04/30/2021 Author: VT-METALL
Issues discussed in the material:
- What are the basic principles of argon welding
- On what equipment is argon welding possible?
- What are the features of argon welding of aluminum and copper
Argon arc welding differs from all other types in that this process uses an electric arc with argon as a protective medium. Inert gas is supplied first to protect the metals from contact with oxygen during processing. From this article you will learn the basic principle of argon welding, as well as in what cases it is used.
What is argon arc welding
Often there is a need to weld plastic materials that do not join with conventional types of welding. For example, copper, aluminum, titanium, etc. To create a durable and permanent structure from these metals, argon welding can be used.
Argon arc welding takes place in an inert gas environment - argon. That is why this welding process is called so.
The use of a gas such as argon in the process of joining parts is due to the need to protect against oxidation due to contact with oxygen. Argon is 38% heavier and denser than air; it covers the welding zone and does not allow oxygen into the area with mating surfaces.
When exposed to oxygen, the quality of welds is seriously affected, and aluminum can ignite. This is why argon is used.
In addition to argon, arc welding uses other gases that create an insulating environment. These are helium, active nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide.
Preliminary work before welding begins
Immediately before starting the welding process, the following steps must be performed:
- Clean the surface on which welding will take place until it shines with an abrasive material.
- Remove chamfers if the wall thickness of the workpieces being welded is more than 4 mm
- Degrease the surface with alcohol, acetone, gasoline or solvent
- Remove moisture by heating the edges with a burner to 100⁰C
- To eliminate internal stress, the metal is heated to 200⁰ before welding.
GOST standards
When using this method, the following legal regulations and standards must be taken into account:
- GOST 5.917-71. Manual torches for argon arc welding;
- GOST 14771-76. Gas shielded arc welding. Welded connections;
- GOST 18130-79. Semi-automatic machines for consumable electrode arc welding;
- GOST 14806-80. Arc welding of aluminum and aluminum alloys in inert gases. Welded connections. Main types, structural elements and dimensions;
- GOST 2246-70. Steel welding wire. THAT;
- GOST 23949-80. Tungsten welding electrodes, non-consumable;
- GOST 10157-79. Argon gaseous and liquid. THAT;
- GOST 7871-75. Welding wire made of aluminum and aluminum alloys;
- GOST 13821-77. Single-station rectifiers with falling external characteristics for arc welding.
Preparing products for welding work
Consists of preparation of parts and filler material. Preparatory operations for products:
- editing;
- marking;
- cutting;
- edge processing;
- assembly.
Preparatory operations may vary depending on the type of metal and the purpose of the structure. Low carbon and alloy steels are treated before the process as follows:
- the ends of sheets and pipes are cut off;
- joints are sanded by hand or by machine;
- the edges are cleaned of dirt, rust and oil;
- degrease with acetone or alcohol.
Nickel: the welding area is polished to a shine and degreased.
Aluminum and alloys:
- are being bullied;
- washed;
- lighten;
- dried.
Copper and titanium are cleaned and degreased.
Types of argon welding
There are several types of argon welding. It can be carried out in the following ways:
- Manual.
- Semi-automatic.
- Automatic.
The classification, in addition to the degree of automation of the process, is based on the types of electrodes used.
Electrodes are either consumable or non-consumable. An example of the latter electrode is refractory tungsten wire, which allows for reliable connection of parts, even if they are of dissimilar materials in type. Graphite is used less frequently.
Electrodes are produced in different diameters and materials for different metals being welded.
Thus, there are such types of argon welding as:
- Manual - using a non-consumable electrode (this type is labeled as RAD).
- Automatic - using non-consumable electrodes (marked as AMA).
- Automatic - using consumable electrodes (marking - AADP).
The two most common welding methods today are AMA and RAD.
The use of consumable electrodes is only possible in automatic mode. For this purpose, special installations and devices are used, which are welded with a special torch equipped with an electric motor that transfers the wire from the spool. The consumable electrode is simultaneously used for ignition and acts as soldering material. During the ignition process, the conductor melts and provides mass for the seam.
Argon arc welding diagram
Automatic argon arc welding is mainly used only at various industrial enterprises (in particular, for the production of metal structures, for welding copper busbars in stationary and installation conditions), which is associated with the high cost of automatic installations and the complexity of their setup. It is much easier to weld several parts manually, but if high productivity is required, then you cannot do without equipment.
Torch for argon arc welding with consumable electrode
If the torch is equipped with a consumable electrode, the arc is fed between the end of the welding wire and the product itself.
Advantages of this type:
- narrow thermal impact zone;
- the ability to influence the quality characteristics of the weld by adjusting the composition of the gas and wire;
- wide possibilities for process automation, which significantly increases the productivity of welding work.
Used for welding stainless steels and aluminum.
Types of equipment
For argon arc welding, 4 types of equipment can be used:
- Manual welding requires the welder to hold the torch and filler wire with his own hands.
- Mechanized version , in which the welder holds the torch and the wire is fed mechanically.
- Automatic argon arc welding - with this method of implementing the process, a welder is not needed, he is replaced by an operator who monitors the process, because the supply of the torch and filler wire is carried out automatically.
- Robotic welding process - in this case, neither a welder nor an operator is needed, the entire procedure is carried out within the framework of a program that is fully responsible for the production process.
Inverter welding machines
The most popular welding device for argon welding, which can be successfully used not only in production, but also in everyday life, is an inverter machine. For those who want to learn how to weld with argon, using a welding inverter is the best option, since even a novice welder who does not have extensive professional skills can understand the principle of its operation by studying “Argon arc welding, instructions.”
An inverter argon arc welding machine has a number of significant advantages:
- High quality characteristics of the weld seam, which allows this equipment to be used for car repairs: welding assemblies and body parts, gearboxes, and engines.
- Small dimensions and light weight compared to transformer devices.
- Easy to use. To start work, you need to lay the filler wire and turn on the device. The wire and inert gas supply are switched on automatically.
As a rule, such modern devices are equipped with a number of additional options and protective devices, such as accelerated ignition, arc stabilization, and welding current modulation.
In total, more than 60 types of metal welding are known. If you need to cut metal quickly and efficiently, use gas cutting for this. Read more in this article.
If you are a beginner jeweler, then the article on https://elsvarkin.ru/materialy/cvarka-cvetnyx-metallov-texnologiya-svarki-medi/ link will be useful to you.
Technology
Let's consider the technology of argon welding based on manual welding with a non-consumable electrode.
Necessary equipment
Welding equipment includes:
- Welding machine of any type for arc welding with a voltage of 60-70 volts.
- Power contactor , which supplies voltage from the welding material to the torch.
- An oscillator is a device that converts a mains voltage of 220 volts and an oscillation frequency of 50 Hz into a voltage of 2000-6000 volts. The specified current parameters make it easy to form an arc.
- Ceramic burner.
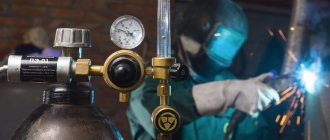
- Device for blowing the welded area with argon.
- Argon cylinder.
- Electrode and filler wire.
Approximate cost of welding machines on Yandex.market
Additional options may include a time regulator for argon blowing, hoses and fittings, etc.
If you want to calculate the economic efficiency of gas-shielded arc welding, then, in addition to the cost of the welding machine itself, you need to take into account the price of consumables: filler rods, wire, argon in cylinders, hoses of different sizes, etc.
Filler wire is made from various materials: aluminum, cast iron, stainless steel, copper, etc.
Approximate cost of welding wire on Yandex.market
Argon is supplied from special cylinders with a standard operating pressure of 150 AM. Cylinders come in different sizes: 5, 10, 20, 40 liters, etc. It is gas that is the main and most expensive consumable for this welding.
Approximate cost of argon cylinders of different volumes on Yandex.market
Hoses, fittings and other work parts wear out frequently and must be replaced periodically.
We also must not forget that personal protective equipment is needed to carry out the work: gloves, mask, overalls.
Execution steps
When performing manual argon arc welding, you must adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- Set welding mode.
- Clean metals to be joined.
- Turn on the button on the torch handle to supply shielding gas to the welded area (take the torch in your right hand). This should be done approximately 20 seconds before welding begins. The filler wire should be in your left hand.
- The burner is lowered so that there is a distance of up to 2 mm between the electrode and the surfaces . The electrode from the burner must be inserted into the burner so that a rod no longer than 5 mm remains on the surface.
- Turn on the welding machine and transfer voltage to the electrode . An arc appears between it and the metal, and argon is supplied from the torch to the welding zone. The filler wire melts under the action of an electric arc and covers the gap.
- Move slowly along the seam.
It is advisable not to ignite the electrode by contact with the metals being welded, as in conventional welding; an oscillator is used for this (it supplies high-voltage pulses to ignite the arc). Without it, the tungsten electrode becomes dirty.
What affects the quality and size of the weld
For proper welding, four basic principles must be observed:
- Correct settings : to hold the desired arc, you need to adjust the supply of gas, current, rod, etc.
- The skill of the welder , which guarantees the continuous creation of a high-quality seam.
- A properly organized workplace . In this case, it is important to have a heat-resistant table, the ability to fix the part, good ventilation, etc.
- Correctly setting up equipment for work.
Knowing certain rules when welding with argon allows you to achieve high quality welds:
- To create a narrow and deep seam, you should adhere only to the longitudinal movement of the electrode and the torch . Any lateral movements and deviations will reduce the quality of the connection. Therefore, during the welding process, the welder needs to be careful and attentive.
- The longer the welding arc, the wider the seam and the shallower its depth . Ultimately, this reduces the quality of the connection. Therefore, during the process it is recommended to keep the non-consumable electrode as close to the joint as possible.
- The filler wire must be fed as evenly and smoothly as possible ; abrupt feeding is unacceptable.
- It is better to supply gas from the opposite side of the welding track . This, of course, will increase its consumption, but will significantly increase the quality.
- The filler wire together with the electrode must be in the welding zone , covered with argon, to prevent nitrogen and oxygen from entering there.
- The wire is fed in front of the torch with the electrode at an angle , which ensures the evenness of the seam and its small width.
- It is important to achieve good penetration values . In argon arc welding, it is determined by visual inspection of the seam: if it is round and convex, then this is evidence of insufficient surface penetration.
- Welding under argon should not start and end abruptly, otherwise the access of oxygen and nitrogen to the welded zone will be open . It is recommended to start welding 15-20 seconds after supplying inert gas, and finish 7-10 seconds before turning off the burner. This is required so that the material has time to crystallize in an argon environment without exposure to oxygen.
- Before welding large products, you need to make test seams on small workpieces or in an unimportant area.
Before starting work, metal products must be cleaned and degreased.
To reduce the financial costs of welding, you can use not only pure argon, but also its mixture with other gases.
Selection of equipment for semi-automatic argon welding
Semi-automatic welding in argon is carried out using three types of equipment:
- Specialized, designed for processing workpieces of one type.
- Special – installed in industrial production and used for workpieces of the same standard size.
- Universal, which can be used for all types of work with argon, including processing stainless steel.
Semi-automatic argon arc welding can be carried out using both inverter and transformer devices. The former are more reliable, as they are more resistant to stress. True, such devices are characterized by relatively low efficiency. But because of them, there is not much interference in the operation of other electrical equipment.
Another advantage of a welding inverter compared to a transformer device lies in its low weight. It can be accurately and adequately adjusted and helps stabilize the welding current. But you need to be prepared for the fact that such devices are very sensitive to condensation - careful handling of the equipment will help you avoid unnecessary problems.
Devices for semi-automatic argon welding are divided into types according to the following principle:
- household appliances that require the use of current up to 200 A, because large amounts are not required for repairs at home;
- semi-professional class with a current of 200–300 A, which copes with systematic simple repair work;
- equipment for specialists with a current of 300 A - used for long hours of daily work, suitable even for very difficult conditions.
Also for semi-automatic argon welding you need:
- Special torch with tungsten consumable.
- An oscillator that is separately connected to a power source. It allows you to ignite an arc when working with a non-consumable tungsten consumable by supplying high-frequency pulses, resulting in ionization of the arc gap. A typical network is characterized by a frequency of 55 Hz and a voltage of 220 V - through the use of an oscillator, these figures increase to 500 kHz and 6,000 V.
- Contactor required to supply voltage to the burner.
- Relay is an element responsible for turning on and off the contactor and oscillator.
- Tungsten base electrodes with wire of the appropriate diameter.
- Argon cylinder with reducer.
- Rectifier - provides direct current with a voltage of 24 V.
- Ammeter - for measuring current strength.
- Timer – allows you to control the time of argon blowing.
- Electrogas valve for supplying 24 V DC or 220 V AC.
- Filter for monitoring high-voltage pulses from the oscillator.
- Battery for serial connection into an electrical circuit to stabilize alternating current.
In cases where semi-automatic argon welding of metals with thicker edges is carried out or it is necessary to increase productivity, the following can be used:
- Special torch for parallel use of several tungsten electrodes. This technology allows you to improve the quality and strength of the seam laid at high speed.
- Device for heating filler wire.
- A pulsating current during pauses in its flow, due to which crystallization of the metal occurs. If the movement of the arc is synchronized with the current pulses, melting will be effective regardless of the position in space.
Also, when semi-automatic argon welding, one must not forget about safety: the welder must work in special clothing and use personal and collective protective equipment. The latter include ventilation, grounding system, fences, mask/shield, gloves, shoes. It is prohibited to weld products if there are fuels and lubricants on their surface. If all the rules are followed, through the use of a semi-automatic machine in an argon environment, it is possible to perform welding work at a truly high level.
Modes
Welding under argon will be of the highest quality if the optimal mode is correctly selected. The choice of mode is based on the following components:
- properties of welded metals . They determine the choice of current supply direction and polarity. For example, for welding steel structures, direct current of direct polarity is used, for welding aluminum and beryllium - direct current with reverse polarity;
- current strength . It is selected based on the diameter of the electrode that the welder uses; based on the type of metal to be welded, the thickness of the metals and the polarity. For example, for welding titanium, the operating mode is determined by the following parameters, from which it follows that the thicker the metal being joined, the larger the diameter of the tungsten electrodes should be:
| Material thickness | Electrode diameter, mm | Current strength, A |
| from 0.3 to 0.7 | 1,6 | 40 |
| from 0.8 to 1.2 | 1,6 | from 60 to 80 |
| from 1.5 to 2.0 | 2 | from 80 to 120 |
| from 2.5 to 3.5 | 3 | from 150 to 200 |
- welding arc length . The tension depends on it (as noted, the length of the arc directly affects the quality of the seam);
- gas consumption depends on the strength and uniformity of its supply by the burner . Experts recommend avoiding pulsations.
Welding copper using the argon welding principle
Copper differs from other metals in that it is highly resistant to rust and is resistant in aggressive environments. Therefore, for its welding, argon of the highest grade is required or in combination with helium (and there should be more argon). Consumable or non-consumable tungsten electrodes and direct current are used.
Preheating to +800 °C is used in cases where the thickness of the copper billet exceeds 4 mm. The filler wire can be made of copper or copper-nickel alloy. The arc in this case must have high stability.
Since copper has high thermal conductivity, the edges of the metal must be cut. If we are talking about a sheet up to 12 mm thick, only one-sided cutting can be done, while for thicker edges it is necessary to carry out double-sided cutting.
Advantages and disadvantages
Argon arc welding has its advantages and disadvantages. Its key advantages are:
- The process provides a low heating temperature . This preserves the shape and size of the workpieces.
- The inertness of argon provides high protection of the welded area.
- The welding process is extremely simple and easy to learn (although it is not possible to start welding without training).
- The process uses a high-power arc , which ensures fast welding.
- The technology allows you to connect different types of metals that cannot be bonded in other ways.
- Requires rare electrode replacement.
The high quality of weld seams obtained by argon arc welding allows the method to be used in industries in which there is a high need for high-quality metal welding. In particular, the method can be used and has found distribution in the aviation, nuclear, food industries, medicine, and mechanical engineering.
Additional advantages of automatic welding are efficiency in joining several parts , as well as the elimination of human error. To maintain such an installation, a minimum number of personnel is required.
The disadvantages of the process are the complex welding equipment, in which it is difficult to adjust the modes . This limits the use of the method by beginners: the welder requires experience and dexterity. When a high-ampere arc is needed during the joining process, the welder needs to consider additional cooling of the joints.
also necessary to provide good protection from wind and draft so as not to lose argon protection, which complicates the practical application of the method. Therefore, it is recommended to perform such work indoors. With the manual method, the limitation of the method is the low cost of performing the work.
Limitations in the use of an automatic installation are the inability to weld any non-standard seams, the high cost of equipment, limitations on setting parameters; if the machine malfunctions, the entire batch of products may become defective.
Another disadvantage of this method is the high cost of argon . In practice, welders sometimes replace it with helium and carbon dioxide, but such a replacement is not always possible: it all depends on the type of metal to be welded.
Content
- Is it possible to cook stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine and what is it?
- Advantages and disadvantages of semi-automatic welding
- Video about semi-automatic welding of stainless steel
- Features of welding stainless steel semi-automatically
- Use of Gas in Stainless Steel Welding
- Materials and equipment required for welding
- Welding wire selection
- Preliminary work before welding begins
- Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel with other types of metals
- Tables with semi-automatic welding settings
- Final work after welding
Welding safety
Almost all safety rules for welding in argon relate to preliminary preparation for the process. The likelihood of a hazardous situation occurring is minimal with proper preparation. Here are the basic principles for ensuring safety when welding using the argon method:
- The specialist has no right to carry out adjustment and repair procedures while the device is running..
- There must be at least 10 meters from the gas source to the fire source.
- During automatic welding, no manipulations are allowed . This can not only disrupt technology, but also harm health.
- Before starting work, you need to check the grounding of the welding machine, the reliability of the hose for supplying argon and water (if the torch is supposed to be cooled with water), check the seals on the pressure gauges, the threads on the union nuts, and the insulation of the holder handle.
- On automatic welding machines, a folding shield with a light filter is installed on the welder's side . Electrical wiring and tubes are contained in a common rubber hose. Burners must not have exposed live parts.
- The burner handles are covered with material and a shield that protects the welder’s hands from burns.
- During the welding process of some metals (in particular, copper and aluminum), toxic gases are released , so the room must be provided with good ventilation or an air supply.
- In exceptional situations, work should be carried out wearing a gas mask . In order to avoid burns from hot aluminum, molding spacers are used on horizontal seams, and movable curtains are used on vertical seams.
- Cleaning of aluminum additives in caustic soda solution should be carried out using rubber gloves and goggles for protection.
Thus, argon arc welding allows high-quality welding of special types of metals that cannot be joined by other methods. These are aluminum, copper and non-ferrous metals. With standard welding, it is not possible to obtain a high-quality and reliable seam for joining refractory workpieces. A special feature of welding is that it is carried out in a shielding gas environment. Argon provides reliable protection of the welding zone from the influence of external adverse factors.
Semi-automatic argon welding of cast iron
There is an opinion that argon is only suitable for working with non-ferrous metals, but this is not true, because quite often it is used for welding cast iron and steel.
Cast iron is an alloy based on iron and carbon. This metal is difficult to weld, as cracks and pores often appear at the seams. In addition, cast iron rapidly oxidizes. For this reason, its welding is usually carried out using flux-cored wire or argon, because the latter allows the formation of seams without slag. This is important, because welding cast iron is still relevant when repairing older cars.
To connect cast iron parts, tungsten-based wire is chosen. In most cases, general or local heating of the metal is used, although the cold method can also be used. The master can also choose between direct and alternating current, the strength of which depends on the thickness of the metal of the product and the diameter of the wire. You need to understand that normally there should be 50–90 A of current per 1 mm of wire. For such work, graphite, cast iron wire, as well as those made on the basis of copper, iron, and nickel are suitable.
Tables with semi-automatic welding settings
Butt bottom position
| Workpiece thickness, mm | Gap, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Welding current, and | Welding voltage, V |
| 0,8 | 0 | 0,8 | 50-80 | 16 |
| 1,2 | 0 | 0,8 | 70-80 | 17 |
| 2,0 | 0,5 | 0,8 | 70-80 | 17,5 |
| 3,0 | 1 | 0,8 | 80-90 | 18 |
| 4,0 | 1,5-2,5 | 0,8 | 100-110 | 20 |
| 5,0 | 2,5 | 1,0 | 135-145 | 21 |
| 6,0 | 2,5 | 1,0 | 140-150 | 22 |
Vertical spatial position
| Workpiece thickness, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Torch direction | Welding current, and | Welding voltage, V |
| 0,8 | 0,8 | down | 50-80 | 16 |
| 1,2 | 0,8 | down | 70-80 | 17 |
| 2,0 | 0,8 | down | 70-80 | 17,5 |
| 3,0 | 0,8 | up | 80-90 | 18 |
| 4,0 | 1,0 | up | 100-110 | 20 |
| 5,0 | 1,0 | up | 135-145 | 21 |
| 6,0 | 1,0 | up | 140-150 | 22 |
Corner connection lower position
| Workpiece thickness, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Welding current, and | Welding voltage, V |
| 0,8 | 0,8 | 60-70 | 15 |
| 1,2 | 0,8 | 70-80 | 16 |
| 2,0 | 0,8 | 80-90 | 17 |
| 3,0 | 0,8 | 90-100 | 19 |
| 4,0 | 1,0 | 130-140 | 22 |
| 5,0 | 1,0 | 155-165 | 24 |
| 6,0 | 1,0 | 175-180 | 26 |
Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel with other types of metals
Today's semi-automatic welding technologies make it possible to join stainless metal with aluminum, high and low alloy metals, as well as other alloys.
Distinctive features of semi-automatic welding of stainless steel with other metals:
- When welding ferrous metal with stainless steel, the yield strength of the metal decreases, protecting the surface from the effects of the environment
- when we weld St40 to stainless steel, we use 08G2S wire, which helps to avoid rupture of the seam at the junction of two types of metal after cooling
- to weld stainless steel with copper it is necessary to use low-melting solders and flux
- The pulse mode is used for welding stainless steel with aluminum and other metals, resulting in increased resistance to corrosion and improved quality of penetration.
- Argon is used for welding aluminum to stainless steel using the pulse mode. Copper cored wire is recommended.