- Peculiarities
- Types and models
- Areas of use
- How to install?
An anchor is a metal fastening unit, the task of which is to fix individual structures and their blocks. Anchors are indispensable when carrying out repair and construction work; they can have different sizes, shapes and functional characteristics. The industry of its use depends on the characteristics of each specific anchor.
In our review, we will dwell in more detail on the description of the technical and operational parameters of the expansion anchor.
Peculiarities
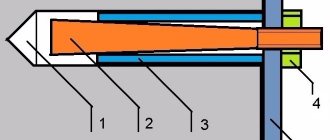
Expansion (self-expanding) anchors are the same self-anchoring expansion bolts. They are made of high-strength, durable metals: galvanized carbon steel or brass. This distinguishes them from dowels, which are mainly made from plastic polymer compounds. The zinc layer effectively protects hardware from corrosion; usually the coating has a yellow or whitish tint.
The active part of the self-expanding bolt resembles a sleeve; there are longitudinal cuts on the sidewalls - they form opening petals. A spacer is built into the inside of the sleeve body - in the process of hammering the hardware into the hole, it presses out its “petals” and thereby makes the fixation of the hardware product as reliable and durable as possible. The upper part of such a mount looks like a pin, with a washer and an adjusting nut placed on the threaded side. The operating principle of the spacer bolt is simple. When the nail located inside the nut is driven into the base, the bottom of the bolt expands and it is fixed to this very base. Such an anchor is easy to install and secures without any problems.
The main advantages of self-expanding anchors are:
- high strength and strength of the connection;
- resistance to external mechanical damage and adverse environmental factors;
- ease of use;
- high speed of creating effective fastening.
This is interesting: Drive-in anchor: design, varieties, installation features
Design
In terms of design, a brass anchor (another common name is collet) is similar to drive-type fasteners. Its feature is the cone-shaped shape of the internal threaded hole of the spacer part.
By studying the figure, you can understand the principle of operation of this fastener. The brass anchor is driven into a pre-prepared hole. Strong retention is facilitated by notches applied to its outer surface. When the bolt is screwed into the collet, its part with the slots expands and the diverging petals rest against the inner surface of the mounting hole with great force.
This nuance is important here. The length of the hole in the base should be slightly larger than this parameter of the anchor itself. Thanks to this, the bolt will protrude slightly beyond its far edge, made in the form of a ring. And then the petals will move apart with maximum amplitude, which will only increase the reliability of the fastening.
What is the main advantage of a double-expansion anchor?
When comparing anchor bolts of the same size, keep in mind that the working pull-out load of a double-spread bolt is 6-8 times higher than similar standard ones.
Comparative data of standard and double-spacer anchor bolts:
Another advantage is the speed of installation and the possibility of dismantling.
A double-expansion anchor bolt should be used precisely in a dense load-bearing base, where the principle of spreading will work. The strength of the assembly/fastening will depend directly on the strength of the base material.
The cost of the fastener corresponds to the quality and this must be taken into account when calculating estimates.
How to choose an expansion anchor
The choice of anchor should be made based on the following parameters:
- types of bolt;
- overall dimensions of the fastening element;
- manufacturing company.
Anchor type
Modern manufacturers produce expansion anchors of the following types:
- Bolts and washer are the most common type of fastening anchors. Wide popularity achieved due to ease of fastening and maximum strength. Anchors with washers can be used for concrete, brick and other monolithic bases, as well as bases with slight porosity.
Mounting anchors complete with washers
If you wish or need to obtain the most durable fixation, any anchor bolt can be independently supplemented with a washer selected according to size.
- Anchors with fixing nuts are mainly used for fastening heavy and large-sized objects, since a pre-installed nut allows you to reduce the time for fixing and, accordingly, holding the object “in weight”.
Mounting bolt with locking nut
- Expansion anchor with ring or hook. This fastening element is used when it is necessary to hang individual objects, for example, a ceiling lamp. The fastening element is pre-installed into the base (ceiling) and after that any structure is hung.
Fastening element for hanging any objects
- A stud anchor is used for through fastening of structures or individual parts. Studs are usually equipped with washers and fixing nuts.
Anchor bolt in the form of a hairpin for through fastening
Fastener dimensions
For strong fixation, it is necessary not only to choose the right type of anchor bolt, but also to first determine the dimensions of the fastening element.
Currently, bolts are produced in different lengths and diameters. The selection of overall dimensions is made depending on the weight of the structure being fixed. The greater the weight of the object being fixed, the larger the expansion anchor must be used.
Typical dimensions of expansion type anchor bolts
Popular manufacturers and their features
Many parameters of the anchor bolt (dimensions, safety factor, etc.) depend on the manufacturer of the fastener. The main manufacturers of expansion anchor bolts at present are:
- Hilti company (Liechtenstein). Fastening elements are made of zinc coated steel. The diversity of the line of spacer bolts allows you to fix structures with different dimensions (HSA or HSV for small shapes and HSL 3 or 3G for large objects), as well as use bolts in seismic zones (HST marking).
Fasteners from the most popular manufacturer
You can learn about the benefits of hilti expansion anchors by watching the video.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
- Fischer company (Germany). Anchors are characterized by increased strength, which allows the use of fastening bolts in various climatic conditions.
Fastening anchors from a German manufacturer
- (Russia). A wide range, reasonable price range, as well as high quality allow you to select expansion anchors for both industry, construction, and domestic needs.
Thus, expansion anchors are the most common types of anchor fasteners, as they can be used in almost any conditions and are capable of holding even objects that are heavy and large in size.
How to properly attach polycarbonate
Choosing horizontal rails for the kitchen: type, color, accessories
How to properly fasten corrugated sheets with your own hands
Clips for fastening pipes: how to choose a good fastener
← Drywall dowel: choosing and fixing it yourself
Self-tapping screw for corrugated sheeting: which one to choose, calculate the quantity and screw in →
Anchor bolt sizes for concrete
Typically, the main dimensions of the anchor bolt are indicated in the format, for example: M10 12x100. This designation is deciphered as follows: M10 is the diameter of the bolt thread, the number 12 indicates the installation diameter in millimeters (a hole of this diameter must be drilled in concrete before installation), the number 100 is the length of the anchor in millimeters.
The range of standard sizes of anchors used in everyday life, as a rule, is limited by these parameters: thread from M6 to M12 with a length from 55 to 160 mm. Of course, there are many other options, but they most likely fall into the category of professional or highly specialized fasteners.
Installing a double-expansion anchor bolt
Installation of fasteners is simple, but practical requirements should not be neglected. Let's look at them in more detail at each installation stage.
| 1. Prepare a hole in the supporting surface using a hammer drill | The diameter of the hole should be slightly smaller than the diameter of the anchor |
| The drill should not be crooked to avoid “walking” in the diameter of the hole | |
| The free space will not allow the fasteners to wedge tightly into the base material and reliably hold the load. It is enough to re-process a narrow hole with the same drill diameter, but avoid drilling. | |
| 2. Clean the hole from construction dust | Use a construction vacuum cleaner, a pump or a rubber bulb |
| 3. Drive the anchor into the prepared fastening area | Use a hammer |
| 4 . Tighten the anchor bolt completely with a wrench | When tightening the bolt, the bushings are expanded: the fastener is fixed in the working material |
| If you tighten the bolt too much, it will cause the material to break. Over time, small cracks will increase during use and the anchor bolt will tear out of the hole. If not tightened enough, the bonding force between the fastener and the working material will be low, which will also lead to tearing out and destruction of the connection. Use a torque wrench! | |
| 5. Unscrew the nut and washer and attach the structure; retighten the nut | The pin is already firmly installed in the supporting material; tighten the nut to complete installation. |
| By first firmly installing the anchor bolt into the load-bearing element, you can avoid poor-quality fastening of a heavy, oversized structure. | |
Sequential installation diagram (using the example of a standard anchor bolt):
The use of a double-expansion anchor bolt is the optimal solution for fastening heavy elements subject to constant mechanical stress into dense load-bearing structures such as concrete and natural stone.
Varieties
In the fastening segment of the global building materials market, there are brass anchors of various sizes. The leading manufacturers are the following companies: Mungo (Switzerland), Fischer (Germany) and Sormat (Finland). Such fasteners coming off their assembly line are characterized by high mechanical strength: they are produced in one piece, without the use of soldering or welding.
Meanwhile, the reliability of the connection also depends on compliance with the dimensional characteristics of the mounting holes. For the most popular types of brass anchors according to metric thread parameters, the corresponding information is presented in the table. The unit of measurement is millimeters.
| Thread | M16 | M12 | M10 | M8 | M6 | M5 | M4 |
| La | 44,0 | 40,0 | 34,0 | 30,0 | 24,0 | 20,0 | 16,0 |
| Da | 20,0 | 16,0 | 12,0 | 10,0 | 8,0 | 6,0 | 5,0 |
| Ho | 44,0 | 40,0 | 34,0 | 30,0 | 24,0 | 20,0 | 16,0 |
| Do | 20,0 | 16,0 | 12,0 | 10,0 | 8,0 | 6,0 | 5,0 |
The following designations are used in the table:
La – anchor length;
Da – anchor diameter;
Ho – minimum hole depth;
Do – hole diameter.
Continuing the conversation about the varieties, we note: the length of the anchor (parameter La) is usually indicated in its marking. For example, the character sequence M10x40 indicates that the length of this fastener with an M10 metric thread is 40 mm.
Information about what maximum load each brass anchor sample is designed for is located not only in the operating instructions, but also on the packaging. When choosing a fastener based on this indicator, you need to follow one important rule. It is formulated as follows: the expected load must be equal to or less than one-fourth of the value of this parameter specified in the accompanying documentation for the brass anchor. Otherwise, the durability and reliability of the mating of structural elements created with its use will be questionable.
One more point should be taken into account. Specialists from companies specializing in the production of fasteners of this type base their calculations on the value of the standard strength of concrete foundations - from 200 to 250 kg/cm2. If you plan to install a brass anchor in a material with other values of this characteristic, the calculation of the permissible load will need to be carried out separately.
Types and models
Self-expanding bolts in accordance with GOST can have different markings; usually, due to the presence of metric threads, it contains the letter “M”, as well as the diameter and length of the hardware. For example, spacer bolts M8x100 mm, M16x150 mm, M12x100 mm, M10x100 mm, M8x60 mm, M20, 10x100 mm, M12x120, M10x150 mm, M10x120 mm, and M12x100 mm are widely used.
Some models are marked with one diameter, for example: M6, M24, M10, M12, M8 and M16. Also on sale you can find products containing markings of three numbers: 8x6x60, 12x10x100, 10x12x110. In this case, the first number indicates the outer diameter of the anchor, the second - the internal size, and the third characterizes the total length of the product.
Important! The size of the anchor used should be selected depending on how heavy the structure is where it will be fixed. If it is bulky, you will need a long and thick fastener.
There are several types of spacer bolts.
- With a washer - includes a wide washer, thanks to which the fasteners are pressed as firmly as possible against the wall or some other base.
- With a nut - used to secure heavy structures. They are inserted into the hole and the nut is screwed on, so there is no need to hold the hardware suspended.
- With a ring - such fastenings are in demand when tensioning a rope, rope or cable. They are also necessary when you need to attach a chandelier to the ceiling.
- With a hook - at the end of such hardware there is a curved hook. These models are indispensable in the process of hanging water heaters.
- With impact spacer - used for fixing structures made of natural material through through installation.
- Double-spacer anchor - has a pair of spacer bushings, due to which the surface of the hardware “embedded” in a solid base is noticeably increased. Widely in demand when working with stone and concrete.
The most widely used expansion bolts are the brands DKC, Metizny Dvor, Tech-Krep and Nevsky Krepezh.
This is interesting: Strength classes of bolts: marking, classification, GOST 7798-70
Areas of use
The expansion anchor is considered one of the most practical and highly durable means of fixation. It allows you to fix a wide variety of surfaces; the anchor creates the most uniform friction with significant force along the entire length, which ensures increased ability to hold the structure. At the same time, the material of the structure itself must have increased density and a solid base.
Important! If there are internal cracks on the surfaces of the materials where the bolt will be fixed, then the load that the fastener can withstand is reduced many times over.
An anchor with spacers is often needed when performing façade fastenings.
It is optimal that the base for fastening is made of stone with a high degree of adhesion or concrete.
Self-expanding anchor can be used to fix:
- window frames;
- door structures;
- flights of stairs;
- suspended ceiling structures;
- chandeliers and other lamps;
- air ducts;
- fences;
- balustrades;
- engineering communications;
- consoles;
- bank terminals;
- foundation elements.
The mechanism of action of a self-expanding anchor is fundamentally different from the mechanism of action of a dowel. The outer part of the latter is in contact with the back of the hole only at some separately located points, while the spacer bolt is adjacent to it along its entire length.
Thus, fastening the expansion anchor provides much greater strength and reliability of the formed fastener.
Manufacturing materials
Various types of materials can be used in the production technology of anchor dowels. But most often it is steel or other alloys and plastics (nylon, polypropylene, etc.). As a rule, metal anchor dowels are used for fastening heavy structures that will subsequently bear loads. These can be windows, doors or elements of facade systems, as well as various structural elements. Steel anchors are also used to secure foundation elements. They are made of alloy steel and can withstand heavy loads.
Plastic anchor dowels are used when installing lighter structures. These are various objects from the profile for gypsum boards. Anchors with nylon dowels have also found their niche in domestic use. For example, they are used for fastening lamps, various decorative elements, paintings, laundry cords and ropes. In such fasteners, the caps are replaced with hooks, rings and other elements for various needs. At the same time, plastic dowels are used for hollow or cellular bases.
How to install?
To install the expansion anchor, you will need a hammer drill, a wrench, as well as a drill and a hammer. The mounting process is quite simple, to do this you need to follow these steps:
- using a hammer drill, you need to drill a hole of a suitable diameter into which the bolt will be inserted;
- it should be cleaned and blown to remove dust and dirt;
- a self-expanding anchor bolt together with the part is inserted into the prepared hole until it stops; in addition, you can tap the hardware with a hammer;
- There is a groove in the upper part of the bobbin; you need to hold it with a screwdriver and tighten the nut tightly a few turns;
- The expansion anchor must be mounted together with the object whose location you will be recording.
You can watch a video review of the new generation Hilti HST3 raptor anchor below.
Parameters and classification
GOST provides a simple and understandable principle for marking expansion anchors. So, the designation of such fasteners may look like this:
- 8x6x60;
- 12x10x100;
- 16x12x110.
The numbers present in such designations mean the following parameters:
- 1st digit – outer diameter of the fastener;
- 2nd digit – internal diameter of the expansion anchor bolt;
- The 3rd number is the total length of the anchor.
The total length and outer diameter of the anchor fastener are selected depending on the mass of the object that needs to be fixed with it. So, the heavier the object, the longer and thicker the anchor should be.
The following types of expansion anchor bolts are available on the modern market:
- fasteners, on the top of which there is a large-diameter washer, with the help of which the fastening of the object to the surface of the structure is ensured;
- anchor bolts with nuts, which are tightened to secure the object being fixed;
- fasteners, the upper threaded part of which ends with a ring (double-spacer anchor with a ring, etc.) - for hanging a chandelier from the ceiling, tensioning a cable, cable or rope;
- anchor fasteners, on the top of which a hook is attached, used for hanging various objects;
- anchor bolts, the design of which is equipped with an impact spacer element for fixing heavy finishing materials on the surface using the method of through installation.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
Chemical Anchor Bolts for Concrete
A fastener of this type is a concrete anchor screw, the fixation of which in the hole is ensured by a special adhesive composition. The adhesive composition with which chemical anchors are fixed is poured into a pre-made and thoroughly cleaned hole to two-thirds of its length. An anchor bolt of the appropriate size is installed in the hole with glue. After the adhesive composition has completely hardened, the required item is attached.
The battery-powered dispenser allows you to introduce the adhesive composition quickly and accurately
Chemical anchor elements are used in cases where fastening must be done on structures made of porous materials. By filling the pores and internal cavities in such materials, the adhesive composition ensures reliable adhesion of the anchor to the construction material. If all installation rules are followed and high-quality materials are used, pulling out or tearing out the anchor from the structure without causing mechanical damage is practically impossible. Tests carried out with fasteners of this type can be seen in photos and videos on the Internet.
Procedure for installing a chemical anchor
To obtain a high-quality connection when using chemical anchors, the holes in which they will be installed must be clean. To supply glue into the hole, special tubes or capsules can be used, in which the adhesive composition and hardener are contained in the required proportions.
Thus, for different types of concrete, different types of anchors are provided, the selection of which should be given special attention.
This bolt is a self-anchoring spacer element that is widely used in construction. The product is standardized according to the Russian system and has the GOST 28778-90 standard. With its help, various elements and structures are installed. For example, pipelines, various components and equipment to the load-bearing walls of buildings, hangars, structures and other objects. The material into which the GOST 28778-90 anchor bolt will subsequently be installed should be brick, reinforced concrete, or concrete.
Expansion bolts have certain requirements that apply to the strength of concrete structures. So, the compressive strength class should be B15 or higher. Otherwise, another brand should be used - M150. This spacer bolt, according to the Russian standard GOST 28778-90, can be of several types, depending on the climatic conditions in which it is planned to be used.
- UZ.1. Such bolts must be made of special steels that are used for the production of products of strength class 4.6 and higher;
- UZ. and UHLZ. These products must be from the steel grades from which foundation bolts are made.
There are some design features that the anchor bolt of the domestic standard GOST 28778-90 has. They belong to the type of jamming elements. Their shape is such that, when placed in holes already prepared for them, they increase in diameter. This occurs during settling. Thanks to this technology for installing anchor products, excellent quality of its adhesion to the material is achieved.
Installation of GOST 28778-90 bolts requires the creation of drilled holes. Moreover, their depth should guarantee sufficiently reliable fastening of the future connection. The best installation is to have the threaded end protruding enough to make the connection strong. However, the diameter of the bolt hole should still not be more than the diameter of the jamming elements. The difference should be no more than 2 millimeters.
Accordingly, the element is installed with the head facing forward. You must first make sure that the jamming elements are installed correctly. That is, the widest part of the turns that the bolts have is oriented towards the head. When installing, several blows are applied to the bushing with a hammer in order to completely seat the jamming elements. Next, the bushing is removed. The tightening torque should not exceed 20% of the calculated one.
An example of a symbol for an expansion anchor bolt. Length L = 100 mm. Thread diameter d = 10 mm. Execution of UHLZ:
Bolts BSR 10×100 UHLZ GOST 28778-90
| Standard size bolts GOST 28778-90 | Nominal bolt thread diameter d | Bolt head diameter D+1.0 | Length L | Length ZE N | Theoretical mass of bolts 1000 pcs., kg |
| M6x65 | 6 | 9 | 65 | 45 | 31,92 |
| M8x85 | 8 | 11 | 85 | 60 | 60,92 |
| M10x100 | 10 | 13 | 100 | 70 | 90,61 |
| M12x110 | 12 | 15 | 110 | 75 | 134,02 |
| M16x150 | 16 | 19 | 150 | 100 | 192,29 |
| M20x200 | 20 | 23 | 200 | 125 | 456,9 |
| M22x250 | 22 | 25 | 250 | 150 | 740,6 |
| M24x300 | 24 | 27 | 300 | 180 | 1159,52 |
In addition, we draw your attention to the fact that during the feasibility study, changes in the standard parameters of the length of the product and jamming elements may be allowed. The anchor bolt can be made to order.
Read also: After repair, the refrigerator does not turn off
| Standard size bolts GOST 287789-90 | d | L | D +1.0 | h, no more | l | Theoretical weight of 1000 pcs., kg |
| M6x65 | 6 | 65 | 9 | 5 | 30 | 16,47 |
| M8x85 | 8 | 85 | 11 | 5 | 35 | 35,22 |
| M10x100 | 10 | 1000 | 13 | 5 | 45 | 60,24 |
| M12x110 | 12 | 110 | 15 | 5 | 50 | 100,18 |
| M16x150 | 16 | 150 | 19 | 5 | 70 | 152,12 |
| M20x200 | 20 | 200 | 23 | 5 | 100 | 408,61 |
| M22x250 | 22 | 250 | 25 | 5 | 110 | 590,58 |
| M24x300 | 24 | 300 | 27 | 5 | 150 | 1099,52 |
The bolt in question has some notes. This applies primarily to its length. An increase in length (L in the table) is allowed with a corresponding increased thread length l (it is indicated in table 2). In this case, the thread tolerance range is 6 g or 8 g. Other requirements that apply to this bolt and other similar anchor products are not standardized.
The design and dimensions of the wedging elements included in the composition and possessed by the GOST 28778-90 anchor bolt must fully comply with the data specified in Table 3.
| Standard size | d | D | H | b | t Nom. | tPrev. off | S | Theoretical weight, 1000 pcs., kg |
| M6x65 | 6,2 | 9,8 | 45 | 10 | 6 | +3 | 0,6 | 15,45 |
| M8x85 | 8,2 | 11,8 | 60 | 12 | 7 | +3 | 0,8 | 25,7 |
| M10x100 | 10,2 | 13,8 | 70 | 12 | 7 | +3 | 0,8 | 30,3 |
| M12x110 | 12,2 | 15,8 | 75 | 14 | 8 | +5 | 0,8 | 34,2 |
| M16x150 | 16,2 | 19,8 | 100 | 14 | 8 | +5 | 0,9 | 40,17 |
| M20x200 | 20,2 | 23,8 | 125 | 16 | 9 | +6 | 1 | 48,29 |
| M22x250 | 22,2 | 25,8 | 150 | 16 | 9 | +6 | 1 | 50,02 |
| M24x300 | 24,2 | 27,8 | 180 | 20 | 11 | +8 | 1,2 | 60,22 |
The jamming element itself is a kind of spiral, which is wound from tape. The spacer bolt can also have various anti-corrosion coatings. Anchor type products are supplied assembled. The kit consists of the bolt itself, a jamming element, a flat washer and a nut.
The bolts look like:
*The use of the term “Analogue” does not mean 100% compliance.
To avoid misunderstandings when purchasing products, check the information with our consultants. All information on the site is for reference only and is not a public offer.
Installation rules
In order to install the expansion anchor effectively and with the least effort, you will need the following tools:
- perforator;
- drill for drilling concrete and other hard materials;
- wrench;
- hammer.
Expansion anchor installation parameters
The installation algorithm itself, which can be performed without special skills, is as follows.
- A hole is drilled in the required location of a structure made of concrete or any building material, the diameter of which should be such that the anchor fits into it with some interference.
- Using a regular medical bulb or brush of the appropriate diameter, the resulting hole is thoroughly cleaned of construction dust and pieces of crumbled material.
- The anchor bolt is inserted into the prepared hole until it stops; if necessary, you can use a hammer for this.
- While holding the fastener pin from rotating (for this purpose, there is a slot on its upper part into which the tip of a screwdriver can be inserted), tighten the adjusting nut on it, which must be turned 4–5 turns.
It should be borne in mind that such a fastening element is mounted together with an object whose position must be fixed.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
What is an anchor: general concept
The word “anchor” means a fastener used for fixing various objects on structures made of solid solid materials - concrete, building bricks, natural stone, etc. To install such fasteners, you should prepare a hole with the appropriate dimensions in which the anchor-type bolt will be placed . The high holding capacity of a bolt placed in such a hole can be ensured by:
- friction forces (expansion-type anchor products);
- adhesive abilities of a special composition (chemical anchor elements);
- a special thrust element interacting with the inner walls of the hole.
Any anchor has a spacer part
The most popular anchor is a fastening element, which, due to its design features, is wedged inside the hole, thereby ensuring high reliability of the connection being created. The surface of such bolts, made of carbon steel, is coated with a zinc composition, which eliminates the risk of the occurrence and development of corrosion.
Alphabetical index of terms in Russian
| anchor | 4 |
| driven anchor | 29 |
| screw-in anchor | 30 |
| injection anchor | 23 |
| capsule anchor | 24 |
| adhesive anchor | 21 |
| metal anchor | 12 |
| mechanical anchor | 10 |
| plastic anchor | 13 |
| drop-down anchor | 19 |
| expansion-adhesive anchor | 22 |
| countersunk anchor | 27 |
| anchor with press washer | 26 |
| anchor with wedge clip | 16 |
| anchor with extension | 15 |
| rigging anchor | 28 |
| disc anchor | 25 |
| persistent anchor | 14 |
| friction anchor | 18 |
| chemical anchor | 11 |
| self-tapping anchor screw | 17 |
| sleeve anchor | 20 |
| anchorage depth | 35 |
| anchor embedment depth | 34 |
| depth of installation hole for anchor | 33 |
| anchor group | 5 |
| diameter of mounting hole for anchor | 32 |
| temperature range for anchor installation | 39 |
| temperature range of anchorage operation | 40 |
| anchor dowel | 8 |
| anchor expansion zone | 31 |
| anchor fastening | 1 |
| pre-installation anchor fastening | 2 |
| Anchor fastening for through installation | 3 |
| construction base | 6 |
| Ultimate condition of anchorage | 37 |
| anchorage load-bearing capacity | 36 |
| anchor life | 38 |
| anchor rod | 7 |
| disc element | 9 |
Test methods
Moscow Standardform 2019
GOST R 58387—2019
Preface
1 DEVELOPED by the Research, Design and Technological Institute of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete named after. A.A. Gvozdev (NIIZhB named after A.A. Gvozdev) - a structural subdivision of the Joint Stock Company "Research and Development (JSC "National Research Center "Construction")
2 INTRODUCED by the Technical Committee for Standardization TC 465 “Construction”
3 APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology dated March 22, 2022 No. 97-st
4 INTRODUCED FOR THE FIRST TIME
The rules for applying this standard are established in Article 26 of the Federal Law of June 29, 2015 Nf 162-FZ “On Standardization in the Russian Federation”. Information about changes to this standard is published in the annual (as of January 1 of the current year) information index “National Standards”, and the official text of changes and amendments is published in the monthly information index “National Standards”. In case of revision (replacement) or cancellation of this standard, the corresponding notice will be published in the next issue of the monthly information index “National Standards”. Relevant information, notifications and texts are also posted in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet (www.gost.ru)
© Standardinform. decor. 2019
This standard cannot be fully or partially reproduced, replicated or distributed as an official publication without permission from the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology
Content
1 area of use
2 Normative references
3 Terms, definitions and designations
4 General provisions
5 Requirements for concrete and foundation
6 Requirements for installing anchors
7 Requirements for testing equipment and measuring instruments
8 Test rules
9 Rules for reporting test results
Appendix A (informative) Permissible temperature change range
operation and testing
Appendix B (for reference) Schematic diagram of equipment for testing under long-term load
Appendix B (for reference) Schematic diagrams of test benches
Appendix D (informative) Mechanisms of failure of anchors during pullout and shear
Appendix E (informative) Schematic diagram of equipment for pull-out testing during cyclic crack opening
Appendix E (for reference) Requirements for drills for installation
holes for anchors
GOST R 58387—2019
NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION
ADHESIVE ANCHORS FOR FIXING IN CONCRETE
Bonded anchors for use in concrete. Test methods
Date of introduction: 2019—09—01
1 area of use
1.1 This standard specifies methods for testing adhesive anchors installed in a finished base of heavy concrete and specifies requirements for testing methods for anchors.
1.2 This standard does not apply to adhesive anchors, the components of which are dosed manually at the construction site, mechanical, plastic and expansion-adhesive anchors and does not contain requirements for assessing their load-bearing capacity.
1.3 Types of tests, requirements for the number of anchors in a series, the value of the constant load Ntusl, requirements for processing test results must be specified in the test program developed before the tests.
2 Normative references
This standard uses normative references to the following standards:
GOST 12.1.004 System of occupational safety standards. Fire safety. General requirements
GOST 12.2.003 System of occupational safety standards. Production equipment. General safety requirements
GOST 3057 Disc springs. General technical conditions
GOST 10173 Portland cement and Portland slag cement. Specifications
GOST 10180 Concrete. Methods for determining strength using control samples
GOST 13015—2012 Concrete and reinforced concrete products for construction. General technical requirements. Rules for acceptance, labeling, transportation and storage
GOST 17624 Concrete. Ultrasonic strength testing method
GOST 18793 Compression springs. Design and dimensions
GOST 22690 Concrete. Determination of strength by mechanical methods of non-destructive testing
GOST 26633 Heavy and fine-grained concrete. Specifications
GOST 28570 Concrete. Methods for determining strength using samples taken from structures
GOST 31108 General construction cements. Specifications
GOST 33530 (ISO 6789:2003) Assembly tool for standardized tightening of threaded connections. Torque keys. General technical conditions
Read also: How to cut thick metal using plasma
GOST R 56731 Mechanical anchors for fastening in concrete. Test methods
GOST R 57787 Anchor fastenings for construction. Terms and Definitions. Classification
Note - When using this standard, it is advisable to check the validity of the reference standards in the public information system - on the official website of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology on the Internet or using the annual information index "National Standards", which was published as of January 1 of the current year, and by
releases of the monthly information index “National Standards” for the current year. If an undated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended that the current version of that standard be used, taking into account any changes made to that version. If a dated reference standard is replaced, it is recommended to use the version of that standard with the year of approval (adoption) indicated above. If, after the approval of this standard, a change is made to the reference standard to which a dated reference is made that affects the provision on which the reference is made, then it is recommended that this provision be applied without regard to this change. If the reference standard is canceled without replacement, then the provision in which a reference to it is given is recommended to apply Part 8, which does not affect this reference.
3 Terms, definitions and designations
3.1 This standard uses terms in accordance with GOST R 57787, as well as the following terms with their respective definitions.
3.1.1 manufacturer: An organization that manufactures or supplies anchors and develops technical requirements for their installation.
3.1.2 tests to determine the mechanical characteristics of anchors; A set of test series designed to determine all the mechanical characteristics of anchors necessary for calculation.
3.1.3 tests to check the susceptibility of anchors to installation and operating conditions: A set of test series designed to evaluate and adjust mechanical characteristics when installation or operating conditions change.
3.1.4 test program: A document regulating the number of test series, the number of tests in each series and other parameters necessary to establish the standardized characteristics of the anchorage, and taking into account the scope of application of the anchorage, as well as operating conditions.
3.2 This standard uses designations in accordance with GOST R 56731, as well as the following designations (see Figure 1):
tf crci is the maximum crack opening width of 0.3 mm in a test under constant load and varying crack opening width;
acge2 - minimum crack opening width of 0.1 mm in testing under the action of a constant load and varying crack opening width:
— diameter of the hole for installing the anchor;
— the greatest depth of the drilled hole;
N is the tensile force acting along the anchor axis;
— axial force in tests of anchors performed under long-term load;
Nmm is the minimum value of axial force in tests under the action of a repeated (pulsating) load;
— the minimum value of the axial force in tests under the action of a repeated (pulsating) load;
L/l - the value of the axial force in tests under the action of a constant load and a changing crack opening width;
V is the shear force acting perpendicular to the anchor axis.
G - base; 2 — adhesive composition; 3 - steel pin. 4 - steel bushing with internal thread
Figure 1 - Main types of anchors and designations
4 General provisions
4.1 The test results provided for by this standard are used to determine or monitor compliance with regulatory documents and technical documentation of the mechanical properties of anchors in heavy concrete foundations, as well as their installation parameters.
4.2 Mechanical properties determined according to this standard:
• ultimate pullout resistance:
• in case of destruction of a steel anchor,
. destruction of the adhesive composition in contact with the concrete or steel element of the anchor.
• puncturing the base concrete to form a concrete cone;
• ultimate shear strength:
• in case of destruction of a steel anchor,
– gouging out the concrete base behind the anchor.
Note - The ultimate resistance of an anchor installed in the base is expressed by the value of the load applied to this anchor, corresponding to the limit state for bearing capacity according to 8.2.2,8.32.
4.3 When testing anchors according to this standard, the center-to-center distance a. as well as the distance to the edge c, the bases should not be less than those specified by the manufacturer.
4.4 This standard specifies requirements for the following tests, taking into account operating conditions or deviations from installation requirements:
• test in concrete with a crack;
– test when the anchor tightening torque is exceeded;
• long-term load testing;
• tests under positive and negative temperatures;
– tests under prolonged exposure to aggressive environments, alternating freezing and thawing.
4.5 Samples of anchors representing the manufacturer’s finished products are selected for testing. The delivery set of anchors must comply with the technical documentation for the presented sample.
4.6 Samples should be collected in random order. The selection of samples is documented in an act.
4.7 Together with the anchor, a set of technical documentation is submitted for testing in the following volume:
– information about the manufacturer;
– requirements for installing the anchor;
• other documentation provided for by regulatory documents or current legislation of the Russian Federation.
4.8 Together with the anchor, a set of installation equipment is presented for testing. used during installation in accordance with the technical documentation.
4.9 Before testing, the submitted samples must be identified in the following order.
– visual inspection to determine the compliance of the anchor with technical documentation;
– control of compliance of the markings on the anchor specified in the technical documentation;
– measuring the overall dimensions of the anchor and establishing their compliance with those specified in the technical documentation.
5 Requirements for concrete and foundation
5.1 Requirements for concrete
5.1.1 For testing, heavy concrete should be used in accordance with the requirements of GOST 26633, made with Portland cement in accordance with GOST 10178. GOST 31108.
5.1.2 Average strength of base concrete corresponding to the accepted class of concrete for testing. must be within the range specified in Table 1.
Table 1 — Permissible range of concrete strength