Rare and expensive
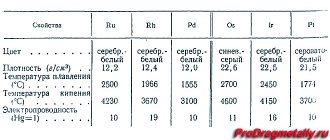
All metals are hard, but their strength varies. Some can be cut with a kitchen knife, while others (chrome, for example) will even scratch steel or glass.
Most of them are present in nature in the form of ores and compounds. They are removed from the earth during mining.
Many metals have their own unique properties. For example, iridium can destroy cancer cells. It fills them with a huge dose of oxygen, which, while killing pathogenic elements, leaves healthy ones untouched.
Interesting fact. It turns out that an ordinary smartphone contains gold, silver and palladium - expensive and quite rare metals. These mobile phones seem especially valuable given the fact that one day humanity will exhaust the reserves of precious elements at a depth acceptable for mining.
There are many metals found in nature, but all in different quantities. There are a lot of some, almost none of others. There are metal isotopes that are obtained artificially. Many of them are not only rare, but also incredibly expensive. So, what is the rarest metal on Earth?
A very light, soft and fusible metal.
These include nitrogen fertilizers (ammonium, sodium, calcium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, urea, etc.), phosphorus (superphosphate, phosphate rock, precipitate, etc.), potassium (potassium chloride, 30 and 40% potassium salt, potassium sulfate, etc.), microfertilizers.
In their composition, the main nutrients can be combined as follows: nitrogen and phosphorus, phosphorus and potassium, nitrogen and potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
If signs of hypokalemia occur (eg, muscle weakness, arrhythmia, or corresponding ECG changes) or if additional potassium is lost from the body (due to vomiting, diarrhea, malnutrition, nephrosis, cirrhosis, hyperaldosteronism, treatment with ACTH or corticosteroids), additional potassium should be administered under the supervision of a doctor.
As it turned out, potassium and sodium, for example, being unevenly distributed in the body - potassium inside the cells, sodium outside - contribute to the transmission of nerve impulses.
In addition, salts of organic acids, mainly potassium tartrate, a small amount of coloring and tannins; plant mucus, pectin, essential oils and, finally, minerals: potassium, sodium, lime, magnesium, iron, aluminum, manganese, chlorine, phosphoric and silicic acids.
In addition, salts of organic acids, mainly potassium tartrate, a small amount of coloring and tannins; plant mucus, pectin, essential oils and, finally, minerals: potassium, sodium, lime, magnesium, iron, aluminum, manganese, chlorine, phosphoric and silicic acids.
Chaga contains 6–8% polysaccharides, up to 60% agaricic and humic acids, 0.5–1.3% organic acids (oxalic, acetic, formic, vanillic, lilac, l-hydroxybenzoic, inonotic and obliquinic), pterins ( pteridine derivatives), the presence of which determines the cytostatic effect of chaga, lipids (di- and triglycerides), sterols, in particular ergosterol, lignin, tetracyclic triterpenes - lanosterol and inotodiol, which exhibit antiblastic activity, fiber, flavonoids, alkaloids, resins. In the fruiting body mushroom contains: macroelements (mg/g): potassium – 41.71, calcium – 3.50, magnesium – 1.90, iron – 0.02; trace elements (µg/g): manganese – 53.40, copper – 3.28, zinc – 28.40, aluminum – 7.04, barium – 1.12, selenium – 0.02, nickel – 0.46, strontium – 6.56, lead – 0.40, boron – 27.60. Potassium is the main element in every living cell.
They are used mainly for tinting varnishes and polishes. Mordants - copper and iron sulfate, potassium dichromate, potassium permanganate, etc. - are used to imitate such rare types of wood as ebony, gray maple, satin wood, etc.
It is best to use an infusion of weeds diluted with water in a ratio of 1:5, to which you should definitely add potassium that does not contain chlorine (sulfate or potassium carbonate).
Californian from California
Californian (Cf) today has the status of the rarest and most expensive metal on Earth. Located at number 98 in the periodic table. It is called the "stone of hope." It is silver-gray in color and is produced by long-term irradiation of plutonium. Plutonium itself was obtained by bombarding uranium with heavy hydrogen nuclei.
Californium was bred by a group of scientists led by Glenn Seaborg in 1950. Naturally, it does not exist in nature. Its creation was carried out by a team from the University of California (where the metal got its name) in Berkeley. Today only 2 laboratories work with it. One is in Russia, the other is in the USA.
Californium is an isotope (isotopes are produced artificially). At the same time, its cost is simply fabulous - up to 10 million dollars per gram. This is not surprising, since the world reserve of the metal is only 8 grams. Every year it is possible to obtain only 20-40 grams of californium.
This metal is radioactive and consists of 17 isotopes. The most studied of them is californium-252. Its half-life is as much as 900 years.
The properties of California are stunning. It is used mainly in medicine and in the field of nuclear physics. It is a powerful source of neutrons, so it is used to treat malignant tumors that are not “treated” by radiation therapy.
It is also used to study outer space - both the Moon and the most distant stars and planets. It is also applicable to the study of nuclear fission. In addition, californium is an indispensable assistant during mining - it allows you to detect silver and gold.
Bombs made with the world's rarest metal are considered very powerful. 1 gram of californium is capable of powering a small nuclear reactor for an hour.
Osmium and osmium-187
Osmium is a natural metal. Formally, he is considered noble. Osmium has a beautiful silver-blue hue. It has the highest melting point. For a long time, scientists could not figure out at what temperature this metal melts - 3000 or 5000 degrees. The results reported that it is better to melt it on the surface of the Sun.
Extraction of osmium in nature is a long process, taking almost a year. Its market price is $10,000 per gram. However, the isotope osmium-187 is much more expensive. Its cost reaches $200,000 per gram. Production of the isotope takes about 9 months. It is noteworthy that the use of osmium-187 has not yet been found. But they are already buying.
Astatine
Astatine is the rarest naturally occurring metal on the planet. Only 70 mg of astatine is present in the earth's crust. For a long time it was considered a halogen (forming salts by reaction with metals). But in 2013, a study was conducted. Scientists have modeled the properties of astatine. Formally, it should be a metal, but at the same time it does not build their inherent crystal lattice. The structure of astatine should be similar to that of mercury, but it is likely to be liquid rather than solid under normal conditions.
During the entire period of studying its properties, laboratories managed to obtain only 0.05 micrograms of the rarest metal on earth, so its main characteristics (color, density) remain a mystery to chemists.
Astatine is obtained by irradiating bismuth and then separating them from each other. All isotopes of this substance are active. It is noteworthy that the decay period of astatine is just over 8 hours. This property allows it to be used in nuclear medicine.
Areas of use
Until the mid-40s, refractory metals were used only as alloying elements to improve the mechanical characteristics of non-ferrous steel alloys based on copper and nickel in the electrical industry. Compounds of molybdenum and tungsten were also used in the production of hard alloys.
The technical revolution associated with the active development of aviation, the nuclear industry and rocket science has found new ways to use refractory metals. Here is a partial list of new applications:
- Production of heat shields for the head unit and rocket frames.
- Structural material for supersonic aircraft.
- Niobium serves as a material for the honeycomb panel of spacecraft. And in rocket science it is used as heat exchangers.
- Thermojet and rocket engine components: nozzles, tail skirts, turbine blades, nozzle flaps.
- Vanadium is the basis for the manufacture of thin-walled tubes of fusion reactor fuel elements in the nuclear industry.
- Tungsten is used as the filament of electric lamps.
- Molybdenum is increasingly used in the production of electrodes used for melting glass. In addition, molybdenum is a metal used to produce injection molds.
- Production of tools for hot processing of parts.
Rate this article:
Rating: 0/5 — 0 votes
Rhenium is one of the rarest metals
Rhenium is one of the rarest metals on Earth. When compiling his table, Mendeleev predicted that a compound with an atomic weight of 180 would soon be discovered. For many years, scientists tried to find the mysterious metal. But it was not until 1925 that this rare, stable metal was discovered by Ida and Walter Noddack.
Until recently he was considered absent-minded. Rhenium minerals are so rare that they are of scientific rather than industrial value. This metal is unique; its properties have no analogues. It is used in the process of creating space and aviation technology. With just 4% rhenium, incredible strength is achieved. This technique can withstand the highest temperatures (up to 2,000 degrees) without losing strength. About 70% of rhenium mined in the world is exploited by Japan.
Today, the demand for rhenium, like other rare elements of the periodic table, is growing every day. The USA especially needs it. This explains the cost of the metal - $800 per 1 gram of crude raw materials.
Grades of heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels
The internal structure of the categories is as follows:
- martensitic;
- austenitic;
- martensitic-ferritic;
- perlite.
Heat-resistant steels can be of two more types:
- ferritic;
- martensitic, or austenitic-ferritic.
Among the steels with a martensitic structure, the most famous are:
- X5 (pipes are made from it that will be operated at a temperature of no more than 650°C).
- Kh5M, Kh5VF, 1 Kh8VF, Kh6SM, 1 Kh12N2VMF (used for the manufacture of products that are operated at 500-600°C for a certain time (1000-10000 hours).
- 3Х13Н7С2 and 4Х9С2 (products made from them are successfully used at 850-950°С, therefore valves for vehicle engines are made from them).
- 1Х8ВФ (products made from this steel are successfully used at temperatures not exceeding 500°C for 10,000 hours or longer; in particular, structural elements of steam turbines are made from the material).
The basis of the martensitic structure is pearlite, which changes state if the chromium content in the material increases. Pearlitic grades of heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels, which belong to chromium-silicon and chromium-molybdenum steels:
- X6S;
- X7SM;
- X6SM;
- X9S2;
- X10S2M;
- X 13N7S2.
To obtain from these steels a material with a sorbitol structure, characterized by high hardness (not less than 25 HRC), they are first hardened at 950-1100°C and then tempered.
Steel alloys with a ferritic structure, from the heat-resistant category, contain 25-33% chromium, which determines their characteristics. To give these steels a fine-grained structure, products made from them are annealed. This category of steels includes:
- 1 Х12СУ;
- X17;
- X18SYU;
- 0Х17Т;
- X25T;
- X 28.
When they are heated to 850°C or more, the grain of the internal structure becomes larger, which increases fragility.
The following are made from heat-resistant stainless steel:
- rolled sheets;
- seamless pipes;
- units for the chemical and food industries.
Steels based on ferrite and martensite are actively used in the production of products for various purposes in mechanical engineering. Products made from such heat-resistant alloys can be successfully used for quite a long time at temperatures up to 600°C.
The most common grades of these heat-resistant steels:
- X6SYU;
- 1Х13;
- 1 X11MF;
- 1Х12ВНМФ;
- 1 X12V2MF;
- 2 Х12ВМБФР.
Chromium in the chemical composition of these alloys is 10-14%. Alloying additives that improve the composition are vanadium, tungsten and molybdenum.
Rhenium on the South Kuril Islands
In the 90s of the last century, a large deposit of rhenium was discovered in Russia. Now the main thing is to build a plant and organize its production. The deposit is located directly in the crater of the active Kudryavy volcano, on the island of Iturup (belongs to the group of the South Kuril Islands).
Gases from the volcano release about 15 tons of rhenium to the surface annually. This confirms the theory of geologists that most rare and heavy metals that are inaccessible to us are located in the bowels of the planet.