Steel grade – St3sp
Standard – GOST 380
Letters St
denote carbon steels of ordinary quality, number
3
- indicates the conventional number of the steel grade,
cn
- degree of deoxidation of steel (calm).
Carbon steel of ordinary quality St3sp is used for load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts.
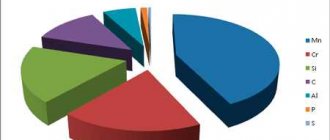
| Mass fraction of basic chemical elements, % | ||
| C – carbon | Mn – manganese | Si – silicon |
| 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,15-0,30 |
| Temperature of critical points, °C | |||
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar1 | Ar3 |
| 735 | 850 | 680 | 835 |
| Technological properties | |
| Forging | Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1300, end 750. Cooling in air. |
| Weldability | Weldable without restrictions. Welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic arc welding, electroslag welding, resistance welding. For thicknesses greater than 36 mm, preheating and subsequent heat treatment are recommended. |
| Machinability | In the hot-rolled state at HB 124 and σв = 400 MPa: Kv carbide = 1.8 Kv high-speed steel = 1.6 |
| Flokensensibility. | Not sensitive |
| Tendency to temper brittleness | Not inclined |
Threaded holes
Table of drills for holes for cutting cylindrical pipe threads.
Wrench nut sizes
Basic spanner dimensions for hex bolt heads and hex nuts.
G and M codes
Examples, description and interpretation of L and M codes for creating control programs on CNC milling and lathes.
Thread types
Types and characteristics of metric, pipe, thrust, trapezoidal and round threads.
Drawing scales
Standard scales for images of parts on mechanical engineering and construction drawings.
Cutting modes
Online calculator for calculating cutting conditions during turning.
Threaded holes
Table of drills and holes for cutting metric threads with large (main) pitch.
CNC machines
Classification of CNC machines, CNC machines for metal for turning, milling, drilling, boring, threading, reaming, countersinking.
Cutting modes
Online calculator for calculating cutting conditions when milling.
Drawing formats
Table of side sizes of main and additional formats of drawing sheets.
CAD/CAM/CAE systems
CAD computer-aided design systems, 3D programs for design, modeling and creation of 3D models.
Reading blueprints
Technical drawing, rules for making drawings of parts and assembly drawings.
Steel is a material in which the main elements are iron and carbon, and other substances are included to change the performance or are controlled within a certain range. Steel 3 has become quite widespread. It is used for the production of a wide variety of workpieces. St3 steel is known to many for its pipes, which are used to create heat supply systems. The characteristics of steel and its features, for example, its chemical composition, determine not only the wide distribution of the metal, but also certain features of heat treatment.
Analogs
As already noted, the St3 grade is in demand in the production of various structures, and in fact, is the most popular structural steel. This is the reason why it is produced by metallurgical plants located in all parts of the world, for example:
- USA – A284Gr.D, A57036;
- Germany – 1.0038;
- Japan – SS330;
- European Union – Fe37-3FN;
- China – Q235.
Suppliers of steel produced outside our country must submit documents confirming the compliance of imported materials with domestic GOST and TU.
Chemical composition
The chemical composition of St3sp steel according to heat analysis of a ladle sample must comply with the standards given in table. 1 (Table 1-2 GOST 380-2005).
Chemical composition of St3sp steel according to heat analysis of a ladle sample
| carbon | manganese | silicon | sulfur | phosphorus | chromium | nickel | copper | arsenic | nitrogen |
| Mass fraction, % | Mass fraction of element, %, no more | ||||||||
| 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,15-0,30 | 0,050 | 0,040 | 0,30 | 0,08 | 0,010 | ||
| Maximum deviations by mass fraction of elements, % | |||||||||
| +0,03 −0,02 | +0,05 −0,03 | +0,03 −0,02 | +0,005 | — | +0,002 | ||||
- Notes:
- It is allowed to reduce the lower limit of the mass fraction of manganese by 0.10% for rolled sheets of thin sheets and thick sheets up to 10 mm thick, provided that the required level of mechanical properties is ensured (clause 4.2 of GOST 380-2005).
- It is allowed to reduce the lower limit of the mass fraction of manganese to 0.25%, and the lower limit of the mass fraction of carbon is not standardized if the melt is intended for the production of long and shaped rolled products (except for those supplied for shipbuilding and carriage building), provided that the required level of mechanical properties is ensured (clause. 4.2 GOST 380-2005).
- It is allowed to increase the mass fraction of copper up to 0.40%, chromium and nickel - up to 0.35% each, in steel made by the scrap process, while the mass fraction of carbon should be no more than 0.20% (clause 4.4 of GOST 380- 2005).
- It is allowed to increase the mass fraction of nitrogen to 0.012% when melting steel in electric furnaces and up to 0.013%, provided that the norm of the mass fraction of phosphorus is reduced by at least 0.005% for each increase in the mass fraction of nitrogen by 0.001% (clause 4.6 of GOST 380-2005).
Sampling methods for determining the chemical composition of steel - according to GOST 7565, chemical analysis of steel - according to GOST 12359, GOST 17745, GOST 18895, GOST 22536.0 - GOST 22536.11, GOST 27809, GOST 28033 or other methods approved in the prescribed manner and ensuring the necessary accuracy .
Determination of the mass fraction of chromium, nickel, copper, arsenic, nitrogen and silicon may not be carried out provided that the manufacturer guarantees that the standards are met (clause 5.3 of GOST 380-2005).
Application of steel St3
The technical parameters of St3 allow it to be used for the production of loaded elements of welded structures and parts of machines and mechanisms operating at positive temperatures.
Some types of rolled products, in particular those of the fifth category, are used in the production of metal structures that can operate at temperatures from -40 to 425 degrees Celsius under alternating loads.
After constructing complex structures, it makes sense to carry out heat treatment, in particular annealing. This operation is necessary to relieve stress arising after welding work.
In addition, this material is used in the production of At400s construction reinforcement.
Sheets made from this steel are used for the production of parts produced using cold stamping technology. It is used to produce troughs for collecting coolants and waste oils installed on machines, containers of various sizes and purposes, covers for machine equipment, casings, etc.
St3sp5 decoding what 5 means
Steel. Types and grades of steel. Their application.
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon with other elements, the carbon content in it is no more than 2.14%.
The most general characteristic is that steel is classified according to its chemical composition:
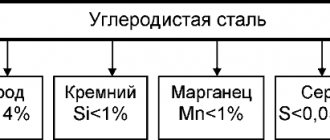
carbon steel (Fe – iron, C – carbon, Mn – manganese, Si – silicon, S – sulfur, P – phosphorus). Based on carbon content, it is divided into low-carbon, medium-carbon and high-carbon. Carbon steel is designed for statically loaded tools.
alloy steel - alloying elements are added: nitrogen, boron, aluminum, carbon, phosphorus, cobalt, silicon, vanadium, copper, molybdenum, manganese, titanium, zirconium, chromium, tungsten, nickel, niobium.
According to the production method and impurity content, steel differs:
ordinary quality steel (carbon less than 0.6%) – corresponds to GOST 14637, GOST 380-94. St0, St1, St2, St3, St4, St5, St6. The letters “St” indicate ordinary quality steel, the numbers indicate the marking number depending on the mechanical properties. It is the cheapest steel, but inferior in other qualities.
high-quality steel (carbon or alloy) - GOST 1577, carbon content is indicated in hundredths of % - 08, 10, 25, 40, the degree of deoxidation and the nature of solidification can additionally be indicated. High-quality carbon steel has high ductility and increased weldability.
Low-carbon high-quality structural steels are characterized by low strength and high ductility. Parts for cold stamping are made from sheet steel 08, 10, 08kp. Bolts, screws, nuts, axles, hooks, studs and other parts for non-essential purposes are made from steels 15 and 20.
Medium-carbon quality steels (st. 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55) are used after normalization and surface hardening for the manufacture of parts that have high strength and core toughness (axles, screws, bushings, etc.)
Steel 60 - steel 85 have high strength, wear resistance, and elastic properties. Crane wheels, rolling rolls, compressor valves, springs, leaf springs, etc. are made from them.
high quality - complex chemical composition with low phosphorus and sulfur content - according to GOST 19281.
Steel is also divided by application:
a) construction steel - carbon steel of ordinary quality. Has excellent weldability. The number indicates the conditional number of the steel composition according to GOST. The higher the reference number, the higher the carbon content, the higher the strength of the steel and the lower the ductility.
St0-3 - for secondary structural elements and non-critical parts (flooring, railings, lining, washers)
St3 is used for load-bearing and non-load-bearing elements of welded and non-welded structures and parts that operate at positive temperatures. GOST 380-88.
The quality standard provides for steel with an increased amount of manganese (St3Gsp/ps, St5Gsp/ps).
b) structural steel - GOST 1050
Carbon-based high-quality structural steels are used in mechanical engineering, for welded, bolted structures, for roofing work, for the manufacture of rails, railway wheels, shafts, gears and other parts of forklifts. The numbers in the marking indicate the carbon content in tenths of a percent.
St20 - lightly loaded parts, such as rollers, copiers, stops,
St35 - experiencing small stresses (axles, rods, levers, disks, traverses, shafts),
St45 (st40Х) - requiring increased strength (shafts, couplings, axles, racks)
Structural alloy steels are used for tractor tracks, the manufacture of springs, leaf springs, axles, shafts, automobile parts, turbine parts, etc.
c) tool steel - used for cutting tools, high-speed steel for cold and hot deformation of materials, for measuring instruments, for the production of hammers, chisels, chisels, cutters, drills, files, razors, rasps.
U7, U8A (the figure is tenths of a percent in terms of carbon content). Carbon steels are produced in high quality and high quality. The letter "A" stands for high quality carbon tool steel.
d) alloy steel - universal steel containing a special impurity. Silicon content more than 0.5%, manganese more than 1%. GOST 19281-89. If the content of the alloying element exceeds 1 - 1.5%, then it is indicated by a number after the corresponding letter.
low-alloy steel - where alloying elements are up to 2.5% (09G2S, 10HSND, 18KhGT). Low-alloy steel can be used in conditions of the far north, from -70 degrees C. Low-alloy steel is distinguished by greater strength due to a higher yield strength, which is important for critical structures.
highly alloyed (from 10 to 50%)
Steel 09G2S is used for steam boilers, apparatus and containers operating under pressure and temperatures from minus 70 to plus 450 degrees; it is used for critical sheet welded structures in chemical and petroleum engineering, and shipbuilding.
Steel 10HSND is used for welded structures in chemical engineering, shaped profiles in construction, and carriage building.
18ХГТ is used for parts operating at high speeds under high pressure and shock loads.
e) special purpose steel - steel with special physical properties. It is used in the electrical industry and precision shipbuilding.
The weldability of steel is affected by the degree of its deoxidation. According to the degree of deoxidation, steel is classified:
mild steel (st3sp) - completely deoxidized with a minimum content of slag and non-metallic impurities,
semi-quiet steel (st3ps) - quality characteristics are similar to calm steel,
boiling steel (08kp) - unoxidized steel with a high content of non-metallic impurities. GOST 1577.
Depending on the standardized characteristics, steel is divided into categories: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. Categories indicate chemical composition, tensile mechanical properties, impact strength)
For example, category 1 - chemical composition is not standardized, category 3 - impact strength at a temperature of +20 is standardized. For the St0 grade, neither the chemical composition nor the yield strength are standardized.
© 2001-2019 JSC Metallotorg, All rights reserved rolled metal, wire rod, galvanized, cold-rolled sheets, cold-rolled galvanized sheets, profile pipes Metallotorg - sale of rolled metal
Steel is a material in which the main elements are iron and carbon, and other substances are included to change the performance or are controlled within a certain range. Steel 3 has become quite widespread. It is used for the production of a wide variety of workpieces. St3 steel is known to many for its pipes, which are used to create heat supply systems. The characteristics of steel and its features, for example, its chemical composition, determine not only the wide distribution of the metal, but also certain features of heat treatment.
Production Features
The properties of the finished material are determined by the substances that make up its composition and largely depend on what technologies were used in the production of a particular alloy.
The basis of the steel alloy is ferrite. It is a component of iron-carbon alloys. It is, in fact, a solid solution of carbon and alloying components. To increase its strength, the melt is saturated with carbon.
Impurities from which nothing but harm can be expected include phosphorus and sulfur, as well as their derivatives. Phosphorus, reacting with ferrite, reduces the ductility of the alloy when exposed to high temperatures and increases brittleness when exposed to cold. During the melting process, iron sulfide may be formed, which can lead to red brittleness. St3 steel contains no more than 0.05% sulfur and 0.04% phosphorus.
For the production of structural steels, two steelmaking technologies are used:
The parameters of the St3 grade, obtained by one or another method, differ little from each other, but the converter technology is simpler and cheaper.
Physical and mechanical properties
St3 steel, the characteristics of which will be discussed in detail, is used as a basis in the manufacture of simply a huge number of different workpieces. This can be attributed to unique physical and mechanical properties. The mechanical properties of St3 steel, which are controlled during the production of blanks, are as follows:
- Temporary resistance.
- Yield limit.
- The degree of bending under high force.
- Relative extension.
- Impact strength at a certain temperature.
The most important technical characteristics of carbon steel 3 are as follows:
- The surface has a hardness of 131 MPa.
- The density of steel is non-uniform, the weight can also vary over a wide range.
- Weldability is not subject to any restrictions.
- The structure is not prone to temper brittleness.
The considered properties of steel 3 determine its widespread use in the construction industry. Various rolled products, which are used in mechanical processing, have also become widespread.
Chemical composition
Grade St3 is classified as carbon structural steel of ordinary quality. The composition includes the following chemical elements:
- carbon up to 0.22%;
- silicon up to 0.17%;
- manganese up to 0.65% and many others, including chromium and nickel.
Metallurgical plants produce the following range of products from the St3 grade:
- Forgings GOST 8479-70;
- Rental GOST 2591-2006;
- Strip and tape products GOST 14918-80;
- Rails GOST 5812-82;
- Pipes and fittings for them GOST 10705-80;
Decoding steel St3
The steel supplied to the customer must be marked in accordance with GOST 380-2005. The full name of St3 should be as follows St3Gsp GOST 380-2005. Its decoding is as follows:
- St – this is the designation for carbon steel of ordinary quality;
- 3 – serial number of the alloy grade according to GOST 380-2005;
- G is the designation for manganese. If the alloy contains more than 0.8%, then it must be indicated.
- Sp – level of deoxidation.
Steel C245 can be used as a substitute; this is defined in GOST 27772-88 and C285
Decoding of St3 stamps
Any brand can be decrypted in accordance with established standards and regulatory documentation. The designation of steel according to GOST allows you to determine the main qualities when deciphering grades. GOST 380 determines the presence of the following types of metal:
It is worth considering that indices must be used for any marking.
Properties of various brands of St3
The brand of material can be deciphered as follows:
- ST is a designation that indicates the ordinary quality of carbon steel. Let's use St3sp5 as an example.
- 3 – a number that is the conventional number of the alloy grade. Depending on the carbon concentration, numbers ranging from 0 to 6 can be used.
- G - in some cases, a similar symbol may be used to designate manganese. A certain type of steel, for example, St3gps, contains 0.8% manganese.
- Sp is the degree of deoxidation of the material. When considering St3ps5, we can say that the structure is semi-quiet, but at the same time the degree of deoxidation is quite high. The designation “ps” is used for semi-quiet alloys, “kp” - boiling alloys.
St3kp2 is deciphered in a similar way relatively recently. Previously, other standards were used for labeling. In addition, previously the metal was divided into several different groups.
Mechanical properties
The mechanical properties of long and shaped rolled steel St3sp (St3sp5) in tension, impact strength, as well as bending test conditions must comply with the requirements of Table 2 (Table 2-3 GOST 535).
Mechanical properties of rolled steel St3sp (St3sp5)
| Thickness, mm | Mechanical characteristics | Bending until the sides are parallel (a is the thickness of the sample, d is the diameter of the mandrel) | Impact strength KCU, J/cm² (kgf m/cm²) | Impact strength KCV, J/cm² (kgf m/cm²) | ||||
| Yield strength σ t, MPa (kgf/mm²) | Temporary resistance σв, MPa (kgf/mm²) | Relative elongation δ5, % | at temperature, °C | after mechanical aging | at temperature, °C | |||
| +20 | −20 | +20 | ||||||
| no less | no less | |||||||
| Mechanical properties of long and shaped steel | ||||||||
| Up to 5 incl. | 255 (26) | 380-490 (39-50) | 26 | d = a | — | |||
| St. 5 to 10 incl. | 108 (11) | 49 (5) | 49 (5) | 34 (3,5) | ||||
| St. 10 to 20 incl. | 245 (25) | 370-480 (38-49) | — | |||||
| From 20 to 40 incl. | 235 (24) | 25 | d=2a | |||||
| Over 40 to 100 incl. | 225 (23) | 23 | ||||||
| St. 100 | 205 (21) | |||||||
- Notes:
- By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to reduce the yield strength by 10 N/mm² (1 kgf/mm²) for shaped steel with a thickness of over 20 mm.
- By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to reduce the relative elongation by 1% (abs.) for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses.
- It is allowed to exceed the upper limit of tensile strength by 49.0 N/mm² (5 kgf/mm²), and by agreement with the consumer - without limiting the upper limit of tensile strength, provided that other standards are met. At the request of the consumer, exceeding the upper limit of temporary resistance is not allowed.
- It is allowed to reduce the impact strength value on one sample by 30%, while the average value must not be lower than the standards specified in this table