You can find forged products in various areas of human life. Window grilles, fences, lanterns, garden furniture and other products made through the forging process look elegant and attract the attention of passers-by. Even with the development of homemade technologies, metal forging did not fade into the background. She continues to gain popularity with renewed vigor.
Forged gates
Interesting about metal forging
Interesting fact, one of the most common surnames in the world comes from blacksmithing. This is Kuznetsov in Russia, in France - Ferrand, in Britain - Smith. This indicates the prevalence of this craft throughout the world.
blacksmith craft
The basis of the word deceit is the verb forge. The fact is that many peoples and tribes considered blacksmithing to be obscure and shrouded in mystery. Kovar (blacksmith) makes forges, knits shackles, so over time the noun cunning denoted wisdom, skills, ability. Over time, it began to mean evil plans and intentions. At the same time, the phrases “forge your happiness” and “forge your destiny”, which have a positive meaning, also appeared.
During the mass unification of production and the use of equipment such as rolling, stamping, the use of computer control practically displaced blacksmithing from heavy industry, but it remained and is popular with designers and interior design specialists. Modern blacksmiths make products that are used to create fences, stairs, architectural design of buildings, etc.
Rolling equipment for cold forging
Hot stamping
But our century has led to the fact that the design of forged products is carried out using special 3D design programs intended for the development of parts for various purposes.
Open forging is used on a variety of metals. With the help of this operation, both household items and objects of artistic value are performed. By the way, this method of metal processing is also used in jewelry. In fact, the most malleable metal is gold. It has plasticity, fluidity, ductility and many other properties that make it possible to obtain priceless products from it.
Jewelry forging
In practice, two main types of forging are used - hot and cold.
Operations of cutting, cutting and trimming metal blanks
Felling operations: a.
cutting with a chisel; b. chopping with a chisel and undercutting; V. cutting flakes in a vice; d. longitudinal cutting; d. cutting (cutting). The workpiece is cut to divide it into elements. To cut metal, it must be heated to a dark red heat temperature, placed on an anvil and, using a special chisel, cut through approximately 75 percent of the thickness. After this, the product is turned over and chopped with a chisel, this time to the end.
If you work with hot thick metal with forging chisels when chopping, then do not forget to cool the tool from time to time, since prolonged contact with a hot metal workpiece may cause the chisel blade to drop. Then, in order to use the tool again, drops of water need to be removed from it by lightly tapping.
Chopping (not to be confused with chopping) only allows you to chop a metal product. This operation is very often used by blacksmith artists when forging. The cut parts are subsequently stretched, twisted, subjected to various forging techniques and ultimately take the form of flowers, leaves and curls. The cutting operation is especially popular for the production of svetzets, zhikovins, etc.
The workpiece is cut only on one side, the front side. First, light blows are performed so that only the groove is cut. The workpiece should be slightly heated, which will make it possible to slowly cut the product. When the workpiece is cut, the metal is heated to high temperatures and cut through with one sharp blow.
Chipping is used to remove a layer of metal along the outer contour. This action is also called pruning. It is often used in the process of forging complex decorative forms: quilts, overlays, etc.
The cutting process is similar to cutting, only in this case the metal is separated along the internal contour. When performing these techniques, semicircular, carbon, straight and other forging chisels are used.
https://moyakovka.ru/youtu.be/ezdpKqWJnq4
Hot forging method
As already noted, hot forging is possible when the metal is heated to temperatures at which it changes its strength characteristics and acquires plasticity, which makes it relatively easy to process using impact tools and various devices. Hot metal processing involves the use of certain metal processing technologies that allow a variety of finished products.
Meanwhile, heating the metal also has certain disadvantages. Firstly, heating the metal means that a forge or muffle furnace must be installed in the workshop. It should be immediately noted that the presence of such equipment implies the presence of costs for its maintenance and fuel. Secondly, the use of open fire is an unsafe activity and requires the master to observe increased safety measures. Thirdly, hot forging requires that the master have certain knowledge and skills regarding the temperature parameters of the metal.
How to heat workpieces correctly?
General view of a high-frequency installation for melting metals.
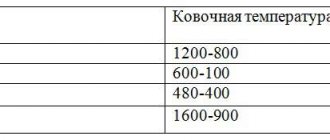
The final quality of a metal product largely depends on the selected temperature regime for heating the workpiece. The appearance of the product and its durability also depend on this. It should be taken into account that the metal can be processed only when it is brought to the temperature required for forging. Thus, the metal’s resistance decreases, it can be deformed, and the degree of ductility becomes very high.
It is necessary to take into account that each metal has its own temperature regime for forging. This temperature regime is determined by the structure of the workpiece and its chemical composition.
Hand forged
Hand forging of metal must be performed in a specially equipped workshop. The list of equipment includes the following equipment and devices:
- forge or muffle furnace;
- air exhaust system;
An anvil, which is a solid-sized (weighing up to 250 kg) metal pig, which may have such technological devices as horns and calibrated holes. For its manufacture, 45L steel is used.
On an anvil, you can forge metal with your own hands and give heated workpieces the required shapes and sizes.
In addition, there is the possibility of forging a sheet on the surface of the anvil.
Puddled iron
Wrought iron is a material that blacksmiths have been working with since time immemorial.
It is more resistant to corrosion than modern mild steel. Proof of this is the forged products that have come down to us from the past, many of which are already several centuries old. Nowadays practically no one is engaged in the production of puddled iron. It is mainly used for the restoration of antique forged items. Wrought iron has remarkable anti-corrosion properties due to its fibrous structure. Using modern terminology, we can say that obtaining pure iron is the primary process of processing iron ore, as a result of which the ore is cleared of slag. The blacksmith himself found the “ore”, burned the coal himself, smelted the iron himself, forged it himself, processed it himself. The presence of porous elements of the metal structure and the softness of the material in a hot state at one time gave people the opportunity to hand forge, which led to the emergence of a new type of art - artistic forging.
Cold forging method
Most cold forging work is performed on equipment specially designed for this purpose. You can name a certain list of equipment that is used for cold metal processing. As a rule, such equipment shows its effectiveness when performing large volumes of work in the architectural design of buildings and structures.
Among the equipment used in the production of cold forging products are the following:
- torsion bar, it is used to twist the rod along its axis;
- wave, various wave-like parts are made on it.
In total, the fleet of cold forging equipment includes about a dozen units. Some are powered by the operator's muscular strength, some are powered by an electric drive. Some craftsmen are engaged in the independent production of such equipment.
Cleaning of forged products
Usually forged products are coated with paint. Once rust forms, marks remain on the paint. In most cases, old paint and rust can be removed by sandblasting. However, you should not resort to this method right away, since such cleaning will damage the secondary scale formed when rolling iron. It cannot be damaged, much less removed, otherwise the forged product will begin to quickly deteriorate.
Therefore, in all possible cases, experts recommend chemical cleaning of forged products from old paint, followed by steam cleaning of chemical reagents. Thus, the forged product will appear before you in its original form, as it originally looked before the first painting. Rust is usually removed by heat treatment of the product; it does not spread further if the metal is calcined. As the metal expands, the rust falls off and is easy to remove. In addition, if a forged product is heated to red heat, it will become covered with a protective film similar to secondary scale. Very often, parts of a forged product with traces of rust require calcination as one of the stages of the restoration procedure.
Attention: forged products are often coated with paints containing lead (up to 75%). When cleaning forged products from this type of paint using the sandblasting method, appropriate safety precautions must be observed.
Types of blacksmithing
Forging is performed using manual or mechanical impact tools, this could be a sledgehammer or a press, which can be powered by an electric, pneumatic or hydraulic drive.
Forging and stamping provide the production of parts that have different overall weight parameters and shapes.
The use of forging leads to an increase in the mechanical parameters of steel and optimizes its internal structure. That is why critical parts, such as connecting rods, are produced using free forging or stamping. Forging can be divided into the following types - hand and machine. For the first, a hand-held percussion tool (hammer, sledgehammer, etc.) is used; all metal processing work is performed on an anvil. The second type of forging is performed on forging equipment equipped with a hammer, etc. When machining, heavy and bulky workpieces are processed under pressing equipment, and smaller ones with less weight are processed using a hammer.
Metal processing by impact can be divided into free forging and die processing. Free forging involves the workpiece being compressed between a press and a base. The formation of the finished part occurs due to the auxiliary tools used by the blacksmith.
Blacksmithing
When stamping, the metal takes on the shape and dimensions within the tool die. To produce a separate part, a new die must be made. In fact, forging and stamping are intermediate technological operations that lead to the production of workpieces, which will subsequently undergo additional processing, for example, milling or welding.
Forging drawing technology
Metal extraction: a.
on the edge of the anvil; b. using the back of a sledgehammer; V. on the hem; g. on a pair of lining; d. with top tamper; e. using a smoothing iron; and. in mandrels. The metal drawing operation is used to increase the length of the product while simultaneously reducing the cross-sectional area.
The workpiece is drawn as follows. The heated metal is placed on an anvil, where it is stretched under the blows of a hammer or sledgehammer. Then they turn the product 90 degrees and hit the bulge from the first blow. After performing several more such cycles, the blacksmith gradually pulls out the metal.
The main condition for drawing is to maintain the square shape of the cross-section of the metal workpiece.
To speed up the drawing process, you can forge on the anvil horn. Then the product will be stretched between a pair of convexities, which accelerates the increase in the length of the product.
There is another way to stretch the workpiece - using rolling or spreading. As a rule, the rolling has a semicircular shape. The direction of the drawing will depend on how the rolling is located on the metal - across or along.
Extraction at the end is used to make svets, zhikovins, and nails.
Types of modern forging equipment
A variety of forging and stamping equipment is widely used in industry. It can be classified according to the following parameters:
- according to the temperature of the workpiece being processed. For this operation, forging machines and equipment for hot and cold stamping, both flat and volumetric, are used;
- on operations performed on equipment. Divide the procurement, main and finishing CSW;
- according to the method of supplying and removing finished products from the workspace of the KShO. In practice, equipment is used on which all these operations are performed manually, in semi- and automatic mode.
- by type of drive. Presses and stamping machines operate on electricity, compressed air, hydraulics, etc.
- by key parameter. As a rule, this is the nominal force created by the press or operating torque.
Charcoal cast iron
Long before the industrial age, blacksmiths processed wrought iron in charcoal kilns. Iron for forging was processed over fire and a qualitatively new material was obtained, the properties of which were exclusively suitable for artistic forging. Forged products made from charcoal cast iron have come to us from the 18th century.
At the end of the 18th century, industrial production of puddled iron began. In this case, the iron underwent heat treatment in charcoal kilns without direct access to fire. Puddled iron, easily malleable when hot and resistant to corrosion, was the main construction material in the 19th century. In the field of cold forging , however, it has significant limitations. It is cold forged only in thin sheet form.
Charcoal cast iron can resist corrosion for hundreds of years. It is very difficult to restore and restore traditional forged products: they are almost impossible to repaint due to the complexity of the elements of these products, especially when they are three-dimensional. When restoring, it is necessary to use only corrosion-resistant materials of the best quality.
Charcoal cast iron sheet is flexible, pliable and malleable. After annealing, it can be used in cold forging without fear of it cracking or splitting. It is softer and easier to work with than mild steel. It has a flat, smooth surface, contains virtually no scale, and is easily smoothed and polished. Only a small number of manufacturing companies can offer you this rare type of malleable iron in our time.
Protection of forged products
Electroplating and hand galvanizing are used to protect forged products. However, there are several reasons why these methods cannot be used when working with malleable charcoal or puddled iron. During galvanization, the forged product, after cleaning with acid, is immersed in a bath of molten zinc. As a result, the product is coated with a fairly thick layer of zinc. However, this often creates drops that have to be sanded off, leaving marks on the metal. If we add to this the acid that fills the smallest joints of the forged product, it is not difficult to understand why galvanizing is not suitable for coating thin, delicate and complex malleable iron products.
Hand galvanizing is a gentler process. In this case, first, secondary scale is removed from the surface of the forged product by sandblasting. Then the zinc coating is immediately applied using a special spray gun. However, we have already indicated the disadvantages of sandblasting above. In addition, the sandblasting method is not suitable for cleaning small joints, which, moreover, cannot be coated with zinc even by hand. And water will get into all unprotected places (small joints and recesses), which will lead to corrosion of the metal. Due to the natural anti-corrosion properties of ductile iron, you can simply coat the wrought iron piece with a thick coat of paint and check its condition periodically, ensuring maintenance if necessary and repainting every 5 years.
Technologies for restoration of ductile iron products
There are 2 types of malleable iron: the malleable iron of ancient times, known as charcoal iron, and the malleable iron of industrial production (19th - early 20th centuries), known as "puddled" iron. If it is necessary to restore forged charcoal iron products (made before the 18th century), puddled iron can be used, since their properties are similar. However, under no circumstances should mild steel be used in restoration work, even cold or hot galvanized.
Assembly of forged products
Most often, forged products begin to corrode due to the constant accumulation of water on horizontal surfaces, at bends and in recesses, as well as on surfaces in contact with plants. If you completely prevent water from entering a forged product, it can last forever. After assembling the forged product, the joints and joints must be coated with paint as well as all visible surfaces. It is recommended to use waterproof but adhesive silicone resin as a filler material. In addition, lead putty is a traditional filler material, and if it is well insulated with paint, it will last a long time. The butt recesses can be filled with epoxy resin or tar, which will melt in the summer and adhere even better to the metal. Previously, molten lead was often used for this, but it does not adhere well to iron, as a result of which water penetrates into the joint, and the situation only gets worse.