Types of muffle furnaces
Modern heating furnaces with a muffle design are represented by a wide variety of types. There are hundreds of modifications of muffle furnaces. At the same time, muffle heaters have a fairly narrow specialization . Furnaces of this type are purchased mainly for specific technological operations.
Although there are also “universal” models, their capabilities do not go far from the potential of highly specialized analogues.
First of all, muffle furnaces can be classified according to the heating method:
- Gas
- Electrical
There is an opinion that gas furnaces provide the ability to heat the muffle to a higher temperature. There are gas muffles with heating up to 2000 ˚C . Classic electric heaters allow you to achieve an average temperature of 1300 ˚C .
But modern technologies are increasingly being introduced into electric furnaces, making it possible to reach a temperature regime similar to gas models. By using a special fibrous heating material that reaches the surface layer of the muffle insulation, the furnace temperature can be increased to 1700 °C and even more.
Of course, in some workshops and production sites there is a place for old solid fuel stoves . Muffles of this type are heated by an ordinary wood/coal firebox. The main advantage of solid fuel muffles is a significant reduction in financial costs for energy.
In the past, muffle furnaces for production purposes were fired with waste from the woodworking industry. In this case, the cost of the heat treatment process itself can be considered zero.
But solid fuel muffles have one significant drawback. Such ovens do not allow temperature control at a fine level . That is, it is difficult to achieve heating stability with an ordinary wood firebox. This point is extremely important, since modern heat treatment technologies require compliance with the temperature regime with an accuracy of ±1 ˚С.
What other types of muffle furnaces exist?
Melting gold
Refractory metals, such as gold, have a high melting point when working. So, to successfully solve the problem, it will be necessary to heat the furnace to 1300 degrees , provided that we are working with steel (for other materials we need to look at the refractoriness coefficient).
It is necessary to take into account the factor of kindling materials . So, you can heat the stove with all unnecessary household materials, excluding toxic ones, that is, those that release toxic substances during the combustion process.
Stages of working with refractory materials
Classification by type of working environment
Muffle furnaces can provide heating of workpieces in various environments:
- Air
- Inert gas
- Vacuum
The simplest type of muffle furnaces are heaters with a traditional air chamber . The heating chamber in such furnaces is simply a hollow space into which the workpiece is placed.
In many cases, the presence of air is not critical for heat treatment. But there are still some technological operations for which the presence of air in the heating chamber is either undesirable or unacceptable.
When hardening many grades of steel and various alloys, air reacts with the surface layer of metals, which worsens the performance characteristics of the workpieces. Furnaces with inert gases or carbon dioxide supplied to the heating chamber have been developed especially for such cases . Neutral gas displaces air, creating a reliable protective layer.
Furnaces that are adapted for melting metals are often equipped with a heating chamber with a vacuum sealer. Metal melted under vacuum conditions acquires a particularly high-quality structure. Aluminum is often melted in a vacuum.
Additionally, muffle furnaces with different types of heating chambers are often equipped with an exhaust hood . Ventilation removes combustion products, moisture and other vapors from the heating chamber, the presence of which is undesirable during heat treatment.
How to choose a muffle furnace based on heating temperature.
Aluminum and copper melting device
Low-melting metals are brittle. It is important to follow the schemes for working with this type of metal.
So, for example, to melt copper or aluminum, the muffle furnace must heat up to 1083 Celsius , and to melt bronze - 930 Celsius.
These materials have the highest melting points among other fusible materials.
This means that the conclusion suggests itself: to work with low-melting metals, you need a furnace that heats up to a maximum of 1100 degrees.
Nuance! For large castings when working with low-melting metals, a forge is installed. You can melt metal in a container with a “spout” (crucible). This way it is easiest to give it a form later.
Stages of working with low-melting materials
- Calcination of the oven for pouring at a temperature of 600 degrees .
- Immersion of form.
- Heating temperature up to 900 degrees.
- We note the time the mold remains in the oven - 120 minutes.
- Remove the mold and cool to 500 degrees.
- The low-melting material is placed in a mold.
Muffle furnace heating temperature
When choosing a muffle furnace, first of all you should pay attention to the temperature conditions of the heating chamber . After all, the area of use of the heating unit directly depends on the temperature.
Very often, muffle furnaces are used for melting metals and alloys . If a master deals with a specific group of metals, then there is no point in overpaying for a furnace with a higher heating temperature.
Jewelers most often face the need for melting:
- Silver
- Gold
- Copper
The melting temperature of silver is 960.8 °C. Gold melts at a temperature of 1063 °C. Copper is slightly more refractory, requiring 1083.4˚C. If a jeweler uses platinum , you will have to use a more powerful furnace, because this metal melts at a temperature of 1768 °C.
Regarding platinum, this metal is rarely melted in a muffle furnace. Due to the increased threshold of temperature resistance, induction furnaces and sometimes crucible heaters are most often used for melting patinas.
If the master is dealing with smelting iron (steel or cast iron), then the furnace should heat up to 1539 ˚C. For melting lead and aluminum, you can use simpler heaters. Lead begins to “float” already at a temperature of 327.5 °C, and aluminum needs a temperature of 660.1 °C.
Often, muffle furnaces are used simply for heat treatment of metal workpieces, and not for melting them. Heat treatment is mostly reserved for steel products. The following technological operations can be used as heat treatment:
- Annealing
- Hardening
- Normalization
- Vacation
Direct hardening of steel is carried out at a temperature of 1000-723 ˚C. But the hardening process is usually preceded by annealing and normalization , which are carried out at a temperature of 1000-1130 ˚C. Thanks to tempering , the steel gets rid of internal stresses; this type of heat treatment is carried out in the heating range of 800-500 ˚C.
It is worth noting separately that to harden steel blanks, the metal is heated in a protective environment. To reduce the cost of production, liquids can be used instead of inert gases. Steel is often hardened in oil and a solution of caustic soda (caustic soda).
What else do you need to know about the types of muffle furnaces?
Methods for hardening metal
There are several ways to process metals using this device:
- Heat treatment: annealing, hardening, tempering, aging.
- Working with valuable materials , melting metals, when the use of open fire is unacceptable.
- To obtain an even surface tone , especially when processing ceramics (highly artistic), a muffle furnace is used.
- Drying dielectrics.
- Cremation , burning to mineral components.
Features of a household forge
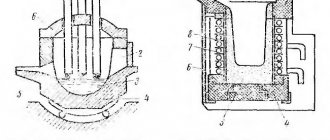
Due to the high cost of melting plants, not every user can buy such special-purpose equipment. For domestic needs, it is not difficult to assemble a gas forge with your own hands, provided that the shape, power and design of the pressurization system are correctly determined. A simple household forge for artistic forging or casting of non-ferrous metal can be assembled from several fireclay bricks and sheet steel.
Making a forge at home for working with ferrous metal is not difficult. You can make the simplest design from a metal container, in the side of which you need to make a hole for a gas burner. The fuel supply system can be assembled from a piece of pipe and coupling; long bolts are suitable for the supporting structure under the container. The lining of a gas fireplace is carried out by filling a solution of alabaster or gypsum, sand and water.
The forge must be equipped with a protective casing, a ceramic tube or a bottle of suitable size. After lining and drilling a hole for the gas supply, the device is installed in a convenient place, but at a distance from flammable materials. The advantages of the design include the ability to move the furnace and regulate the degree of heating of the workpiece, which is especially convenient when working with different forging materials.
Purpose of the equipment
Why do you need a homemade heating chamber at home? It can be intended for various needs: firing of ceramic products, hardening of cutting steel elements and melting of metals. The thermal chamber can be heated either by electricity or run on gas.
The external shape and internal design of the furnace can take different configurations. The main task is to achieve a certain temperature regime in a limited container space.
Making a stove from a blowtorch
When making a forge for forging with your own hands, the blowtorch must be installed in a recess, around the perimeter of which fireclay bricks with a grate must be laid. When laying refractory bricks, it is necessary to maintain the distance between the enclosing elements in order to ensure the flow of air masses into the combustion chamber. The angle of location of the blocks of building material relative to each other is determined by the master.
Charcoal or coke is poured into a recess made of bricks on a grate, and a pipe is put on the blowtorch, which is fed under the grate. The blank for forging is placed in the gap between the brickwork, and the coal concentrate is ignited from below. To remove smoke, a probe, tent or chimney is installed above the grate.
Solid fuel device for forge
The simplest model of a solid fuel device for a private forge is an outdoor open stove, which does not require the installation of a ventilation system. The construction of the structure involves pouring a reinforced concrete base; wall bricks must be laid at the base of the structure. The table is installed at a convenient height; a hole is left in one wall for the blower.
The mountain pit is laid out of fireclay bricks supported on steel corners; a cavity for the grate is left in the middle part of the structure. A chimney or probe will help ensure sufficient draft in the fireplace; the air supply system is installed at the final stage of construction work. Installing an electric fan in the chimney or installing blacksmith bellows will help increase the draft.
In a home forge, a container for hardening parts and a gas-air chamber are not mandatory elements. They can be useful in cases where thermal or shock hardening is required when working with damask steel. In the gas-air chamber the following is carried out:
- drying and heating oxygen;
- filtering oxygen from condensate and foreign impurities;
- mixing air with additives for alloying steel.
To melt precious metals and create an alloy of non-ferrous metals, it is necessary to make a crucible from a heat-resistant material. The device, made in the form of a cap, allows you to increase the operating temperature in the furnace without the risk of overheating the workpiece and the formation of soot.
Home gas forge
To make a simple home gas forge, you can use parts from an old bicycle. If you turn the sprocket from the gearbox on a lathe, the device can operate on butane or propane and heat closed furnaces of small volume. An important condition for using a portable design is to prohibit the operation of the burner with acetylene, since the high temperature of the flame can burn the former “star” and the stove will simply explode.
Assembling such a device is not difficult, and a homemade forge for forge is not much inferior to industrial ones, but is much cheaper. The main thing is to follow safety rules during manufacture and use.