Chemical composition
Each category of steel is characterized by its specific chemical composition. It largely determines the scope of application of the workpieces being created and the difficulties that arise during heat treatment.
The chemical composition of St3 steel makes it one of the most common materials that can be found on the market. It is difficult to imagine modern construction work without this metal.
The key points regarding the chemical composition are the following:
- As previously noted, the main chemical elements are iron and carbon. The first element has a concentration of 97%, carbon is only 0.14-0.22%. It is carbon that determines the hardness index and some other physical and chemical properties of the structure.
- The structure includes a relatively small amount of alloying elements. The main elements are chromium and nickel, the concentration of which is 0.3%. Copper is included in the composition at the same concentration.
Chemical composition
With a large number of varieties of steel, the concentration of harmful impurities, which are phosphorus and sulfur, is strictly controlled in the one under consideration. In addition, the composition contains nitrogen in high concentrations, which accounts for about 0.1 mass.
Chemical composition of steel ST3
St3 steel is characterized by high ductility and the presence of a minimum amount of alloying additives. This makes it possible for the alloy to gain maximum popularity among other similar representatives. Characterized by a wide range of applications in construction. It is almost impossible to find at least one object being constructed during the work on which this steel was not used.
The alloy consists of the following elements:
- the share of iron is 97 percent;
- from 0.14 to 0.22 percent - carbon;
- 0.3 percent each of nickel, copper and chromium;
- from 0.05 to 0.17 percent silicon;
- 0.4 to 0.65 percent manganese;
- up to 0.05 percent sulfur;
- 0.087 percent arsenic;
- no more than 0.04 percent phosphorus.
Each of the constituent elements is responsible for its own area. Strength, hardness, ductility, and weldability depend on carbon. Phosphorus and sulfur act as harmful impurities. Nickel, manganese, copper, chromium are alloying elements that affect the technical characteristics of the alloy.
Physical properties of steel 3 (ST3)
| T | E 10-5 | a106 | l | r | C | R 109 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2.13 | |||||
| 100 | 2.08 | |||||
| 200 | 2.02 | |||||
| 300 | 1.95 | |||||
| 400 | 1.87 | |||||
| 500 | 1.76 | |||||
| 600 | 1.67 | |||||
| 700 | 1.53 |
Technological properties of steel 3 (ST3)
| Weldability: | no limits. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | not sensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | not inclined. |
Designations:
| Mechanical properties of steel 3 (ST3): | ||
| sв | — Short-term strength limit, [MPa] | |
| sT | — Proportional limit (yield strength for permanent deformation), [MPa] | |
| d5 | — Elongation at break, [%] | |
| y | — Relative narrowing, [%] | |
| KCU | — Impact strength, [kJ/m2] | |
| HB | — Brinell hardness | |
| Physical properties of steel 3 (ST3): | ||
| T | — Temperature at which these properties were obtained, [degrees] | |
| E | — Modulus of elasticity of the first kind, [MPa] | |
| a | — Coefficient of thermal (linear) expansion (range 20o - T), [1/degree] | |
| l | — Thermal conductivity coefficient (heat capacity of the material), [W/(m deg)] | |
| r | — Material density, [kg/m3] | |
| C | — Specific heat capacity of the material (range 20o — T), [J/(kg deg)] | |
| R | — Electrical resistivity, [Ohm m] | |
| Weldability of steel 3 (ST3): | |
| no limits | — welding is performed without heating and without subsequent heat treatment |
| limited weldability | — welding is possible when heated to 100-120 degrees. and subsequent heat treatment |
| difficult to weld | — to obtain high-quality welded joints, additional operations are required: heating to 200-300 degrees. during welding, heat treatment after welding - annealing |
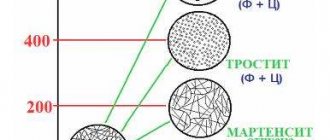
Physical and mechanical properties
St3 steel, the characteristics of which will be discussed in detail, is used as a basis in the manufacture of simply a huge number of different workpieces. This can be attributed to unique physical and mechanical properties. The mechanical properties of St3 steel, which are controlled during the production of blanks, are as follows:
- Temporary resistance.
- Yield limit.
- The degree of bending under high force.
- Relative extension.
- Impact strength at a certain temperature.
The most important technical characteristics of carbon steel 3 are as follows:
- The surface has a hardness of 131 MPa.
- The density of steel is non-uniform, the weight can also vary over a wide range.
- Weldability is not subject to any restrictions.
- The structure is not prone to temper brittleness.
Steel corners
The considered properties of steel 3 determine its widespread use in the construction industry. Various rolled products, which are used in mechanical processing, have also become widespread.
Steel St3sp: characteristics, chemical composition and properties
Welding steel St3sp
St3sp is characterized by unique weldability, which provides a wide range of technical characteristics that can be improved with the help of alloying additives.
The properties of steel make it possible to use arc welding - automatic and manual, welding using contact spot and electroslag technology. It is important for all welding work that steel of this grade can be easily welded without preparatory measures - special preparation, and the products do not require processing after welding. Although this only applies to welding products with a thickness of less than 3.6 cm. It is recommended to preheat steel products with greater thickness (100 ° C) and perform heat treatment after welding.
To weld products made from St3sp, it is advisable to use wire electrodes (most often with a large cross-section) with melting nozzles.
Delivery form of steel St3sp
This steel is supplied in various forms - forgings and castings, section steel - sheets, square and round pipes, shaped rolled products (I-beams, T-bars, channels, angles), ingots, slabs and blooms, sutunki, blanks, hardware, wire, strips, stampings etc.
Application area
Manufacturing of elements of load-bearing structures, welded and non-welded parts and products operated under positive temperature conditions. As well as sheet and shaped rolled products, the operation of which is carried out at temperatures of -40°C - +425°C, and/or loads with variable values (static, dynamic).
Application of St3sp steel, taking into account characteristics and properties
This type of steel is one of the most popular in construction and industry.
The absence of oxygen in the alloy and a homogeneous structure are factors that increase resistance to corrosion in aggressive environments. These qualities, as well as high ductility, make this steel indispensable in the production of structures and elements that have high rigidity requirements.
These are rolled products - sheet and shaped (channels, I-beams and T-beams, angles), blanks for fittings, pipeline elements (in particular, square pipes), etc.
The characteristics of steel make it possible to construct supporting load-bearing structures and frames from it, the operation of which is carried out in difficult conditions.
Elements and parts are made from St3sp steel without heat treatment, which makes it possible to preserve all the characteristics of the alloy - flanges, tees, transitions.
Steel is also used as a base layer in the production of hot-rolled 2-layer sheets that are resistant to corrosion.
Analogs St3sp
Brand st3sp (analogs - S255, VSt3sp5-1 and 18sp, E 235-C according to ISO 630:1995)
Decoding of St3 stamps
Any brand can be decrypted in accordance with established standards and regulatory documentation. The designation of steel according to GOST allows you to determine the main qualities when deciphering grades. GOST 380 determines the presence of the following types of metal:
- Steel St3sp.
- Steel St3ps.
- Steel St3kp.
It is worth considering that indices must be used for any marking.
Properties of various brands of St3
The brand of material can be deciphered as follows:
- ST is a designation that indicates the ordinary quality of carbon steel. Let's use St3sp5 as an example.
- 3 – a number that is the conventional number of the alloy grade. Depending on the carbon concentration, numbers ranging from 0 to 6 can be used.
- G - in some cases, a similar symbol may be used to designate manganese. A certain type of steel, for example, St3gps, contains 0.8% manganese.
- Sp is the degree of deoxidation of the material. When considering St3ps5, we can say that the structure is semi-quiet, but at the same time the degree of deoxidation is quite high. The designation “ps” is used for semi-quiet alloys, “kp” - boiling alloys.
Channel ST3PS5
St3kp2 is deciphered in a similar way relatively recently. Previously, other standards were used for labeling. In addition, previously the metal was divided into several different groups.
Download GOST 380-2005
Table of material elasticity indicators
Before moving directly to this characteristic of steel, let us first consider, as an example and additional information, a table containing data on this value in relation to other materials. The data is measured in MPa .
Modulus of elasticity of various materials
As you can see from the table above, this value is different for different materials, and the indicators also differ, if we take into account one or another option for calculating this indicator.
Everyone is free to choose exactly the option for studying indicators that suits them best. It may be preferable to consider Young’s modulus, since it is most often used specifically to characterize a particular material in this regard. After we have briefly reviewed the data on this characteristic of other materials, we will move directly to the characteristics of steel separately.
First, let's look at the hard numbers and derive different indicators of this characteristic for different types of steels and steel structures:
- Modulus of elasticity (E) for casting, hot-rolled reinforcement from steel grades called St.3 and St. 5 equals 2.1*106 kg/cm^2.
- For steels such as 25G2S and 30KhG2S this value is 2*106 kg/cm^2.
- For periodic wire and cold-drawn round wire, there is an elasticity value equal to 1.8 * 106 kg/cm^2. For cold-flattened reinforcement the indicators are similar.
- For strands and bundles of high-strength wire the value is 2·10 6 kg/cm^2
- For steel spiral ropes and ropes with a metal core, the value is 1.5·10 4 kg/cm^2, while for cables with an organic core this value does not exceed 1.3·10 6 kg/cm^2.
- The shear modulus (G) for rolled steel is 8.4·10 6 kg/cm^2.
- And finally, Poisson’s ratio for steel is equal to 0.3
These are general data given for types of steel and steel products. Each value was calculated in accordance with all physical rules and taking into account all existing relationships that are used to derive the values of this characteristic.
Below will be given all the general information about this characteristic of steel. Values will be given both by Young's modulus and by shear modulus, both in some units (MPa) and others (kg/cm2, newton*m2).