Types of materials for making the cylinder body
Gas containers are made from metal and polymers. Both materials are used to make cylinders for storing certain types of gas. Each has advantages and disadvantages regarding ease of use, cost, and reliability.
Metal containers
Metal cylinders are made from low-carbon or alloy steel. Capacity of containers from 5 to 50 liters. Large volume tanks are stored in special metal cabinets protected from sunlight and other heat sources. Heating above 50 degrees is unacceptable.
Advantages:
• low cost;
• possibility of manufacturing large volume containers;
• high strength;
• the ability to exchange or refill at any gas filling station.
These cylinders have been produced for decades. They are the most popular for use in private homes, country houses, cars, medicine and production.
But such containers also have disadvantages:
• High explosion hazard. A cylinder rupture or valve failure is possible when heated or suddenly turned over, as these factors lead to a pressure surge inside the container.
• Heavy weight. The weight of the tank without gas is from 4 to 22 kg, depending on the volume. This somewhat complicates the installation and transportation of equipment.
Metal vessels are filled with gas to 85% of the total volume; exceeding the permissible amount increases the risk of explosion.
Polymer cylinders
Composite cylinders or Euro cylinders are produced by winding fiberglass onto a mandrel and then impregnating it with epoxy resin. The finished container is placed in a polymer casing with a handle for transportation. The flask is translucent, through it you can see how much gas remains in the vessel. Tank volumes range from 12.5 to 33.5 liters. Such containers are designed for transportation, storage and use of liquefied gas. They are highly secure.
Advantages of polymer cylinders:
• light weight – up to 8 kg;
• do not explode – equipped with a valve that melts at high temperature and gradually releases gas, eliminating explosion;
• attractive appearance;
• in case of an accidental fall, the impact will be on the casing, but the bulb will remain intact;
• does not accumulate static electricity - random sparks are excluded;
• the kit includes a factory gearbox;
• does not corrode;
• remains operational at low temperatures;
• service life up to 30 years, recertification is carried out once every 10 years, which is half as often as for metal containers.
The main disadvantage of cylinders of this type is the high price. Expensive equipment and raw materials are used for their production.
Metal composite gas tanks
These containers are of medium weight. Their performance characteristics are slightly better than conventional steel cylinders, but the risk of explosion upon impact or overpressure remains. Their body is made of metal, so these cylinders look like steel ones. They are also subject to corrosion on the outside. Metal composite containers are not widely used and are used quite rarely.
Gas container arrangement
The substance is under high pressure in a special vessel. Compressed gas under any pressure is in a gaseous state, and liquefied gas, with an increase in this parameter, passes into a liquid state.
The tank in the form of a cylinder is an all-welded structure, the minimum thickness of its walls is 2 mm. It is made from two materials: steel or polymer. Consists of a shell, neck and bottom.
The tapered thread on the neck of the cylinder allows the shut-off valve to be hermetically closed. This is done so that when the gas expands, it can break, and then the pressure in the vessel will quickly return to normal.
The bottom of such containers is convex at the top and bottom. Due to this, the gas pressure on the walls of the tank is the same.
Classification of gas cylinders
Types of cylinders by area of use
Gas cylinders are easy to transport and use in places where there is no gas pipeline or other source of gas. All cylinders are classified into groups:
• Tourist (for travelers, hunters, fishermen). These containers have a small volume and are designed for heating and cooking food in natural conditions.
• Household. Filled with propane or propane-butane mixture. They are used in private homes and cottages to connect gas stoves and boilers.
• Automotive. For equipment with a gas engine.
• Medical. Most often - oxygen. Designed for therapeutic and preventive procedures, preparation of oxygen cocktails. The same ones are used in aviation and rescue services.
• Industrial. Filled with gas for metal welding, electrical production, and for the needs of the chemical industry.
There are also universal cylinders, but it is preferable to use special ones, since their safety standards and volume meet the requirements of operation in certain conditions.
Rules for use and storage
There are two main types of gas cylinders; metal gas cylinders are the most common. The volume of different products varies based on the amount of gas pumped under pressure. To connect the cylinder to special equipment, valves, flanges and other connectors are connected. To ensure the product's durability and high-quality performance over a long period of time, you need to follow some rules for safe use.
Small and medium-sized cylinders are, as a rule, used exclusively for solving household and domestic problems. Such cylinders are characterized by mobility and compactness, very convenient and reliable.
It is necessary to remember the specifics of working with gas. Since gaseous fuel is used, careless operation poses the risk of unintentional fire. When there is a leak, a specific smell immediately appears, and it is by this that the leak can be identified in a timely manner. Gas for domestic use is designated class 4 (IV), this is a toxicity index.
Construction of a household gas cylinder
Using gas for economic purposes does not in itself pose a risk, but only if used carefully and using suitable equipment:
- tightness of the supplied connections;
- gas cylinders must undergo certification and technical testing;
- The production date, expiration date, volume and weight of the required unit are subject to mandatory examination.
Gas can serve not only for the benefit of a person, but also fail at the most unexpected moment. A gas leak can lead to a very disastrous outcome, which is why you should operate any gas appliance correctly. By incorrectly storing a gas cylinder in your home or any other premises, you expose yourself to mortal danger. Let's consider the main points of how to behave with gas:
- allow only qualified specialists to install, repair and inspect gas equipment;
- do not illuminate the gas meter dial;
- Do not leave the gas device running overnight;
- under no circumstances give children the opportunity to somehow interact with gas appliances;
- make sure that the gas supply is carried out in accordance with all the rules;
- there should be no gaps in the flame;
- do not turn the gas tap using keys or pliers, do not knock on the taps or meters with various objects.
Video - Composite gas cylinder, refilling trick
Most of the various disasters, including explosions, occur not because of a bad manufacturer, but because of the carelessness of the buyer. If you want the product to serve you faithfully for a long time, then you yourself must treat it with care, being aware of the full responsibility of working with gas appliances.
Classification by type of injected gas
Cylinders for different types of gas have different designs, degrees of safety and operating features. For convenience, their body is painted in a certain color corresponding to the type of substance, and an inscription is made with the name of the gas.
• Type of cylinder:
Propane or propane-butane
• Case color:
Red
• Lettering color:
White
• Scope of application:
In everyday life, for vehicles, in the production of lighters, solvents
• Type of cylinder:
Oxygen
• Case color:
Blue
• Lettering color:
Black
• Scope of application:
Medicine, aviation, rescue services, fire stations, agriculture, ecology
• Type of cylinder:
Helium
• Case color:
Brown
• Lettering color:
White
• Scope of application:
For inflating balloons and balloons, as a coolant, for welding
• Type of cylinder:
Acetylenic
• Case color:
White
• Lettering color:
Red
• Scope of application:
In the chemical industry, for cutting metals
• Type of cylinder:
Carbon dioxide
• Case color:
Black
• Lettering color:
Yellow
• Scope of application:
Refrigerant in the food industry, used for the production of carbonated water, for refilling fire extinguishers
• Type of cylinder:
Argon
• Case color:
Grey
• Lettering color:
Green
• Scope of application:
In the metalworking and food industries, medicine, in the production of incandescent and fluorescent lamps
• Type of cylinder:
Compressed air
• Case color:
Black
• Lettering color:
White
• Scope of application:
For the operation of pneumatic devices and for the production of inert gases
• Type of cylinder:
Hydrogen
• Case color:
Green
• Lettering color:
Red
• Scope of application:
Food and chemical industries, used as rocket fuel and for welding
Voting for the best safe gas cylinder for household needs
Which safe gas cylinder would you choose or recommend?
Volchansky Mechanical Plant 3-50-3.0-k steel 50 l
9.68 % ( 3 )
Hexagon Ragasco LPG composite 18.2 l
3.23 % ( 1 )
NOVOGAS steel 27 l
12.90 % ( 4 )
Hexagon Ragasco LPG composite 12.5 l
6.45 % ( 2 )
NOVOGAS steel 5 l
3.23 % ( 1 )
NOVOGAS 12 l steel
6.45 % ( 2 )
Gas cylinder Hexagon Ragasco LPG composite 33.5 l
16.13 % ( 5 )
Gas cylinder NOVOGAS 12 l with steel safety valve
16.13 % ( 5 )
Gas cylinder NOVOGAS 27 l with steel safety valve
22.58 % ( 7 )
Cylinder selection
You should buy a cylinder in accordance with the purpose of its use. When choosing, it is worth considering the material from which the case is made and the degree of safety of the device. It is important to inspect the container for damage or malfunction. You should check the valve - it should move smoothly and softly. You should not choose a cylinder whose flywheel rotates with great force or too sharply.
It is better to immediately purchase a reducer - it will reduce the likelihood of an explosion and allow you to control the gas level in the container.
The most popular gas cylinders are produced in Russia and Europe. Most Russian products are made of metal, while European products are made of composites. Some European brands have already organized the production of polymer tanks in Russian cities and are producing containers that are in no way inferior in quality and properties. The only difference is the cost: when transporting a cylinder from another country, its price increases.
Conclusion
In terms of technology, composite gas cylinders are not inferior to metal cylinders, and in some ways even surpass them, not to mention the fact that they look much more presentable. Whether it is worth overpaying for convenience and safety - everyone determines based on their own reasons. But in any case, this is a viable and promising product.
In previous materials you can read about backup heating of a house with a gas convector, as well as about the organization of an autonomous heating system based on gas cylinders. For these purposes, you can also use composite containers rather than metal ones. In the video - how to make a designer lamp with your own hands with minimal investment.
Subscribe to our Telegram channel Exclusive posts every week
Chemical composition (%, maximum)
| steel grade | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | S | P | Cu | N |
| 45 | 0,42…0,45 | 0,17…0,37 | 0,50…0,80 | 0,25 | ||||||
| 30ХГСА | 0,28…0,34 | 0,90…1,20 | 0,80…1,10 | 0,80…1,10 | 0,30 | 0,005 | 0,025 | |||
For reliable fixation in a vertical position and for traumatic-free operation, special clamps are used for tables, racks and cages.
To heat the cylinders, special belts and heaters are used.
At the customer's request, cylinders are shipped in protective nets or covers.
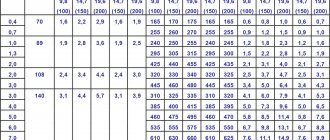
MAIN PARAMETERS AND DIMENSIONS
1.1. Cylinders must be manufactured for a working pressure of 9.8; 14.7; 19.6 MPa (100, 150 and 200 kgf/cm2) from carbon steel and for working pressure 14.7 and 19.6 MPa (150 and 200 kgf/cm2) from alloy steel.
1.2. The main parameters and dimensions of the cylinders must correspond to those indicated in the drawing and table. 1.
Official publication Reissue (June 1992) with Changes N? ], 2. 3, 4, approved in October 1976, October 1980, February 1982, June 1986 (IUS 11-76.1-81, S-82. 10-86).
© Standards Publishing House, 1974
© Standards Publishing House, 1992
Dimensions in mm
Table 1
| Cylinder volume, l | Diameter of cylindrical part | Wall thickness of pressure cylinders, MPa (kgf/cm2), not less | Pressure cylinder body length, MPa (kgf/cm2) | Mass of cylinders for pressure MPa (kgf/cm2), kg | ||||||||||||
| carbon steel | alloy steel | carbon steel | alloy steel | carbon steel | alloy steel | |||||||||||
| 9.8 (100) | 14.7 (150) | 19.6 (200) | 14,7 (150) | 19.6 (200) | 9.8 (100) | 14.7 (150) | 19,6 (200) | 14,7 (150) | 19,6 (200) | 9,8 (100) | 14,7 (150) | 19.6 (200) | 14,7 (150) | 19.6 (200) | ||
| 0,4 | 70 | 1,6 | 2,2 | 2,9 | 1,0 | 1,9 | 165 | 170 | 175 | 165 | 165 | 0,6 | 0,8 | 1,0 | 0.6 | 0,7 |
| 0,7 | 255 | 260 | 270 | 255 | 255 | 0,9 | 1,2 | 1,5 | 0,9 | 1,0 | ||||||
| 1,0 | ,89 | 1,9 | 2,8 | 3,6 | 1,9 | 2,5 | 240 | 250 | 255 | 240 | 245 | 1,2 | 1,8 | 23 | 1.2 | 1,6 |
| 1,3 | 295 | 305 | 315 | 295 | 300 | 1,5 | 2,2 | 2,? | 1.5 | 1,9 | ||||||
| 2,0 | 425 | 440 | 455 | 425 | 435 | 2,1 | 3,1 | 4,0 | 2,1 | 2,7 | ||||||
| 2,0 | 108 | 2,4 | 3,4 | 4,4, | 2,4 | 3,0 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 320 | 325 | 2,5 | 3,7 | 4.7 | 2,5 | 3,1 |
| 3,0 | 445 | 460 | 480 | 445 | 455 | 3,4 | 5,0 | 6.4 | 3,4 | 4,3 | ||||||
| 3,0 | 140 | 3,1 | 4,4 | 5,7 | 3,1 | 3,9 | 310 | 325 | 335 | 310 | 320 | 4,1 | 6,0 | 7,9 | 4,1 | 5,3 |
| 4,0 | 385 | 400 | 415 | 385 | 395 | 5,0 | 7,3 | 9,6 | 5,0 | 6,5 | ||||||
| 5,0 | 460 | 475 | 495 | 460 | 470 | 5,8 | 8,5 | 11,4 | 5,8 | 7,6 | ||||||
| 6,0 | 535 | 555 | 575 | 535 | 550 | 6,7 | 9.8 | 13,1 | 6,7 | 8,8 | ||||||
| 7,0 | 610 | 630 | 660 | 610 | 625 | 7,6 | 11,1 | 14,9 | 7,6 | 9,9 | ||||||
| 8,0 | 140 | 3,1 | 4,4 | 5,7 | 3,1 | 3,9 | 680 | 710 | 740 | 680 | 700 | 8,5 | 12,4 | 16,6 | 8,5 | 11,1 |
| 10,0 | 830 | 865 | 900 | 830 | 850 | 10,2 | 15,0 | 20,1 | 10,2 | 13,4 | ||||||
| 12,0 | 975 | 1020 | 1060 | 975 | 1005 | 1,9 | 17,6 | 23,5 | 11,9 | 15,6 | ||||||
| 20,0 | 219 | 5,2 | 6,8 | 8,9 | 5,2 | 6,0 | 730 | 740 | 770 | 730 | 28,5 | 33,3 | 42,0 | 28,5 | ||
| 25,0 | 890 | 900 | 935 | 890 | 34,0 | 38.7 | 50,5 | 34,0 | ||||||||
| 32,0 | 1105 | 1120 | 1165 | 1105 | 42.0 | 47,7 | 62,5 | 42,0 | ||||||||
| 40,0 | 1350 | 1370 | 1430 | 1350 | 5i,5 | 58,5 | 76,5 | 51,5 | ||||||||
| 50,0 | 1660 | 1685 | 1755 | 1660 | 62.5 | 71,3 | 93,0 | 62,5 | ||||||||
Notes:
- 1. The weight of cylinders is indicated without valves, caps, rings and shoes and is a reference value and a nominal value for the manufacture of cylinders with a weight limit.
- 2. The lengths of the cylinders are indicated as reference and are accepted as nominal when manufacturing cylinders with a limited length.
- 3. The approximate weight of the metal cap is 1.8 kg; from fiberglass - 0.5 kg; rings - 0.3 kg, shoes - 5.2 kg.
1.1; 1.2. (Changed edition, Rev. N4).
1.3. Cylinders must be manufactured with normal and increased precision.
1.4.
Conventional precision cylinders are manufactured with a limited volume; cylinders of increased precision - by volume and outer diameter or by length and outer diameter. Maximum deviations should not exceed those indicated in the table. 2. Table 2
| Limit deviations | For standard precision cylinders | For high precision cylinders |
| By volume: | ||
| for small volume cylinders | +10% ‘ | . +5% |
| for medium volume cylinders | + 5% | +5% |
| By lenght: | ||
| for small volume cylinders | — | ´6 mm |
| for medium volume cylinders | — | ´15 mm |
| By outer diameter: | ||
| for carbon steel cylinders | — | ´1,5% |
| for alloy steel cylinders | — | ´2,0% |
Notes:
- 1. Maximum deviations in outer diameter for medium-volume cylinders made of carbon steel, which have been assigned the State Quality Mark, must not exceed ´1.0%.
- 2. The curvature of medium-volume cylinders is no more than 0.5% of the length of the cylindrical part of the cylinder.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 3).
1.5. At the customer's request, alloy steel cylinders can be manufactured with weight restrictions. In this case, the mass of the cylinders should not exceed by more than 10% the mass indicated in the table. 1. Examples of symbols:
cylinder with a volume of 4 liters for a pressure of 14.7 MPa (150 kgf/cm2), made of carbon steel, standard manufacturing precision, for air:
- Air cylinder 4-150U GOST 949-73
the same, from alloy steel, increased manufacturing precision, with volume limitation, without weight limitation, for nitrogen:
- Nitrogen cylinder 4p-150L GOST 949-73
the same, with normal manufacturing precision, with mass restrictions, for air:
- Air cylinder 4-150 L-M GOST 949-73
the same, with increased manufacturing accuracy in terms of volume, with mass restrictions, for medical oxygen:
- Cylinder for medical oxygen 4P-150L-M GOST 949-73
the same, increased manufacturing precision, cylinder body length 400 mm, with weight limitation, for nitrogen:
- Nitrogen cylinder 4-150L-400-M GOST 949-73
the same, short volume 2 liters for a pressure of 14.7 MPa (150 kgf/cm2), made of carbon steel, increased manufacturing precision with a length limitation, without a weight limitation, for air:
- Cylinder for. air K2-150U-330 GOST 949-78 (Changed edition, Amendment No. 4).