This article is dedicated to homemade heating devices. Sometimes they do not shine with beauty; however, the opportunity to provide heat to a garage or workshop with your own hands at minimal cost certainly attracts many of our readers. We will get acquainted with several structures of varying complexity, made from recycled materials, old pipes and other extremely affordable materials.
Homemade heating devices can have the most unexpected designs.
Radiators for water heating
First, we will examine radiators designed for operation in central and autonomous heating circuits.
Register
The simplest and most affordable homemade heating radiators are made from pipes of large (100 - 250 mm) diameter, capped at the ends and connected by jumpers. These devices - the so-called registers - have a large internal volume and, accordingly, significant thermal inertia, which makes them an ideal solution for systems with solid fuel boilers.
Hint: a solid fuel boiler needs lighting every few hours. The greater the inertia of the heating system and, in particular, heating devices, the less the heated room will cool down between kindlings.
How to make a simple horizontal register?
- Pipes are cut into sections of 1.5 - 4 meters (depending on the expected length of the register).
- Holes for jumpers are drilled or burned with a gas cutter . An important point: the configuration of the jumpers should create a closed circuit inside the device, eliminating stagnation of the coolant in dead-end areas.
- The pipes are connected by jumpers - pipes of sizes DN20 - DN32.
- Parallel to the jumpers, pipe sections of the same length are welded, but already welded to the blank walls . They will add rigidity to the structure.
- The ends are capped with bottoms cut from a steel sheet 4 - 5 mm thick.
- Nozzles are welded into the lower and upper sections , which will subsequently connect the register to the supply line.
In most cases, a regular round water and gas pipe is used as register sections. It is attractive due to its low price per linear meter and maximum tensile strength with minimal wall thickness, which is ensured by a circular cross-section.
Homemade register device.
However, sometimes you can find homemade heating radiators made from a profile pipe - square or rectangular. Its advantages are the relative compactness of the register and a slightly larger surface area for the same cross-sectional area.
Important: at a constant temperature of the heating device, its heat transfer linearly depends on the surface area on which heat exchanges with air.
Convector
The simplest convector is a coil of pipe with plates pressed onto it, increasing the notorious heat transfer surface. The most accessible material is steel. New buildings often serve as sources of ready-made convectors for garage owners: apartment owners in them en masse replace the heating devices installed by the builders with sectional radiators that are more attractive in appearance and have greater heat output.
Residents of new buildings often remember the creators of this masterpiece with quiet, kind words.
However, steel has a serious drawback - low thermal conductivity. In order not to be unfounded, we will present the thermal conductivity values for three metals that are most often used in the manufacture of heating devices.
| Metal | Thermal conductivity, W/(m*K) |
| Steel | 47 |
| Aluminum | 220 |
| Copper | 401 |
It is obvious that when creating a convector it is advantageous to use non-ferrous metals: their thermal conductivity will sharply increase heat transfer, making the heating of the fins more uniform.
Homemade heating radiators made of copper are all kinds of designs based on a copper water pipe and plates - copper and aluminum. Aluminum fins are much more affordable compared to copper; some difference in heat transfer is compensated by its increased area.
To assemble the convector, solder intended for copper water pipes is most often used; somewhat less commonly, the plates are simply pressed onto the pipe.
The convector in the photo is completely soldered from a copper water pipe.
Here, plates are pressed onto the copper core, increasing heat transfer.
DIY radiator made of copper tubes
In general, after the repair, an extra floor connection point for the battery was formed. Ordinary radiators did not fit into the furniture layout. The idea came to make a decorative battery ala “grill” from a copper tube. The tube was found quickly. Hard quality copper 15X1mm, Germany. The guys from Romstal at the Levoberezhnaya metro station helped to select fittings and consumables. By the way, they are very patient professionals - many thanks to them for that. The story is this: 1. A dimensional layout was made for a niche. 2. Connectors were cut and sawed into tees. 3. Everywhere, all cut chamfers are processed inside and outside. 4. Assembly of the structure and rigid fixation in wood. 5. Soldering. 6. Pressure test 7. Roughing.8. Pilot installation.
| 30.06.2014, 23:20 | #1 |
9. Continued rough cleaning. 10. Sandblasting. 11. Varnishing. 12. Standard installation.
13. Admiring a lot of wasted time and effort.
PS. There are still 20 meters of pipe left. Cut into 2m pieces. There is a gas burner, a hair dryer with attachments, a good expensive eco-friendly flux paste with solder and the same solder. I will help you make an “exclusive” beautiful external copper water supply system.
Despite the fact that the price of a modern heating battery is not so high, you can do without purchasing such devices, because you can handle their assembly yourself.
In this article we will talk about how and using what materials homemade batteries can be made, which in terms of energy efficiency will be practically not inferior to their factory counterparts.
Heating register - the basis of homemade structures
Homemade pipe heating radiators are the most common type of homemade heating devices. And this is not surprising, since soldering a sealed system from a pipe is much easier than making a heating device using factory technologies.
Products assembled from a single pipe or combination of pipes are called a register. The register is a sealed system through which one or another coolant circulates. The energy efficiency of the register is determined by the diameter and configuration of the pipes, as well as the material from which they are made.
The practice of assembling radiators with your own hands shows that the most appropriate solution is to use smooth-walled steel pipes with an internal cross-sectional diameter of 32 - 200 mm. In order to achieve maximum heat transfer surface area while maintaining compact dimensions, the device is given the shape of a coil or the register is made sectional.
The choice of steel pipes for installation work is not accidental, since they are easy to weld with household welding machines.
Tip: In order to make a register, it is not at all necessary to go to a metal depot to purchase new pipes. After all, to carry out the planned work, you can use old pipes that do not have visible defects caused by mechanical deformations or corrosion.
Autonomous heaters
What to do if there is no central heating or gas in the garage, and the frequency of your visits to the premises does not allow organizing a scheme with a solid fuel boiler?
In this case, it would be quite logical to use electricity for heating.
Oil radiator
The simplest homemade oil radiator is a welded register already familiar to us with several modifications.
- There are no welds for connecting to the connections.
- The register, as a rule, is made portable, which implies the presence of legs.
- Jumpers between sections are present on both sides. Their diameter is made slightly larger than when assembling a register for water heating. The instruction is due to the fact that natural convection implies a minimum hydraulic pressure, and if so, the hydraulic resistance should also be minimal.
- A heating element or several parallel connected heating elements are installed at the end of the lower section.
- Oil acts as a coolant. Ideally, a transformer one, but even testing will do.
- The register is equipped with a small open expansion tank. As an option, the oil is not added a little to the top of the register, and the weld on its upper section is equipped with an automatic air vent.
Homemade oil radiator.
Warning: installing a safety valve instead of an air vent is a bad idea. When triggered, it can douse the owner of the room with oil at a temperature of 60 - 90 degrees, which obviously will not benefit his well-being and mood.
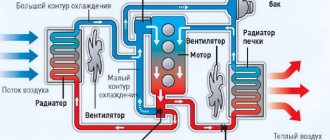
Heater from a car radiator
Another interesting solution is a homemade garage heater made from a radiator.
Heater from an old radiator.
The diagram is indicated by numbers:
- Radiator.
- Expansion tank.
- Forced air fan.
- A casing that protects the fan blades.
- Water pump.
- Oil supply pipe.
- Actuator.
- Fan drive belt.
- Electric motor.
- Frame stand.
- Drain tap.
- Block of heating elements.
- Blinds for adjusting the direction of air flow.
A few tips for assembling this product:
- Partially clogged radiator tubes are not a problem. They will miss the oil.
- Optimal motor characteristics are 300 - 500 watts at 1500 rpm.
- To heat the oil, heating elements with a total power of up to 3 kW are used. It is better to provide stepwise power adjustment by switching them on separately.
Use a block of three 1 kW heating elements with each of them switched on independently.
- Due to the small diameter of the radiator tubes, it is not worth using mining in this design. Transformer oil or antifreeze A-40 is suitable.
- The heater will operate most efficiently at an oil temperature of about 80C. The temperature is regulated by selecting the power of heating elements and fan speed.
Instructions for thrifty owners: how to make a heating radiator with your own hands?
Homemade radiators for the heating system can significantly reduce the cost of repairs. More often, self-made registers are used for greenhouses, utility rooms, garages, and workshops.
Some use homemade (custom) radiators to add effect to the interior.
Radiators made by yourself are much cheaper even than used ones. The big advantage of homemade batteries is the ability to freely “play” with shapes and easily fit the dimensions into the calculated space.
Copper radiator: device, features and advantages
Heating devices made of non-ferrous metals are becoming increasingly popular due to their increased heat transfer, high efficiency and attractive appearance. Today we will look at the most effective of them - copper heating radiators.
Installing a copper radiator with your own hands is not difficult.
Design and device
Copper radiators can be divided into several types:
- tubular products (divided into tubular and tubular-sectional). Tubular - batteries are made of copper pipes through which coolant circulates. They have restrictions on the length of the device. Tubular-sectional – radiator sections are made of copper pipes, which allows you to more accurately select the required battery power;
- copper convectors - are a core made of copper pipe with soldered copper plates. The plates are heated by copper pipes and heat rooms using both radiation and convection. To improve circulation, convectors are placed in a special casing made of wood, steel or aluminum;
- bimetallic – copper-aluminum convectors, which, unlike copper convectors, have vertical aluminum plates connected to a lightweight aluminum body. Externally, they look like flat steel radiators. These devices eliminate contact between aluminum and the coolant, which makes them resistant to corrosion. At the same time, air convection increases due to the larger (compared to copper convectors) area of the plates.
Those same copper convectors, which are also popularly called radiators. It is advisable to install them together with screens or casing.
Copper radiators
Features of copper as a material for radiators
Radiator copper pipes are hidden in a protective casing.
For a long time, ferrous metal products were used as heating devices, mainly cast iron; later they began to make convectors from steel. This practice was justified by the availability and low cost of raw materials, especially in conditions of mass state construction.
If we look at ferrous metals in more detail, we will find a number of significant disadvantages that they have from the point of view of use in heating systems.
The photo shows a modern cast iron appliance.
The most significant disadvantages include the following qualities:
More recently, the market has been filled with new products consisting of aluminum alloys, pure copper, as well as combinations of aluminum and steel, aluminum and copper (the so-called bimetals).
Aluminum radiators and a copper heat exchanger are a typical combination for a bimetallic device.
Aluminum appliances required high quality and purity of the coolant, as well as stable pressure parameters in the system, which is a utopia with a centralized supply from open heating systems. Therefore, urban central heating systems continue to use cast iron and steel, because these materials are durable and not so demanding on the coolant.
But if we look at copper, we see a completely different picture:
- The thermal conductivity of copper is 401 W/(m*K) , while the thermal conductivity of aluminum is 202–236 W/(m*K), steel is 47 W/(m*K), cast iron is 25–60 W/(m*K) ). As you can see, copper conducts heat twice as well as aluminum and about eight times better than ferrous metals;
- In an aqueous environment, copper is covered with a strong oxide film within the first 90 hours, which protects the metal from further corrosion . Copper water pipes last 100 years or more;
- The metal is quite strong, but at the same time it is plastic , so it can easily withstand operating pressure of 16 atm, and pressure testing - up to 25 atm. That is, there is a high resistance to water hammer;
- The internal surfaces of pipes, unlike cast iron, are not overgrown with deposits;
- The material can be soldered with lead-tin solder , which makes it easier to install pipes and repair copper radiators.
Copper is the best raw material for heating devices.
Important! As you can see, copper is the most suitable material for the manufacture of heat exchangers, radiators and other heating devices for liquid coolant systems.
Design and types of copper batteries
The outer casing protects the device and helps it fit into a modern interior.
To understand what we are actually talking about, let’s look at the design of the most common models and types of copper radiators. Let's start with the simplest - a tubular register:
Tubular heating register.
The product is a system of two or more pipes of large or medium cross-section, communicating with each other through side collectors. Such devices are installed in large rooms, workshops, concert halls, etc.
A more advanced type can be considered a register made of small-section tubes onto which thin plates are pressed or soldered:
Simple plate convector.
Further development followed the path of complicating the system of tubes and plates, optimal distances and sizes, areas of heating surfaces, etc. were selected. An external casing was added, which closed the space between the plates and created unique air ducts that increased vertical draft and increased heating efficiency:
The distance between the plates is selected so as to create turbulent air flows.
Bimetallic copper-aluminum heating radiators appeared, which combined the advantages of both materials and reduced the total cost of production by reducing the use of copper raw materials. Today these are perhaps the most progressive and effective devices.
Aluminum fins are pressed onto copper tubes.
Important! Manufacturers of copper-aluminum models provide a 25-year guarantee on their products, and also claim the absence of overheating and positive air ionization.
DIY copper tube radiator
6 Jan by admin
23.11.2015
Every person planning to create or update a heating system is interested in which radiators to use for this.
The choice is really huge, but if you don’t know the features and key criteria, you can waste your money. Recently, you can increasingly hear about copper heating radiators.
What is their advantage? This is what we will try to find out in this article.
articles:
Copper radiators
Over the past years, traditional radiators made of cast iron and steel have somewhat lost their market position. There are two reasons for this: poor heat transfer and rather low operating efficiency. Moreover, the use of such radiators is not always possible, since heating systems are constantly being modernized, and their technical characteristics are only increasing.
Electric radiators
Previously, we talked about the operating principles and technical characteristics of electric radiators; in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information; see all the details here
And radiators made of ferrous metals are gradually being replaced by copper products - more reliable, high quality and productive.
If they are installed in the heating network, this will not only increase heat transfer several times, but will also reduce heating costs.
Of course, the cost of copper batteries is much higher than, for example, cast iron, but still, due to the excellent characteristics of the popular former, it is only growing.
Main technical characteristics
In the manufacture of modern copper batteries, exclusively high quality materials are used. Copper must be exclusively in pure form, while the ratio of impurities should be no more than 0.1 percent. It is this ratio of components that ensures the operation of the system at elevated pressure, maximum heat transfer, and also eliminates possible corrosion.
Note! Don’t forget that copper batteries in an apartment/house increases the amount of heat transferred by the working fluid by about 2 times.
Finally, copper itself is a fairly durable and strong metal, and therefore radiators made from it work quite effectively even at a working fluid temperature of 150 degrees and a pressure of 16 atmospheres.
– How to choose a radiator?
Heating radiators made of copper, as well as those made of other materials, are original elements that differ not only in their composition, but also in their design features. In most cases, copper heating radiators consist of pipes with a working fluid circulating inside and special finned plates.
Do not forget that the number of pipes (as well as their shape or cross-section) varies and depends on the individual characteristics of a particular battery model.
Moreover, some of these batteries are even equipped with a special protective casing, which not only decorates the wall product, but also increases its performance.
Often, manufacturers offer consumers not just copper batteries, but full-fledged heating devices that have many functions and allow you to control the temperature in order to ensure the most efficient heating of the room.
Such properties are made possible thanks to built-in shut-off valves, thermostats and other fittings. Agree, all this is very convenient, which is why, in fact, such radiators are of high value in heating systems.
Note! There are several basic ways to connect copper batteries to risers and heating lines in general. More specifically, there is a threaded connection and soldering, due to which the versatility of the products increases significantly, they become an ideal option for most systems, but installation costs are reduced.
There are several methods of heating using these devices, let’s get acquainted with them.
- Convection is when heat is transferred by air currents and depends on the area/shape of the heating devices.
- Radiation of heat due to the fact that heated bodies are capable of transmitting thermal energy through IR electromagnetic waves.
- Thermal conductivity is the unique ability of heated bodies to transfer part of their heat to other, colder objects. This indicator depends mainly on the characteristics and structure of the metal used in the manufacture of radiators.
The main advantages of copper batteries
The products described in this article are considered the most optimal option for any heating system, regardless of whether it is individual or centralized.
And if we compare them with other types of radiators, then there are a lot of advantages and unique properties, which can only indicate one thing: copper radiators are one of the most profitable financial investments.
And among the many advantages, it is worth highlighting the following.
- High degree of heat transfer. As already noted, pure copper is used in the production process, due to which the heat from the working fluid is transferred to the house fully and without any losses. It turns out that this is an ideal choice for many systems, in particular for a centralized pipeline in apartment buildings, where the liquid temperature, as is known, rarely exceeds 60 degrees.
- Long service life. Copper is resistant to various types of deformation, the action of corrosion inhibitors and other harmful phenomena; Copper batteries can last 15-20 years, and sometimes even 50, without causing any trouble to the user at all.
- Light weight. The copper from which these radiators are made weighs little, and therefore even the largest products with a large number of sections are light in weight. Consequently, there is no excessive load on the walls, and, accordingly, there is no longer a need to use special reinforcing fasteners.
- Low temperature resistance. At sub-zero temperatures of the working fluid, copper products may be slightly deformed, but in no case should they burst. For this reason, the risk of defrosting is practically reduced to zero.
- Economical. In the images in this article you can see for yourself that all copper heating radiators are characterized by a small cross-section. In this regard, little working fluid is required, and the user can save on fuel without any damage to the efficiency of the heating system.
- The maximum permissible temperature of the working fluid in the system is 250 degrees. This is one of the reasons why copper batteries are the best solution for grids. By the way, according to the instructions from the manufacturers, some models are quite capable of functioning at higher temperatures, achieving maximum efficiency.
- Possibility of functioning at high pressure. As noted at the beginning of the article, copper batteries also work well with a pressure of 16 atmospheres. As for the crimping pressure, for these products it can reach 25 atmospheres. It is precisely because of their increased resistance to pressure that radiators can be installed in both individual and centralized networks, and the quality of the working fluid does not play a special role.
Note! Experts recommend installing copper radiators in those heating networks where the working fluid contains a large amount of chlorine salts. After all, if you use, say, traditional steel devices for such a liquid, then in any case problems will arise - up to clogging of the pipeline.
In short, buying a copper radiator is definitely a profitable investment that will soon pay off.
Replacing heating batteries in an apartment
Previously, we talked about how to change the battery in an apartment yourself, in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information, see all the details here
Features of device operation
If you plan to use copper radiators in your heating system, you must comply with certain requirements and rules regarding not only installation, but also the operation process.
For example, manufacturers do not advise installing several copper and steel devices simultaneously along the flow of the working fluid, as this can lead to a certain electrochemical reaction that can destroy the entire system.
Note! If you cannot refuse this combined option, then be sure to use brass fittings for the connection. Today, these are sold in almost any specialized store, the assortment is huge, and the cost is quite affordable.
It is also undesirable to install copper devices in those lines that may contain small abrasive particles - the latter will, over time, “undermine” the material and sooner or later lead to wear of the radiators.
Finally, do not install such batteries if the operating fluid is very hard or highly acidic. Although some of these difficulties can be solved by installing additional special filters.
– Installation of a copper battery
What to look for when purchasing?
If your plans include the purchase and installation of copper batteries, then you simply must know about some important points. Let's look at them.
- The main one, which we have already mentioned in passing, is the following: you should not use elements made of different materials within the same network. If the appliances are copper, then the fittings should be so too. And this need is explained not only by the risk of a special electrochemical reaction that can destroy the system, but also by the fact that different materials have different thermal expansion, which appears under the influence of elevated temperatures.
- Make sure that the working fluid is free of abrasive impurities. They can damage the internal cavities of heating devices, because copper is a fairly soft material. In short, be sure to install special filters.
- Connecting fittings must be made of non-ferrous metal - ideally brass.
In addition to all this, try to buy batteries only from trusted sellers. The fact is that there are a large number of counterfeit products on the modern market.
So, for example, in the manufacture of a battery, cheap low-quality metal can be used, which is covered with a thin layer of copper on top.
What else do you need to know when choosing copper heating radiators? Yes, there are still a few nuances.
- Temperature conditions necessary to maintain comfortable living conditions.
- Total area of heated rooms.
- Condition and number of different types of openings. If required, they can be additionally thermally insulated.
- Dimensions of the room. One of the main parameters in this case is the height of the ceilings.
Note! It is quite obvious that the number of sections in a copper device will be less than in a similar product made of ferrous metals. It is thanks to this that the rather high cost of radiators is compensated.
Carry out the installation efficiently; ideally, you should involve a qualified specialist in the work if you need to solder copper elements. Do not skimp on this under any circumstances! Copper is an expensive material, and if you managed to find the money to buy batteries made from it, then do not neglect the quality of work.
As a small conclusion
Copper heating radiators are the best option for both a city apartment and a private house, when compared with similar devices made of ferrous metals.
Such products are characterized by high heat transfer, which ensures fast and high-quality heating of the heated room.
Despite the high prices, the radiators will pay for themselves in the near future, since energy bills will noticeably decrease. That's all. Good luck and have a warm winter!
You may like
Features of homemade radiators made of metal pipes: types and characteristics
Design of a homemade heating battery
The design of such devices is a system that consists of horizontal or vertical pipelines interconnected by jumpers. Smooth pipes with a round cross-section are used for the production of heating radiators much more often than analogues with a rectangular or square profile. However, combined designs are also possible.
Without a doubt, registers made of carbon steel are considered the most convenient to use. The option made of galvanized or stainless steel looks much better in terms of characteristics. But, firstly, it is expensive, and secondly, only experienced specialists can work with such material.
Homemade heating devices are suitable for both single-pipe and two-pipe systems. They can be wall and floor mounted. The simplest example of execution is a heated towel rail in bathrooms. Handicraft registers are divided into two main types:
- Sectional.
- Serpentine.
Section registers
They are a pipe structure, where elements of a larger caliber are parallel and capped at the ends, and tubes of a smaller cross-section serve as connecting elements. For strength, additional jumpers can be used.
The coolant in such a battery always moves from the top tank, then through the connecting pipes it passes to the bottom row, and so on. This scheme practically eliminates the situation when the radiators are hot and the house is cold.
Judging by practical application, sectional registers cope with their tasks quite well. However, there was a fly in the ointment here. During operation of the device, it will not be possible to get rid of high hydraulic resistance; the reason for this is the difference in the diameters of the pipes and jumpers.
Serpentine registers
Such batteries look like an S-shaped structure assembled from components welded in series. The main advantage of this solution is that the diameter of the pipes is the same, which means that the hydraulic resistance is quite low. For the same reason, the coil is effective, since heat exchange is carried out over the entire surface of the homemade radiator.
A register bent from solid pipe is much more reliable in terms of operation than a welded one. But, unfortunately, it is almost impossible to carefully bend a steel pipe with a diameter of 70-100 mm at home - ideally, you need a pipe bender, and in extreme cases, a gas torch. This is where register prefabricated structures come to the rescue.
The heating system with S-shaped radiators, assembled only from metal pipes, is particularly reliable and durable; moreover, it is not so difficult to carry it out step by step. Compared to sectional batteries, there are significantly fewer welds, which means there are fewer potential sources of leakage.
Characteristics of homemade heating devices
Registers of this type can withstand pressure up to 10 kgf/m² and are able to work with any coolant: water, oil, antifreeze and steam. The permissible cross-section of pipes used in sections must be in the range of 32-219 mm.
Do-it-yourself radiator made from a copper tube - Metalist's Guide
Despite the fact that the price of a modern heating battery is not so high, you can do without purchasing such devices, because you can handle their assembly yourself.
In this article we will talk about how and using what materials homemade batteries can be made, which in terms of energy efficiency will be practically not inferior to their factory counterparts.
“Warm baseboard” made of copper pipes
Assessing your capabilities
It is clear that not every person can assemble a homemade oil radiator, since such a design is complex, but making a device through which water will circulate as a coolant is not so difficult.
"Warm floor" - a type of radiator
According to the principle of operation, home-made heating devices also do not differ from factory-made analogues, however, it is not recommended to install these products in centralized systems with high pressure.
Homemade pipe heating radiators are the most common type of homemade heating devices. And this is not surprising, since soldering a sealed system from a pipe is much easier than making a heating device using factory technologies.
Products assembled from a single pipe or combination of pipes are called a register. The register is a sealed system through which one or another coolant circulates. The energy efficiency of the register is determined by the diameter and configuration of the pipes, as well as the material from which they are made.
The practice of assembling radiators with your own hands shows that the most appropriate solution is to use smooth-walled steel pipes with an internal cross-sectional diameter of 32 - 200 mm. In order to achieve maximum heat transfer surface area while maintaining compact dimensions, the device is given the shape of a coil or the register is made sectional.
The choice of steel pipes for installation work is not accidental, since they are easy to weld with household welding machines.
Tip: In order to make a register, it is not at all necessary to go to a metal depot to purchase new pipes. After all, to carry out the planned work, you can use old pipes that do not have visible defects caused by mechanical deformations or corrosion.
Homemade Device Configuration
Copper tube coil
Homemade heating radiators made of copper or steel can be made in two design options:
- Sectional registers consisting of straight pipes of large diameter with sealed plugs at the ends, connected by pipes with a smaller cross-sectional diameter.
- Serpentine registers with an S-shape or a more complex configuration.
Important: For optimal heat transfer, the coil register configuration should have a distance between adjacent pipes that is 5 cm greater than their diameter.
Let's take a closer look at the design features of the listed configurations:
- A sectional register consists of several pipes located horizontally.
The photo shows a sectional register
To circulate the coolant, the horizontal elements of the register are connected to each other by pipes of smaller diameter. As a result, the coolant begins to move along the upper pipe, reaching the connecting pipe, through which it flows into the lower section, and so on.
In the factory version, such structures are made for heating entrances and other auxiliary premises, where the aesthetics of the appearance of the device is not so important.
Operating principle of a sectional register
The inlet and outlet pipes are made threaded. In some cases, to speed up installation work, the pipes are simply welded tightly.
The location of the transition pipes is selected as close as possible to the end of the section. This is done for better coolant circulation and to ensure greater strength of the prefabricated structure.
The optimal materials for self-assembly of sectional registers are galvanized steel pipes with an internal diameter of 76-160 mm. The structure should be welded so that the tightness of the seams is maintained at an operating pressure of up to 13 atm.
Important: The optimal register configuration is one with no more than 3 horizontal sections. Excessive accumulation of sections will lead to a decrease in the efficiency of heated air circulation inside the room.
- Serpentine registers are structurally similar to the selection analogue. The main difference is that the function of the jumper here is performed by the bend of the main pipe.
Coil welded from steel pipe and fittings
A significant disadvantage of coil structures is the difficulty of self-assembly, since it is difficult to bend large-diameter pipes and therefore you have to weld two elbows at each bend.
To make homemade heating radiators from a profile pipe you will need a bending machine
As a result, the welded structure becomes more complicated due to a large number of seams, which can negatively affect the durability and tightness of the register.
Nevertheless, the S-shaped configuration of registers is an order of magnitude more efficient than horizontal sections, since both the horizontal and vertical parts of the radiator are involved in heating the air in the room. Moreover, due to the constant diameter in coil radiators, the hydraulic resistance is significantly lower than in sectional analogues.
Selection of materials
Homemade specimen with vertical sections
The service life, heat dissipation and, finally, the price of a homemade radiator largely depend on the correct selection of production materials.
The selection of production materials is carried out in accordance with such criteria as ease of machining, ease and quality of welding, resistance to corrosive processors and price. In addition, if the radiator is assembled for subsequent use in the bathroom, as a heated towel rail, the pipe should look good.
Homemade garage heater from a car radiator
The following conclusion can be drawn:
- When assembling heating devices for operation in entrances, garages and other utility rooms, it is advisable to use smooth-walled pipes made of ordinary structural steel grade St-3 . The wall thickness should be 2 mm, both for the strength of the entire structure and for better quality of the weld.
- To assemble a heated towel rail, it is advisable to purchase more expensive pipes made of AISI 304 stainless steel (passport designation 08Х17М10) . As a result, the finished coil, subject to high-quality assembly, will look great due to its shiny surface and at the same time will last an order of magnitude longer than an analogue assembled from ferrous metal due to its greater corrosion resistance.
The radiator assembly instructions also depend on the type of materials used. For example, pipes made of ordinary structural steel are welded using ordinary electrodes. To assemble stainless steel structures, it is better to use argon welding, since the use of conventional electrodes will not allow you to obtain a neat and visually attractive seam.
Conclusion
So, we found out what types of homemade radiators you can assemble with your own hands. In addition, we found out what materials the assembly should be used to use. It's a small matter, all that remains is to purchase the necessary materials and assemble the heating device with your own hands.
Do you have any questions that require further clarification? In this case, we recommend watching the video in this article.
Review of copper heating radiators - Home insulation school
Batteries and radiatorsOverview of copper heating radiators
23.11.2015
Every person planning to create or update a heating system is interested in which radiators to use for this.
The choice is really huge, but if you don’t know the features and key criteria, you can waste your money. Recently, you can increasingly hear about copper heating radiators.
What is their advantage? This is what we will try to find out in this article.
Comparative review of popular models
The choice of copper batteries, as noted above, is huge. But when choosing a particular model, focus not only on the cost, but also on the performance characteristics of the device.
So, depending on the individual parameters of the heated room, you can select devices that are designed for 10-22 m2 of area. In this case, the heat transfer of one device ranges from 1 to 3 kilowatts.
Do not forget about the large weight of the radiator - some models can weigh up to 13 kilograms.
The table below shows the most popular models. Check out their features to make the right choice.
| SR-800-1000 Power – 2.4 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 80x100x100 cm Price – 75,000 rubles | SA-550-1000 Power – 1.7 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 55x100x10 cm Price – 51,400 rubles |
| Classic Style 2195 W Power – 2.195 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 42x83x11 cm Price – 34,850 rubles | Classic Style pomni 1517 RK Power 1.517 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 83x11x42 cm Price 20,950 rubles |
| “Thermia 20/40 RB” Power – 0.24 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 21x40x12.5 cm Price – 2500 rubles | Copperi Art V Power – 0.98 kilowatts Height/Length/Thickness – 180x75x10 cm Price – 107,400 rubles |
Basic heating register calculation
If the level of heat transfer of a purchased battery can be found out from its passport, then in the case of homemade heaters you have to calculate everything yourself. Otherwise, it will not be possible to heat the room effectively and evenly.
Calculating the required radiator power to heat a room
For calculations, they use formulas that may be simple, but require certain mathematical skills. Another option is online calculators, of which there are now more than enough on the Internet. Strictly speaking, the topic is quite extensive and deserves a separate article, so we will use simple calculation methods. In any case, this issue should be given close attention, otherwise your family will complain that the radiators do not heat well and the room is cold.
A simplified method for calculating the required thermal energy is to calculate the heating area and then multiply by 100. Why is this so? Because for comfortable living per square meter you need 100 W of heat. To be more precise in the calculations, let’s take into account the number of window openings and walls:
- A room with one window and one external wall – 100 W per 1 m² of area.
- A room with one window and two external walls - 120 W per 1 m².
- A room with two windows and two external walls - 130 W per 1 m².
Important! The calculations are suitable for rooms with ceilings of no more than 3 meters, when the house is located in a moderate climate in the middle zone. If the building is located in the northern regions, then the result must be multiplied by a factor of 1.2-2.0, and if in southern latitudes - by 0.7-0.8.
Simple calculation of the thermal power of a radiator made of steel pipes
Knowing what to strive for, all that remains is to choose the design of the heating device that would satisfy your needs. How to do this?
There is an elementary solution - use a table. It already calculates the heat transfer rates of rolled pipes. The values take into account the temperature regime, in which the supply temperature of the coolant is +90℃, and the return temperature is +20℃.
Technical and operational characteristics
Copper equipment has unique characteristics, so it can be installed not only in autonomous heating systems, but also in central ones. It is noteworthy that some models of copper heaters can be used for heating with both liquid and steam.
| Technical and operational characteristics | Range of values of existing models |
| Heat output (thermal power), kW | 0,1 — 2,195 |
| Working pressure, bar | 14-16 |
| Test pressure, bar | 20-50 |
| Required volume of coolant in the radiator, l | 0,26-4,81 |
| Maximum operating temperature, °C | 110-150 |
| Heated room area, m2 | 2-23 |
| Weight, kg | 1,6-22,6 |
| Warranty period, years | 20-25 |
| Service life, years | 35-50 |
| Connection type | Side, bottom |
| Thread of holes for connection to heating mains, inches | G ½, ¾ |
Heat transfer from heating radiators Comparison of indicators and calculation methods
How can you solder a radiator?
On the Internet you can find many photos of how to solder a radiator. But before looking at the pictures, you need to read the recommendations of experts, otherwise you won’t understand anything.
To do everything correctly, pay attention to the procedure for soldering the damaged surface. The repair method depends on the material from which the radiator is made.
In most cases, radiators are soldered using cold welding. Instructions on how to solder a radiator are as follows:
- For convenience and quality work, dismantle the radiator;
- Find the place where the liquid may be leaking;
- To accurately calculate the fault, cover the radiator holes;
- Immerse it in water, you will see small water bubbles above the breaks;
- The damaged area must be prepared for repair - sanded and degreased well;
- We take a dose of cold welding, knead it and put it on the crack.
Due to the activator, cold welding can be turned into a liquid, which is intended for those places where it is difficult to penetrate. Let everything dry, clean and paint.
Aluminum radiator repair
Soldering an aluminum part is a labor-intensive process. How to solder an aluminum radiator? Before repairs, you need to prepare many tools, which are sold in specialized stores.
Due to the aluminum oxide film, the alloy does not adhere well to the crack, so follow this process:
- find the damaged surface;
- melt and mix rosin with iron filings;
- Apply the resulting mixture to the damage and blend with a heated blowtorch;
- when the flux covers the surface, add part of the resulting mixture. This will destroy the oxide film;
- if the gap is large, then we use a compound of bismuth and tin;
- To make the seam more reliable, we use flux - this is a composition of potassium and lithium chloride, cryolite, ordinary salt, and sodium sulfate.
The resulting mixture is heated with a hot soldering iron. At the end of the work, we check the result. Pour water with potassium permanganate into the radiator and wait a couple of hours. If it doesn’t ooze anywhere, then everything was done correctly. We work with gloves and in a well-ventilated area.
Copper radiator repair
I use the same method to solder a radiator made of copper and brass; I do this using tin. To solder a copper radiator, it is better to use a hammer soldering iron, which works without electricity. A blowtorch is used for heating.
First of all, you need to sand the cracks that have formed, then coat them with zinc chlorine. To prepare it you need: zinc and hydrochloric acid; We put the zinc in the acid and wait until the mixture combines.
Next, use a heated blowtorch to transfer the tin to the damaged area. We check the quality of work with water, then paint.
Operating requirements
Although the cost of heating copper is higher than plastic, copper products are resistant to high temperature, overheating, gas diffusion through pipe walls, or mechanical damage.
According to technical and operational characteristics, copper and copper-aluminum radiators can be used both in an autonomous heating system and in a central heating system. It must be remembered that the guarantee of a long service life of any radiator is to build the system from a homogeneous material that is resistant to the most harmful factors, which is almost impossible to implement in an apartment building. The maximum service life of the devices will be possible only if the entire system is made of copper.
However, copper radiators can be used in multi-storey buildings with a central heating system. They are resistant to water hammer and have low demands on the quality of the coolant.
Most models of copper radiators can be used in single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems of open and closed type. They will be effective in systems with forced and natural coolant circulation. Copper radiators are not sensitive to temperature changes and can withstand negative values. Can be installed in rooms with high humidity. Contact of copper with aluminum is unacceptable.
Repairing a radiator at home
The radiator is one of the most vulnerable parts of a car. If it malfunctions, it is not necessary to contact specialists; you can repair it yourself. To solder a radiator with your own hands, you need to have room and the necessary tools.
To repair the radiator, just go through the following steps:
- remove the radiator from the car and drain the liquid;
- find the right tools;
- solder the damage;
- check the result of the work;
- put the radiator back in place.
To properly fix the problem, be sure to dismantle it. At the same time, it will be possible to inspect all damage to the radiator and properly solder the gaps. We find cracks using polyethylene, a vessel and water. We cover the holes with film and then lower them into the water. Small bubbles will appear from the water above the cracks.
We wash and clean defective areas. You can sand it using sandpaper, a fine file (semicircular, thin, flat), or an iron brush. This stage must be taken seriously, since the rest of the work will depend on it.
The next step is degreasing, then sealing, it depends on the choice of the necessary tools.
To solder the radiator you will need the following tools:
- electric soldering iron;
- gas burner;
- a mixture of lead and tin;
- flux;
- rosin dissolved in alcohol.
The choice of tools for soldering depends on the material of the radiator, for example, a copper radiator is soldered with solder with a low melting degree, etc.