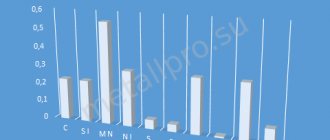
Chemical composition.
Steels are usually called alloys of iron and carbon containing up to 2.14% carbon.
Depending on the chemical composition, carbon steels (GOST 380-71, GOST 1050-75) and alloy steels (GOST 4543-71, GOST 5632-72, GOST 14959-79) are distinguished. In turn, carbon steels can be:
- low-carbon, i.e. containing less than 0.25% carbon;
- medium-carbon, carbon content is 0.25-0.60%;
- high-carbon, in which the carbon concentration exceeds 0.60%.
Alloy steels are divided into:
| Table of elements MS Word, 40Kb |
- low alloy content of alloying elements up to 2.5%;
- medium alloyed, they contain from 2.5 to 10% alloying elements;
- highly alloyed, which contain over 10% alloying elements.
Delivery 18kp
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-2006 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-2006 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 1133-71 Forged round and square steel, GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles , GOST 8509-93 Hot rolled equal flange steel angles , GOST 8510-86 Hot rolled unequal flange steel angles , GOST 103-2006 long steel strip , GOST 503-81 Cold rolled low carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot rolled steel strip , GOST 8 2-70 Hot-rolled broadband universal steel, GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wire , GOST 3262-75 Steel water and gas pipes .
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 8239-89; GOST 8240-97; GOST 8510-86; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 8509-93; GOST 1133-71; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 23570-79; GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; GOST 82-70; GOST 19903-74; |
| Ribbons | GOST 3560-73; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 7417-75; GOST 1051-73; GOST 8559-75; GOST 1050-88; GOST 14955-77; GOST 8560-78; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 803-81; GOST 4405-75; |
| Ribbons | GOST 1530-78; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 3262-75; |
| Low carbon steel wire | GOST 792-67; |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 26366-84; GOST 9389-75; GOST 9850-72; GOST 3920-70; GOST 7372-79; |
Purpose
Structural, intended for the manufacture of construction and engineering products.
Tools, from which cutting, measuring, stamping and other tools are made. These steels contain more than 0.65% carbon.
With special physical properties, for example, with certain magnetic characteristics or a low coefficient of linear expansion: electrical steel, superinvar.
With special chemical properties, for example stainless, heat-resistant or heat-resistant steels.
Application
The steel alloy can be machined satisfactorily. When turning, it does not provide a clean surface, and when cutting threads, it does not allow high-quality execution of small steps. Therefore, to improve machinability, 08ps steel is often subjected to normalization and cold working.
It is widely used for the manufacture of products that do not require heat treatment, and for cladding bodies, machines and units. Also, 08ps steel is used for the production of cemented parts, the operating conditions of which require high surface hardness and wear resistance while maintaining the viscosity of the core. On an industrial scale, it is used to produce washers and brackets, rods and cups, lugs and stops, rollers and shells, disks and bushings, as well as other non-critical and unloaded parts.
Degree of deoxidation
According to the degree of oxygen removal from steel, i.e. according to the degree of its deoxidation, there are:
- calm steel, i.e., completely deoxidized; such steels are designated by the letters “sp” at the end of the grade (sometimes the letters are omitted);
- boiling steels - slightly deoxidized; are marked with the letters “kp”;
- semi-quiet steels, occupying an intermediate position between the previous two; are designated by the letters "ps".
Ordinary quality steel is also divided into 3 groups based on supplies:
- Group A steel is supplied to consumers based on its mechanical properties (such steel may have a high sulfur or phosphorus content);
- steel group B - by chemical composition;
- steel group B - with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition.
Depending on the standardized indicators (tensile strength, elongation, yield strength, cold bending), the steel of each group is divided into categories, which are designated by Arabic numerals.
Treatment
Steel grade 08PS can be subjected to various types of processing. We are talking about both thermal and mechanical operations. Let's take a closer look at each of the options.
Thermal
Heat treatment of material marked 08PS helps improve its characteristics. In this case, there is no need to introduce other additional components into the alloy. Upon completion of the procedure under consideration, the strength level of the metal increases noticeably. Heat treatment is often used for those workpieces that are planned to be used in load-bearing structures in the future. For the steel processing under consideration, steps such as hardening, tempering and annealing can be used.
The hardening operation helps the material obtain the required level of rigidity. When the hardening stage is completed, the workpieces are allowed to be cooled under various conditions. Both water and oil media are suitable.
To eliminate the excess stress that appears inside the metal structure, they resort to an operation such as tempering. Upon completion of this processing stage, products made from 08PS alloy become much harder, and their strength level also increases. To effectively align the internal structure, as well as get rid of excessive levels of ductility, the alloy undergoes an annealing operation.
Mechanical
To obtain rolled steel parts, it is advisable to thoroughly clean the surfaces from scale, as well as oil traces and other similar contaminants. For this purpose, it is allowed to use both brushes with metal bristles and components of small-scale mechanization. For example, you can use a grinder.
In the procurement areas of production that use rolled metal from alloy 08PS, special guillotine-type shears are used, as well as special Geller sawing machines, press shears and other similar technical equipment. With such equipment it is possible to cut rolled metal. We are talking about both profile and sheet products.
The technological features of 80PS make it possible to use this raw material for the production of parts using bending methods. This operation can be performed using a variety of devices. Both simple manual models of bending machines and specialized high-tech machines are suitable. Of course, working with the latter is much easier, and much less time is spent bending steel.
To process mechanical parts and parts made from raw materials marked 08PS, you do not need to use any special specialized tools or devices.
It is allowed to carry out the operations under consideration using hard alloys, for example, T15K6.
Unalloyed structural steels of ordinary quality
Designated according to GOST 380-94 with the letters “St” and a conventional brand number (from 0 to 6) depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. The higher the carbon content and strength properties of the steel, the higher its number. The letter “G” after the brand number indicates a high manganese content in the steel. The steel group is indicated before the grade, and group “A” is not included in the designation of the steel grade. To indicate the category of steel, the number corresponding to the category is added to the brand designation at the end; the first category is usually not indicated.
For example:
- St1kp2 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, boiling, grade No. 1, second category, supplied to consumers based on mechanical properties (group A);
- VSt5G - carbon steel of ordinary quality with a high manganese content, calm, grade No. 5, first category with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition (group B);
- Vst0 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, grade number 0, group B, first category (steel grades St0 and Bst0 are not separated by degree of deoxidation).
| Steel designation | Carbon content |
| St0 | < 0,23% |
| St1 | 0,06-0,12% |
| St2 | 0,09-0,15% |
| St3 | 0,14-0,22% |
| St4 | 0,18-0,27% |
| St5 | 0,28-0,37% |
| St6 | 0,38-0,49% |
Unalloyed structural quality steels
In accordance with GOST 1050-88, these steels are marked with two-digit numbers showing the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent: 05; 08; 10; 25; 40, etc. So steel with a carbon content of 0.07-0.14% is designated 10, steel with a carbon content of 0.42-0.50% is designated 45, and steel with a carbon content of 0.57-0.65% is designated 60.
In this case, for steels with C < 0.2% that have not been subjected to complete deoxidation, the letters kp (for boiling steel) and ps (for semi-quiet steel) are added to the designation.
For mild steels, letters are not added at the end of their names. For example, 08kp, 10ps, 15, 18kp, 20, etc.
The letter G in the steel grade indicates a high manganese content. For example: 14G, 18G, etc.
High-quality steels with improved properties, used for the production of boilers and high-pressure vessels, are designated according to GOST 5520-79 by adding the letter K at the end of the steel name: 15K, 18K, 22K.
Technological properties
Steel is highly reliable; this ensures the absence of defects during casting, has excellent weldability, and is not prone to brittleness.
These properties make it possible to use methods of bending the material both manually and on specialized machines.
Tempering brittleness
Steel 08 PS is not prone to temper brittleness, since its hardness is HB 10-1 = 131 MPa. In addition, the material does not react to flocking.
Weldability
The steel is characterized by excellent weldability properties in the absence of preheating, and microcracks do not occur on the plane.
In welding work, any technique can be used. If the thickness of the sheets is large, multilayer welding will be used.
Corrosion resistance: does it rust or not?
In general, 08 PS steel is corrosion resistant and does not rust for a long time. But if the manufacturing technology is broken, corrosion will appear in the near future.
Structural alloy steels
In accordance with GOST 4543-71, the names of such steels consist of numbers and letters. The first digits of the brand indicate the average carbon content in steel in hundredths of a percent. The letters indicate the main alloying elements included in the steel. The numbers after each letter indicate the approximate percentage content of the corresponding element, rounded to the nearest whole number; for an alloying element content of up to 1.5%, the number behind the corresponding letter is not indicated.
For example, steel of composition C 0.09-0.15%, Cr 0.4-0.7%, Ni 0.5-0.8% is called 12ХН, and steel of composition C 0.27-0.34%, Cr 2.3-2.7%, Mo 0.2-0.3%, V 0.06-0.12% - 30×3MF.
In order to show that the content of sulfur and phosphorus in steel is limited (S < 0.03%, P < 0.03%) and the steel belongs to the high-quality group, the letter A is placed at the end of its designation.
Particularly high-quality steels subjected to electroslag remelting, which ensures effective purification from sulfides and oxides, are designated by adding the letter Ш through a dash at the end of the name of the steel. For example: 12×2N4A, 15×2MA, 18ХГ-Ш, 20ХГНТР-Ш, etc.
Classification and designation of various steel grades
Home / Reference materials / Steel grade / Classification and designation of various steel grades
Chemical composition.
Steels are usually called alloys of iron and carbon containing up to 2.14% carbon. Depending on the chemical composition, carbon steels (GOST 380-2005, GOST 1050-88) and alloy steels (GOST 4543-71, GOST 5632-72, GOST 14959-79) are distinguished.
In turn, carbon steels can be:
- low-carbon, i.e. containing less than 0.25% carbon;
- medium carbon, carbon content is 0.25-0.60%
- high-carbon, in which the carbon concentration exceeds 0.60%
Alloy steels are divided into:
- low alloy content of alloying elements up to 2.5%
- medium alloyed, they contain from 2.5 to 10% alloying elements;
- highly alloyed, which contain over 10% alloying elements.
Purpose
Structural, intended for the manufacture of construction and engineering products. Tools, from which cutting, measuring, stamping and other tools are made. These steels contain more than 0.65% carbon. With special physical properties, for example, with certain magnetic characteristics or a low coefficient of linear expansion: electrical steel, superinvar. With special chemical properties, for example stainless, heat-resistant or heat-resistant steels.
Quality
Depending on the content of harmful impurities: sulfur and phosphorus, steel is divided into:
Steel of ordinary quality, content up to 0.06% sulfur and up to 0.07% phosphorus.
· High-quality - up to 0.035% of sulfur and phosphorus each separately.
· High quality - up to 0.025% sulfur and phosphorus.
· Extra high quality, up to 0.025% phosphorus and up to 0.015% sulfur.
Degree of deoxidation
According to the degree of oxygen removal from steel, i.e. according to the degree of its deoxidation, there are:
· calm steel, i.e., completely deoxidized; such steels are designated by the letters “sp” at the end of the grade (sometimes the letters are omitted);
· boiling steels - slightly deoxidized; are marked with the letters “kp”;
· semi-quiet steels, occupying an intermediate position between the previous two; are designated by the letters "ps".
Ordinary quality steel is also divided into 3 groups based on supplies:
· group A steel is supplied to consumers based on its mechanical properties (such steel may have a high sulfur or phosphorus content);
· group B steel - by chemical composition;
· Group B steel - with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition. Depending on the standardized indicators (tensile strength, elongation, yield strength, cold bending), the steel of each group is divided into categories, which are designated by Arabic numerals.3
Structural steels
Unalloyed structural steels of ordinary quality
Designated according to GOST 380-2005 with the letters “St” and a conventional brand number (from 0 to 6) depending on the chemical composition and mechanical properties. The higher the carbon content and strength properties of the steel, the higher its number. The letter “G” after the brand number indicates a high manganese content in the steel. The steel group is indicated before the grade, and group “A” is not included in the designation of the steel grade. To indicate the category of steel, the number corresponding to the category is added to the brand designation at the end; the first category is usually not indicated. For example: St1kp2 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, boiling, grade No. 1, second category, supplied to consumers based on mechanical properties (group A); VSt5G - carbon steel of ordinary quality with a high manganese content, calm, grade No. 5, first category with guaranteed mechanical properties and chemical composition (group B); Vst0 - carbon steel of ordinary quality, grade number 0, group B, first category (steel grades St0 and Bst0 are not separated by degree of deoxidation).
| Steel designation | Carbon content |
| St0 | < 0.23%, |
| St1 | 0.06 — 0.12%, |
| St2 | 0.09 — 0.15%, |
| St3 | 0.14 — 0.22%, |
| St4 | 0.18 — 0.27%, |
| St5 | 0.28 — 0.37%, |
| St6 | 0.38 — 0.49%. |
Unalloyed structural quality steels
In accordance with GOST 1050-88, these steels are marked with two-digit numbers showing the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent: 05; 08 ; 10 ; 25; 40, etc. So steel with a carbon content of 0.07 - 0.14% is designated 10, steel with a carbon content of 0.42 - 0.50% - 45, and steel with carbon 0.57 - 0.65% - 60. Moreover, for steels with C < 0.2%, not subjected to complete deoxidation, in designation the letters kp (for boiling steel) and ps (for semi-calm) are added. For mild steels, letters are not added at the end of their names. For example, 08kp, 10ps, 15, 18kp, 20, etc. The letter G in the steel grade indicates a high manganese content. For example: 14G, 18G, etc. High-quality steels with improved properties, used for the production of boilers and high-pressure vessels, are designated according to GOST 5520-79 by adding the letter K at the end of the steel name: 15K, 18K, 22K.
Structural alloy steels
In accordance with GOST 4543-71, the names of such steels consist of numbers and letters. The first digits of the brand indicate the average carbon content in steel in hundredths of a percent. The letters indicate the main alloying elements included in the steel (see Table 2, stainless steels.) The numbers after each letter indicate the approximate percentage of the corresponding element, rounded to the nearest whole number, with an alloying element content of up to 1.5% the number behind the corresponding letter is not indicated. For example, steel of composition C 0.09 - 0.15%, Cr 0.4 - 0.7%, Ni 0.5 - 0.8% is called 12ХН, and steel of composition C 0.27 - 0.34%, Cr 2.3 - 2.7%, Mo 0.2 - 0.3%, V 0.06 - 0.12% — 30Х3МФ. In order to show that the steel has a limited content of sulfur and phosphorus (S < 0.03%, P < 0.03%) and the steel belongs to the high-quality group, the letter A is placed at the end of its designation. Particularly high-quality steels subjected to electroslag remelting, which ensures effective cleaning of sulfides and oxides, are designated by adding the letter Ш through a dash at the end of the name of the steel. For example: 12Х2Н4А, 15Х2МА, 18ХГ-Ш, 20ХГНТР-Ш, etc.
Cast structural steels
In accordance with GOST 977-88, they are designated according to the same rules as high-quality and alloy steels. The only difference is that at the end of the names of casting steels the letter L is given, for example, 15L, 20G1FL, 35 KhGL, etc. Construction steels. Construction steels according to GOST 27772-88 are designated by the letter C (construction) and numbers corresponding to the minimum yield strength of the steel. The letter K at the end of the name indicates steel with increased corrosion resistance, the letter T indicates heat-strengthened rolled steel, and the letter D indicates a high copper content. For example: S255, S345T, S 390K, S440D, etc.
Ball bearing steels
GOST 801-78 is marked with the letters “ШХ”, after which the chromium content is indicated in tenths of a percent. For steels subjected to electroslag remelting, the letter Ш is also added at the end of their names separated by a dash. For example: ShKh15, ShKh20SG, ShKh4-Sh.
Automatic steels
GOST 1414-75 begin with the letter A (automatic). If the steel is alloyed with lead, then its name begins with the letters AC. To reflect the content of other elements in steels, the same rules are used as for alloyed structural steels. For example: A20, A40G, AS14, AS38HGM
Tool steels
Unalloyed carbon tool steels
These steels, in accordance with GOST 1435-90, are divided into high-quality and high-quality. High-quality steels are designated by the letter U (carbon) and a number indicating the average carbon content in the steel, in tenths of a percent. Thus, U7 steel contains 0.65 - 0.74% carbon, U10 steel - 0.95 - 1.04%, and U13 steel - 1.25 - 1.35%. The letter A is added to the designations of high-quality steels (U8A, U12A, etc.). In addition, the designations of both high-quality and high-quality carbon tool steels may contain the letter G, indicating an increased content of manganese in the steel. For example: U8G, U8GA.
Tool alloy steels
The rules for designating tool alloy steels according to GOST 5950-2000 are basically the same as for structural alloy steels. The difference lies only in the numbers indicating the mass fraction of carbon in the steel. The percentage of carbon is also indicated at the beginning of the name of the steel, in tenths of a percent, and not in hundredths, as for structural alloy steels. If the carbon content in alloy tool steel is about 1.0%, then the corresponding figure is usually not indicated at the beginning of its name. Let us give examples: 4Х2В5МФ steel has a content of C 0.3 - 0.4%, Cr 2.2 - 3.0%, W 4.5 - 5.5%, Mo 0.6 - 0.9%, V 0.6 - 0.9%, and KhVG steel - C 0.9 - 1.05%, Cr 0.9 - 1.2%, W 1.2 - 1.6%, Mn 0.8 - 1.1%.
High speed steels
Designated by the letter “P”, the number following it indicates the percentage of tungsten in it: Unlike alloy steels, the names of high-speed steels do not indicate the percentage of chromium, because it is about 4% in all steels and carbon (it is proportional to the vanadium content). The letter F, indicating the presence of vanadium, is indicated only if the vanadium content is more than 2.5%. In accordance with the above, R6M5 steel has a composition C 0.82 - 0.9%, Cr 3.8 - 4.4%, Mo 4.8 - 5.3%, V 1.7 - 2.1%, W 5.5 - 6.5%, and steel composition C 0.95 - 1.05%, Cr 3.8 - 4.3%, Mo 4.8 - 5.3%, V 2.3 - 2.7%, N 0.05 - 0.1%, W 5.7 - 6.7% called P6AM5F3
Stainless steels
The designations of standard stainless steels according to GOST 5632-72 consist of letters and numbers and are based on the same principles as the designations of structural alloy steels. The letter L is added to the designation of cast stainless steels. Let us give examples: stainless steel of composition C < 0.08%, Cr 17.0 - 19.0%, Ni 9.0 - 11.0%, Ti 5*C - 0.7% is designated 08Х18Н10Т, and cast steel 16Х18Н12С4ТУЛ has composition C 0.13 - 0.19%, Cr 17.0 - 19.0%, Ni 11.0 - 13.0%, Si 3.8 - 4.5%, Ti 0.4 - 0.7%, Al 0.13 - 0.35%. In the event that steels are produced by electroslag remelting, the letter Ш (06Х16Н15М3Б-Ш) is added to their names (as well as for alloy steels) separated by a dash. In addition, letters can be added to the names of the specified steels separated by a dash, meaning the following: VD - vacuum-arc remelting (09Х16Н4Б-ВД), VI - vacuum induction smelting (03Х18Н10-VI), EL - electron beam remelting (03Н18К9М5Т-EL) , GR - gas-oxygen refining (04Kh15ST-GR), ID - vacuum-induction smelting followed by vacuum-arc remelting (EP14-ID), PD - plasma smelting followed by vacuum-arc remelting (KHN45NVTYUBR-PD), IL - vacuum induction smelting followed by electron beam remelting (EP989-IL), etc.
Home / Reference materials / Steel grade / Classification and designation of various steel grades
Unalloyed carbon tool steels
These steels, in accordance with GOST 1435-90, are divided into high-quality and high-quality.
High-quality steels are designated by the letter U (carbon) and a number indicating the average carbon content in the steel, in tenths of a percent. Thus, U7 steel contains 0.65-0.74% carbon, U10 steel - 0.95-1.04%, and U13 steel - 1.25-1.35%.
The letter A is added to the designations of high-quality steels (U8A, U12A, etc.).
In addition, the designations of both high-quality and high-quality carbon tool steels may contain the letter G, indicating an increased content of manganese in the steel. For example: U8G, U8GA.
Tool alloy steels
The rules for designating tool alloy steels according to GOST 5950-73 are basically the same as for structural alloy steels. The difference lies only in the numbers indicating the mass fraction of carbon in the steel. The percentage of carbon is also indicated at the beginning of the name of the steel, in tenths of a percent, and not in hundredths, as for structural alloy steels. If the carbon content of alloy tool steel is about 1.0%, then the corresponding figure is usually not indicated at the beginning of its name.
Let us give examples: steel 4×2V5MF has a content of C 0.3-0.4%, Cr 2.2-3.0%, W 4.5-5.5%, Mo 0.6-0.9%, V 0.6-0.9%, and HVG steel - C 0.9-1.05%, Cr 0.9-1.2%, W 1.2-1.6%, Mn 0.8-1, 1%.