04/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- How was aluminum discovered and what are its main properties?
- Basic physical properties of aluminum
- Basic chemical properties of aluminum
- How to use the basic properties of aluminum
- How to use the basic properties of aluminum in construction
The basic properties of aluminum make this material truly versatile and valuable. It is used in all types of industrial production, in agriculture, in everyday life, in commerce. It has a huge number of advantages over steel and other types of metal.
The most popular applications of aluminum are the manufacture of metal structures and metalworking. Read on to learn about the properties of the metal and where exactly they found their application.
How was aluminum discovered and what are its main properties?
Aluminum is a paramagnetic metal, quite light, with a silvery color. It lends itself well to machining and casting, and is easy to mold. In the earth's crust, this element is the third most abundant, ahead only of oxygen and silicon. Our subsoil contains as much as 8% of this metal, which is significantly more than gold, the amount of which is no more than five millionths of a percent.
Aluminum is actively used in most areas of production. Its alloys are used for the manufacture of household appliances, transport, mechanical engineering and electrical engineering. Capital construction also cannot do without it.
VT-metall offers services:
It is extremely common in the earth's crust, being the first of the metals and the third chemical element (the first place is for oxygen, the second is for silicon). The share of aluminum in our subsoil is 8.8%. The metal is part of a large number of rocks and minerals, the main of which is aluminosilicate.
In the form of compounds, aluminum is found in basalts, feldspars, granites, clay, etc. However, it is mainly obtained from bauxites, which are quite rarely found in the form of deposits. In Russia, such deposits are found only in the Urals and Siberia. On an industrial scale, aluminum can also be mined from nephelines and alunites.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
Animal and plant tissues contain aluminum as a trace element. Some organisms, for example, mollusks and mosses, are its concentrators, accumulating it in their organs.
Humanity has been familiar with an aluminum compound called potassium alum for a long time. It was used in the process of tanning leather, as a means that, when swelling, binds the various components of the mixture. In the second half of the 18th century. scientists discovered aluminum oxide. But the substance was obtained in its pure form much later.
This was first achieved by C.K. Oersted, who isolated aluminum from chloride. While conducting the experiment, he treated potassium salts with amalgam, as a result of which a gray powder emerged, recognized by all as pure aluminum.
Subsequently, by studying the metal, scientists determined its chemical properties, manifested in its high ability to recover and activity. That is why they did not work with aluminum for a long time.
But already in 1854, the French scientist Deville, using electrolysis of the melt, managed to obtain metal in ingots. This method is still used today. Aluminum began to be produced on an industrial scale at the beginning of the 20th century, when enterprises were able to gain access to large amounts of electricity.
Today, aluminum is one of the most used metals in the production of household appliances and construction.
Necessary equipment
The following equipment is required to mine bauxite, convert the ores into alumina, and extract the pure metal:
- Alumina distribution mechanisms: designed for transporting powdered aluminum oxide inside the workshop and dosed supply of alumina to electrolysis machines.
- Cathode bus bars: These are flexible strips of cathode runs attached to cathode bus bars made of steel materials.
- Gas cleaning plants: used to clean the room from gases generated during the production of aluminum fluoride by the dry method.
- Installation equipment: cranes for linear and technical purposes.
- Electrolyser: A device for separating the major components of alumina using electric current during electrolysis.
Depending on the technological features of production, a large number of drum rotary kilns are required. They are used in dry production methods. When organizing an enterprise, it is important to provide equipment for alumina electrolysis with electricity.
Basic physical properties of aluminum
The main characteristics of aluminum are high electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, resistance to cold and corrosion. It can be processed by rolling, forging, stamping, drawing. Aluminum is highly weldable.
Impurities present in the metal in varying quantities significantly worsen the mechanical, technological and physicochemical properties of pure aluminum. The main ones are titanium, silicon, iron, copper and zinc.
According to the degree of purification, aluminum is divided into technical metal and high purity. In practice, the differences between these types lie in their resistance to corrosion in different environments. The cost directly depends on the purity of the aluminum. Technical metal is suitable for the production of rolled products, various alloys, cable and wire products. Pure is used for special purposes.
Aluminum has high electrical conductivity, second only to gold, silver, and copper. However, the combination of this indicator with low density allows it to be used in the production of cable and wire products on a par with copper. The electrical conductivity of a metal can increase during prolonged annealing or deteriorate during cold-working.
By increasing the purity of aluminum, manufacturers increase its thermal conductivity. Impurities of copper, manganese and magnesium can reduce this property. Only copper and silver have higher thermal conductivity. It is thanks to this property that this metal is used for the production of cooling radiators and heat exchangers.
The specific heat of aluminum, as well as its melting point, is quite high. These indicators significantly exceed similar values for most metals. As the purity of the metal increases, its ability to reflect light rays from the surface also increases. Aluminum is highly polishable and anodizes well.
The metal is close in properties to oxygen; its surface in air is quickly covered with a thin and durable film of aluminum oxide. Possessing anti-corrosion properties, it protects the metal from rust formation and prevents further oxidation. Aluminum does not interact with nitric acid (concentrated and diluted) and organic acids, it is resistant to fresh and salt water.
These features of aluminum make it resistant to corrosion, which is what people use. That is why it is especially widely used in construction. Interest in it is also increasing because of its lightness combined with strength and softness. Not every substance has such characteristics.
In addition to the above, aluminum has several more interesting physical properties:
- Malleability and ductility - aluminum has become a material for the manufacture of strong and lightweight thin foil, as well as wire.
- Melting occurs at a temperature of +660 °C.
- Boiling point +2 450 °C.
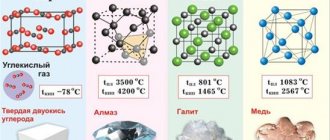
- Density – 2.7 g/cm³.
- The presence of a volumetric face-centered metal crystal lattice.
- Connection type: metal.
Aluminum ore mining methods
It is impossible to extract aluminum directly from ore; it oxidizes too quickly. For this reason, the valuable metal is obtained in several stages:
- Extraction of alumina (aluminum oxide) from aluminum ores with subsequent transportation using dump trucks to processing plants.
- Producing aluminum from alumina is the most difficult and time-consuming part of the process:
- minerals are crushed using crushing machines;
- then sintered in ovens;
- subsequently, leaching occurs with the help of strong alkalis - the period of raw material processing. It is worth noting that alumina can be extracted using various methods: acidic, electrolytic and alkaline. The most popular method is the alkaline method, it was used back in the 18th century;
- decomposition, i.e. a process in which the resulting aluminate pulp enters the separation, where the liquid component is evaporated;
- refining of aluminum, otherwise - purification from excess alkalis;
- calcination in ovens is the final stage.
As a result of complex operations, dry alumina is obtained. Pure aluminum is obtained from this raw material using hydrolysis treatment.
In order to obtain 1 ton of pure aluminum, it is necessary to extract 2 tons of alumina. This amount of alumina will be contained in approximately 4–4.5 tons of bauxite. The number of alunites or nephelites should, accordingly, be even greater. It is easy to conclude that the extraction and production of aluminum is a complex, energy-intensive and costly process.
Basic chemical properties of aluminum
From a chemical point of view, aluminum is an extremely strong reducing agent, capable of being a highly active substance in its pure form. The main condition is to remove the oxide film.
Aluminum is capable of reacting with:
- alkaline compounds;
- acids;
- gray;
- halogens.
Aluminum does not interact with water under normal conditions. Iodine is the only halogen with which the metal reacts without heating. To interact with others, an increase in temperature is required.
Let's look at a few examples showing the chemical properties of this metal. These are equations illustrating the interaction with:
- alkalis: 2Al + 6H2O + 2NaOH = Na[Al(OH)4] + 3H2;
- acids: AL + HCL = AlCL3 + H2;
- gray: 2AL + 3S = AL2S3;
- halogens: AL + Hal = ALHal3.
The main property of aluminum is its ability to restore other substances from their compounds.
The reactions of its interaction with oxides of other metals clearly demonstrate all the reducing properties of the substance. Aluminum perfectly separates metals from various compounds. An example would be: Cr2O3 + AL = AL2O3 + Cr.
The metallurgical industry actively uses this ability of aluminum. The method of obtaining substances, which is based on this reaction, is called aluminothermy. The chemical industry uses aluminum most often to produce other metals.
How to use the basic properties of aluminum
Aluminum in its pure form has weak mechanical properties. That is why its alloys are most often used.
There are quite a lot of such alloys, here are the main ones:
- aluminum with manganese;
- duralumin;
- aluminum with magnesium;
- aluminum with copper;
- avial;
- silumins.
These alloys are based on aluminum; they differ only in additives. The latter make the material durable, easy to process, and more resistant to wear and corrosion.
There are several main applications for aluminum (pure or alloyed). Made from metal:
- foil and wire for household use;
- dishes;
- sea and river vessels;
- aircraft;
- reactors;
- spacecraft;
- architectural and construction elements and structures.
Aluminum is one of the most important metals along with iron and its alloys. These two elements of the periodic table are most widely used by humans in their activities.
Melting process at home
The relatively low melting point of aluminum allows this operation to be carried out at home. It should be noted right away that using a powdered mixture as a raw material in a home workshop is too dangerous. Therefore, either ingots or cut wire are used as raw materials. If there are no special quality requirements for the future product, then anything made from this metal can be used for melting.
Melting aluminum in a homemade forge
In this case, it is not particularly important whether the raw materials are coated with paint or not. When aluminum melts, all foreign substances will simply burn out and be removed along with the slag.
To obtain a high-quality melting result, it is necessary to use materials called fluxes. They are designed to solve the problem of binding and removing foreign impurities and contaminants from the melt.
How to use the basic properties of aluminum in construction
Construction is one of the main aluminum consuming industries. 25% of all metal produced is used in it. The modern appearance of megacities would be impossible without the use of aluminum. It makes it possible to create functional and beautiful buildings that strive upward. Skyscrapers of office centers have glass facades mounted on durable, lightweight aluminum frames.
Modern shopping, entertainment and exhibition centers are based on aluminum frames. Structures made from this metal are used for the construction of swimming pools, stadiums and other sports buildings. Aluminum is one of the most popular materials among architects, builders, and metal designers. Why? Let's figure it out.
Aluminum is a strong and lightweight metal that is resistant to corrosion, has a long service life and is completely non-toxic. It can be easily processed, welded, soldered, simply drilled, sawed, tied and connected with screws. This metal can take any shape through extrusion. Aluminum will help realize the most daring plans of the architect. It is used to make structures that cannot be made from other materials: plastic, wood or steel.