т; electrodes of the EA-48M/22 brand - for manual welding with AK type steel and other ferromagnetic steels; wire grade Sv-08G35Yu6M2 + flux 48-OF-11 - for automatic and semi-automatic welding of Yu3 steel to each other and to AK type steels and ferromagnetic steels. Heat treatment after welding is not recommended. |
| Machinability | Turning, milling and gouging are possible at lower speeds compared to conventional structural steels. Drilling, cutting and cutting internal and external threads with conventional tools is difficult. |
Steel 45G
Structural alloy steel 45G
Brand 45G – purpose
Structural alloy manganese steel 45G is used for the manufacture of parts - driveshafts/crankshafts, anchor bolts, gear/spline shafts, gears, friction discs, brake levers, axles, connecting rods, and other products.
Steel 45G - domestic analogues
Material 45G - characteristics
Alloy structural steel
Brand 45G – technological features
Flock sensitivity
Machinability Ku
Tendency to temper brittleness
Steel 45G - chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
Material 45G – mechanical properties
Depending on the cross-section of the workpiece
Quenching (water) 840 0 C. Tempering (air) 570 0 C
Hardness, MPa
Temperature of critical points, 0 C
Endurance limit, MPa
Brand 45G - exact and closest foreign analogues
Steel 45G – area of application
Material grade 45G is used in mechanical engineering for the manufacture of high-strength parts.
Legend
Elongation at break
Short-term strength limit
Relative machinability factor
Proof of yield strength with 0.2% tolerance when loaded to plastic strain value
Torsional endurance limit (symmetrical cycle)
Endurance limit under compression-tension (symmetrical cycle)
number of deformation/stress cycles sustained by an object under load before fatigue failure/crack appears
You can buy 45G structural alloy steel in St. Petersburg by calling +. Specialists will place your order and advise you on the assortment, prices, and delivery conditions.
Attention! All emails and invoices from Lenspetsstal LLC are sent only from the mail domain @lsst.ru Documents sent from other addresses are invalid!
Electronic document management - EDI. A secure way to transfer documents, quickly, conveniently, an archive of all files, a modern solution for accounting and supply. We work with Kontur.Diadoc and VLSI, join us!
Source