Currently, the market offers a wide selection of different knives. From familiar kitchen items to combat ones, with special certificates confirming the legality of production and sale.
Despite the huge assortment, not every purchased product turns out to be useful and pleases with its efficiency of use and long service life. The reason for this is the low quality of the product, which quickly becomes unusable.
Despite the presence of markings on the packaging of the product, it is difficult for the average buyer to understand the information presented, and visually identifying the best quality product is also not easy.
To buy a good quality knife, it is important to know some of the nuances of choice.
How to determine the hardness of metal at home?
Mechanical engineering parts and mechanisms, as well as tools intended for their processing, have a set of mechanical characteristics. Hardness plays a significant role among the characteristics. The hardness of metals clearly shows:
- wear resistance of metal;
- possibility of processing by cutting, grinding;
- resistance to local pressure;
- ability to cut other materials and others.
Hardness of metals
In practice, it has been proven that most of the mechanical properties of metals directly depend on their hardness.
Hardness concept
The hardness of a material is its resistance to destruction when a harder material is introduced into the outer layer. In other words, the ability to resist deforming forces (elastic or plastic deformation).
The hardness of metals is determined by introducing a solid body called an indenter into a sample. The role of the indenter is performed by: a metal ball of high hardness; diamond cone or pyramid.
After exposure to the indenter, an imprint remains on the surface of the test sample or part, the size of which determines the hardness. In practice, kinematic, dynamic, and static methods of measuring hardness are used.
The kinematic method is based on the compilation of a diagram based on continuously recorded readings that change as the tool is pressed into the sample. Here the kinematics of the entire process is traced, and not just the final result.
The dynamic method is as follows. The measuring tool acts on the part. The reverse reaction allows you to calculate the expended kinetic energy. This method allows you to test the hardness of not only the surface, but also a certain volume of metal.
Static methods are non-destructive methods that allow you to determine the properties of metals. The methods are based on smooth indentation and subsequent holding for some time. The parameters are regulated by methods and standards.
The applied load can be applied:
- pressing;
- scratching;
- cutting;
- rebound
Machine-building enterprises currently use the Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers methods, as well as the microhardness method, to determine the hardness of materials.
Based on the tests carried out, a table is compiled indicating the materials, the applied loads and the results obtained.
Hardness Units
Each method of measuring the resistance of a metal to plastic deformation has its own methodology, as well as units of measurement.
The hardness of soft metals is measured using the Brinell method. Non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, magnesium, lead, tin) and alloys based on them, cast iron (except for white) and annealed steel are subjected to this method.
Brinell hardness is determined by indentation of a hardened, polished ball made of ShKh15 ball bearing steel. The circumference of the ball depends on the material being tested. For hard materials - all types of steel and cast iron - 10 mm, for softer materials - 1 - 2 - 2.5 - 5 mm. Required load applied to the ball:
- iron alloys – 30 kgf/mm2;
- copper and nickel – 10 kgf/mm2;
- aluminum and magnesium – 5 kgf/mm2.
The unit of hardness measurement is a numerical value followed by a numerical index HB. For example, 200 NV.
Rockwell hardness is determined by the difference in applied loads to the part. First, a preliminary load is applied, and then a general load, at which the indenter is introduced into the sample and held.
A pyramid (cone) of diamond or a ball of tungsten carbide (hardened steel) is introduced into the test sample. After removing the load, the depth of the indentation is measured.
The unit of measurement for hardness is conventional units. It is generally accepted that one is the amount of axial displacement of the cone, equal to 2 μm. The hardness designation is marked with three letters HR (A, B, C) and a numerical value. The third letter in the marking indicates the scale.
The technique reflects the type of indenter and the load applied to it.
| Scale type | Tool | Applied load, kgf |
| A | Diamond cone with 120° apex angle | 50-60 |
| IN | 1/16" ball | 90-100 |
| WITH | Diamond cone with 120° apex angle | 140-150 |
Basically, measurement scales A and C are used. For example, the hardness of steel is HRC 26...32, HRB 25...29, HRA 70...75.
Products of small thickness or parts with a thin, hard surface layer are measured by Vickers hardness. The blade used is a regular tetrahedral pyramid with an apex angle of 136°. The display of hardness values is as follows: 220 HV.
Hardness measurement using the Shore method is carried out by measuring the rebound height of a fallen striker. Indicated by numbers and letters, for example, 90 HSD.
Microhardness is determined when it is necessary to obtain the values of small parts, thin coatings, or individual alloy structures. The measurement is made by measuring the imprint of a tip of a certain shape. The value notation looks like this:
Н□ 0.195 = 2800, where
□ — tip shape;
0.196 — tip load, N;
2800 – numerical value of hardness, N/mm2.
Hardness of base metals and alloys
The hardness value is measured on finished parts sent for assembly. Control is carried out for compliance with the drawing and technological process. Tables of hardness values have already been compiled for all basic materials, both in the initial state and after heat treatment.
Non-ferrous metals
The Brinell hardness of copper is 35 HB, the values of brass are 42-60 HB units, depending on its brand. For aluminum, the hardness is in the range of 15-20 HB, and for duralumin it is already 70 HB.
We carry out a visual inspection
In order not to buy the “wrong” knife, you need to carefully consider the product. To do this, you need to direct your gaze along its surface, which should represent an absolutely straight line. The existing curvature is a signal that the buyer has a defect in his hands, which may be the result of a violation of steel smelting technology. It's hardly worth buying such a knife.
How to determine the hardness of a metal at home - Metals, equipment, instructions
Mechanical engineering parts and mechanisms, as well as tools intended for their processing, have a set of mechanical characteristics. Hardness plays a significant role among the characteristics. The hardness of metals clearly shows:
- wear resistance of metal;
- possibility of processing by cutting, grinding;
- resistance to local pressure;
- ability to cut other materials and others.
Hardness of metals
In practice, it has been proven that most of the mechanical properties of metals directly depend on their hardness.
Black metals
The Rockwell hardness of cast iron SCH20 HRC 22, which corresponds to 220 HB. Steel: tool – 640-700 HB, stainless steel – 250 HB.
To convert from one measurement system to another, tables are used. The values in them are not true, because they are derived imperially. Not the full volume is presented in the table.
| HB | H.V. | H.R.C. | HRA | HSD |
| 228 | 240 | 20 | 60.7 | 36 |
| 260 | 275 | 24 | 62.5 | 40 |
| 280 | 295 | 29 | 65 | 44 |
| 320 | 340 | 34.5 | 67.5 | 49 |
| 360 | 380 | 39 | 70 | 54 |
| 415 | 440 | 44.5 | 73 | 61 |
| 450 | 480 | 47 | 74.5 | 64 |
| 480 | 520 | 50 | 76 | 68 |
| 500 | 540 | 52 | 77 | 73 |
| 535 | 580 | 54 | 78 | 78 |
Hardness values, even if produced by the same method, depend on the applied load. The lower the load, the higher the readings.
Hardness measurement methods
All methods for determining the hardness of metals use mechanical action on the test sample - indentation of an indenter. But this does not destroy the sample.
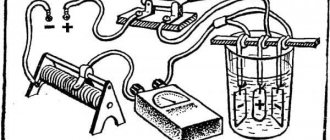
The Brinell hardness method was the first to be standardized in materials science. The principle of testing samples is described above. It is subject to GOST 9012. But you can calculate the value using the formula if you accurately measure the imprint on the sample:
HB=2P/(πD*√(D2-d2),
- where P – applied load, kgf;
- D – ball circumference, mm;
- d – circumference of the imprint, mm. The ball is selected relative to the thickness of the sample. The load is pre-calculated from accepted standards for the relevant materials: iron alloys - 30D2; copper and its alloys - 10D2; babbits, lead bronze - 2.5D2.
Symbol of the test principle
Download GOST 9012-59
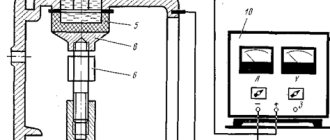
Schematically, the Rockwell research method is depicted as follows according to GOST 9013.
Steel - only - stainless steel
It is clear that not every buyer understands the grades of steel and alloys that are used to make knives, and the quality of the steel of knives is almost impossible to determine at a glance. But it is important to consider that products must not only be strong and durable, but also not react to the influence of aggressive substances that lead to metal corrosion and the appearance of rust on them.
If a knife begins to become covered with rusty spots after being placed in a humid environment, it will not last long and may be unsafe to use. Reaction with substances that cause a change in the color of the tool, the appearance of dark spots on the surface of the blade is an indicator of danger. Using food cut with such a knife can lead to chemical poisoning. In addition, you should be wary of the cost: products made from low-grade steel or alloy are much cheaper than high-quality analogues. They can only be used for technical work.
Safety knives are made of stainless steel and alloys that do not contain toxic or poisonous components hazardous to human health.
How to determine the hardness of metal at home
Mechanical engineering parts and mechanisms, as well as tools intended for their processing, have a set of mechanical characteristics. Hardness plays a significant role among the characteristics. The hardness of metals clearly shows:
- wear resistance of metal;
- possibility of processing by cutting, grinding;
- resistance to local pressure;
- ability to cut other materials and others.
Hardness of metals
In practice, it has been proven that most of the mechanical properties of metals directly depend on their hardness.
Importance of processing
The next important point is checking the quality of processing. On the so-called heel of the blade, which is an unsharpened flat part at the “root”, if processed poorly, the cutting section of the blade will not fit tightly to it, which will create difficulties in use, and the knife will very quickly fail.
All elements of the product must be accurately adjusted and securely fastened. In addition, there should be no nicks on the surface. A good quality knife cannot have obvious traces of processing, and the transitions from one element to another must not have sharp breaks and be smooth and smooth to the touch.
Hardness of metals
Mechanical engineering parts and mechanisms, as well as tools intended for their processing, have a set of mechanical characteristics. Hardness plays a significant role among the characteristics. The hardness of metals clearly shows:
- wear resistance of metal;
- possibility of processing by cutting, grinding;
- resistance to local pressure;
- ability to cut other materials and others.
Hardness of metals
In practice, it has been proven that most of the mechanical properties of metals directly depend on their hardness.
How to test the hardness of metal - the main secrets
When it comes to metals, an important indicator is its hardness.
A factor of this kind plays a significant role in the choice of whether or not to use a particular metal in production for the manufacture of products for a specific purpose.
It is worth understanding this issue in more detail, which requires testing the hardness of metal in the production line of various industries.
What is metal hardness
This concept refers to a characteristic closely related to metals and their alloys. This is the ability to resist damage when the top layer is synchronized with a harder metal.
Based on this knowledge, various equipment and parts are manufactured that play a role in the durability of objects, structures, machines, and tools. Simply put, resistance to deformation.
You can check this parameter in different ways.
Methods for testing metal hardness
Experts distinguish several options for checking characteristics:
- According to the Brinnell method, a steel ball takes part in the verification process. It is pressed under great pressure into a metal surface. Then a special magnifying glass comes into effect, and with its help the specialist measures the diameter of the hole. Hardness is determined from tabular data. This method is the first method for determining the nature of the metal. This is how soft alloys are measured.
- Rockwell's technique involves impacting a metal surface with a diamond cone. A special press is used to measure the hardness of soft, colored, thin Me. It is not considered very accurate, although it is successfully used for the study of hard alloys.
- Similar actions to the previous one are included in the Vikxer method, which involves turning to a diamond pyramid, only the angle of the top is not 120, but 136 degrees. The load is carried out strictly perpendicular to the metal and increases slowly. Refers to high-precision methods.
- Shore's method involves the presence of a striker with a diamond-coated tip. It falls from a specific height onto the surface of the material being tested. Hardness is measured by the height of the striker's rebound. This methodology is distinguished by a large scatter of readings; for the most part it is used to measure curved objects and large parts.
At home, the indicator is also measured, but you should not expect high accuracy. When you turn to professionals, you can get a highly accurate result, and this is a crucial moment.
Some conduct home education to determine this value, using an ordinary bottle and scratching it with a metal object, for example, a knife blade.
Metal of 62 units easily scratches glass, which cannot be said about 56 units.
What does the hardness of the metal indicate, what does it give
The question arises as to why this parameter needs to be measured at all. The characteristics of metals are important to those involved in the steel heat treatment industry. The conclusion about the mechanical properties of the weld is also obtained by studying the heat-affected surface.
The feasibility of the research being carried out is also predetermined by the intention of manufacturers to obtain high-strength products so that they can withstand different operating conditions, temperature changes, and ensure reliability. The hardness of a metal product is a primary structural characteristic.
Research is carried out with the following objectives.
- Analyze the state of the material under the influence of time.
- Obtain knowledge of likely destructive consequences to improve operational capabilities.
- Monitor the results obtained as part of the temperature treatment.
According to the information acquired during the experiments, it is possible to determine the resistance to abrasion and wear of the source material.
Conclusion
To carry out the analysis, certain conditions are imposed on the material being tested. In particular, the workpiece is selected to be level. It should fit tightly to the hardness tester, with carefully processed edges.
As a result, fundamental mechanical quality is achieved, which plays a role in the production of high-quality products.
Specialists use the results obtained during the study, compare them with previously known analysis, and this is a lot of work that helps determine the production methodology. Information is necessary for mechanical engineering, metalworking, and metallurgical enterprises.
The concept of “hardness” is associated with elasticity, plasticity, and strength, although there is no direct connection between mechanical qualities. It is important to turn to professionals to perform such work; the home method is only suitable for tasks of hardening knives.
Tests you can do right in the store
The simplest test
, which can be done without prior preparation, is a shaving test for the hair on the forearm. You don’t even have to ask the seller for permission, just run the blade across your forearm. A well-sharpened knife will shave hair easily. You should not be afraid of this test, although it is scary to check the quality of sharpening on your hand for the first time. The main thing is not to press the blade on the skin and hold it at a certain angle. It’s difficult to explain this in words, just try it and everything will work out (just be careful!).
The next test is paper cutting
. If the blade does not shave hair, then at least it must cut paper. In the worst case, sheets of A4 size writing paper, in the best case, a newspaper. This test will show how responsibly the manufacturer took such a procedure as sharpening the blade. Take a sheet and start shredding the paper. If the paper tears, it is better to immediately refuse to purchase such a knife. Although sharpening it is not a problem, this already indicates that the manufacturer was negligent in making the knife.
A good knife will do a great job of whittling paper and you'll just get tired of doing it before it gets dull. But if the knife first cuts the paper and then begins to tear it, it means either the steel is bad or the thermal agent has let us down.
Steel homogeneity test
. To be honest, I seriously doubt its effectiveness, and I would not recommend focusing on its indicators. They say you just need to wipe the knife blade dry and then breathe on it. By the way the perspiration comes off, you can understand the homogeneity of the metal. To me this sounds like nonsense, before this test the knife needs to be at least degreased, otherwise the fatty places on the blade will be different anyway. It's possible that this test works, but I don't believe it.
Sound test
allows you to determine the quality of hardening. A similar method was used in Rus'. This is exactly how axes were tested, and even now many of them are tested in stores this way. It works pretty much the same way on knives. You need to take the tool by the end of the handle, after which you need to click the blade with your fingernail. If the sound is ringing and long, it means the hardening is good. It should be especially noted that folding knives cannot be checked in this way.