Files are intended for manual and mechanical processing of parts and workpieces made of metal, plastic, wood and other materials. They are used for layer-by-layer filing and cleaning of surfaces, sharpening cutting edges, making grooves and performing other operations.
The main criterion for choosing a tool is the purpose, which determines the type, shape and types of file cuts. At the same time, the characteristics of materials, dimensions and other features of the parts being processed are taken into account.
Purpose of files
A file is a universal-purpose hand tool capable of cutting off a thin layer from the surface of the material being processed with one forward movement. It can be used to solve many different problems:
- Clean parts and workpieces from rust and other types of corrosion.
- Remove a layer of dirt or paint.
- Turn the part until the required size is obtained.
- Sharpen other tools used in everyday work.
- Clean electrical contacts in electrical equipment systems.
- Grind and polish the surface of metal and other materials.
Types of files
Modern schoolchildren, finding themselves in tool shops on excursions, often look with a grin at the tools used by toolmakers. There may be sophisticated machines nearby that can cut off thick layers of metal within a few seconds.
And mechanics process the part using hand tools with handles, moving them over the workpieces, achieving the desired size or type of part. Often, to clarify some features, the results of work are viewed through magnifying glasses.
However, sometimes the fine finishing of a product cannot be entrusted to a machine. Only with the help of a file or its younger brother, the needle file, can the required parameters be achieved. These tools are used to remove a layer of metal.
Most often, a strong steel strip has a notch on it. These are low teeth located in a certain sequence (a special notch is applied). A special standard (GOST 1465-80) approves the rules for the location of teeth and their shape.
For manufacturing, carbon steels (U9...U11) or special iron alloys with alloying elements are used. The files undergo heat treatment, as a result of which the surface hardness reaches up to 54...60 HRC (Rockwell hardness).
For ease of use, the end has a triangular or cylindrical shank. A handle is placed on the shank. It is made from different materials (wood, plexiglass, metal). Professionals prefer to use wooden handles made of birch or walnut.
Important! To prevent the handle from splitting when the shank is driven in, a metal ring is installed at the end.
Criterias of choice
In order not to make a mistake when choosing, you should follow simple recommendations for choosing files. We invite you to consider each aspect in more detail.
Purpose
Before purchasing such a tool, you should first decide what type of surfaces will be processed. The needle file is an excellent solution for working with small structures and small elements. Plumbing tools are preferred if you plan to work with different materials.
Working base shape
The working base for such devices comes in several types. There are the following types:
| Type | Review |
| Rhombic | The best solution if you plan to process sprockets and gears. |
| Semicircular or round | Used to increase the diameter of round holes. Also used for processing concave surfaces. |
| Triangular | Popular models are in demand among builders who often work with grooves and various holes. |
| Flat | A multifunctional device that is used to work with flat surfaces. |
| Square | A popular hand tool used in construction and repair for turning corners and working holes. |
Holder
The following materials are used to make the handle:
- Rubber. Devices with such handles are classified as professional tools. Their average price is appropriate. This product fits comfortably and securely in your hand. The material is not afraid of moisture and does not deteriorate over time.
- Plastic. According to buyers, a tool with a plastic handle is an excellent option for home use. The material belongs to the budget category. Plastic is not afraid of moisture, but over time the handle may crack. A similar thing is observed as a result of a strong blow. It's uncomfortable to hold in your hand.
- Tree. The most common material. Tools with wooden handles are in demand. The wear rate of such handles is colossal. The material quickly cracks and loses its appearance.
Grain
We are talking about the number of notches applied to the working surface. The indicator is measured on 1 cm of surface. The functional features of the tool in question depend on it. There are six grain classes. Indicated by numbers 0-5. The higher the value on the packaging, the fewer notches applied to the working surface. In addition to numbers, the product passport may also contain the following designations:
| Designation | Characteristic |
| Velvet (4-5) | Here about 24 notches will be applied, which will fit on 1 cm2 of the surface of the working element. Used for processing products made of delicate and soft materials. |
| Personal (2-3) | 13-24 notches will be placed on 1 cm2 of surface. Used for processing products made from hard materials. |
| Drachevaya (0-1) | On such a product there will be about 4-12 notches per 1 cm2 of surface. It is used for processing metal structures made of steel, cast iron, etc. |
Features of notches
The elements differ from each other not only in size, but also in direction
Before purchasing, you should pay attention to the fact that the larger the size of the applied notches, the faster the working surface is processed. This will not have the best effect on the quality of work.
Manipulation will lead to the formation of uneven surfaces, scratches and other damage. To avoid damage to products, preference should be given to designs with small notches.
Blade length
When choosing a product, you should focus on the dimensions of the working surface and the dimensions of the product itself. On the shelves you can find the following options:
- 15-18 mm. Used for processing small structures and workpieces.
- 20-30 mm. Used for working with large elements and workpieces.
Sputtering
The best manufacturers produce tools with and without diamond coating. We are talking about covering only the working element, and not the entire device. Diamond spraying is needed to work with very hard materials. They are characterized by a high service life and no risk of mechanical damage. Used for processing stone and metal structures.
Tool steels for making files
While studying the properties of steel, we noticed that at a certain carbon content it becomes possible to obtain high hardness using special heat treatment. The low carbon content does not allow hardening, which increases the strength properties of the metal.
Only at a concentration of 0.8% and above do the properties of the Fe-FeC₃ alloy change (the properties are studied in a special course in metal technology, called “Materials Science”). Annealed steel is quite ductile and can be processed on metal-cutting machines. There is a condition in which high plasticity is noted. It is called austenite. Achieved at a temperature of 727 ⁰C and above.
Only hypereutectoid steels can be quenched and tempered. If there are no other additives, then they are usually designated as U8...U13. The letter “U” characterizes carbon steel, and the number indicates the carbon content in hundredths of a percent.
Attention! To carry out hardening, it is necessary to heat the steel part to the austenite temperature and above. It can be easily identified using a magnet. When the desired value is reached, the magnetic properties completely disappear when heated.
Some people believe that heating to the appropriate temperature is enough. When heated, the thermal conductivity of the metal decreases sharply. Within one minute, parts weighing about 1 kg are heated to a depth of 0.10...0.13 mm.
Important! To harden the surface to a depth of 1.5...2.5 mm, you will need to hold it at the desired temperature for at least 15...20 minutes. Less deep hardening may result in the measuring cone on the Rockwell instrument falling through a thin layer of hardened metal. The result will be disappointing.
Hardening is carried out in water, air and mineral oil. A high cooling rate promotes deeper hardening of the metal. When making cutting tools, they are hardened in oil. Steel cooling occurs at a rate of 400…450 ⁰/sec.
After hardening, the parts acquire a certain fragility. Therefore, to relieve internal stresses, low tempering is performed. It occurs at a temperature of 180...250 ⁰С. The part is placed in muffle furnaces heated to a given temperature. Keep in them for at least 30...40 minutes. Then they allow it to cool slowly.
In practice, heat treatment of file metal occurs in the following sequence:
- The workpiece is heated to a temperature of 900…920 ⁰С (the higher value is explained by the fact that less time is required for internal heating of the metal).
- Maintain in a heated state for 15...20 minutes.
- It is hardened in mineral oil (it is allowed to use waste from internal combustion engines).
- Hardness testing is carried out, and with proper heating and cooling, hardened trostite (HRC 54...58) is obtained.
- The workpiece is placed in a muffle furnace at a temperature of 200…210 ⁰С.
- Leave for 30...40 minutes and take out.
- It cools down in air (temperature 18...22 ⁰С) on its own.
- The hardness is checked; for tempered trostite (the state of hardened and tempered metal), the hardness increases by 2...4 units.
To increase the strength and hardness of steels, alloying elements are added during welding. They make it possible to improve performance characteristics and obtain metal with desired properties.
Sharpening methods
The file can be returned to its working shape using chemical, mechanical, sandblasting and electrochemical methods. Each tool sharpening option requires a special approach and is used for specific purposes.
Chemical:
One of the simplest and most effective methods for sharpening a file. Etching in chemical solutions allows you to completely restore the working surface of an old, dull instrument covered with rust.
Before treating a file with a chemical liquid, its surface is prepared:
- All dirt is removed with a metal brush.
- If there is rust, the instrument is treated with a special solution.
- Then the cutting part of the tool is degreased. To do this, you can use any dishwashing detergent or washing powder.
- The file, cleaned of grease deposits, is washed under running water. After this, it must be dipped in acetone to wash away any remaining oil deposits.
After such procedures, the rod with the teeth of the file will become completely clean and prepared for the etching process. For restoration, a special solution is used, the component composition of which has the following ratio:
- 86% – water;
- 8% – nitric acid;
- 6% – sulfuric acid.
The file is dipped into this mixture for ten minutes. The chemical solution allows you to increase the height of the teeth on the cutting surface without changing the thickness of the tool.
After the specified time, a check is performed on the work area. A file that is not sharpened well enough can be re-etched. The restored instrument is washed with soda solution.
Electrochemical:
This method of sharpening a file also requires preliminary cleaning of its cutting surface from dirt and grease deposits. After this, the instrument is immersed in an acid mixture:
- 80% – water;
- 11% – sulfuric acid;
- 9% – nitric acid.
In this case, a low voltage direct current is passed through. Aluminum plates are used as cathodes, the area of which must correspond to or slightly exceed the surface area of the file - the anode.
READ Unusual Facts About the Bit
Mechanical:
This option for restoring a file involves replacing old notches with new teeth. The working part of the tool is pre-fired.
Heat treatment is performed in a special oven at a temperature of 760 – 820 degrees. After this, the old notch is removed on a milling machine and the surface is completely sanded.
New tooth cutting can be done manually using a chisel. Factories use special sawing equipment to produce the ribbed surface of the tool.
The final stage of mechanical restoration of a file is hardening. For this, a solution consisting of 50 liters of water, 2 kilograms of table salt and 1 liter of hydrochloric acid is used. After this, the tool is cleaned, washed in water with a small amount of lime to protect against corrosion and dried.
Sandblasting:
For this method of file restoration, fine-grained sand is used. It is directed towards the cutting part of the tool at a slight angle. Sharpening is carried out from the shank side. Sand is passed under a pressure of 5 kgf/cm. sq. through a nozzle measuring 5 to 7 centimeters.
Sandblasting restoration method
The speed of sandblasting depends on the degree of flooding of the teeth and the grade of steel from which the file is made. The sand is directed towards the tool at a right angle. Initially, the main notches are sharpened, and then the surface of the auxiliary teeth is restored.
File shapes
Types of files for metal have been developed over the past two hundred and fifty years. Dimensions and parameters were determined depending on the tasks that needed to be performed. Therefore, the shape of the teeth was also adjusted.
Initially, craftsmen were required to process cast iron, as well as products made of brass and bronze. The castings had a gating system and a burr. They were sawed off, and then the surface was polished. Files with different tooth sizes were used. For rough processing, a tool was used that was capable of removing up to 0.5...1.0 mm of a layer in one movement.
In the future, modern craftsmen have sets of hand-held cutting tools, which they use to bring parts to the required parameters. At manufacturing enterprises there is a category of workers (mechanics). One of the main tools is files.
general information
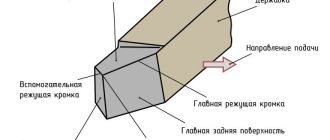
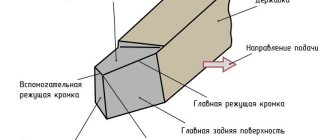
A file is usually called a product that contains two elements:
- Steel bar . Its surface is intended for notches applied in production using special templates. There are several types of notches, among which the most common are rectangular, triangular and round.
- Handle . It is secured to the tool with a clamping ring and is necessary to prevent cracks. It is fastened to a cone-shaped shank. With the help of a handle, which can be made of plastic or wood, more convenient conditions for working with a file are provided. In case of breakdown, replacing it will not be difficult. This element is most often made from beech, birch and pressed paper. The handle should be one and a half times longer than the shank.
Files may differ from each other in their sizes. So, on sale you can find instruments with a length of 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 cm. They can also differ in diameter, which can be 12, 16, 20, 23, 25 and 28 mm.
All files belong to the category of cutting tools. Their main purpose is to give the processed products certain sizes and shapes. The operation of the tool is based on the principle of layer-by-layer grinding of the surface .
Materials
These devices for grinding metal products are most often made of very hard, high-quality tool steel:
- Brands ШХ15 or 13Х. This is the designation for alloy chromium steel.
- U10A or U13A. Marking indicates the use of improved unalloyed steel.
During the manufacturing process, files must undergo a hardening procedure, which allows them to be provided with a hardness level of 54-58 HRC. Tools intended for processing metal products are made from steel of the indicated grades. If you need to grind wood and other materials, then use tools made of softer steel.
Classification by section shape
The form determined the name and purpose of the files, and the main classification was created on it. Depending on the profile of the surface being processed, the cross-section of the tool is selected. Manufacturers of files suggest using special hand tools with the following sections:
- Flat – files of this shape are suitable for processing flat and rounded (protruding) surfaces. This is the most common cross-section for such a tool.
- Square files are used for processing rectangular and square holes. They grind rectangular grooves on the surface.
- Round - they are used to process internal cavities and holes, remove sagging from welds and flash from castings. The desired configuration is achieved by finishing elliptical surfaces inside the part.
- Triangular - in cross-section they represent a regular triangle with an angle of inclination of the surfaces of 60 ⁰ to each other. Most often, such a tool is used to sharpen the teeth of another tool, for example, a hacksaw for sawing wood.
- Special - at some enterprises, specially shaped files are made in tool shops. For example, in the manufacture of air-cooled two-stroke internal combustion engines, the inlet ports must be modified. The blanks are produced by casting, but finishing is done manually (cheaper than using a specialized machine).
- Oval or semi-cylindrical files are used for processing cylindrical or conical cavities.
Depending on the size of the parts being processed, hand tools are made in different lengths. When steam locomotives were used, each crew of drivers had a file 720 mm long. Used to clean soot and other contaminants from the surface of steam boiler pipes.
Modern files are rarely made longer than 500 mm (the size is determined by the length of the working part where the teeth are). For small jobs, for example, watchmakers use needle files with a working length of about 50 mm.
There is an accepted rule: the larger the tooth, the longer the working part. The explanation is quite simple. The work is performed in a forward motion. By moving the working part further, we achieve deeper removal of the layer when grinding.
Large teeth leave deep marks on the treated surface. To achieve a better surface, allowance is left to obtain a high-quality surface. It is obtained by processing using files with smaller teeth.
Using velvet files, you get a shiny surface with a minimum amount of scratches. Subsequent polishing is done using other tools. In practice, processing is carried out in several stages (at least two). The first is processing with a rough tool, the second is finishing surfaces.
Storage options
Let's immediately decide that we will talk specifically about a workshop, which can be set up in a garage, a detached shed, a summer kitchen, or on a fairly spacious loggia or balcony. There are usually not many tools in the apartment, and the existing screwdrivers, hammer and pliers can be put in a specially designated box or bag, which can take place on the mezzanine or in the hallway.
If there are noticeably more hand tools, they need their own separate corner, in which you will have to put things in order. The main condition is that the place where the tools are stored must be dry, because metal parts do not like moisture.
There are many benefits to a well-designed storage system. You will always know exactly what is and where it is, you won’t have to look for anything. If the tools are always in their place, you will remember in time that a month ago you gave your neighbor a nail puller that he needed for literally an hour. In addition, properly positioned tools take up less space in the workshop, freeing up space for work.
First of all, you should decide whether you will buy ready-made shelves for tools, a metal mobile cabinet with drawers, or set up a workshop with your own hands from scratch. Let us immediately note that ready-made storage systems for hand tools are not always 100% suitable; they often have to be remade to suit your needs.
Let's look at a few ideas for self-organizing the storage of hand tools in the workshop.
1. First of all, you should take care of the little things: nails, screws, bolts, which tend to get lost and scatter throughout the room. To store them, you can use ordinary plastic bottles with cut off necks - you can immediately see what is where. Small plastic boxes are also suitable, which are best labeled, noting that, for example, there are nails of a certain size here. It is convenient to place such containers for storing small items on a shelf above the desktop so as not to clutter it. But glass jars should not be used in the workshop. There are too many heavy metal objects that could accidentally hit such a fragile container.
2. Magnet. Real craftsmen usually have a large magnet on their work table, to which small metal tools can be successfully attached. Now there are special magnetic surfaces and holders on which you can conveniently and simply store many tools and parts.
3. Plywood panel - the choice of old-school craftsmen. From pieces of bars on such a shield you can create an entire storage system that will not take up much space and will allow you to place almost all hand tools. The costs for such storage areas are minimal, and everything will be done according to the needs of the master.
4. You can also buy a ready-made metal sheet with holes for tool holders. However, you can do this yourself. On ordinary nails or self-tapping screws, saws, keys, and other tools with special holes in the handles are hung in the required order.
5. It is convenient to allocate separate storage for screwdrivers, for example, a regular school stand for pencils and pens.
6. Plastic boxes with compartments, which in the kitchen are usually used for forks and spoons, can also be adapted for small hand tools.
7. If you don’t really want to build panels and make shelves, you can move an old sideboard or buffet to the garage workshop. It has a lot of shelves and drawers where many tools can fit. The main thing is to lay everything out yourself so that you know exactly where the garden tools are stored and where the carpentry tools are stored.
8. For drills and bits of a certain size, it is better to buy a ready-made cradle - an insert with tools. Or drill holes in a wooden beam where the drills will fit. And sign - 3, 4.5, 9 and so on, so that you immediately know the required size of the cutting tool.
9. When arranging storage areas in the workshop, you should take care of safety, especially if small children can get into the room. In this case, it is better to hang stabbing and cutting tools on the wall higher, and chemical liquids to be securely locked in a cabinet with lockable doors.
10. A free-standing rack with holders for long handles of shovels and hoes is perfect for garden hand tools. Of course, you can just lean them against the wall, but remember the proverb about the same rake?
Let us state that organizing a workshop is not that difficult; there are plenty of simple ideas. Just prepare yourself for the fact that one time you will have to tinker in the garage a little longer and make an effort, but then there will always be strict order in your workshop and there will definitely be no problems with finding a “cross” screwdriver.
Features of the use of manual turning tools
There is a very conditional division according to purpose. The main categories are identified.
- Bench files are the most common files. They are used in any industrial enterprise. It is not difficult to find such a tool in home workshops and personal households.
- Needles are used for fine work. The main users are jewelers and metalworkers. Without small tools it is difficult to handle hard-to-reach places. For example, Mikhail Timofeevich Kalashnikov, already a famous designer of automatic weapons, modified individual parts independently using a set of needle files.
- Sharpening files (mostly triangular and diamond-shaped) are used to sharpen teeth on hacksaws, saw chains and other places where cutting edges need to be restored to the required sharpness.
- Rasps are a special class of tools used for processing wood and other non-metallic materials. They are distinguished by the presence of teeth of a special point shape. Sometimes rasps are called bastard files, although this is not entirely true.
Types of notches on the surface of the tool
Based on the nature of the notches, it is customary to speak of a single or double design.
Single execution is more common with rough instruments. Here the tooth has a long cutting edge. Its length corresponds to the width of the file. To make it easier to penetrate into the thickness of the metal being processed, the notch is made inclined at an angle of 25⁰. The result is cutting with some displacement. It makes it easier to penetrate deeper into the part. The effort is slightly reduced.
The double design of the notches is made at an angle to each other. The second cut is made at an angle of 45⁰. Now the cutting teeth are limited in length. Where the lines intersect, places where chips break are formed. Consequently, such files require less physical effort during operation (no need to waste effort on twisting long shavings).
Numbering of notches on tools
Table for determining the notch number in relation to different section shapes
The size of the tooth on the surface depends on the density of the notches. The more there are, the smaller the teeth.
The classification of notches according to digital values from 0 to 5 is accepted. The largest teeth can remove up to 0.8...1.1 mm of metal. It is customary to assign the number “0” or “1” to such an instrument. Such an instrument was called “drachevy”.
Files that cut metal to a depth of 0.02...0.04 to 0.08...0.10 mm in one pass are numbered “2” or “3”. Such files are called “personal”.
If the tool removes 0.010...0.015 mm, then it is assigned the number “4” or “5”. They are called "velvet". When working with them, the highest processing quality and accuracy are obtained.
Typically, the notch is applied using the rolling method. The workpiece heated to the austenitic state is fed to the forming machine. The roller system rolls channels on the working surface of the tool.
The milling method is used to make personal and velvet files. The treatment is performed on workpieces before hardening.
Coating thickness control
Magnetic method
This technique is based on recording changes in the level of magnetic resistance, which is due to different thicknesses of the layer being tested. For this purpose, special measuring devices (magnetic thickness gauges) are used.
The inspection process involves taking a minimum of 5 measurements in the central part and at the edges of the inspected surface of one part. The arithmetic mean value is taken as the result, based on the measurements obtained.
The permissible error of the magnetic method is ±10%.
Metallographic (arbitration) method
The technique is based on measuring the thickness of galvanized coating using a transverse section using metallographic microscopes of various types. The sample for creating a thin section is cut directly from the galvanized part.
Measurements of the coating thickness are carried out on a thin section in three or more zones, which are evenly distributed on the surface of the product (the length of the section is about 1 cm). The arithmetic mean of the measurements taken is taken as the result.
The permissible error of the metallographic method is ±10%.
Gravimetric method
Determination of the average thickness of the coating is carried out using non-destructive methods or using the gravimetric method based on data on the weight of the sample before and after receipt or before and after removal of the coating. This is due to the requirements regulated by GOST 9.302.
To remove the coating, use a solution consisting of 2 g of antimony trioxide or 3.2 g of antimony chloride, which is dissolved in 500 cm of hydrochloric acid, the density of which, according to GOST 3118, should be 1.19 g/cm, analytical grade. To prepare the solution in the required proportion, use a 1 dm3 flask, in which the mixture is added to the mark with distilled water, according to GOST 6709 standards.
The permissible error is ±10%.
Control of the chemical composition for hot-dip galvanizing is regulated by the requirements of the following GOSTs: 19251.1, GOST 19251.2, GOST 19251.3, GOST 19251.5.
According to the requirements of these standards, the mass volume of zinc in the working mass of the bath must be at least 98%.
Tooth sizes
The dimensions depend on the number of notches. The following classification is accepted:
- Files numbers 0 and 1 have 10…13 teeth per centimeter of length.
- Numbers 2 and 3 are characterized by the presence of 14...25 depressions per centimeter of length.
- Velvet files can have from 30 to 80 cavities per 1 cm of working surface.
A tall tooth gets clogged less often. Small teeth when processing soft metals can become clogged quite quickly. Therefore, metal brushes are used for cleaning; they remove metal residues from the cavities.
Marking
The produced file must be marked. The marking is an image of the necessary information about the characteristics of the tool. The marking includes a class designation from 1 to 6; length indicated by the letter L; type of notch with numbers from 0 to 5. The last indicator is considered the most important by practitioners; it determines the choice of the right tool in a particular situation.
The tooth hardness indicator is designated by the letters HRC and two numbers - for example, HRC 55. The type of steel is designated as 13X or U13A.
DIY file handles
Real craftsmen equip their existing tools with handles made by themselves. With the advent of plastics, there was a wider choice of materials for homemade products.
If you have a lathe, then the handle can be turned from hardwood: walnut, birch, ash. There are quite a lot of drawings on the Internet, using which a suitable handle is made.
Some craftsmen use epoxy resin to make unusual handles.
- First, possible porous materials that can be impregnated with epoxy resin are selected. Most often, fabrics of different colors are used. Micarta is created - a multi-layer fabric impregnated with epoxy.
- They are placed in the desired sequence.
- The epoxy resin is diluted according to the attached recipe.
- Wet each layer.
- Lay in the chosen sequence and place under a press.
- After polymerization is completed, a new material is formed - micarta.
- A file handle is made from micarta.
Video: Cuban files.