04/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- How laser cutting works
- Types of laser cutting
- Pros and cons of laser cutting of metal
- The nuances of using laser cutting for some metals
- Laser cutting quality parameters
- How can you improve the quality of laser cutting?
Understanding how laser cutting works is essential to performing or evaluating laser cutting. It is also necessary to know the quality requirements for laser cutting, permissible deviations in size and roughness.
In addition to the above, laser cutting of some metals has its own characteristics, and to carry out this work you need certain knowledge in setting up the equipment. Only all this together will help to obtain high-quality products.
How laser cutting works
The very name “laser cutting” reveals to us the essence of the process, which consists of cutting metal with a laser beam emitted by a special installation. The laser beam has a number of properties that allow it to be focused on the surface being treated, and the beam will carry a high-density energy charge. Under its influence, almost any material actively burns, melts, evaporates, etc. - in general, it is destroyed.
The beam energy with a density of 108 watts per 1 cm2 created by a laser cutting machine is concentrated on the metal surface. To understand the essence of the process and, in particular, how this effect is obtained, you need to learn about all the properties of the laser beam.
Unlike light waves, a laser beam has a constant wavelength and frequency. This property is called monochromaticity, and the radiation itself is monochromatic. It makes it possible, using simple optical lenses, to easily focus the beam on the surface being treated.
Another property of the laser beam is its very high directivity, as well as a small divergence angle. This property helps the equipment create a highly focused laser beam.
The next important property of a laser beam is its coherence. Its essence lies in the consistency of a large number of wave processes occurring in the beam, as well as in their resonance with respect to each other. This allows you to significantly increase the total radiation power.
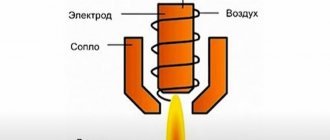
Under the influence of the beam, the metal surface heats up very quickly and then melts, leaving an even cut.
Due to a number of factors, one of which is thermal conductivity, the melting zone of the metal quickly spreads deep into the workpiece. The laser beam works by affecting the surface of the part and brings the temperature at the cutting point to a boil, at which point the metal begins to evaporate.
There are two types of laser cutting of metal:
- Melting.
- Evaporation.
Evaporation of metal requires the operation of high-power equipment, which results in large expenditures of energy resources. This is not always economically feasible. In addition, this method is not suitable for processing thick workpieces, which is reflected in the rather strict cutting requirements. Therefore, its use is limited to cutting thin-walled products.
Laser cutting by melting metal is used much more often. Recently it has been improved by using various gases such as air, oxygen, nitrogen or inert gases. Special installations blow them into the laser cutting area. You can view a video recording of this type of work by typing the appropriate request on the Internet.
The innovation made it possible to reduce energy costs, increase cutting speeds and use low-power equipment to process thicker material. However, it would be more correct to change the name of this method from laser to gas laser.
Let's consider a number of advantages that allow the use of oxygen as an auxiliary gas for laser cutting:
- oxidation of the metal is activated and makes it possible to reduce its reflectivity;
- the thermal power of the processing zone increases due to a more active process of metal combustion in an oxygen environment;
- oxygen supplied under pressure helps to blow combustion products and small metal particles out of the processing zone, which simplifies the entry of new waves of gas into the cutting zone.
Laser thermal splitting
The three previous technologies are mainly used in metal processing. But thermal splitting allows you to separate glass. In fact, when using it, it is not a cut that appears, but a crack - only smooth and controlled.
This technology exploits the fragility of glass and the possibility of its destruction due to temperature changes. The laser beam sharply heats the desired area, and a jet of inert gas sharply cools it. The crack has started. At the same time, the beam moves, directing it further.
Types of laser cutting
The intensity of radiation, the composition of the gas used for work and the pressure when processing different metals must differ. Therefore, several types of cutting have been developed.
1. Laser-oxygen cutting.
The oxygen used in this type of treatment is a cutting gas. During its interaction with hot metal, an exothermic oxidation reaction occurs. And the oxides formed during the same process are instantly blown away by an oxygen stream.
Features of work using this type of laser cutting are the speed of work and the diameter of the focused beam, which affect the width of the cut. At the same time, the diameter of the beam is smaller than the diameter of the oxygen jet (usually from 1 to 2 mm). The cut becomes narrower as the speed increases and the thickness of the workpiece decreases. The cut has a minimum width of just under 100 µm. There is an inverse relationship between the pressure of the oxygen flow and the thickness of the material - as the thickness of the metal decreases, the pressure increases.
VT-metall offers services:
The pressure in the process of cutting a thin sheet reaches 3-4 atm, and when the thickness increases to 25 mm or more, it becomes about 0.3 mm. The jet forms a gap between the nozzle cut. Its size depends on the thickness of the metal being processed. Fluctuations in the size of the gap can be from 0.5 mm for sheets of thin metal to 3 mm for metal with a thickness of 2.5–3 cm. The maximum thickness of a steel sheet cut by a laser with a power of 6 kW is 3 cm. The process speed for a given thickness is minimal , about 0.5 m per minute. If the operating speed continues to decrease, the quality of cutting decreases even faster.
2. Oxygen cutting with laser beam support (LASOX).
To work with thick steel sheets, it makes sense to use a technology that has become widespread in recent years, in which a laser beam heats the surface of the metal until it reaches a temperature of +1,000 ° C, after which a jet of oxygen is used, which cuts the metal at supersonic speed. The use of this method makes it possible to significantly increase the depth of the cut when compared with simple oxygen laser cutting.
A supersonic oxygen jet is formed by high pressure, reaching 6–10 atm. The cut has a width equal to the diameter of the oxygen jet. It has a size ≥ 3 mm. The distance from the nozzle exit to the surface should be approximately 7 mm. The cutting speed is reduced to 0.2 m per minute. The operating speed when using the presented technology is significantly reduced compared to oxygen laser cutting. But the thickness of the processed metal reaches 10 cm.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
3. Laser cutting in inert gas.
If oxidation of the edges of the metal being processed cannot be allowed, then inert gas laser cutting technology works great. It is suitable for metals such as titanium, stainless steel, aluminum alloys. This technology does not provide for the use of an additional heating source, which, unfortunately, reduces the efficiency of metal cutting.
The speed of work in an inert gas environment, which can be argon, used when cutting titanium, or nitrogen, used in other cases, is quite low. The cutting gas pressure must be more than 10 atm. The diameter of the nozzle depends on the width of the sheet of metal being processed. And it, accordingly, influences the amount of gas used, increasing it. Which affects the increase in cutting costs.
4. Laser thermal splitting of glass.
This technology works well for cutting fragile and brittle materials such as glass. The laser beam heats the material unevenly, and then a jet of inert gas works to cool it. As a result, a crack forms. The direction of its advancement can be controlled by moving the heat source along the surface of the material. The result of the work is a smooth, even edge.
5. Sublimation cutting (evaporative laser).
If it is necessary to minimize the thermal effect on the substrate, sublimation cutting technology is used. Its main application is microtechnology. The laser radiation intensity for this type of cutting must be very high. Let's take a look at how a laser cutting machine works. In short, the equipment operates on radiation of picosecond and nanosecond pulse durations, that is, very short ones. The radiation wave has a length of less than 1 micron. For such radiation, excimer and solid-state lasers are used, as well as those that operate on metal vapors. The efficiency of such processes is minimal.
Consequently, oxygen laser technology is the most common and standard type of cutting materials. The remaining types are specific in nature and solve individual problems.
Laser cutting in an inert gas environment
The opposite of the two previous technologies.
Oxidation comes in very handy when working with iron and low-alloy steels - but with non-ferrous metals and high-alloy steels it is not the topic. Due to the presence of oxygen during cutting, stainless steel, aluminum and titanium form unusable compounds on the edges that spoil the properties of the material.
At the same time, the decision “to use not pure oxygen, but just air” does not help, because there is still oxygen in the atmospheric air. And the cutting will not go so fast, but the edges will still be damaged - although not as much. This cannot be called quality work.
Therefore, when working with “capricious” materials, inert gases are used. A jet of compressed gas is supplied to the cutting zone, which does not enter into a harmful reaction with the material - but at the same time it also blows the melt out of the hole and cools the edges of the cut.
- For most “capricious” materials - for example, stainless steel and aluminum alloys - nitrogen is used. It is called conditionally inert gas. “Conditionally” - because in principle it is not inert. Nitrogen quite easily reacts with other substances. But it is not an oxidizing agent. In this case, this is enough.
- But there are also “particularly capricious” materials - for example, titanium. When cutting titanium, even nitrogen will be harmful. Because not only titanium oxides are undesirable, but also its nitride, that is, a compound with nitrogen. Titanium nitride can be quite beautiful - in particular, it is used as gold plating for domes and dentures. But its unexpected appearance in detail is no good, because titanium nitride is fragile. Argon, a truly inert gas, is used to cut titanium.
And here is an example of a case produced by Metal-Case:
Black panel with ventilation folds
Pros and cons of laser cutting of metal
The use of laser cutting technology for materials occurs everywhere in various sectors of industrial production, such as aviation, mechanical engineering, medicine, etc. The reason lies in its advantages, such as:
- high-precision cutting of metals;
- laser cutting equipment works to create curved structures of all degrees of complexity, as well as volumetric parts and shaped products;
- the surface of the workpiece does not heat up during operation;
- a high quality cut is formed;
- there is no deformation of the material during work;
- there is no mechanical impact on the workpiece;
- a non-contact working method is used;
- the technology copes with the creation of even fragile and complex parts;
- work is carried out without creating dust;
- the technology has proven itself to be excellent when working with any metals, including those with a high level of thermal conductivity, and their alloys;
- it is possible to perform work in automatic mode;
- the method is used for cutting not only metals, but also plastic and wood, cardboard, textiles and leather, and other materials;
- the products come out of high quality and do not require additional processing;
- the method is almost ideal for working with workpieces that are easily deformed during mechanical work;
- the heating zone of the product surface is minimal;
- there is no overheating of products during operation;
- production times are very short;
- The equipment is extremely easy to operate.
In addition to its advantages, the technology also has disadvantages. They are high cost compared to other types, uneven production speed and strict restrictions on the size of the workpiece being processed. Sheets with dimensions of no more than 15x30 m can be subjected to laser cutting. Another limitation is the thickness of the material - the workpiece should not be thick-walled. It is also necessary to take into account that the type of laser greatly affects the cutting efficiency and other parameters.
Evaporative laser cutting
Evaporation or sublimation cutting is one of the peaks in the development of laser technology. With classical laser cutting, the material being cut melts. But here, as the name implies, instantaneous evaporation occurs.
Naturally, the temperature must be very high. And for this you need a very powerful laser, into which a lot of electricity is pumped. In this case, cutting occurs not with a continuous beam, but in short pulses. How short? Often less than 0.000000001 seconds (nanoseconds).
At the same time, the efficiency is, of course, monstrously small. This energy would be used for iron and oxygen - and it would be possible to cut and cut. But the use of sublimation cutting can also be justified - of course, in delicate and innovative areas, when it is important to cut the material and not touch the substrate material.
Watch a video from our workshop:
Video - radius bending of metal on a press brake
The nuances of using laser cutting for some metals
- Aluminum.
The high thermal conductivity of aluminum and poor ability to absorb a laser beam due to the optical and thermophysical characteristics of the metal determine the features of its processing.
All this leads to difficulties in cutting metal. The equipment is computer controlled and easy to set up.
When working with aluminum, the laser beam power must be greater than for other materials.
However, the power indicators and speed of work are greatly influenced by the thickness of the metal, as well as the percentage of aluminum contained in the material being processed.
Let's look at how laser cutting of this metal works. It occurs on solid-state equipment of various operating modes and power, as well as on gas devices.
The latter are more powerful and can operate in pulsed or continuous mode.
And solid-state equipment, as a rule, operates in a point (pulse) mode.
The technological process has a number of features. Aluminum is cut better by a laser beam than conventional metal cutting equipment. The reason is that when working with a laser, the equipment does not touch the workpiece, unlike other equipment.
The laser beam is a focused beam of light with which cutting occurs. Precise focusing allows processing of aluminum at high speed. Gas is supplied to the work site and its influx is created. A jet of gas blows away pieces of molten metal from the cut site, preventing them from settling, and makes the surface even and smooth.
High-quality results can be achieved by working at a lower speed. Because it eliminates any deformations, both large and small.
To eliminate any roughness on the cut edges, even minor ones, nitrogen is used when operating the equipment.
The equipment is equipped with software that makes it possible to carry out ultra-precise, high-quality work. In addition, the workpiece does not need to be secured before starting work, since there is no physical contact between the equipment and the product. The part lies on the surface without moving.
Automatic equipment works as follows: a drawing is entered into the computer, the required parameters are set, and then the cutting is completed.
- Brass.
Brass is an alloy of red copper and zinc. The fragility and hardness of the alloy are determined by the percentage of zinc in it - the more of this metal, the higher these indicators. However, an increase in the amount of zinc makes brass unsuitable for technical purposes, since it is practically impossible to cut. It has been established that zinc in brass can be no more than 42%.
Brass has a high melting point because it is a two-component alloy, that is, it consists of zinc and copper. The temperature required to melt brass typically ranges from +880 °C to +950 °C. In addition, brass has significant thermal conductivity, resistance to laser radiation and increased hardness.
The setting of an industrial laser machine depends on the thickness of the processed brass workpiece:
- for brass with a thickness of less than 5 mm, pulse mode is used;
- if the workpiece has a thickness from 5 to 12 mm, then the plasma cutting mode is used.
The pulse mode heats the surface in short intervals (pulses), rather than constantly. This reduces the heating area, resulting in a minimized cutting width and higher quality edges. When cutting brass, which is highly reflective, the equipment operates in pulse mode, delivering a low laser beam power at a threshold intensity.
The melt (plasma) mode allows you to apply heat evenly to the cut area. The laser beam heats the metal using an inert gas. The plasma that is formed during operation maintains the temperature throughout the entire thickness of the workpiece.
If the end of the product has roughness or porosity, this can be removed from the underside of the product. A copper sheet absorbs radiation very poorly. And cutting equipment operates at low speed. In addition to the precise selection of the operating mode, it is necessary to correctly fulfill the conditions for laser cutting of metal sheets of various thicknesses. They differ for aluminum, steel, copper, as well as its alloys with tin, that is, bronze, and with zinc, that is, brass.
High-quality results are obtained when using fiber units or Nd:YAG lasers with a wavelength of 1.06 microns. CO2 lasers are not suitable for cutting brass, since its surface completely reflects them.
How does a metal cutter work?
Let's look at the main components of the machine to understand how it works.
For each point we will release a separate video in which we will analyze everything in detail, but for now briefly (what a laser machine consists of):
- Fiber ytterbium emitter - here the laser beam itself is generated and fed through an optical fiber to the laser head. 90% of companies, including ours, install IPG and Raycus emitters on their machines, which have their own advantages: Raycus has a relatively low price, and IPG has an advantage in terms of cutting non-ferrous materials. (Comparison of fiber emitters from different manufacturers in this article).
- The laser head receives and focuses the laser beam. On our machines we mainly use the RayTools laser head. Sometimes, at the client's request, we install a WSX head. We will talk about the settings, advantages, disadvantages and some customer misconceptions in a separate article. You can buy a laser head with a manufacturer's warranty here.
- We call kinematics all machine components that are responsible for moving the laser head - these are motors, racks and guides. After using and testing various servo motors for a long time, we chose Mitsubishi because they are compact, have less vibration, are reliable and can be easily replaced in case of breakdown. Although it is rare for a servo motor to fail, in such a case under warranty we will replace it within 3-4 days depending on your location. Hiwin guides are a brand that has proven itself all over the world and are also always and everywhere available. The Lean B2 helical rack is specially designed for heavy loads.
- The control system and software determine how convenient it will be for you to work with the machine and what its performance parameters will be. We can also supply software at the client’s request, but as a rule, CYPONE or CYPCUT is used on our machines. These programs support the most common vector drawing formats ADOBE ILLUSTRATOR and DXF, which is more than enough for any production.
- The frame of the machine largely determines what other components can be installed on the machine. For example, if the maximum cutting speed is no more than 20 m/min, and the idle movements are no more than 50, there is no point in overpaying and buying a frame with a thickness of 15-20 mm, or even more so buying cast iron, which is generally impractical today. We will also talk about this in more detail, maybe even argue with someone, in one of the following articles.
- There is also a chiller - this is a mandatory cooling system that comes with the kit. The chiller for metal cutters has two circuits: for cooling the emitter and the laser head.
- Smoke removal system or ventilation. There are different types: the first - when smoke is removed from the entire area of the machine at the same time, the second is used on more expensive machines - they use pneumatic dampers, thanks to which the exhaust operates only in the place where the laser head is currently located.
- Another important element of a metal laser machine is the electrics. Wattsan machines use proprietary Schneider electric electrics.
Laser cutting quality parameters
Indicators of the quality of metal cutting are roughness, width of the cut, depth of temperature exposure, non-perpendicularity of the edges, accuracy of parts, burrs on the edges. They are influenced by the thickness and type of metal being processed, cutting speed, auxiliary gas, and laser radiation parameters. For a certain material thickness, the processing speed is selected, which should approach the maximum, but maintain the best cutting quality indicators.
The cutting quality deteriorates significantly with increasing diameter of the focused radiation, and, as a result, the thickness of the melt of the rake surface increases.
Criteria for choosing a metal laser machine
What affects the performance of a laser machine? What is the most important thing when choosing?
To simplify, the cutting speed and thickness of the material that you can cut depend on the laser emitter and head, and the machine frame, its motors, racks, guides and software affect the speed characteristics, accuracy and durability.
Metal thickness for cutting
Obviously, the thicker the material you are going to cut, the more powerful the emitter should be. And the higher the speed of the machine, the stiffer the body must be to avoid vibrations, as well as the more powerful and reliable the engines and other indicators.
We will make a separate detailed article about each component on our website, so don’t forget to subscribe.
What tasks
We recommend that all our clients, when choosing a machine and its characteristics, be guided by the principle of sufficiency, which we ourselves use in the design of our machines together with our Chinese colleagues from the Wattsan plant.
Select all machine parameters in accordance with the tasks that your production needs to solve.
Service and technical support
A metal laser machine brings great profits to any production where it is installed. It can process more than 700 tons of metal per year. Therefore, the continuity of its operation is VERY important for production. Usually it is bought on lease and the money for its purchase needs to be repaid as quickly as possible, and here reliability and continuity of operation are more important than ever, otherwise how will you pay for leasing if your machine has been under repair for half a month, and you also have to maintain a staff and other costs .
Many companies can sell metal cutters (bring them from China), but not everyone has the same experience and knowledge as our managers and service employees. Perhaps this article contained many terms that were unclear to you, do not be alarmed, we will clearly tell you about all the nuances and teach you how to operate the machine correctly.
Look at the machine bed. Its service life also depends on them.
Cast or made from thick steel channel beds will last a long time.
Pay attention to the way the carriage moves. Always choose servo motors over manual stepper motors - they are more expensive, but they do not get stuck when moving.
Do not skimp on the smoke removal and gas purification system, otherwise during intensive work you risk getting poisoned.
How can you improve the quality of laser cutting?
1. It is necessary to clean the lens or protective glass in accordance with all rules.
Each type of laser has its own cleaning procedure. When working with a disk or fiber laser, technicians should clean the glass that protects the cutting head lenses.
Operators working with carbon dioxide lasers need to clean the lenses. Industrial professionals prefer Topol polish from TRUMPF when cleaning lasers. However, a large number of specialists do not even know how to work with it. It happens that the lenses are seriously scratched. And instead of regular polishing, workers buy a new lens. But frequent replacement is very expensive.
How to work with lens polish correctly? Do not press too hard on the lens as scratches may occur. But at the same time, polishing must be carried out under pressure sufficient to remove dirt. The most important thing is to teach balance.
You need to work in a circular motion, applying polish in moderation.
To properly polish a lens, a specialist must know and see all its imperfections. It is recommended to supplement the carbon dioxide laser equipment with an expensive polarizer, the cost of which amounts to hundreds of dollars. Despite the high price of the device, its operation will more than pay for the investment, and very quickly.
The laser technician needs to place the lens on a device that illuminates it with bright light from below. Most of all, the device's operation resembles a school projector. When you turn the lens of the device, it polarizes the laser lens placed at the top. This way you can see all its flaws: scratches, internal cracks, etc.
2. It is necessary to check the focusing (centering) of the nozzle.
To check, a specialist must break through the tensioned tape. For a second, he directs a low-power laser beam at it, after which he examines the hole and its location.
The worker shines a light on the tape, trying to understand how exactly the hole is located in the center. Its shift should not exceed 1 mm. How can you accurately determine that the hole is in the center of the nozzle? To do this, use a 10x magnifying glass equipped with a backlight.
Accurate centering of the nozzle allows you to increase the speed by 20–80% of the initial speed if the other settings are correct.
3. Focus should be checked regularly.
Most modern equipment allows automatic focus testing. And on older machine models, manufacturers recommended doing tests in various ways. Some machines use a "light test".
An example would be the old Mazak machine. During the testing process, the specialist turns on the laser beam at low power, then turns the knob to look for absolute focus. He watches the light of the beam turn blue as the handle rotates in a circle. Then he writes down the number. Returns the cutting head to its original place and repeats the procedure three times. As a result, the specialist calculates the arithmetic mean of the obtained numbers, which is loaded into the controller.
The worker is required to find the thinnest strip on the test sample, and then make sure that for this strip the controller focus is 0. If the thinnest strip corresponds to the number 3, the specialist moves the focus point by 3 mm and returns to the test again. The operation is carried out until the thinnest strip corresponds to zero.
When working with a laser, it is necessary to study factors such as gas consumption or the use of additional optical protection in carbon dioxide systems. However, the principles we have discussed are just a starting point from which you can begin setting up the necessary cutting conditions. In the future, specialists will understand that there are many circumstances affecting the operation of the laser: from the material being processed to the location of the enterprise.
Training on how to use a metal laser machine
Our training lasts three days, during which time you will learn everything you need about the structure of the machine and its maintenance, we will teach you how to select settings for different types of materials of different thicknesses and show you how to work with cutting modes that simplify your work and help save time and materials .
We have successful experience working with various industries and therefore can teach you a lot, share our experience and give you unique advice on how to optimally set up your production process.
We have successful experience working with various industries and therefore can teach you a lot, share our experience and give you unique advice on how to optimally set up your production process.
If you have questions, ask them directly to our managers in the chat and we will definitely answer you. Also, do not forget to subscribe to our channel, because this is only the first article about solid-state machines; we are preparing a whole series for you that will fully cover this topic.
In the next article we will talk about the machine frame and tell you how to choose a machine with a good frame.
Nuances of laser cutting of metal in industrial conditions
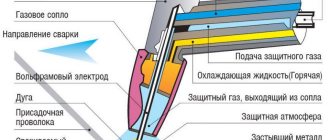
For cutting and engraving metal, enterprises use solid-state and gas lasers (liquid lasers are not suitable for this purpose). Compared to a gas laser, a solid-state laser is simpler in design, has higher efficiency and is more economical to operate. However, its power usually ranges from 1 to 6 kW - significantly less than that of a gas laser. A solid-state laser system can operate in continuous or pulsed mode, the latter makes it possible to increase power.
The working fluid (active medium) of a solid-state laser is a rod made of a crystal or glass with special “laser” properties. The most commonly used crystals are neodymium yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG), neodymium glass or rubies. By the way, the very first laser in history was ruby.
Under the influence of a pumping system (usually special lamps with radiation suitable for the spectrum), the rod emits photons. Light energy is amplified and focused thanks to an optical resonator - a system of mirrors and lenses. Their position can be changed to fine-tune the laser. Control of the light flux, adjustment of its parameters, as well as concentration of the beam at the desired point in accordance with the contours of the workpiece occurs automatically, and the computer is responsible for this.
What equipment is used today for laser cutting of sheet metal?
With the advent of laser cutting machines, the production of metal structures has become much cheaper and faster. Laser cutting ensures the highest accuracy and speed of work. This technology is optimal for processing metal sheets of small and medium thickness. It is used in the metallurgical industry and in almost any machine-building industry.
In Russia there are laser machines manufactured by Mitsubishi, Durmazlar, Trumpf, TST LASER, Mazak, FINN-POWER, Knuth, Halk, Mattex.
The most popular equipment is:
- Laser machines ARAMIS.
- Laser equipment from Durmazlar.
- Installation 2D/3D CO2 Space GEAR MarkII manufactured by MAZAK.
- CNC machines for welding and laser cutting of sheet metal Laserdyne manufactured by PRIMA NORS.
The cost of laser cutting equipment averages 350,000 rubles.
A laser beam is a concentrated stream of high-energy light particles. It hardly dissipates and creates a tiny spot of light on the surface of the material being cut, the size of which is usually several microns. At this point, the metal instantly melts, boils and evaporates, while the rest of the surface is not heated. These features make it possible to achieve an extremely narrow cut, while the dimensions and shape of the part are maintained with an accuracy of tenths of a millimeter.
Principles of laser technology for cutting sheet metal
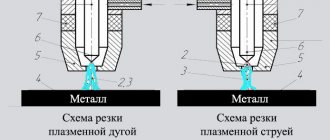
The most accurate cutting of sheet metal is provided by plasma and laser cutting - two technologies associated with thermal (thermochemical) effects on the material.
These methods are based on the rapid and intense heating of a metal sheet at a targeted point using a laser beam or plasma jet. Local melting and evaporation of the metal occurs. When the cutter moves along the contour of the future part, the heating zone also moves. The result is a neatly cut piece. The laser is also capable of making holes of a given shape and size.
VT-metall offers services:
What is the operating principle of laser systems? The energy of the source (the flash of a special lamp, an electrical discharge or a chemical reaction) is converted into light energy and amplified many times over. The growth is facilitated by an optical resonator - a system of two or more special mirrors. The process occurs in the so-called active medium, which can be a gas, liquid or solid. A narrow beam of concentrated high-power energy is formed, which burns the material at a given point. Solid-state (including fiber optic) and gas laser machines are used for metal cutting.
Laser cutting of sheet metal occurs with minimal error due to very precise focusing of the beam - all its energy can be concentrated at a point with a diameter of 1 micron. Software control ensures that the cut parts perfectly match the drawing. Moreover, it is possible to cut blanks of any, even the most complex shape. A distinctive feature of this technology is the high speed of the process with excellent product quality.
Advantages and disadvantages
Laser cutting of metal has a number of advantages:
- There is no mechanical contact with the surface of the processed material. This makes it possible to process even fragile materials, as well as those that are easily deformed.
- Suitable for cutting materials with different thicknesses.
- The process happens quickly.
- Parts with any configuration can be manufactured.
- There is minimal waste and the edges are clean and neat.
- The operating accuracy reaches 0.1 mm.
- Sheet material is consumed economically due to the dense distribution of parts on the sheet.
REFERENCE! The main disadvantages of laser cutting are expensive equipment and high energy consumption.
Laser is one of the modern methods of processing materials. There are several options that are selected according to several criteria. The most important selection criterion is the material being processed and its properties.
- November 30, 2020
- 693
What are the advantages of laser engraving and cutting?
This technology is especially useful for forming parts directly from sheet metal or applying markings and logos to parts or finished goods. The process is very fast and quite reliable. This is especially effective where production time is of the essence. This technology significantly speeds up the production process.
Laser engraving can work on a wide range of materials, from wood to cardboard and plastic, where traditional methods may not be effective. In this way, laser engraving can complement your production with new materials and give you new design freedom.
Laser cutting produces highly precise cut parts suitable for anything from bottle openers to circuit boards. It is both faster and more efficient than manual manufacturing methods.
The best laser engravers and cutters
OMTech 40W Laser Engraver and Cutter
- CO2 laser type
- Working area 300 x 200 mm
- Laser power 40 W
- Price $389
OMTech is a Chinese manufacturer of laser engravers and cutters. OMTech imports equipment to the USA, where it carries out enhanced quality control.
This 40W laser engraver and cutter is a compact machine with a cutting area of 300 x 200mm, 4500dpi resolution and a maximum cutting speed of 80mm/s. In fact, this is a great model for beginners, it costs less than $400 and offers excellent value for money. Some components can be upgraded, such as an exhaust fan, a water pump, or even a laser.
Depending on the material, this laser should cut to a depth of 2–3 mm, leather and wood, as well as rubber, and engrave metal.
Laser engraver cutter Flux Beamo 30 W
- CO2 laser type
- Working area 300 x 210 mm
- Laser power 30 W
- Market price $1499
The Beamo 30W is Flux's entry-level laser engraving and cutting machine that hits the sweet spot between affordability, ease of use, looks and functionality.
There are some disadvantages. Etching and shading could be better, the app didn't always work, and the camera preview mode doesn't capture the entire work area.
OMTech 80W Laser Engraver and Cutter
- CO2 laser type
- Working area 710 x 500 mm
- Laser power 80 W
- Price: $2,799
This OMTech 80 W is a powerful semi-industrial laser cutter capable of handling a wide variety of cutting jobs. It offers a working area of 500 x 710 mm and can work with a variety of materials such as wood, leather, rubber and plexiglass. This particular model can handle long jobs that extend beyond the cutting area.
Overall, this company offers high-quality equipment suitable for small businesses and industries. The laser is also relatively easy to set up, but keep in mind that this is a large machine - 119 x 86 x 91cm - and you'll also need plenty of space for exhaust fans.
The CO2 laser is particularly powerful, but OMTech offers an even more powerful unit with a power rating of 100W.
Full Spectrum Muse Core Laser Cutter
- CO2 laser type
- Working area 508 x 305 mm
- Laser power 40 W
- Price $3500
The Muse Core from Full Spectrum Laser is a 40W (45W optional) CO2 laser cutting machine with a 508 x 305mm workspace and several useful features.
At around $3,500, the Muse Core isn't the cheapest cutter on this list, but it is slightly cheaper than the Glowforge (its main competitor) and also has a slightly larger build area. Full Spectrum Laser also has some pedigree: the Las Vegas-based firm is a well-known manufacturer of much more sophisticated industrial cutters.
Particularly for manufacturers and small businesses, Muse Core can be a worthy alternative to the likes of Glowforge. This cutter is not capable of cutting glass or metal, but wood, fabric, leather, paper, acrylic and rubber should not cause problems.
It also comes with browser-based software that doesn't require an internet connection to operate, an optional rotary tool for cylindrical work, and support. Additional attachments and accessories are also available for those looking for something more suited to their needs.
Glowforge Plus Laser Cutter
- CO2 laser type
- Working area 500 x 280 mm
- Laser power 40 W
- Price: $3,995
Equipped with a 40W CO2 laser tube that delivers high cutting power and precision down to 0.025mm, the Glowforge Plus is a cross between the much-loved Glowforge Basic and Glowforge Pro. Optimized for home and office use, this device is equipped with packaging features such as water cooling, a HEPA filter and an air compressor to blow stray particles out of the laser and prevent fires.
It is compatible with a wide range of materials including leather, wood, acrylic, glass, fabric, cardboard and can cut up to 12mm deep depending on the material. This laser cutting machine is often used by small businesses looking for a versatile and reliable laser cutting machine.
Let's talk in detail?
But these are all, in essence, general words. “More expensive”, “cheaper”. For different orders in different areas, these words mean very different things. We have understood the general principles - now let's talk specifically. You are probably interested in cutting some order. Since you are studying information about laser cutting.
So let us calculate its cost and timing for you. So that you can compare with others or estimate your plans. With concrete numbers, this will be serious planning. And the calculation does not oblige you to anything. Send us your contact phone number so that our specialist will call you back, listen and calculate everything necessary.
Quick cost calculation