Characteristics of steel 08Х18Н10Т
The chemical composition of steel 08Х18Н10Т is determined according to GOST-5632. The three main elements of this alloy are iron, chromium and nickel; it is their ratio that determines the key characteristics of steel 08Х18Н10Т. Due to the high chromium content, steel is resistant to corrosion, while nickel ensures strength and performance at high temperatures. Among other stainless steels, 08Х18Н10Т is characterized by increased resistance to intergranular corrosion, which makes it possible to use it in more aggressive environments. Steel is almost non-magnetic after heat treatment and weakly magnetic in its normal state. The alloy can be processed and has good weldability.
The main areas of application of steel 08Х18Н10Т
Stainless steels are widely used in industrial areas where contact with moisture or aggressive external environments is inevitable. Where products made from carbon steels quickly fail or require constant renewal of protective coatings, stainless steels demonstrate high durability indicators, which more than cover the difference in cost.
Welded fittings, electrodes and spark plugs are made from steel grade 08Х18Н10Т. It is used in the production of stainless pipes, shut-off valves, and equipment for the chemical industry used in alkaline or acidic environments. Steel 08Х18Н10Т is suitable for the manufacture of parts operating at high temperatures up to 800C. These include furnace fittings, elements of heat exchangers, boilers, etc. Stainless steels, in particular steel 08Х18Н10Т, are used in the oil and gas industry. Tanks for storing and transporting fuel are made from it, because this metal is not sensitive to aggressive environments.
Well-polished stainless steel has an attractive appearance and is used to make decorative elements.
Types of delivery
Steel 08Х18Н10Т is supplied in the form of steel sheets of different thicknesses, strips, strips and pipes, long and shaped rolled products. Ground rods, calibrated rods of different sections, silver, and forgings are in demand.
Analogues of steel 08Х18Н10
If steel of this grade is not available, you can select grades that are similar in properties and composition. An analogue of steel 08Х18Н10 is the international grade AISI 304; it also has American analogues - 304H, S30400 and German - 1.4301, 1.5301. The analogue in Japan is SUS304; from French steels it corresponds to grades 304F00, X5CrNi18-10, Z4CN19-10FF, Z5CN17-08, Z6CN18-09 and Z7CN18-09. English steels that are analogues of 08Х18Н10 or similar to it are 304S11, 304S15, 304S16, 304S17, 304S18, 304S25, 304S31. Among the Chinese brands are 0Cr19Ni9, OCr18Ni9.
Explanation of markings and chemical composition of steel 08Х18Н10Т
- 08 - this number at the beginning of the brand indicates the percentage of carbon in hundredths - 0.08%;
- Х18 – chromium content 18%;
- H10 - indicates 10% nickel in the composition;
- T – titanium up to 1%.
In addition to the elements indicated in the marking, the alloy contains additives and impurities in small quantities. A chemical element is displayed in the mark only if its concentration has a noticeable effect on the properties of the steel. The content of harmful impurities, such as phosphorus and sulfur, affects the quality of steel, which is also displayed in the marking with a special letter.
If the quality of steel is not indicated in the marking with a special letter, then it is steel of ordinary quality.
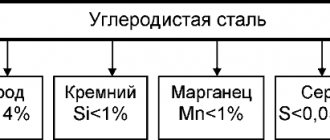
Chemical composition in%
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | V | Ti | Cu | W | Fe |
| <0,08 | <0,8 | <2,0 | <0,035 | <0,02 | 17,0-19,0 | <0,3 | 9,0-11,0 | <0,2 | <0,7 | <0,4 | <0,2 | Rest |
The influence of chemical composition on the properties of steel
Carbon. Forms the chemical compound cementite (Fe3C) with iron. Starting from 1.2% content, it significantly affects the properties of steel, increases strength, hardness, elasticity, but reduces ductility and impact strength. Increased carbon content also negatively affects the machinability of steel, in particular weldability. The negative impact of both high and low carbon content in steel can be compensated by using alloying additives.
Silicon . Deoxidizes steel, removes gases (oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide). In small concentrations it does not affect the quality and properties of alloys.
Manganese. It is also a deoxidizing agent, improving some characteristics of steel if contained in the alloy in large quantities. Does not affect quality when its concentration is negligible. It is especially useful in that it binds sulfur into the MnS compound - manganese sulfide, which neutralizes its harmful effect on the alloy.
Phosphorus. Deteriorates the performance of the alloy in any quantity. Due to the harmful effects of phosphorus, at low temperatures steel becomes brittle, loses its toughness, and becomes cold-brittle.
Sulfur. Like phosphorus, it negatively affects the quality of steel in any concentration. Causes red brittleness - loss of viscosity at high heating temperatures. In addition, sulfur makes steel susceptible to fatigue, susceptible to corrosion, and loses overall resistance.
Chromium. Alloying element, one of the most popular and accessible alloying additives. Steels with a chromium content of 8% or more are called high-chromium steels; these are the most common alloy alloys in industry. Steel alloyed with chromium is called chromium or stainless steel, and steel coated with a thin layer of chromium is called chrome plated. Chromium enhances the beneficial properties of steel - hardness, strength, elasticity, with almost no effect on ductility.
Molybdenum. An alloying element that increases a number of important characteristics of steel - red resistance, anti-corrosion properties, tensile strength, elasticity.
Nickel. Expensive additive, increases the cost of production of alloy steel; whenever possible, it is replaced by cheaper additives.
Vanadium. Expensive and rare deoxidizer. Promotes the formation of a fine-grained metal structure, increases density, strength and hardness.
Titanium. Thanks to titanium, steel can be processed well and acquires a fine-grained structure. Titanium also has a positive effect on the anti-corrosion properties, deoxidizes and increases the strength of the alloy.
Copper. Gives steel strength and prevents rusting. Steels with a high copper content are in demand primarily in construction.
Tungsten. Alloying carbide-forming element. Increases red resistance, hardness, allows the metal to maintain a fine-grained structure at high temperatures, and protects against temper brittleness. Expensive and rare supplement.
Iron. It forms the basis of any steel; up to 99% of the iron content can be seen in carbon unalloyed alloys.
Technical characteristics and properties of steel
The tables below show the physical, mechanical and technological properties of steel 08Х18Н10Т.
Mechanical properties of the material
| Mechanical properties of steel 08Х18Н10Т (old 0Х18Н10Т EI914) at T=20oС | |||||||
| Rental | Size | Eg. | σв (MPa) | s T (MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (kJ/m2) |
| Bar | Æ 60 | 490 | 196 | 40 | 55 | ||
| The leaf is thick | 520 | 210 | 43 | ||||
| The wire is annealed. | Æ 8 | 1400-1600 | 20 | ||||
| Hot deformed pipes | 510 | 40 | |||||
| Forgings | 490 | 196 | 35 | 40 | |||
Properties according to GOST 5582-75
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets: hardening at 1050-1080 °C, water, air | Up to 3.9 | — | 520 | 40 | — |
Properties according to GOST 5949-75 standard
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Rods. Quenching at 1020-1100 °C, air, oil, water. | 60 | 196 | 490 | 40 | 55 |
Properties according to GOST 7350-77
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Hot-rolled and cold-rolled sheets: hardening 1000-1080 °C, water, air. | Over 4 | 206 | 509 | 43 | — |
Properties according to GOST 9940-81
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Seamless hot-deformed pipes without heat treatment | 3,5 — 32 | — | 510 | 40 | — |
Properties according to GOST 18907-73
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Ground rods, processed to a specified strength | 1 — 30 | — | 590 — 830 | 20 | — |
Properties according to GOST 25054-81
| Delivery condition, heat treatment mode | Section, mm | Yield strength, σ0.2, MPa | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Forgings. Quenching 1050-1100 °C, water or air | 1000 | 196 | 490 | 35 | 40 |
| Rental | Size | Direction | Tensile strength σ in , MPa | Short-term strength limit, S T , MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Relative narrowing, ψ, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Bar | F 60 | — | 490 | 196 | 40 | 55 | — |
| Thin sheet | — | — | 520 | 210 | 43 | — | — |
| Annealed wire | F 8 | — | 1400 — 1600 | — | 20 | — | — |
| Hot-deformed pipes | — | — | 510 | — | 40 | — | — |
| Forgings | — | — | 490 | 196 | 35 | 40 | — |
Impact strength of steel as delivered
| Assortment | Heat treatment | Index | Т= +20 °С | Т= -25 °С |
| Bar | Quenching at 1050 °C, water | KCV, J/cm2 | 216 | 181 |
| Bar | Quenching at 1050 °C, water | KCV, J/cm2 | 167 | 147 |
Mechanical properties in long-term strength tests
| Mechanical properties of 08Х18Н10Т (old 0Х18Н10Т EI914) during long-term strength tests | ||||
| Test temperature, °C | Creep limit, MPa | Creep rate %/h | Long-term strength limit, MPa, not less | Test duration, h |
| 600 650 | 74 29-39 | 1/100000 1/100000 | 147 108 78-98 | 10000 100000 10000 |
| Test temperature, °C | Creep limit, MPa | Creep rate %/hour | Long-term strength limit, MPa | Test duration, hours |
| 600 | 74 | 1/100000 | 147 | 10000 |
| — | — | — | 108 | 100000 |
| 650 | 29 — 39 | 1/100000 | 78 — 98 | 10000 |
Mechanical properties of steel at elevated temperatures
| Mechanical properties of steel 08Х18Н10Т (old 0Х18Н10Т EI914) at elevated temperatures | |||||
| Test temperature, °C | σ0.2 (MPa) | σв (MPa) | δ5 (%) | ψ % | KCU (kJ/cm2) |
| 20 300 400 500 600 700 | 275 200 175 175 175 160 | 610 450 440 440 390 270 | 41 31 31 29 25 26 | 63 65 65 65 61 59 | 245 — 313 363 353 333 |
| Test temperature, °C | Yield strength, σ 0.2 , MPa | Tensile strength, σ in , MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Relative narrowing, ψ, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| 20 | 275 | 610 | 41 | 63 | 245 |
| 300 | 200 | 450 | 31 | 65 | — |
| 400 | 175 | 440 | 31 | 65 | 313 |
| 500 | 175 | 440 | 29 | 65 | 363 |
| 600 | 175 | 390 | 25 | 61 | 353 |
| 700 | 160 | 270 | 26 | 59 | 333 |
Physical properties
| Temperature, °C | Modulus of elasticity, E 10 5 , MPa | Linear expansion coefficient, a 10 6 , 1/°С | Thermal conductivity coefficient, l, W/m °C |
| 20 | 1,96 | — | — |
| 100 | — | 16,1 | 16 |
| 200 | — | — | 18 |
| 300 | — | 17,4 | 19 |
| 400 | — | — | |
| 500 | — | 18,2 |
Technological properties
| Mass fraction of basic chemical elements, % | |||||
| C - carbon | Si - silicon | Mn - manganese | Cr - chromium | Ni - nickel | Ti - titanium |
| No more than 0.08 | No more than 0.80 | No more than 2.00 | 17,00-19,00 | 9,00-11,00 | No more than 0.70 |
| Forging | Forging temperature, °C: beginning 1220, end 900. Sections up to 300 mm are cooled in air. | ||||
| Weldability | Weldable without restrictions. Welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic arc welding, electroslag welding, resistance welding. | ||||
| Machinability | At HB 143 and σв = 510 MPa: Kv carbide = 1.1 Kv high-speed steel = 0.35 | ||||
Resistance of steel 08Х18Н10Т against crevice erosion
| Durability group | Point | Erosion resistance against steel 12X18H10T |
| Persistent | 2 | 0,75-1,5 |
Resistance of steel 08Х18Н10Т to sulfide corrosion cracking
| Method of forming blanks | Name of parts |
| Forgings, stampings, rolled products | Body, bonnet, stem, spindle, valve seal parts, bellows end parts |
Assortment of hot-rolled steel 08Х18Н10
| steel grade | Thickness mm | Standard size, mm | Surface group | ||||
| 1000x2000 | 1000x4000 | 1250x2500 | 1500x3000 | 1500x6000 | |||
| 08Х18Н10 | 4-6 6-25 | Find out the price | Find out the price | Find out the price | M2B-M5B | ||
| Find out the price | Find out the price | ||||||
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т taking into account characteristics and properties
Below are tables for the use of steel for various parts, indicating the temperature of the working environment and additional instructions for use.
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Long products GOST 5949, Sheets GOST 7350 M3b, M2b. Pipes GOST 9940, GOST 9941. Forgings GOST 25054 | -270 to 610 | For welded fittings operating in aggressive environments: HNO3, alkalis, ammonium nitrate, food media, special equipment media, ship fittings, cryogenic media, hydrogen sulfide-containing media; for membranes |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for fittings fasteners (GOST 33260-2015)
| Steel grade, according to GOST 1759.0 | Material standard or specification | Application options | |||||
| Bolts, studs, screws | Nuts | Flat washers | |||||
| Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Ambient temperature, °C | Nominal pressure Pn, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||
| 08Х18Н10Т | GOST 5632 | -196 to 600 | Not regulated | -196 to 600 | Not regulated | -196 to 600 | Not regulated |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for the manufacture of spindles and rods (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | Working environment temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use |
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Long products GOST 5949 | -270 to 610 | It is used for work in aggressive environments: nitric acid, alkalis, ammonium nitrate, food environments, environments of special equipment, shipbuilding, cryogenic equipment and hydrogen sulfide-containing environments. Used for welded joints |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for bellows (GOST 33260-2015)
| steel grade | ND for supply | RD for the production of bellows | Working environment temperature, °C | Operating pressure Pp, MPa (kgf/cm2), no more | Additional instructions for use |
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Sheet GOST 5582. Tape GOST 4986, (for steel 1.4541) | GOST 21744, GOST 22388 | -260 to 550 | From 0.6 to 25.0 (from 6 to 250) | For water, steam, inert gases and cryogenic temperatures. For mildly aggressive environments - up to a temperature of 350°C. For corrosive environments - up to 150°C |
| Pipe GOST 10498. Pipe blank |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for valve valve assembly
| steel grade | Working environment temperature, °C | Hardness | Additional instructions for use |
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | -100 to 300 | 155…170 HB | The functionality of the valve assembly is ensured by the presence of surfacing or other wear-resistant coating in the mating part |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for gaskets
| steel grade | Type of semi-finished product | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions for use | |
| Name | ND for supply | |||
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632 | Thick heat-treated sheets | GOST 7350 | -253 to 600 | Suitable for use in corrosive environments |
Maximum permissible temperature for using steel 08Х18Н10Т in environments containing ammonia
| steel grade | Temperature of application of steels, °C at partial pressure of ammonia, MPa (kgf/cm) | ||
| St. 1(10) to 2(20) | St. 2(20) to 5(50) | St. 5(50) to 8(80) | |
| 08Х18Н10Т | 540 | 540 | 540 |
Maximum permissible temperature for the use of steel 08Х18Н10Т in hydrogen-containing environments
| steel grade | Temperature, °C, at partial pressure of hydrogen, PH2, MPa (kgf/cm2) | ||||||
| 1,5(15) | 2,5(25) | 5(50) | 10(100) | 20(200) | 30(300) | 40(400) | |
| 08Х18Н10Т | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 | 510 |
Application of steel 08Х18Н10Т for the manufacture of main parts of nuclear power plant fittings
| steel grade | Type of semi-finished product or product | Maximum permissible temperature of use, °C |
| 08Х18Н10Т GOST 5632, GOST 24030 | Sheets, pipes, forgings, long products. Fasteners | 600 |
Application of stainless steel circles 08Х18Н10
Steel of this grade is used for the production of pipes and furnace fittings. Heat exchangers are made from it, as well as other devices that can withstand high temperatures - muffles, retorts, pipes and exhaust manifolds. The steel is intended for the production of electrodes for spark spark plugs; welding machines are made from it, as well as chemical engineering vessels designed to operate at temperatures ranging from -196 to 600 ° C in medium activity environments.
Steel is used in the oil and gas industry for the production of pipes and fittings. It is also actively used in medicine.
Hot rolled circle 08Х18Н10 is produced by hot rolling on rolling mills by drawing or cold rolling.
A stainless steel circle is often used in construction, in particular in the construction of metal structures. Forged, riveted, bolted and welded steel structures and gratings are made from round stainless steel rods. In the field of metallurgy, the circle is used as a semi-finished product. In modern mechanical engineering, it also acts as a raw material for the production of components and parts. Some of the most commonly used industries for this grade of steel are agricultural engineering and instrument making.
The closest equivalents (analogues) of steel 08Х18Н10Т
| USA (ASTM/ASME) | 321, S32100 |
| Germany (DIN, WNr) | 1.4541, 1.4878, X10CrNiTi18-9 |
| Japan (JIS) | SUS321 |
| France (AFNOR) | 321F00, Z6CN18-10, Z6CN18-10 |
| England (BS) | 321S12, 321S18, 321S20, 321S22, 321S31 |
| Euronorms (EN) | 1.4541, X10CrNiTi18-10, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| Italy (UNI) | X6CrNiTi18-11, X8CrNiTi1811 |
| Spain (UNE) | F.3523, X6CrNiTi18-10 |
| China (GB) | 0Cr18Ni11Ti, 1Cr18Ni9Ti, 0Cr18Ni10Ti |
| Sweden (SS) | 2337 |
| Poland (PN) | 0H18N10T, 1H18N10T, 1H18N9T |
| Czech Republic (CSN) | 17246, 17247, 17248 |
| Austria (ONORM) | X6CrNiTi18-10S, X6CrNiTi1810K, KW |
| Russia (GOST) | 10Х14Г14Н4Т, Х14Г14Н3Т |