Decoding
The interpretation of steel st3ps is given in GOST 380-2005. According to the document:
- st indicates that the steel belongs to alloys of ordinary quality. Depending on the sulfur and phosphorus content, steels are of ordinary quality, high-quality, high-quality and especially high-quality. For steel st3ps and other steels of this class, the sulfur content cannot exceed 0.06%, phosphorus 0.07%.
- 3 serial number of the grade according to GOST 380-2005 means that the steel corresponds to the chemical composition specified in the document for grade 3.
- ps - means that the degree of deoxidation of the steel is semi-quiet. Deoxidation is the process of removing oxygen and nitrogen gases. There are three categories of steel according to the degree of deoxidation: calm (sp), semi-quiet (ps), boiling (kp). The less gases are released during the solidification of the alloy, the fewer pores and bubbles in the metal structure, the higher the strength.
Substitutes
A substitute is an alloy that is closest in performance characteristics to the main one. Substitutes for St3 are usually one of three domestic brands: S245, S285, VSt3Sp.
It is acceptable to use foreign analogues that differ in markings, but are available in any corner of the world map. They are:
IN THE USA:
- A57036;
In Great Britain:
- 40B;
- 722M24;
In Germany:
- 0038;
In France:
- E24-2;
- E24-4.
In Japan:
- SS330;
- In Italy:
- Fe360B;
In China:
In Austria:
In Hungary
Chemical composition
St2ps steel is 98% iron. The remaining 2% includes carbon, manganese, nickel, chromium, silicon, copper, sulfur, phosphorus, arsenic, scandium, nitrogen, aluminum. The table below shows the exact content of the most significant elements. Minor impurities do not seriously affect the characteristics of the metal and are therefore not taken into account.
The most important alloy elements, besides iron, are:
- carbon high carbon content provides steel with hardness, strength and elasticity;
- manganese in the composition is responsible for deoxidation and removal of sulfur, and also makes steel stronger;
- silicon deoxidizer, which forms a fine-grained structure of steel, improves technological properties, strength, and does not reduce ductility.
Harmful impurities are sulfur and phosphorus; the lower their concentration in the alloy, the higher quality the steel is considered.
Chemical composition, % (GOST 380-94)
| C carbon | Mn manganese | Si silicon | P phosphorus | S sulfur | Cr chrome | Ni nickel | Cu copper | As arsenic |
| no more | ||||||||
| 0,14-0,22 | 0,40-0,65 | 0,05-0,17 | 0,04 | 0,05 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,30 | 0,08 |
Processing and use of 3ps steel
3ps steel can be welded by several methods without losing its physical properties: submerged arc, KTS, gas protection, ADS, EShS and DS. If the steel thickness is more than thirty-six millimeters, it is strongly recommended to subject the material to heat treatment before welding: hardening, annealing or tempering.
Hardening makes it possible to radically change the basic characteristics of the alloy without introducing foreign chemical elements into its composition. This allows you to seriously save time and money. Annealing imparts a uniform structure to the metal, and at the same time reduces its ductility. Tempering is used to reduce the internal stress formed in the metal, due to which the metal acquires surprisingly high strength and hardness.
Due to thermal effects, the properties of the alloy are improved without creating the need to make changes to its chemical composition. Thus, for example, it is possible to extend the service life of products made from 3sp steel . Laboratory tests have confirmed the fact that this type of steel, after heat treatment, is ideal as the main material for the production of load-bearing structures for buildings.
Application
St3ps steel is a carbon structural steel of ordinary quality; it is a general purpose steel. It is used at normal temperatures, and is used to make welded and non-welded structures in construction and mechanical engineering. The properties of steel allow it to be used in load-bearing structures and loaded elements, such as load-bearing trusses, beams, channels, rails, etc. Steel is not alloyed and is not protected from corrosion in direct contact with water, and is also vulnerable in alkaline and acidic environments. A thick layer of galvanic coating or paint is required for protection.
Standardized indicators of St3ps steel by rolled category (GOST 535-2005)
| Category | Chemical composition | Temporary resistance σв | Yield strength σt | Relative elongation δ5 | Cold bending | Impact strength | ||||
| KCU | KCV | |||||||||
| At temperature, °C | After mechanical aging | At temperature, °C | ||||||||
| + 20 | -20 | + 20 | -20 | |||||||
| 1 | — | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | — |
| 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — |
| 4 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | — | — | — |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | — | + | + | — | — |
| 6 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | + | — |
| 7 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | — | + |
NOTE
- The “+” sign means that the indicator is normalized, the “-” sign means that the indicator is not normalized.
- The chemical composition of steel according to heat analysis or in finished rolled products is in accordance with the order.
Parameters for the use of electric-welded straight-seam pipes made of St3ps steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZps4 GOST 380 | ||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | GOST 10706 group B | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 400-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | GOST 10706 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | Group B media, except LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤1,6 | |
| Maximum temperature, °C | 200 | ||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | — | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 20 | |
| no more than 0.35[σ] | minus 40 | ||
- NOTE. Groups of media, see table 5.1 GOST 32569-2013
Parameters for the use of electric-welded spiral-welded pipes made of St3ps steel (GOST 32569-2013)
| Steel grade, strength class, standard or specifications | StZps2 GOST 380 | ||
| Technical requirements for pipes (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-954-80 | ||
| Nominal diameter, mm | 500-1400 | ||
| Types of tests and requirements (standard or specifications) | TU 14-3-954-80 taking into account the requirements of clause 2.2.10 GOST 32569-2013 | ||
| Transported medium (see designations in table 5.1) | All media except group A and LPG | ||
| Pipeline design parameters | Maximum pressure, MPa | ≤2,5 | |
| Maximum temperature, °C | 300 | ||
| Pipe wall thickness, mm | ≤12 | ||
| Minimum temperature depending on the pipe wall thickness with stress in the wall from internal pressure [σ], °C | more than 0.35[σ] | minus 20 | |
| no more than 0.35[σ] | minus 20 | ||
Conditions for using St3ps steel for bodies, covers, flanges, membranes and valve assembly made from rolled products, forgings (stampings) (GOST 33260-2015)
| Material | ND for supply | Temperature of the working medium (wall), °C | Additional instructions for use |
| St3ps GOST 380 | Forgings GOST 8479 Long products GOST 535, categories 3-5 | -30 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN≤2.5 MPa (25 kgf/cm2) |
| Sheet GOST 14637, categories 3-6 | -20 to 300 | For welded fittings for pressure PN 5 MPa (50 kgf/cm2). For categories 4, 5, sheet thickness for St3ps is no more than 25 mm; for category 3 sheet thickness no more than 40 mm |
Brand analogues
According to the production system, the St3ps steel grade is related to other similar alloys, both domestic and foreign produced. Among them we can note C245 manufactured in accordance with GOST 27772, VSt3ps6 - GOST for which is 23570-79 and foreign E-235-B (better known as Fe 360-B). All of them are united by the characteristic of universal rolled steel intended for the construction of building structures with welded and non-welded type of connection.
Steel 245
Of course, alloys of different markings cannot be called complete analogues of each other. For example, the same domestic C245, although it has characteristics similar to 3ps steel in terms of strength, withstand temperature and pressure, conditions for welding and construction of structures, is endowed with differences in composition. Namely, the amounts of iron and manganese are the same, but other components, such as flint or carbon, have a smaller or larger percentage of the total mass. With other analogues the situation is approximately the same.
Assortment
- Channels are parallel (P), with sloped flanges (U), equal-flange bent;
- round sections circle and reinforcement;
- VGP pipes, electric welded (ES), seamless (BGD), nominal diameter 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 90, 100 mm;
- I-beams, wide-flange, column, special, with flange slopes;
- steel square;
- steel wire rod;
- corners equal and unequal;
- square and rectangular profile;
- sheet steel: hot-rolled, corrugated, expanded metal, strip.
Description
St3ps steel is used : for the production of shaped and sheet metal (5th category) with a thickness of up to 10 mm, used for load-bearing elements of welded structures operating under variable loads in the temperature range from -40 °C to +425 °C; rolled from 10 to 25 mm. — for load-bearing elements of welded structures operating at temperatures from - 40 °C to +425 °C, subject to delivery with guaranteed weldability; for the manufacture of blanks for pipeline fittings; forgings with a diameter of up to 300 mm. strength classes KP 175, KP 195; expanded metal sheets; hot-rolled trough and single-groove profiles for agricultural machines; profile for the tractor final drive housing; hot-rolled profiles for the manufacture of wheel rims for agricultural machines; electric welded pipes for the manufacture of parts and structures in the motorcycle and bicycle industry; double-headed, T-bar and P5 type rails intended for ground and overhead tracks; steel bent closed welded square and rectangular sections intended for use in agricultural engineering, tractor manufacturing and other sectors of the national economy; hot-rolled steel profiles for sheet piles intended for cellular structures and impervious curtains; spikes of accuracy class C, designed for fastening railway rails to wooden sleepers and beams.
Note
Degree of deoxidation - ps.
Type of delivery
| B03 - Metal forming. Forgings | GOST 8479-70; |
| B20 - Classification, nomenclature and general standards | GOST 380-2005; |
| B22 – Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 5267.0-90; GOST 5781-82; GOST 8239-89; GOST 8240-97; GOST 8510-86; GOST 8509-93; GOST 10884-94; GOST 30136-95; GOST 9234-74; GOST 4781-85; GOST 10551-75; GOST 25577-83; GOST 5422-73; GOST 535-2005; GOST 19240-73; GOST 19425-74; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 11474-76; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 30565-98; |
| B23 - Sheets and strips | GOST 14637-89; GOST 16523-97; GOST 8568-77; GOST 14918-80; GOST 19903-74; GOST 103-2006; |
| B24 - Tapes | GOST 3560-73; GOST 6009-74; |
| B34 - Tapes | GOST 19851-74; |
| B42 - Rails. Overlays. Linings. Crutches | GOST 8142-89; GOST 5812-82; GOST 16277-93; |
| B62 — Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 12132-66; GOST 10705-80; GOST 10706-76; GOST 3262-75; GOST 24950-81; GOST 8696-74; GOST 10707-80; GOST 20295-85; |
Differences between st3ps and st3sp
Alloys st3sp and st3ps, being varieties of the same steel, differ from each other in the degree of deoxidation.
- Steel st3sp is considered calm, the degree of deoxidation is maximum.
- St3ps steel is semi-quiet, with a medium degree of deoxidation.
As a result of deoxidation, the intensity of gas formation during steel hardening decreases. The resulting gas bubbles make the steel porous and, as a result, less strong, affecting technological properties such as weldability. Calm steel (sp) is the highest quality in terms of the degree of deoxidation, boiling steel (kp) is the least quality, and semi-quiet steel (ps) occupies an intermediate position between them.
The differences between calm and semi-quiet steel for widely used metals are insignificant; both varieties cope quite well with average loads. At the same time, mild steel is more expensive, its production process is more complicated, and its use is advisable where the requirements for the quality of the metal are increased.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main distinguishing feature of St3 steel is its combination of positive characteristics or versatility. This means that it does not have any one key advantage, it shows decent characteristics from all sides, which makes it the first on the market. This steel is not intended for highly specialized applications in special conditions, but is ideal for a wide range of everyday applications.
The disadvantages of steel include low performance at low temperatures.
Advantages of steel st3Gsp:
- homogeneous structure, due to which the steel becomes homogeneous, ductile and protected from adverse environmental influences;
- resistance to atmospheric corrosion;
- high elasticity and hardness;
- insensitivity to flakes;
- impact strength, allowing to withstand dynamic loads well;
- not subject to temper brittleness;
- simple production process, no expensive alloying additives;
- relatively low cost.
Separately, it should be mentioned that the material is perfectly weldable. It can be carried out using any known technology without preliminary and subsequent treatments.
Production
St3ps steel is produced in two ways: converter and open-hearth. A converter furnace is a pear-shaped vessel lined with brickwork on the inside and covered with sheet steel on the outside. Scrap metal (scrap) is placed into the converter, then liquid cast iron heated to 1400C is poured. At the oxygen purge stage, oxygen is supplied to the converter under high pressure, causing the oxidation of cast iron impurities, resulting in the formation of steel. In open hearth furnaces, steel is produced using the same oxidation method, but using a different principle through slag. Deoxidation and alloying (if necessary) is carried out at the final stages of production.
St3ps steel does not change its characteristics depending on the production method, but the converter method is cheaper, and therefore is considered more preferable.
Why does steel deoxidize?
Deoxidation is part of the metal refining process. If you do not deoxidize the steel before it hardens, the structure of the steel will be heterogeneous, porous, with gas pockets. Such steel welds worse, wears out and breaks faster. Deoxidized steel has a homogeneous and solid structure. Undeoxidized steel is also used in various industries, but is not suitable for the manufacture of loaded parts operating under pressure. The production of such steel has its advantages: it is waste-free, cheap and simple.
Comparison with alloy structural steels
Steel st3 is a carbon structural steel of ordinary quality. It is used to produce welded and non-welded structures, heavily loaded trusses and other load-bearing elements. St3 is resistant to atmospheric corrosion, but without a protective coating it will deteriorate upon prolonged contact with moisture or an aggressive chemical environment.
Alloy structural steel is protected from corrosion by alloying elements, so it can be used without a protective layer when in contact with moisture and aggressive environments. Alloy steel is more difficult to produce, more expensive and more prone to brittleness. The processing of such steel may require special conditions, while the more affordable and easier to produce steel 3 does not require any special processing conditions.
Technological properties
| Forging | Cooling of forgings manufactured | ||||
| Type of semi-finished product | Forging temperature range, ºС | from ingots | from blanks | ||
| Section size, mm | Cooling conditions | Section size, mm | Cooling conditions | ||
| Ingot | 1280-750 | ≤1000 | On air | — | On air |
| Blank | 1300-750 | >1000 | In a closed sand pit | — | On air |
| Weldability: | no limits. |
| Flock Sensitivity: | not sensitive. |
| Tendency to temper brittleness: | not inclined. |
Comparison with alloy tool steels
Alloy tool steel is used in the production of tools. Alloying additives are aimed at improving the quality of steel, thanks to them it is possible to achieve a significant advantage over carbon alloys. These include:
- red fastness;
- high hardenability;
- resistance to impact loads (especially important for impact tools);
- wear resistance.
St3 steel is structural and, as a rule, is not used for the manufacture of moving parts of tools.
How to weld
St3ps steel is unpretentious in processing; it can be welded without restrictions by any existing method. Pre- and post-temperature treatment is not required. The seams are strong and not prone to cracking. The following types of welding are widely used:
- contact using high voltage current;
- automatic submerged arc using a welding machine with a wire electrode;
- electroslag using molten flux (slag);
- manual arc welding with coated electrodes;
- manual argon arc manual welding in an argon gas environment;
- mechanized welding in a carbon dioxide environment with a consumable electrode in a gas environment.
Welding materials for electric arc welding
| Base material grade | Electrode type according to GOST, TU (recommended brands of electrodes) | Application temperature, °C | Additional instructions |
| St3ps | E42, E46 GOST 9467 (ANO-4, ANO-5,OZS-6) | Not lower than -15 | — |
| E42A, E46A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/45, UONI-13/45A, 0ZS-2, SM-11) | Not lower than -30 | — | |
| E50A GOST 9467 (UONI-13/55) | below -30 to -40 | After welding, heat treatment normalization plus tempering (630660) °C, 2 hours |
Welding materials for gas shielded welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, recommended shielding gas or mixture of gases | Application temperature, °C |
| St3ps | Sv-08G2S Carbon dioxide GOST 8050, argon GOST 10157 | -20 to 300 |
Welding materials for submerged arc welding
| Base material grade | Welding wire grade according to GOST 2246, TU, Recommended flux grade according to GOST 9087 | Additional instructions | ||
| Electrodes, type according to GOST 10052 (recommended brands) | Welding wire, GOST 2246 or TU | |||
| Group A | Group B | |||
| 10Х18Н9Л, 12Х18Н9ТЛ GOST 977 08Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9Т, 12Х18Н10Т, 12Х18Н9 GOST 5632 08Х18Н10Т-VD TU 14-1-3581 10Х18Н9, 10Х18Н9-VD, 10Х1 8N9-Sh TU 108.11.937 15Х18Н12СЧТУ (EI 654) GOST 5632 10Х17Н13М3Т (EI 432) 10Х17Н13М2Т ( EI 448) GOST 5632 | St3ps GOST 380 | E-10Kh15N25M6AG2 (EA-395/9) E-10Kh25N13G2 (OZL-6, ZIO-8), E-11Kh15N25M6AG2 (NIAT-5, TsT-10) | Sv-07Х23Н13 | The welded joint is of unequal strength |
| E-10Х15Н25М6AG2 (EA-395/9) 582/23, 855/51 | Sv-10X16N25AM6 Sv-06X15N35G7M6B Sv-03X15N35G7M6B | The welded joint is of unequal strength. Welding materials are used for products under the jurisdiction of Rostechnadzor | ||
Welding materials for welding St3ps steel with other steels
| Grades of welded steels | Welding materials | Application temperature, °C |
| St3ps | Sv-08, Sv-08A AN-348A, OSTS-45 ANTS-1 | Not lower than -20 |
Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating and tempering when welding structures made of St3ps steel
| Grades of welded steels | Thickness of welded edges, mm | Temperature of preliminary and accompanying heating, °C | Interval between the end of welding and the start of tempering, hour | Temperature, °C | |
| welding | surfacing with austenitic class materials | ||||
| St3ps | Up to 36 | Not required | Not required | Not limited | Not required |
| Over 36 to 100 | 630-660 | ||||
| Over 100 | 100 | ||||
Recommended welding modes for correcting weld defects
| Welding materials | Main material | Diameter of electrode, wire, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A* USENI 13/55 | St3ps | 3,0 4,0 5,0 | From 100 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
| Sv-08G2S | 1,6 | From 100 to 120 | From 12 to 14 | |
| 2,0 | From 140 to 160 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of electric arc welding of samples and products
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| USENI 13/45A*, USENI 13/55 | St3ps | 3 4 5 | From 110 to 130 From 160 to 210 From 220 to 280 | From 22 to 26 |
NOTE. * - along with the electrode brand UONI 13/..., it is possible to use the brand UONII 13/..., depending on the designation of the brand in the specifications of the electrode manufacturer.
Modes of argon arc welding of samples for incoming inspection of welding materials
| Electrode brand | Main material | Electrode diameter, mm | Welding current strength, A | Arc voltage, V |
| Sv-08G2S | St3ps | 1,6 2,0 3,0 | From 100 to 120 From 150 to 170 From 200 to 240 | From 12 to 14 |
Density ρ p kg/cm 3
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C | |
| 20 °C | ||
| st3ps | 7850 | |
Young's modulus (normal elasticity) E, GPa
| Steel grade | At test temperature, °C | ||||||||
| 20 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 | ||
| VSt3ps | 213 | 208 | 202 | 195 | 187 | 176 | 167 | 153 | |
Specifications
The characteristics of ST3PS steel include: weldability, hardness HB (HB 10-1), melting range, density, increase in tensile length.
| weldability | weldable; |
| hardness HB 10-1 | 131 MPa; |
| melting range | 1300-1400 degrees; |
| density | 7850 kg/m3; |
| increase in length when stretched | 23-25%; |
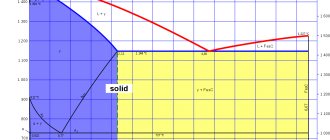
Temperature of critical points, °C
| Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar3 | Ar1 |
| 735 | 850 | 835 | 630 |
Mechanical properties
| GOST | Delivery status | Section, mm | σ0.2, MPa | σв, MPa | δ5(δ4), % |
| no less | |||||
| GOST 380-94 | Hot rolled products | Up to 20 | 245 | 370-480 | 26 |
| St. 20 to 40 | 235 | 25 | |||
| St. 40 to 100 | 225 | 23 | |||
| St. 100 | 205 | 23 | |||
| GOST 16523-89 (transverse samples) | Hot rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (20) |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (22) | ||||
| Cold rolled sheet | Up to 2.0 incl. | — | 370-480 | (22) | |
| St. 2.0 to 3.9 incl. | (24) | ||||
Impact strength KCU (GOST 380-94)
| Type of rental | Pattern cutting direction | Section, mm | KCU, J/cm2 | ||
| + 20 °C | -20°С | after mechanical aging | |||
| no less | |||||
| Sheet | Transverse | 5-9 | 78 | 39 | 39 |
| 10-25 | 69 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 49 | — | — | ||
| Wide band | Longitudinal | 5-9 | 98 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 78 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 69 | — | — | ||
| Varietal and shaped | Same | 5-9 | 108 | 49 | 49 |
| 10-25 | 98 | 29 | 29 | ||
| 26-40 | 88 | — | — | ||
Mechanical properties of rolled products under tension, as well as cold bending test conditions (GOST 535-2005)
| steel grade | St3ps | |
| Tensile strength σв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thicknesses, mm | up to 10 incl. | 370-480 (38-49) |
| Yield strength σт, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for rolled thickness, mm (not less) | up to 10 incl. | 245(25) |
| St. 10 to 20 incl. | 245(25) | |
| St. 20 to 40 incl. | 235(24) | |
| over 40 to 100 incl. | 225(23) | |
| St. 100 | 205(21) | |
| Relative elongation δ5, %, for rolled thicknesses, mm (not less) | up to 20 incl. | 26 |
| over 20 to 40 incl. | 25 | |
| St.40 | 23 | |
| Bending until the sides are parallel (a - sample thickness, d - mandrel diameter), for rolling thicknesses, mm | up to 20 incl. | d = a |
| St.20 | d = 2a | |
NOTE
- By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the following is allowed:
- reduction in yield strength by 10 N/mm2 (1 kgf/mm2) for shaped steel with a thickness of over 20 mm;
- reduction in relative elongation by 1% (abs.) for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses.
- It is allowed to exceed the upper limit of tensile strength by 49.0 N/mm2 (5 kgf/mm2), and by agreement with the consumer - without limiting the upper limit of tensile strength, provided that other standards are met. At the request of the consumer, exceeding the upper limit of temporary resistance is not allowed.
Legend
Mechanical properties
| HRСе | HB | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| MPa | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |
| Rockwell hardness | Brinell hardness | Impact strength | Relative narrowing | Elongation at break | Yield strength | Short-term strength limit |
| Ku | s0.2 | t-1 | s-1 |
| Relative machinability factor | Proof of yield strength with 0.2% tolerance when loaded to plastic strain value | Torsional endurance limit (symmetrical cycle) | Endurance limit under compression-tension (symmetrical cycle) |
| N | number of deformation/stress cycles sustained by an object under load before fatigue failure/crack appears |
Physical properties
Physical properties of the material St3ps
| T | E 10- 5 | a106 | l | r | C | R 109 |
| hail | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 7850 |